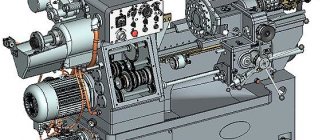
Main purpose
Machines of this type are used primarily, of course, for boring holes of different diameters in workpieces. But if necessary, they can also be used for:
- turning the external surfaces of cylindrical parts;
- machining the ends of workpieces;
- countersinking and reaming of holes;
- thread cutting;
- milling.
Types of boring machines
Equipment of this type can be classified according to several criteria. According to the scope of application, such machines can be:
- universal turning and boring machines;
- specialized.
The machines of the second group are in turn divided into the following varieties:
- horizontal boring;
- coordinate boring;
- diamond boring.
Recently, CNC boring machines have become very widespread in enterprises.
Boring machines: domestic and foreign models
Boring machines are represented quite widely on the domestic market. There are many brands of this equipment. Examples include:
- Machines of the WH, WHN, WRD series produced by TOS Varnsdorf.
- Mobile Climax models made in the USA.
Soviet models of this group are still very popular on the market. For example, if you wish, you can purchase horizontal boring machines 2A614, 2A622, 2A635 or coordinate boring machines 2421, 2E440, 2E450, etc.
What can a jig boring machine be like?
Equipment of this type is intended primarily for the most precise processing of workpieces. Coordinate boring machines can be:
- single-post;
- two-post.
The design of such machines includes:
- bed;
- rack;
- table with slide;
- boring head.
Also, the design of such equipment includes a traverse.
Characteristics of machines
Types of boring machines depend on the specifics of their use in production.
- Drilling. Previously, the most popular type of device that could be found in any metalworking enterprise. Currently, most drilling operations are performed on milling machines. Drilling equipment is divided into standard and specialized (for specific parts).
- Lathes. They are actively used by craftsmen for processing planes and holes inside cases. They are also called coordinate ones.
- Mobile surfacing. Portable devices used for repair work and restoration of cylindrical holes on large-sized equipment. Indispensable in the field of machine, ship and aviation types of construction.
Features of working on a coordinate boring machine
When using this type of equipment, the workpiece being processed is first secured on the work table. Next, the required cutting tool is installed in the spindle. The work is then done in the following order:
- depending on the height of the workpiece, adjust the traverse and boring head;
- set the spindle to the specified coordinates.
The last operation on equipment such as a jig boring machine, depending on its type, can be performed in different ways. On a single column model, the spindle is installed properly by moving the work table in two perpendicular directions. On two-rack equipment:
- the table is moved longitudinally;
- the boring head is moved in the transverse direction along the traverse.
Equipment types
As a rule, there are three main types used in production:
- Horizontal boring machines;
- Coordinate boring;
- Diamond boring.
The first two types are the most common.
Horizontal boring machines
The main feature of such equipment is the horizontal position of the spindle, which allows it to extend. Thus, it is possible to make a hole even in inaccessible places of large parts (booms, frames, metal structures).
The main movement of the unit is rotational-translational, performed through a spindle. Not only the tools move, but also the workpieces themselves. If the need arises, you can change the feed and speed during operation. Sometimes a special substrate is used when feeding.
Depending on the configuration, there may be additional auxiliary movements:
- The spindle head moves along a vertical axis;
- The table moves along previously specified coordinates.
In some models, the design provides that the rest and rear pillar can move. They can be used for processing products made of cast iron or cast steel.
Boring machines are used to work with complex parts that contain numerous holes, grooves, and ledges. According to their layout they are divided into:
- Models with a spindle no more than 125 mm. Designed for processing small workpieces. The table is movable along two axes, the boring heads move in the vertical direction.
- Models with spindle 100−200 mm. Allows you to work with medium and large parts. The table moves only along one axis.
- Models with spindle 125−320 mm. With their help you can process very large parts. The table is motionless.
Jig boring machines
Such machines are designed for drilling holes according to certain parameters. Perform operations on various workpieces. High-precision processing is obtained due to the presence of special devices: electronic, mechanical and optical. In addition, rotary tables also help to achieve the desired results: the hole can be made without moving the part. The models are not too large and take up little usable space.
