Artistic processing of metal
Modern technologies have made it possible to largely automate all processes for processing metal products and have minimized manual labor, however, for small-scale production and the manufacture of unique products, manual methods are still widely used, thanks to which artistic metal processing is carried out. At the same time, it is possible to replace many labor-intensive processes with automated ones.
Features of metal processing
Numerous types of metalworking can be classified into one of the large groups:
- mechanical (cutting);
- casting;
- thermal;
- pressure;
- welding;
- electric;
- chemical
Casting is one of the most ancient methods. It consists of melting metal and pouring it into a prepared mold that repeats the configuration of the future product. This method produces durable castings of various sizes and shapes.
Other types of processing will be discussed below.
Welding
Welding has also been known to man since ancient times, but most of the methods were developed in the last century. The essence of welding is to connect the edges of two parts heated to the plasticity temperature or to the melting temperature into a single integral whole.
Depending on the method of heating the metal, several groups of welding technologies are distinguished:
- Chemical. The metal is heated by the heat released during the chemical reaction. Thermite welding is widely used in hard-to-reach places where it is impossible to supply electricity or haul gas cylinders, including under water.
- Gas. The metal in the welding zone is heated by the flame of a gas burner. By changing the shape of the torch, you can carry out not only welding, but also cutting of metals.
- Electric welding. The most common method: Arc welding uses the heat of an electric arc to heat and melt the work area. Special welding machines are used to ignite and maintain the arc. Welding is carried out using spatter electrodes or special welding wire in an atmosphere of inert gases.
- In resistance welding, heating is carried out by a strong electric current passing through the point of contact of the workpieces being joined. There are spot welding, in which parts are connected at individual points, and roller welding, in which a conductive roller rolls along the surface of the parts and connects them with a continuous seam.
Arc welding
Welding is used to connect machine parts, building structures, pipelines, ship and car hulls, and much more. Welding goes well with other types of metal processing.
Casting
The mold must be made of a metal whose melting point is higher than that of the raw material.
Those metals that have a high degree of fusibility can easily be modified using molds. This method is called casting, it is one of the oldest, but even today it remains relevant and often used. Even before our era, people mastered and widely used casting.
Before starting work, you need to make a mold. The choice of material can be any convenient, for example, wax, sand, if you plan to manufacture several identical parts, the form can be used many times. In the case when the future metal product will have a complex structure, it is advisable to make several molds for different parts, and then connect them to each other by soldering.
Casting can be classified according to casting metal:
Sand casting is a widely used casting method in the industry.
- cast iron;
- copper;
- gold and silver.
By design and materials of molds:
- temporary forms - earth, sand;
- shell;
- permanent – wax, plaster, metal.
By casting method:
- centrifugal;
- under pressure;
- classic.
After preparing the molds, you need to bring the metal to liquid form - melt it. This can be done in a special furnace; in ancient times, metal was melted in cauldrons over a fire. The melting point of different metals is different, so if there is no automated heating detection, it is necessary to monitor the process and after the metal becomes liquid, it is poured into the mold.
Metal casting at home
When the material has hardened, the product can be removed from the mold; to achieve perfectly smooth surfaces, the workpiece is cleaned and ground.
At the stage of heating and melting the metal, various components can be combined to obtain improved characteristics, for example, copper and tin form a more durable alloy - bronze.
Electrical processing
The method is based on the partial destruction of metal parts under the influence of high-intensity electrical discharges.
It is used for burning holes in thin sheet metal, when sharpening tools and processing workpieces made of hard alloys. It also helps to remove a broken or stuck tip of a drill or threaded tap from a hole.
A graphite or brass electrode, to which high voltage is applied, is brought to the processing site. A spark jumps, the metal partially melts and spatters. To trap metal particles, the gap between the electrode and the part is filled with special oil.
Ultrasonic metal processing
Electrical methods of metal processing also include ultrasonic. High intensity vibrations with a frequency of over 20 kHz are excited in the part. They cause local resonance and point destruction of the surface layer; the method is used for processing durable alloys, stainless steel and jewelry.
