Theodolite 2T2A
Theodolite 2T2A is designed for measuring horizontal and vertical angles in triangulation and polygonometry of the 3rd and 4th classes, for astronomical observations, measuring distances using a filament rangefinder of a telescope and determining magnetic azimuths.
| Specifications: | |
| Root mean square error of vertical angle measurement in one step | 4″ |
| Zenith distance measurement range | 30°…145° |
| Telescope magnification | 25X |
| Field of view angle | 1o30? |
| Sighting range, m | 2…? |
| Minimum sighting distance, m | 2 |
| Outer diameter of the lens barrel, mm | 46 |
| The cost of dividing levels for alidades of horizontal and vertical circles | 15″ |
| Weight of theodolite with stand, kg | 5 |
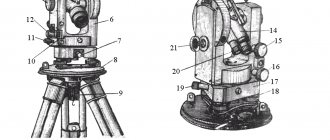
Theodolite device
The main elements that make up a theodolite:
- Dials with degree and minute divisions (horizontal and vertical).
- Alidade is a movable part of the theodolite, to which the dial and sighting system is attached.
- Telescope (sighting device) with fixing and aiming screws.
- Plumb to center over a point. It can be both optical and laser.
- A tribrach (stand) with lifting screws and a round level for leveling the theodolite.
- Microscope for taking readings.
The complete set of theodolite depends on the area in which it will be used. It can be supplemented with a compass guide, rangefinder attachments, sighting markers, etc. In some works, highly specialized theodolites are used: surveying, astronomical, gyroscopic.
Theodolite 2T30P
Theodolite 2T2A is designed for measuring angles in theodolite and tacheometric traverses, when laying out in planned and high-altitude survey networks, for measuring distances using a filament telescope rangefinder.
| Specifications: | |
| Root mean square error of vertical angle measurement in one step | 30″ |
| Vertical angle measurement limits | +60°…-55° |
| Telescope magnification | 20X |
| line of sight | 2° |
| Sighting range, m | 1.2…? |
| Rangefinder coefficient K | 100±0.5 |
| Outer diameter of the lens barrel, mm | 38 |
| Limb division price | 1″ |
| Weight of theodolite with stand, kg | 8.1 |
Theodolite 4T30P
The 4T30P technical theodolite is designed for measuring horizontal and vertical angles, measuring distances with a filament rangefinder, geometric leveling using a level with a telescope, and determining magnetic azimuths using a compass. It is used when laying theodolite and tachometer traverses, planned and high-altitude surveys, during reconnaissance and survey work.
| Specifications: | |
| Root mean square error of vertical angle measurement in one step | 30″ |
| Rangefinder constant term | 0 |
| Telescope magnification | 20X |
| line of sight | 2° |
| Sighting range, m | 1.2…? |
| Rangefinder coefficient K | 100±0.5 |
| Outer diameter of the lens barrel, mm | 38 |
| Limb division price | 1″ |
| Weight of theodolite with stand, kg | 6,8 |
Theodolite TZO. Small-sized optical repeating theodolite with a cylindrical vertical axis (Fig. H.1.). The telescope is moved through the zenith at both ends. The theodolite stand is not removable, but the three theodolite lifting screws are hinged to the bottom of the case, which serves as the base of the theodolite. This allows you to cover the theodolite with a case when moving from point to point and protect it from mechanical damage, especially when working in the forest.
The TZO theodolite has a hollow vertical axis and a hole in the bottom of the case, which makes it possible to center the theodolite above the theodolite stroke point using a telescope mounted vertically with the lens down.
When transporting the theodolite, the hole at the bottom of the case is closed with a screw cap attached to the boss at the bottom of the case.
With the TZO theodolite, you can perform geometric leveling using a cylindrical level UT20-T2, installed on the telescope parallel to the sighting axis.