Diamond boring type models
They allow fine boring of cylindrical surfaces. If there are additional components, then conical surfaces and ends with rotation grooves can be processed. It is permissible to drill a pair of holes that have parallel axes. Machines of this type can be:
- Vertical;
- Sloping;
- Combined;
- Horizontal, the table is movable.
Model range of jig boring machines
Many manufacturers produce such equipment today. But most often, enterprises use jig boring machines:
- 2E450. This single-column model has table dimensions of 630 x 1120 mm and is equipped with an optical measuring system complemented by an on-screen readout. This boring machine also has an automatic slide stop function. Another addition to this model that increases ease of use is the device for pre-setting coordinates.
- 2D450. This model also has table dimensions of 630 x 1120. The optical device included in its design can measure both whole and fractional parts of coordinates.
Of course, other coordinate boring machines can also be used in enterprises. Models 2A450, 2L450AF11-01, for example, are also in great demand today.
Horizontal boring machines
Such equipment is also used quite often in enterprises and workshops. Its main distinguishing feature is that the spindle in it is located horizontally. The main movement of the latter is rotational-translational relative to the axis. In this case, during turning, both the feed of the workpiece and the movement of the working tool itself can be carried out.
Moving the spindle head on equipment such as a horizontal boring machine is an additional movement.
Main technical characteristics of boring machines
The main technical characteristics include the following indicators:
Work table dimensions mm; Diameter of retractable spindle mm; Maximum dimensions and weight of the workpiece being processed Maximum movement along the axes mm.; Spindle speed range rpm; Range of working feeds mm/min.; Main drive electric motor power kW; Dimensions of the machine and its weight.
Considering the fact that many boring machines are unique equipment, their cost can range from several hundred thousand to several tens and hundreds of millions of rubles. The monetary cost of metal-cutting equipment depends, first of all, on its technical and technological characteristics, as well as the general technical condition of the boring machine model of interest.
What models can be used
Equipment of this type can be supplied to the market today, both ordinary universal with a spindle with a diameter of 110-130 mm, and heavy. The machines of the latest variety are usually additionally equipped with a slider and a movable column.
Manufacturers also produce many models of such equipment. For example, units of the VFC and FORT lines are very popular among consumers
The VFC horizontal boring machine can be designed for processing workpieces weighing up to 10 tons. Such machines are used mainly for boring parts made of cast iron and steel. These models are built on a modular basis and have a rotary table.
FORT series machines are also presented on the market in a very wide range. They can have a classic design with a cross-shaped table or with a movable column. The table dimensions of FORT horizontal boring machines vary from 1250 x 1400 mm to 4000 x 4000 mm. The spindle diameter can be 100-260 mm.
Lectures on the section “Drilling and boring machines”
Topic Drilling and boring machines
Purpose and classification.
Drilling machines
are designed for drilling blind and through holes in solid material, drilling, countersinking, reaming, cutting internal threads, cutting disks from sheet material. To perform such operations, drills, countersinks, reamers, taps and other tools are used. The forming movements when processing holes on drilling machines are the main rotational movement of the tool and the translational movement of the tool feed along its axis.
The main parameter of the machine is the largest nominal drilling diameter (for steel). In addition, the machine is characterized by overhang and maximum spindle stroke, speed and other indicators.
a B C D
Figure 4.16. Single-spindle (a, b) and multi-spindle (c, d) vertical drilling machines:
a - desktop; b - medium size; c - on a common bed; g - with adjustable spindles
a B C
Figure 4.17. Radial drilling machines:
a - stationary; b - mobile on rails; in - portable
Depending on the area of application, universal and special drilling machines are distinguished. Specialized drilling machines for large-scale and mass production are also widely used, which are created on the basis of universal machines by equipping them with multi-spindle drilling and tapping heads and automating the work cycle. Devices that allow the use of universal drilling machines as special and specialized ones are discussed in the textbook.
From a fairly large range of drilling machines, the following main types of universal machines can be distinguished: single- and multi-spindle vertical drilling machines (Figure 4.13); radial drilling (Figure 4.14); horizontal drilling for deep drilling (Figure 4.15).