Features of artistic metal processing
Artistic types of metal processing include casting, forging and embossing. In the middle of the 20th century, welding was added to them. Each method requires its own tools and devices. With their help, the master either creates a separate work of art, or additionally decorates a utilitarian product, giving it aesthetic content.
Artistic embossing
Embossing is the creation of a relief image on the surface of a metal sheet or the finished product itself, for example, a jug. Embossing is also done on heated metal.
Interior design and architecture
It is difficult to imagine a modern interior without decorative items made of metal. These are chased paintings and cast sculptures, forged products and objects decorated with inlay.
Craftsmen who use a variety of metal processing techniques work on the manufacture of metal products. Today, there are several main methods of artistic metal processing, among which are the following:
- Embossing (punching) is a special method of processing metals by pressing and pressing with special tools that have ends of different sizes and shapes. As a rule, these instruments have the form of metal rods with different protrusions - strikes.
The embossed image can be flat-relief, relief or three-dimensional. Embossing on metal is carried out in two main ways: knocking out on a finished matrix and on resin rubber, lead or wooden pads with a mallet or round hammer.
The second method is to press and press with special rods - strikes, which are called poisons and mints.
Embossing on metal
- Shotting is one of the varieties of poisson embossing, during the manufacturing process of which an image is applied by punching out a grainy texture on the surface of a metal sheet or metal product.
Shotting
- Inlay (notch) - used to decorate products with images or ornaments made from various types of materials: precious metals (gold and silver), non-ferrous metals (bronze, copper, tin) on the surface of wood, bone, horn, amber or mother-of-pearl.
Brooches - inlay using the Damascus technique.
During the notching process, the design is applied to the surface of the product using burrs, which make indentations. Next, individual parts for inlaying are made and inserted into predetermined places.
Metal inlay
- Filigree is one of the special types of artistic metal processing, during which the master twists thin wires or metal threads = the so-called rope. Next, the individual fragments are connected to each other using soldering. The technique of making products in which a filigree pattern is set on a metal base is called filigree.
Filigree
Scan can be either twisted from individual metal threads or smooth wire, which is given a flat shape by rolling. Most often, filigree is made from copper or silver; gold is used much less frequently due to its high cost.
Scan
- Enamel (enamel) is a special glass-like colored coating that is applied to a metal surface cold or hot. With the cold method of making enamel, paint is applied using a brush or a special sprayer and left until completely dry.
The set of jewelry is made using the enamel technique.
The design is applied to hot enamel with paste using a spatula. Next, the products are dried and then subjected to the firing procedure. This makes the enamel coating smooth, shiny and durable.
Set "Blizzard" (enamel)
Enamels differ in the level of light transmission: they can be transparent, translucent and dull, that is, painted in pure, monochromatic colors.
Painting on enamel
- Champlevé enamel is a type of artistic processing of metal products, during which enamel crushed into powder is mixed with water and this plastic mass fills shaped recesses and depressions applied to the surface of the metal.
Next, the product is fired at high temperature, and then the hardened enamel is ground until its layer is equal to the level of the metal surface. In this way, products of amazing beauty are obtained, the recesses and patterns on which are filled with areas of colored enamel.
Champlevé enamel
- Filigree enamel - the internal cells of ornaments formed by interlacing wires or metal threads are filled with enamel mass of various colors. After firing, a hard and smooth enamel surface is formed, on which a relief contour of filigree stands out.
Enamel on filigree
- Cloisonne enamel - on a metal base - a plate with slightly curved edges is soldered with thin partitions made of metal wire. Then contour cells. forming patterns or drawings, filled with enamel mass of different colors.
After a process of firing and careful grinding of the plate, a color image is obtained, limited by narrow strips of metal partitions that are in the same plane as the enamel surface.
Gold was most often used to make products using the cloisonne enamel technique, resulting in amazingly beautiful and luxurious jewelry and expensive interior decor items.
