- Reports and messages
- Geography
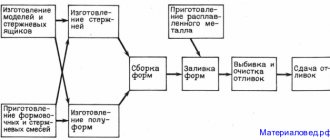
- Metal casting
Metal, as many people know, is capable of taking the form that a person offers it.
This fact was noticed back in ancient times. The ability to use iron to melt various figures was made possible by meteorites. Autumn meteorite iron is soft and easy to work, so the basics of casting have been studied for a very long time. In Russia, some of the most honorable residents are engaged in metal casting. Thus, such grandiose structures as the “Tsar Bell” and “Tsar Cannon” were attributed to this craft. Both monuments, despite their names, were never involved in military affairs.
Metal suitable for casting:
The most important property for a metal that must be present is fluidity. From one container to the next, the molten metal should flow easily, filling the entire space. If the metal does not have this property, then it will be much more difficult for craftsmen to cope with it. It simply will not have time to fill all the gaps in the form and will freeze. One of the most “convenient” metals is cast iron. This alloy has ideal fluidity.
Start:
First, you need to melt the cast iron billets in special furnaces. If a single mold is required, then the alloy is poured into it using a special ladle. If a large volume of figures is needed, then a tape is used for this, which automatically advances. After the process, grinding machines are used to remove scale.
Injection molding:
Firstly, to implement this casting method, special molds are needed. Secondly, injection equipment will be needed. One of the main advantages of the method is increased productivity. The quantity of goods consumed is much less than when using conventional equipment. The complexity of the method lies in the fact that during the separation of the product itself from the figure, technical injury is possible. And another disadvantage is that you cannot create products with thin walls. The reason is that a large layer will not be able to harden evenly.
Option No. 2
Metal casting is not a simple, but very interesting process. Its essence is to pour molten metal into special molds. As the metal cools, it hardens into the shape of the finished product.
Any metal can be melted and used for casting, but not all metals have the same casting properties. These properties directly depend on the structure of the metal and its chemical composition.
Basic casting properties of metals.
Fluidity is the ability of liquid metal to fill a casting mold and reproduce its contours and surface
Crystallization is the transition of a metal from a liquid to a solid state, with the formation of a structure. This process directly depends on the shape, pouring temperature and metal structure.
Shrinkage. The property of metal is that after cooling and solidifying, it reduces its size and volume.
There are the following types of casting:
One of the most ancient methods is casting into the ground. It is considered a very labor-intensive, but at the same time cheap method. A special wooden model of the future casting and a molding mixture that contains earth are made. Molten metal is poured into the finished casting mold. The cooled workpiece is separated from the mold and polished.
Chill casting. This method consists of pouring metal into a special mold, where it cools quickly enough and you can get a finished product in a short time. The casting mold is called a chill mold, and consists of two parts that are connected by a core. This method is convenient to use for metals with high fluidity.
Injection molding. The casting mold is filled with metal using a piston or under high air pressure. This method makes it possible to produce fairly accurate products that require a minimum of further grinding.
Static fill. Molten metal is poured into a stationary mold and remains there until it hardens completely.
Nowadays, metal casting has become an automated process and is widely used in production. Casting is used for the manufacture of both large and small parts, with both simple and complex product shapes. This process is quite popular due to the possibility of its comprehensive application and use in mass production.
A little history
At the current scale of industry, modern civilization processes metal in just one year in such a volume, the extraction of which in previous times would have taken at least a couple of centuries. And it’s not just about improved technologies and increased speed of production processes. Such a volume of metal industrial products is an urgent need of modern humanity.
In a report on physics on metal casting, it is impossible not to pay a little attention to the origin and development of foundry. The ability of iron to harden in a given form under certain conditions was highly valued by people back in ancient times. According to the assumptions of many scientists and researchers, mankind's acquaintance with metal was carried out through meteorites.
Meteoric iron had all the characteristics necessary for successful casting (fusibility, etc.). It was this substance that marked the beginning of the foundry business. Ancient people quickly learned the basics of the process of “taming” metal, after which the stage of development of casting as a component of life began. By the Middle Ages, foundry was already a large industry with a large turnover of funds.
For many centuries, humanity has comprehended the secrets of metal and not in vain. Now knowledge has already reached such a high level that almost any amateur craftsman can make a simple and small metal part at home.
Report on the topic Metal casting in physics
Due to their properties, metals are in demand in industry. In order to reduce the oxidation process, they are used in the form of alloys with the addition of elements that give them additional properties: ductility, the desired structure, weight, density, durability: antimony, magnesium, sulfur, phosphorus, chromium, nickel, vanadium, aluminum, silicon. The production uses mainly cast iron alloy, consisting of iron with carbon of more than 2.14%, and steel, which contains iron of at least 45% and carbon up to 2.14%. The different percentages of the alloy composition are determined by the necessary properties of the resulting parts.
Used in:
- automotive industry,
- mechanical and instrument engineering,
- dentistry.
Manufacturing of parts by casting:
- Static, in which molten metal fills a fixed mold. When cooled it hardens and comes out. The result is castings of the simplest configuration.
- In metal molds (chill);
- Die casting,
- In shell forms,
- In lost wax models.
Chill casting.