Figure 4.18. Horizontal drilling machines for deep drilling of rotating (a) and stationary (b) workpieces:
Dn Ds - directions of main movement and feed, respectively
Boring machines
are divided into universal horizontal boring and coordinate boring.
Horizontal boring
The machines are designed for boring, drilling, countersinking and reaming holes, threading and for processing flat surfaces in parts such as housings, brackets, etc. These machines are used in small-scale and mass production. The tools used in boring machines are cutters, milling cutters, drills, countersinks, reamers, and taps. The main rotational movement is imparted to the tool. The feed motion is communicated to the tool or workpiece.
Vertical drilling machines.
The main components are located on the frame 1 of the machine. The bed has vertical guides along which the table moves 9
and a drilling head
3,
carrying a spindle 7 and an electric motor
2.
The workpiece or device is installed on the machine table
9
, and the alignment of the workpiece hole and the spindle is achieved by moving the workpiece.
The gearboxes and feeds are controlled by handles 4, p
scientific feed - with a steering wheel
5.
The depth of processing is controlled by the dial
6.
The counterweight is placed in a niche, the electrical equipment is placed in a separate cabinet
12.
The base plate 11 serves as the support of the machine.
In medium and heavy machines, its upper plane is used to install workpieces. The internal cavities of the foundation plate in individual machine designs serve as a reservoir for coolant. The table 9
can be moved along the vertical guides manually using a lead screw by rotating the handle
10.
In some models, the table is fixed (removable) or rotary (folding).
Coolant is supplied by an electric pump through a hose 8.
The drill head units are lubricated using a pump, the remaining units are lubricated manually.
Drill head 3
It is a cast iron casting in which the gearbox, feed mechanisms and spindle are mounted.
The gearbox contains two- and three-crown blocks of gear wheels, by switching which with the help of one of the handles 4
the spindle receives different angular speeds.
The spindle rotation speed, as a rule, changes in steps, which is provided by the gearbox and two-speed electric motor 2.
Figure 4.19. Vertical drilling machine:
1 — column (bed); 2 - electric motor; 3 - drilling head; 4 — shift handles for gearboxes and feeds; 5 — manual feed steering wheel; 6 — dial for controlling the depth of processing; 7— spindle; 8— hose for coolant supply; 9 - table; 10 — table lift handle; 11 - foundation slab; 12 - electrical cabinet
Figure 4.20. Vertical drilling machine 2S132
Figure 4.21. General view of the vertical drilling machine model 2A135
Radial drilling machine
Unlike a vertical drilling machine, in a radial drilling machine the axes of the workpiece and spindle holes are aligned by moving the spindle relative to the stationary workpiece in the radial and circular directions (in polar coordinates). By design, radial drilling machines are divided into general-purpose machines (Figure 4.22), portable ones for processing holes in large workpieces (the machines are carried by a crane to the workpiece and machine vertical, horizontal and inclined holes) and self-propelled, mounted on trolleys and secured during processing using shoes.
Figure 4.22. General view of a radial drilling machine
On general-purpose radial drilling machines, the workpiece is secured to a foundation plate 1
(see Figure 4.23) or side table
9;
very large workpieces are placed on the floor.
A cabinet 2 is mounted in the base of the slab,
in which a rotary column
3
. The column clamp is hydraulic.
Sleeve 6
moves along the column from the lifting mechanism
4
and the lead screw
5.
The spindle head 7 is mounted on the sleeve and can be moved along it manually.
The spindle head contains gearboxes, feeds and controls. The spindle 8
with the tool is installed relative to the workpiece by turning the sleeve and moving the spindle head along it.
Figure 4.23. Radial drilling machine:
1 - plate; 2 - cabinet; 3 - column; 4 — lifting mechanism; 5 — lead screw; 6 — sleeve; 7 — spindle headstock; 8 — spindle; 9 - side table
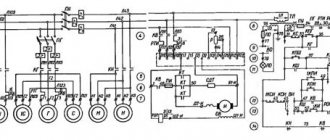
CNC drilling machines
CNC vertical drilling machine.
The machine is designed for drilling, countersinking, reaming, threading and light straight-line milling of parts made of steel, cast iron and non-ferrous metals in small-scale and mass production.