Cloisonne enamel
- Openwork enamel - openwork elements are cut out of a metal sheet using a jigsaw. Next, using a scraper, the cut areas are carefully cleaned and a set of scanned tracery is performed. This technique also has other names - window or stained glass enamel.
Openwork (stained glass) enamel
Then the cells and spaces between the partitions are filled with transparent, slightly colored enamel. Transparent, clean enamel also covers images engraved on metal. As a result of firing, the enamel forms a beautiful transparent film on the surface of the metal product.
Openwork enamel
- Enamel in relief - fine engraving is applied to the hammered metal surface, which helps to fix the enamel. Next, the product is covered with a layer of enamel and fired.
Champlevé Limoges enamel (enamel in relief).
- Enamel painting - the image is applied to blank enamel of various colors. Painting enamel or special dyes for ceramics are used to paint portraits, create subject compositions and make ornaments. The paints are mixed with oily substances - lavender oil or turpentine. During the process of repeated firing, the painting is fixed, and the applied paints merge with the ground. This results in a colorful, multi-color image.
Painting on enamel (enamel).
- Niello - this technique of artistic metal processing consists of applying or fusing a niello alloy onto the engraved surface of a silver plate. The ferrous alloy consists of a sulfur compound of copper, lead, silver or other metals. The alloy is applied in crushed form, after which the product is fired. The niello melts and all the depressions on the surface of the product are filled.
Black on silver
- Casting is a very popular technique for processing various metals, for which cast iron, bronze, aluminum and zinc alloys are used. Casting is also widely used in jewelry work where gold or silver is used.
Solid products or parts are molded in various ways: by casting into a single-sided or double-sided sand mold using flasks filled with molding sand. Solid sand molds are used to make complex models.
Cast product
In another case, a piece molding method is used, in which a casting mold is obtained from several component parts. To form hollow castings, sand blanks are placed into a split mold or a casting method is used with metal splashing onto the walls of the mold. The process of making jewelry involves injection molding.
Casting
- Stamping is a method of artistic processing of metal under pressure, which involves a certain plastic deformation of the workpiece in a stamping mold. Using the stamping method, flat blanks are produced from a metal sheet, three-dimensional parts are drawn out or bent, and relief images are also made using the embossing method.
Stamped metal products
- Pressing work - used for drawing out voluminous hollow products of concentric shape on a rotating blank. A solid or split blank in the shape of the future product is fixed in the chuck of a lathe, and a metal blank is installed between the tailstock of the machine and the outer end of the blank. With the gradual rotation of the spindle, the master, using a steel rod with an oval tip, firmly presses the workpiece to the blank, and thus gives the product a pre-thought-out shape.
Pressing work (product sample).
- Knurling is a method of applying an image or desired texture to a concentrically shaped product. A specified pattern or design is engraved on the surface of the steel wheel, which, when rotated, leaves a relief pattern on the surface of the workpiece mounted in the chuck of the lathe.
Turning knurling - knurling
- Forging is a special type of metal processing, during which the metal is heated and softened, and then given the required shape. The forging process can be divided into several separate operations: stretching, shortening, flattening, bending, twisting and pressing (used for the manufacture of complex products using a mold).
Forged gates
- Pickling is a method of removing the surface layer of metal using special chemical compounds - acids and alkalis. This helps degrease products before soldering and plating, and also serves to remove scale. Using a deep etching procedure, flat-relief images are created.
Multilayer metal etching
- Electroplating is a method of manufacturing metal products using the electrolytic method from zinc, pure copper and silver. Forms made of plaster, wax or graphite are placed in an electrolyte solution, and then, under the influence of an electric current, the process of metal growth occurs to give the product the desired shape.
Product based on the painting “Hunters at Rest” (electroplasty).
- Mounting is the process of assembling metal products from individual parts or elements. To assemble a solid product from parts, welding, soldering, rolling or crimping on a lathe is used. When making jewelry, several different types of fastening are used to connect precious stones to the metal base of the product:
1) The stone is firmly fixed with a smooth metal rim.
Stone in a durable metal rim
2) The lateral beveled parts of the stone are grabbed with pointed teeth.