Rice. 2.25. Wooden pole mounted on a concrete monolith
Rice. 2.26. Type of sign for long-term fixation of survey network points in forested areas
Rice. 2.27. Geodetic signs for securing points of survey networks on areas with hard surfaces (concrete, stone, asphalt) of the earth's surface
Rice. 2.31. sign:
Rice. 2.30. Ground geodetic sign - rail
Ground geodetic
Rice. 2.35. Metal pipe with guard
Rice. 2.34. Wooden stake, wooden post with cross 40
Rice. 3.2. View of the field of view of the reference microscope
Rice. 3.3. Theodolite T15:
Rice. 3.4. View of the field of view of the T15 reading microscope
1 - mirror; 2 — level window with a vertical circle of theodolite; 3 — diopter ring of the vision tube; 4 - mirror; 5 — porthole; 6 - setscrew; 7 - key; c — stand body; 9 — fixing screw of the theodolite stand; 10 - lifting screw
By special order, a level is supplied for the UT20-T2 telescope, which allows you to perform class IV leveling with a horizontal sighting beam.
Theodolite T15K - Optical scale repeating theodolite (Fig. 3.5).
The telescope has a direct image, which allows you to quickly and accurately find the sighting target.
The level when alidating a vertical circle in the T15K theodolite was replaced by a self-aligning optical compensator, which, when measuring inclination angles, freed the observer from bringing the level bubble to the zero point before reading along the vertical circle.
The use of sector digitization in the vertical circle of the T15K theodolite makes it possible to count the measured inclination angle on a scale without additional calculations. The angle of inclination when circling to the left is positive if the target is located above the horizon, and negative if the target is located below the horizon.
In the T15K theodolite, the vertical circle to the left of the observer is taken as the main position. Sector digitization of a vertical circle reduces calculations.
The field of view of the T15K theodolite reading microscope is shown in Fig. 3.6. The reading along the horizontal circle is 38°02.5′, the reading along the vertical circle is 0°25.5′. If there were no minus sign in front of the number O, then the reading would be 0°34.5′.
The optical plummet is embedded in the validating part of the theodolite.
Theodolite T15K can be used for leveling with a horizontal sighting beam. To do this, it is necessary to set the reading on the microscope equal to the zero point.
Theodolite T5. Optical scale repeating theodolite (Fig. 3.7). with the field of view of the reference microscope, like that of the T15 theodolite (see Fig. 3.4). Serves for measuring horizontal and vertical angles, measuring distances using a filament rangefinder or using a telescope mounted on the lens supports, rangefinder attachments DNR-06, DNT, DDZ, determining magnetic and astronomical azimuths.
In the T5 theodolite, the vertical circle to the right of the observer is taken as the main position when measuring angles.
With the T5 theodolite, you can perform technical leveling using a cylindrical level UT20-T2, installed on the telescope parallel to the sighting axis.
Theodolite T5K. Optical scale repeating theodolite (Fig. 3.8) with a self-aligning optical compensator instead of a level when alidating a vertical circle.
In the T5K theodolite, the circle to the right of the observer is taken as the main position. 46
Rice. 3.6. View of the field of view of the T15K reading microscope
Rice. 3.5. Theodolite T15K:
/ — eyepiece of the optical plummet; 2 — porthole mirror; 3 - lens hood; 4 — porthole; 5 — stand body; 6 - lifting screw
1 — fixing screw of the theodolite stand; 2 — optical plummet; .1—guide screw; 4 — level screw; 5 — key, 6 — stand body; 7 — lifting internal
I - fixing screw; 2 — optical plummet; 3 — optical micrometer guiding screw; 4 - porthole: 5 - round level; 5—fixing vnnt limb; 7 — stand; 8 — fixing screw of the stand; 9 — lifting vnnt
Rice. 3.7. Theodolite T5:
I
Rice. 3.8. Theodolite T5K:
Theodolite T5K has exactly the same field of view of the reading microscope as in theodolite T15 (see Fig. 3.4).
Theodolite T5K can perform technical and class IV leveling. To do this, it is necessary to install the pipe so that the reading on the microscope is equal to the zero point.
Theodolite 2T5. Optical scale non-repetitive theodolite (Fig. 3.9). belongs to the group of unified theodolites of the 2T series, with a level at the alidade of a vertical circle.
In the 2T5 theodolite, the circle to the left of the observer is taken as the main position.
The field of view of the reading microscope is also divided by color: the upper half, depicting the strokes of a vertical circle, is colored blue, the lower half, depicting the strokes, is yellow-green, which helps eliminate possible errors when measuring angles.