Turret 3
(Figure 4.20) with automatic tool change and cross table
4
allow coordinate processing of parts such as flange covers, panels without preliminary marking and the use of jigs. The accuracy class of the machine is usually P.
The machine is equipped with a closed CNC system; synchronizers are used as feedback sensors. The process of positioning and processing in a rectangular coordinate system is controlled by the CNC. There is a digital display and a correction for tool length is provided. The positioning accuracy of the table and slide is 0.05 mm, the discreteness of specifying movements and digital display is 0.01 mm. The number of controlled coordinates is 3/2 (total/simultaneous).
The CNC, mounted in cabinet 1, contains a reading device 10,
code converter
9,
technological command block
6,
control units for the drives of the slide 8 and table 7. For ease of visual observation of the operation of the mechanisms, a manual control and signaling unit 11 is provided. The CNC is equipped with various additional blocks: devices for correcting the radius, length and position of the tool, feed values, cutting speed; indication of movements, feedback sensors when cutting threads; stop control units on working and auxiliary strokes, etc.
Having received information through a reading device 10,
The CNC issues commands to the automatic drive of movement of the working parts of the machine, for example to the stepper motor
5
of the slide drive.
The power electrical equipment is located in cabinet 2
from where
The working body of the machine—turret 3
with a set of tools—provides processing with various tools (up to six) in the sequence specified by the program.
Figure 4.24. CNC Vertical Drilling Machine:
1 — autonomous CNC rack; 2 — power electrical equipment cabinet; 3 - turret head; 4—table; 5—stepper motor; 6, 7, 8, 11 — control units; 9 - code converter; 10 - reading device.
Figure 4.25 CNC Vertical Drilling Machine
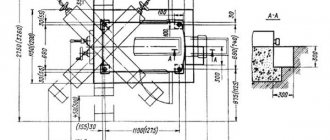
Horizontal boring machines
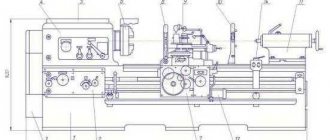
Universal horizontal boring machine with manual control.
The machine is designed for processing workpieces of large sizes and weight.
The machine (Figure 4.26) has a fixed front post 3
6
and faceplate
5
can move up and down On the base guides there is a slide
10,
and on them a table 9, which can move in the longitudinal and transverse directions relative to the spindle axis and make a circular motion.
On the base there is a rear stand 1 with a steady rest 2,
intended for additional support of the end of the boring bar when boring long holes.
4
is mounted on the faceplate in the radial guides which ensures the processing of flat surfaces and recesses with a cutter.
The machine is controlled from a remote control 8.
The coordinates of movement of the spindle head, steady rest, rear rack and table are counted using dials or using mounted optical devices (with an accuracy of 0.01 mm).
The main movement
is rotation - spindle and faceplate
Figure 4.26. Universal horizontal boring machine:
1.3 - racks; 2 - steady rest; 4 — caliper; 5 — faceplate; 6 - spindle; 7 - spindle head; 8 — remote control; 9 — table; 10 — sled; 11 - base
Figure 4.27. Universal horizontal boring machine model W100A.
Jig boring machines
Purpose and design features.
Jig boring machines are designed for machining holes with high accuracy of relative position relative to the base surfaces in body parts, jig plates, dies in single and small-scale production. These machines perform almost all operations typical of boring machines. In addition, marking operations can be performed on jig boring machines.
To accurately measure coordinate movements, the machines are equipped with various mechanical, optical-mechanical, inductive and electronic readout devices, which make it possible to measure the movements of moving parts with high accuracy - 0.003...0.005 mm. The machines are equipped with universal rotary tables, making it possible to process holes in the polar coordinate system and inclined holes.
According to the layout, the machines are single-column and double-column. The main motion is the rotation of the spindle, and the feed motion is the vertical movement of the spindle. Installation movements in single-column machines - longitudinal and transverse movement of the table to given coordinates and vertical movement of the spindle head depending on the height of the part; in two-column machines - longitudinal movement of the table, transverse movement of the spindle head along the traverse and vertical movement of the traverse with the spindle head.