The precious stone in the product is secured with the help of teeth.
3) The stone is glued to the surface of the precious metal, treated with a gravel.
Stone glued to metal base
- Product finishing - this method of metal processing consists of polishing its surface and coating it with a thin layer of a stronger and more resistant metal. Often chromium, copper, nickel, as well as silver and gold are used for these purposes. In order to make the product more decorative, coatings of any shade can be applied to the metal surface.
Gold-plated jewelry
Thus, we looked at all sorts of artistic metal processing methods that allow craftsmen to make unique jewelry and interior design items. Today, new technologies make it possible to facilitate many types of work, as well as to do most operations much faster than in previous times.
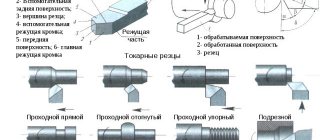
Methods of mechanical processing of metals
A large group of methods for machining metals have one thing in common: each of them uses a sharp and hard tool in relation to the workpiece, to which mechanical force is applied. As a result of the interaction, a layer of metal is separated from the part, and its shape changes. The workpiece exceeds the dimensions of the final product by an amount called “allowance”
There are such types of mechanical processing of metals as:
- Turning. The workpiece is fixed in a rotating tooling, and a cutter is brought to it, removing a layer of metal until the dimensions specified by the designer are reached. Used for the production of parts shaped like a body of revolution.
- Drilling. A drill is immersed into a stationary part, which quickly rotates around its axis and is slowly fed towards the workpiece in the longitudinal direction. Used for making round holes.
- Milling. Unlike drilling, where processing is carried out only with the front end of the drill, the side surface of the cutter is also working, and in addition to the vertical direction, the rotating cutter moves both right and left and back and forth. This allows you to create parts of almost any desired shape.
- Planing. The cutter moves back and forth relative to the stationary part, each time removing a longitudinal strip of metal. In some machine models, the cutter is fixed and the part moves. Used to create longitudinal grooves.
- Grinding. The processing is carried out by rotating or performing longitudinal reciprocating movements with an abrasive material that removes thin layers from the surface of the metal. It is used for treating surfaces and preparing them for coating.
Metal grinding
Each operation requires its own special equipment. In the technological process of manufacturing a part, these operations are grouped, alternated and combined to achieve optimal productivity and reduce intra-shop costs.
Methods of decorating metal products
Decorating items made of precious metals is also to some extent akin to processing, the most common being filigree and enameling.
Depending on the design, the openwork pattern can be soldered onto metal or take on a relief shape
Filigree is a fairly ancient technique. The term itself consists of two Latin horses - “phylum” means thread, and “granum” means grain. Filigree is a collection of thin threads intertwined and decorated with polka dots. This technique was first used in ancient Egypt in the second millennium BC.
From those times to this day, filigree has been exclusively handmade. There are many techniques, they are named after the cities or localities where they are widespread. But in general they can be classified as follows:
The development of filigree art, suspended by the Mongol-Tatar invasion, flourished again in the 15th-16th centuries.
- soldered;
- openwork;
- volumetric.
Brazed filigree is the simplest way to decorate metal products. It is a wire pattern, with decorative elements, which is soldered to a sheet of metal; it will act as a background. Perforated filigree can also be used, when after soldering the base is removed by sawing it out.
There may be enameled filigree, when after soldering the pattern to the base, the space is filled with enamel. The openwork technique involves soldering wire elements together, without using a background, so the product becomes like lace.
Volumetric filigree is presented in such products as vases, goblets, boxes, caskets, etc. To obtain such an item, the elements are first prepared, which are then connected to each other by soldering or attached to the base.
Enamel is a substance obtained by melting glass or other inorganic materials that have an oxide composition. The enamel is applied to the metal in a liquid state and left to harden.
The variety of colors and the ability to paint on enamel have made this technique in demand and popular for many centuries. Products with the addition of enamel are most often found in jewelry, as well as in home furnishings.
Pressure treatment
Metal forming is used to change the shape of a part without compromising its integrity. The following types exist:
- Stamping.