The technological process consists of pouring metal at its melting temperature into a chill mold without forced pressure. The form consists of two parts, which are connected by locks. The internal cavity of the chill mold is cleaned and covered with a layer of fire-resistant paint to protect the internal surface from contact with melts. At the end of the process, in order to remove the finished product, the mold is cooled either naturally or forcefully. All structural elements are cast iron or steel.
Advantages of the method:
- stable characteristics of casting properties.
- complex product configurations are available.
- the real creation of an automated process due to the rare replacement of the die. No time is wasted on surgery.
- fairly environmentally friendly production.
Flaws:
- Cooling speed is not suitable for all manufactured parts.
- It is beneficial to use the process only for large volumes of manufactured products; a cast iron chill mold produces 20 large and 400 small-sized products per year.
Die casting.
The principle of the process is the formation of a casting under pressure in the range of 7 – 700 MPa. The press piston moves the hot alloy into the mold cavity. The castings are then solidified and ejected. Parts are obtained with characteristics close to the specified values.
Advantages of the method:
- Large output of products per unit of time.
- Reducing the cost of production due to long-term use of one mold. The spent parts of the structure are melted down. The result is work without waste.
Flaws:
- It is impossible to make products of complex design; when removed from the working chamber, they will become deformed.
- Inability to make large-size castings.
Lost wax casting.
The technological process uses disposable forms made of ceramics or non-metals paraffin and stearin. The chill mold is made according to a model that is dissolved or burned out.
The mold is heated to a high temperature and filled with alloy. At the end of the operation, the finished parts are knocked out with a special pusher.
Advantages:
- Production of products from any alloys, different sizes, with specified accuracy.
- Small amount of metal loss, reduced material consumption.
- Used in small industries.
Flaws:
- The need for manual labor.
- Variety of materials used.
Shell mold casting.
Principle of the method:
A prepared mixture of various elements is applied to a heated cast-iron model at a temperature of 230-315 degrees.
The elements are sintered and a shape is obtained, which is released from the model by a special pusher.
The shells are either clamped or glued together for use together. Can be used in a single version.
Advantages of the method:
- Reducing labor costs.
- You can reduce the costs of materials and metal.
- A small percentage of defective output.
Flaws:
- The mold is intended for one casting only.
- Expensive molding sand.
- High percentage of harmful gases released.
8th grade
Areas of use
The technological process of metal casting is in demand, since its use makes it possible to produce a variety of high-quality products without resorting to bulky equipment and a huge number of workers.
This production method is used to create and produce various metal products, which, in turn, are widely used in the following industries:
- automotive;
- aviation;
- mechanical engineering;
- electrical engineering;
- medical (in particular, dental and orthopedic);
- jewelry, etc.
In the modern metal industry market, this production technology is in high demand. Moreover, metal casting is one of the top ten best technologies in the world, the most effective and most used.
Popular message topics
- Ursa Minor constellation
The clear night sky is beautiful with its star diversity. Since ancient times, people, admiring the sky, assigned different names to certain groups of stars, looking for similarities in their outlines with objects or animals. - City of Kostroma
Kostroma is an ancient Russian city that was founded back in the 12th century. But, a century later, it was formed as an independent, appanage principality. The origin of the city is connected with the activities of Prince Yuri Dolgoruky. - Flower Geocinth
Hyacinth is a perennial bulbous herbaceous plant belonging to the Asparagus family. The name "hyacinth" comes from the Greek language. And it translates as “flower of rain.”
Casting classification
Casting includes many subcategories that differ significantly from each other according to a variety of criteria. The classification of metal casting into main types is shown in the table.
| Classification criterion | Categories and varieties |
| Material (i.e. metal) of the castings |
|
| Low tide technology |
|
| Requirements for castings (dimensional accuracy, degree of surface roughness, etc.) |
|
| Purpose of castings |
|
The main criteria are the product material and casting technology. Therefore, it is worth considering the categories related to them in more detail.
Casting material
All existing metals can be cast, but their suitability for this process is far from the same. They differ from each other in their casting properties - key parameters for the process. The main indicator of the suitability of a material for casting is its fluidity. This parameter reflects the ability to fill a mold of any configuration . The degree of fluidity of a substance depends on its following characteristic features:
- chemical composition;
- internal structure;
- melting temperature.
The material for casting must have a high fluidity value. To do this, it must, in particular, have a low melting point. The lower this indicator is for a material, the easier it is to cast and, accordingly, the less cost the production process requires. That is why the most popular and common metals in industry are those with a low melting point.
Metals suitable for casting and actively used in this process are divided into three categories:
- black;
- colored;
- rare earths.
In addition, sometimes alloys based on ferrous or non-ferrous metals are classified into a separate category (for example, for the former it is cast iron with nodular graphite). The group of ferrous metals includes castings from iron-based alloys:
- become;
- malleable cast iron;
- foundry cast iron.
Rare earth metals are the names given to 17 elements of Mendeleev's periodic table. Of course, in terms of demand in the metal industry, they are significantly inferior to the scale of casting ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
As for non-ferrous metals, they are represented by precious materials, as well as substances that do not include large amounts of iron:
- aluminum;
- bronze;
- bismuth;
- gold;
- brass;
- copper;
- magnesium;
- nickel;
- tin;
- platinum;
- lead;
- silver;
- titanium;
- zinc, etc.
For each type of material, the preferred casting technologies have been determined in accordance with its properties and characteristics. This allows you to produce a product with the required parameters and qualities, and also, no less important, to avoid defects.