Figure 4.28. Single column jig boring machine with manual control:
1
— flywheel for manual table movement;
2
— button for moving the slide;
3
— control panels;
4
- spindle;
5
— handle for manual accelerated movement of the spindle;
6
— spindle speed indicator;
7 - gearbox; 8 — spindle head; 9
- stand;
10 —
indicator of the speed of movement of the spindle sleeve;
11
— flywheel for setting the spindle speed;
12
— handle for manual precise movement of the spindle;
13
— button for moving the spindle sleeve;
14
— table movement button;
15
— button for the mechanism for dialing coordinates of the sled;
16
- table;
17 —
sled;
18
— guides;
19 -
bed;
20
— flywheel for manual accelerated movement of the table;
21
— flywheel for manual table movement with micrometric feed;
22
— handwheel of the device for bringing the optical system reference to zero;
23
— button for the mechanism for dialing table coordinates;
24
- flywheel for manual movement of the slide with micrometric feed
Figure 4.29. Coordinate —
boring machines model 2E450
Control questions
1. What is the difference between vertical drilling and jig boring machines?
2. What movements does the cutting tool of a vertical drilling machine perform when processing holes?
3. Name the main components of a radial drilling machine. What parts is it intended for processing?
4. How does a horizontal boring machine differ from a lathe, and is there anything in common in the movements of their units?
5. What cutting tool is used when processing products on a CNC horizontal boring machine?
6. Where is the workpiece mounted on a horizontal boring machine?
7. What is the purpose of jig boring machines? Name their main components.
Diamond boring machines
Equipment of this type is intended mainly for fine finishing of workpieces. The tools in such machines, as can already be judged by their name, are either diamond or carbide. A boring machine of this type can be used for processing workpieces made of both steel and cast iron, as well as alloys of non-ferrous metals, hard rubber, textolite, rubber, etc. In some cases, diamond boring can even replace grinding.
Cutting on such equipment is carried out at a significant speed and at the same time with a small depth of material removal. Depending on the location of the spindle, diamond boring machines can be horizontal or vertical.
Boring machines: purpose and areas of use
Such equipment can be used to perform such operations as:
- thread cutting, internal and external;
- drilling blind and through holes;
- countersinking;
- trimming the ends of workpieces;
- face and cylindrical milling, etc.
Most often, this equipment is used for finishing or semi-finishing. However, it happens that with its use they also produce finishing. The part body is rarely processed on such machines, but sometimes this operation is still performed. Repair of a boring machine is carried out using approximately the same technology as a turning machine. The same applies to operating features. The design of these two types of machines is similar. Like many other special types of equipment designed for processing metal and wood workpieces, a boring machine was once designed on the basis of a lathe.
Turning and boring machines
The main feature of this type of equipment is the very high spindle speed. A boring and turning machine can be used to process both flat and cylindrical parts.
When working on such equipment, the workpiece is mounted on the table. In this case, the spindle makes a rotational-translational movement.
Modern industry also produces large-sized turning and boring machines. The turning diameter of such equipment can be equal to 4 m. At the same time, the machine can process parts up to 32 m long. The most popular model of turning and boring machine at the moment is 2A656RF11.
Types by layout
A boring machine is typically used to machine complex parts with many holes, grooves, and shoulders. According to the layout, this equipment is classified into:
- Models with spindle diameter up to 125 mm. Using such equipment, small workpieces are usually processed. The table of such models can move along two axes. The boring head is capable of moving along the column in a vertical direction.
- Equipment with a spindle diameter of 100-200 mm. This boring machine is designed to work with medium-sized and large workpieces. With such machines, the table moves only in one direction.
- Models with spindle 125-320 mm. This equipment is used for processing very large parts. These machines have a stationary table.
CNC equipment
CNC can be complemented by both diamond and horizontal, turning or jig boring machines. Modern electronics, of course, greatly increases the ease of use of this equipment. The turner controls the operation of a CNC machine not manually, but through a computer. This allows you to achieve the highest precision drilling or cutting and maximum productivity.
CNC boring machines can be used for both roughing and finishing machining of workpieces. They cost, of course, much more than conventional models. Only turners who have undergone requalification under the appropriate program can work on such machines.