- Forging.
Before forging, the workpiece is heated, supported on a hard surface, and a series of blows are applied with a heavy hammer so that the workpiece takes the desired shape.
Historically, forging was done by hand; the blacksmith heated the piece in the flame of a forge, grabbed it with tongs and placed it on an anvil, and then hit it with a smith's hammer until a sword or horseshoe was made. A modern blacksmith acts on a workpiece with a hammer from a forging press with a force of up to several thousand tons. Billets up to tens of meters long are heated in gas or induction furnaces and fed to the forging plate by transport systems. Instead of a hand hammer, forging dies made of high-strength steel are used.
Forging
For stamping, two forms are required that are mirrored in relation to each other - a matrix and a punch. A thin sheet of metal is placed between them, and then moved with great force. The metal, bending, takes the form of a matrix. For large sheet thicknesses, the metal is heated to the point of plasticity. This process is called hot stamping.
During stamping, operations such as:
- flexible;
- pulling;
- settling;
- and others.
Stamping is used to produce a wide range of products - from household appliance housings to wheel rims and gas tanks.
Coinage
Embossing a relief on a thin metal sheet or plate is called embossing. This process is carried out using a hammer and a special rod. As the hammer hits the rod, it leaves a mark on the plate or gives it a three-dimensional appearance. The hammers are called accelerating hammers, and the metal is preliminarily cold rolled to obtain the desired thickness.
Artistic embossing of products requires high precision due to the complexity of the forms; accordingly, you need a material that can be easily processed
This is the initial stage, preparatory, after its completion they proceed directly to artistic decoration. This is a very delicate and painstaking work, for it they use a whole set of rods of various shapes and sizes, they are called mints. It is much easier to carry out embossing on several small plates, which can then be joined into a single three-dimensional object by soldering.
Even in ancient times, a method of chasing figures was invented. It consists of several processes: first, thin sheets of metal, mostly precious, are pressed onto a tin or bronze model, then a shape or design is given using hammers, and finally the sheets are carefully removed from the mold and soldered together.
Often, the artistic processing of metal by hammering can combine the processes of engraving, casting and carving.
There are three types of minting technique:
- from sheet metal;
- for defense or casting;
- embossed.
The traditional method of minting is on the thinnest sheet with rods, and the processing is completed and the artistic form of the cast products is completed in two other ways. Modern casting techniques make it possible to achieve ideal shapes and designs of the product, however, various defects can often occur:
- shells;
- growths;
- neslitins;
- skew;
- roughness.
Embossing is a process of embossing using matrix boards, which are called basma boards, from which another name for the technology is basma. The embossing process is carried out as follows: a wooden matrix is prepared, which will display the relief of the future product.
Basmen board
A thin gold or silver sheet is placed on the matrix, then covered with a thicker lead sheet. The blows applied by the hammer fall on the lead cushion, which becomes compacted and acquires the relief of the matrix, repeating all the contours, volumes and patterns. The metal, sandwiched between the lead gasket and the matrix, takes exactly the same shape.
When the embossing process is completed, the lead pad is removed and the layer of metal - basma - is carefully removed; it has softer design features than the matrix, as if smoothed out. The thicker the sheet layer, the smoother the image will be, so it is not recommended to use metal larger than 0.3 mm for basma.
Basma, as a minting technology, is used for forging products such as iconostases, frames, book bindings, caskets, and to create portrait images.
Metal minting technology
Processing by cutting
The metal is supplied to the enterprise in the form of rolled products - sheets or profiles of standard sizes and thicknesses. To separate a sheet or profile into products or blanks of the required size, cutting processing is used.
For profiles, cutting with an abrasive wheel or circular saw is most often used.
Several types of cutting are used for cutting metal sheets:
- Manual. A gas welder with a gas torch cuts out pieces of metal of the required size and shape. It is used in small workshops and pilot production.