The vertical circle in the 2T5 theodolite has sector digitization, which allows you to count the measured inclination angle on a scale without additional calculations. The angle of inclination measured with a circle to the left is positive if the target is located above the horizon, and negative if the target is
Rice. 3.9. Theodolite 2T5:
1 — carrying handle; 2. 5 — fixing screws; 3, 6 — guiding screws; 4 — quotation screws; 7 — level window; S - setscrew
1 — guiding viit of the alidade of the horizontal circle, 2 — fixing screw of the alidade of the horizontal circle, I — set screw, 4 — handle for transferring the theodolite, 5 — eyepiece of the telescope, 6 — eyepiece of the optical plummet, 7 — handle for adjusting the horizontal circle, 8 — body theodolite stands. 9 — securing screw of theodolite stand, 10 — lifting screw
Rice. EVIL. Theodolite 2T5K:
located below the horizon. The vertical circle is divided into four sectors, of which two opposite sectors have a positive digitization [there is no plus sign (+)], and the other two are negative and have a minus sign (-) when digitized. The upper digitization of the scale is used for readings of positive angles, the lower - for readings of negative angles.
The field of view of the 2T5 theodolite reference microscope is similar to the field of view of the T15K theodolite reference microscope (see Fig. 3.6).
The optical plummet is built into the alidade part, the eyepiece is pointed towards the observer.
The 2T5 theodolite can be used for leveling with a horizontal sighting beam using the UT20-12 level.
Theodolite 2T5K. The optical scale non-repetitive theodolite (Fig. 3.10) belongs to the group of unified ones; it has a self-aligning optical compensator system with a vertical circle. In it, as in all other theodolites of the unified group, a vertical circle is adopted to the left of the observer.
Rice. 3.11. View of the field of view of the 2T5K theodolite reading microscope
The vertical circle in the theodolite, as well as in the T15K, is used with sector digitization, which allows you to count the measured inclination angle on a scale without additional calculations.
In Fig. Figure 3.11 shows an example of reading using a reading microscope. The reading in the vertical circle is 0°38.0′, in the horizontal circle it is 6°01.0′. If there was a minus sign before the number 0, then the reading would be 0°22.0′.
The 2T5K theodolite can be used for leveling with a horizontal beam. To do this, it is enough to set the reading on the microscope equal to the zero point by tilting the telescope.
Theodolite T2. An accurate optical non-repetitive theodolite (Fig. 3.12). The telescope gives a reverse image, through the zenith it is translated at both ends. The alidade level of the vertical circle is located inside the theodolite body. Observation of the alignment of the ends of the level bubble is carried out through a rotating prism-magnifying glass located on the side cover of the theodolite.
In the T2 theodolite, the circle to the left of the observer is taken as the main position.
To measure horizontal and vertical circles, use an optical micrometer located on the right side of the column.
In the field of view of the reference microscope, two windows are visible - large and small (Fig. 3.13). In the large left window, the images of strokes are separated by a horizontal line: in the upper part you can see a direct image of one side of the circle, and in the lower part you can see a reverse image - the diametrically opposite side of the circle. In the right small window you can see the micrometer scale and the horizontal fixed index, the number of whole units is counted along the left row of numbers, and tens of seconds along the right.
Before counting along the horizontal circle, the switch handle is set horizontally, in which case the field of view of the microscope will have a white background, and the visible strokes of the horizontal circle will be double (bifilar). By rotating the micrometer (see Fig. 3.10), carefully align the strokes of the upper and lower images of the parts of the circle in the large window.