- Gas. The gas cutting installation cuts with the flame of an automated gas burner and allows you not only to quickly cut sheets, but also to arrange the cut pieces into containers for delivery to assembly areas
- Laser. Cuts metal with a laser beam. It features high accuracy and low waste ratio. In addition to cutting, it can perform welding and engraving operations - applying permanent inscriptions to metal.
- Plasma. Cuts metal with a torch of highly ionized gas - plasma. Used for cutting sheets of hard and special alloys.
Laser cutting
In conditions of industrial production and medium or large series, the concept of metal utilization rate comes to the fore. It is increased both due to a denser arrangement of parts over the area and due to advanced cutting technologies that produce less waste
Sales of metal crafts
The main goal of creating forged grilles with beautiful patterns, magnificent coinage, amazing tin soldiers or an unusual sculpture from spare parts of an old Zaporozhets is to earn money. It's important to think about how to market your creations.
In this matter, you cannot do without the help of advertising. The Internet is the best advertising platform. It is worth sharing with everyone you know your desire to sell your creation, asking them for help so that they pass on the information to their friends. There are special sites for such advertisements. Finally, you can use the services of online stores.
But you shouldn’t neglect the old proven method - go to the market and try to sell the products yourself. You can contact local commercial establishments that specialize in selling souvenirs and artistic products. It is important to remember that water does not flow under a lying stone. Therefore, if you want to make money, then do not give up and success will certainly come.
Making something worthwhile with your own hands from unnecessary things is not only interesting, but also quite profitable. It can improve not only your mood, but also your financial situation.
Chemical processing of metals to increase the protective properties of the material
Chemical treatment of metal is the action of special substances on it in order to cause a controlled chemical reaction.
They are performed both as preparatory operations to clean the surface before welding or painting, and as finishing operations to improve the appearance of the product and protect it from corrosion.
Metal galvanizing
Protective coatings are applied using electrochemical treatment using the galvanic method.
Elements and alloys used in the work
Every craftsman engaged in this business at a professional level must perfectly know all the varieties and features of specialized raw materials. The work is performed using ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
The following types of materials are mainly used:
- Steel with high carbon content. The iron-based alloy has practically no foreign impurities. It is distinguished by its special hardness of the outer layer, combined with internal elasticity. Easily amenable to cutting and technological deformation when heated.
- Copper. An easily processed, corrosion-resistant element with a reddish tint. High thermal and electrical conductivity and plasticity determine the widespread use of metal in the manufacture of various souvenirs using artistic metal processing.
- Brass and bronze. These copper-based alloys are used to create inlaid items and embossing.
- Zinc. The metal is white, slightly blue. It is easily soldered, so engravers often use it to produce embossed drawings and cast miniature sculptures.
- Lead. Poisonous metal. In industry it is used as a component of low-melting alloys, which in turn are used for decorative casting.
Silver, tin and aluminum are also used for inlay.
Thermal types of metal processing
Heat treatment of metals is used to improve their physical and mechanical properties. This includes operations such as:
- annealing;
- hardening;
- vacation;
- aging;
- normalization.
Heat treatment of steel
Heat treatment involves heating a part to a certain temperature and then cooling it according to a special program.
Annealing
The workpiece is heated to the plasticity temperature and slowly cooled directly in the furnace.
Annealing reduces the hardness of steel, but significantly increases ductility and malleability.
Annealing
Used before stamping or rolling. During annealing, internal stresses that arise during casting or machining are relieved.
Hardening
When hardening, the workpiece is heated to the plasticity temperature and kept in this state for a certain time, during which the internal structures of the metal are stabilized. Next, the product is quickly cooled in a large amount of water or oil. Hardening significantly increases the hardness of the material and reduces its impact strength, thereby increasing brittleness. Used for structural elements subject to large static and small dynamic loads.
Vacation
Carried out after hardening. The sample is heated to a temperature slightly lower than the quenching temperature and cooled slowly. This allows you to compensate for the excessive fragility that appears after hardening. Used in tool production
Aging
Artificial aging involves stimulating phase transformations in the metal mass. It is carried out with moderate heating to give the material properties that arise during natural aging over a long time.