The number of degrees is counted from the upper direct image, tens of minutes equal to the number of intervals concluded between the counted upper and lower digitized
Rice. 3.12. Theodolite T2:
/ - guiding screw of the alidade of the horizontal circle; 2 — dial switch handle; 3 — switch handle; 4 — micrometer handle; 5 — carrying handle; 6 — eyepiece; 7 — eyepiece of an optical micrometer; S—horizontal circle shift handle; 9 — stand body; 10 - lifting screw
Rice. 3.13. View of the field of view of the T2 theodolite reading microscope with horizontal circle reading
Rice. 3.14. View of the field of view of the T2 theodolite reading microscope with vertical circle reading
Rice. 3.15. Optical and reticle
plummet
Rice. 3.17. View of the field of view of the 2T2 theodolite reading microscope with horizontal circle reading
Rice. 3.16. Theodolite 2T2:
1 — guiding screw of the alidade of the horizontal circle; 2 — eyepiece of the optical plummet; 3—porthole; 4 — telescope eyepiece; B — handle for carrying the theodolite; 6 — installation vnnt; 7 — stand body; 8 — fixing screw of the theodolite stand; 9 - lifting screw
strokes differing by 180°; in this case, the lower digitized stroke will always be located to the right of the upper one or, as a special case, can be combined with it. Units of minutes are counted in a small window along the left row of numbers. Tens of seconds are counted there along the right row of numbers. The reading along the horizontal circle will be 57°58'02.4″ (see Fig. 3.13). To count in a vertical circle, the switch handle (see Fig. 3.12) is turned until it clicks into a vertical position, in which case the field of view of the microscope will have a yellow-green background, and the visible strokes of the dial will be single. Readings along a vertical circle are made in the same way. Before counting along a vertical circle, it is necessary to align the ends of the contact level bubble, observing them through a prism magnifying glass. The reading along the vertical circle (Figure 3.14) will be equal to 10°48'05.8″.
When using the UT20-T2 level on a telescope with a T2 theodolite, you can perform class IV leveling with a horizontal beam. To perform work on a three-post system, there is a set of sighting targets (SVT), marks, and optical centrifuges (Fig. 3.15).
Theodolite 2T2. Precision optical theodolite (Fig. 3.16)
Rice. 3.18. Theodolite Theo020:
/ - eyepiece of the reference microscope; 2 — telescope eyepiece; 3 - vertical circle guide screw: 4 - round level; 5 — guiding screw of the alidade of the horizontal circle; b - co-opus of the theodolite stand; 7 - lifting screw
Rice. 3.19. View of the field of view of the Theo020 theodolite reference microscope
Rice. 3.20. Theodolite Theo020A: Fig. 3.21. Type of field of view count-
guiding internal alidade of the horizontal microscope theodolite Theo020L circle; 2 - optical centrifuge. 3 - lens; 4 - eyepiece; 5 - mirror; 6~ stand fixing screw; 7—lifting screw
has a contact level at the alidade of the vertical circle, which is observed through a rotating prism.
In the field of view of the reading microscope (Fig. 3.17), three windows are visible. Before counting, double images of the upper and lower strokes of the goniometric circle are combined in the central middle window, divided by a horizontal line. In the upper large window the number of degrees and tens of minutes are counted (a number from 0 to 5). The number located under the number of degrees shows the number of tens of minutes. The units of minutes and seconds are counted along a horizontal fixed line (index) in the small right window. In Fig. Figure 3.17 shows a horizontal circle reading equal to 11°35'26.5″. Before measuring along a vertical circle using a set screw, it is necessary to align the ends of the level bubble with the vertical circle.
Theodolite Theo 020. Optical scale repeating theodolite (Fig. 3.18). The circle to the left of the observer is taken as the main position. Counting along the limbs of the horizontal and vertical circles is carried out using a reference microscope located next to the eyepiece of the telescope. In the field of view of the reference microscope, images of the strokes of the horizontal circle, designated by the letters “Ir,” and the vertical circle, designated by the letter “V,” are simultaneously visible.
In Fig. Figure 3.19 shows an example of reading using a reading microscope. The reading on the horizontal circle is 36°02.0′, on the vertical circle 9°02.0′.
The level during alidade of the vertical circle is replaced by a self-aligning compensator, which, when measuring inclination angles, does not require the observer to bring the level bubble to the zero point before reading along the vertical circle.
The Theo 020 theodolite can be used for leveling with a horizontal beam; to do this, you need to set the zero reading.
Theodolite Theo 020 is adapted to work on a three-stand system.
Theodolite Theo 020A. Optical scale repeating theodolite (Fig. 3.20). The telescope has a direct image.
Division fractions are counted by eye with an error of up to 0.1 or 6″. When measuring horizontal angles in bulk, the image of a vertical circle can be included, which eliminates possible reading errors.
In Fig. Figure 3.21 shows an example of reading using a reading microscope. The reading on the horizontal circle is 57°07.0′, on the vertical circle 92°05.0′.
In the absence of instruments for measuring angles using a three-stand system, poles with a round level are used (Fig. 3.22).
Technical characteristics of theodolites are given in table. 3.2