How to screw a self-tapping screw into thick metal?
It is quite possible to screw any roofing screw or galvanized one with a press washer into thick metal, even if the hardware is not equipped with a drill.
To do this, you just need to pre-drill the base. Using this method, you can tighten screws even into metal thicker than 5 mm. The main principle for such operations is that the diameter of the drill should differ from the diameter of the screw by only a few tenths of a millimeter. The thicker the base and the harder the metal, the smaller the difference. For example: for tightening galvanized products 4.2 mm. in metal 2 mm. You will need a 3.5 - 3.8 mm drill, and 5 mm for screwing into metal. You will need a 4.0mm drill. To achieve this goal, it is worth purchasing several drills, in increments of 0.1 mm, up to the stated diameter of the self-tapping screw.
Before screwing it into a critical place, it is better to drill a test hole and try to tighten the screw. After all, if the diameter is poorly chosen, the cap will easily break off and it will be difficult to remove the stuck tip.
Which screwdriver to choose for installing corrugated sheets
One of the important components of installing corrugated sheets are the tools with which the installer will carry out his work.
The quality of his work largely depends on the quality and convenience of these tools.
As for the tools used by installers when installing corrugated sheets, a screwdriver comes first.
It is the screwdriver that takes on the most critical part of the installation - fastening the sheet.
Let's try to figure out what kind of screwdriver we need to install corrugated sheets.
An ideal screwdriver for installing corrugated sheets should have the following characteristics:
1. Light weight, lightweight screwdriver will be easy to use, when working with large volumes, as well as in difficult conditions (on the roof), this is a very important characteristic.
2. The screwdriver must have a powerful battery, or preferably two. Two batteries will allow you to work without interruptions, without being distracted by charging the device. Using screwdrivers without batteries makes working with them on the roof very difficult. Long extension cords will always get in the way, and there is a risk of them being damaged by the sharp edges of the corrugated board.
Self-tapping screws for metal
For metal work, self-tapping screws belonging to the following categories are used:
- Hardware with a sharp tip. It is thanks to him that the self-tapping screw can cut holes during the screwing process. A metal sheet up to 0.5 mm thick is susceptible to its action, but with a larger thickness you will have to drill a hole in advance so that the hardware can fit into it.
- Hardware with drill. The shape of their head is hemispherical, and on the back there is a press washer. The drill-shaped end allows the self-tapping screw to be carefully screwed into the metal without damaging its surface. The thread on such fasteners reaches all the way to the head, so they are screwed to the maximum possible depth. This ensures high reliability of the connection.
Both types have fine threads, which ensures good adhesion to the metal and reliability of the fastened unit.
Although the self-tapping screw is supposed to drill its own hole, when working with metal, some preparatory work is inevitable.
State standards for wood screws
According to GOST parameters, wood screws received a certain marking - they correspond to a single standard number 1145. This GOST was adopted back in the 80s of the last century. It hasn't changed since then.
In addition to the standard sizes that were mentioned above in the table, the standard determines the material from which the self-tapping screw is made. This steel is of three types: carbon, low-carbon and corrosion-resistant
The standards clearly standardize the fastener manufacturing process down to the size of its head and the applied coating. Thus, you can know exactly which screw is needed for certain purposes and buy it anywhere in our country.
How to twist?
To make the connection strong and reliable, you need to install the self-tapping screw correctly. Installation technology may vary depending on what material is being fastened. When connecting concrete blocks, installation will be carried out using dowels. It is in them that the self-tapping screw is placed. If you are screwing fasteners into tiles, screeds, bricks, then you should use the same technology as for concrete, but you can use a regular drill with a special drill, rather than a hammer drill. To screw into solid metal parts, holes must first be formed, their diameter should be either equal to the diameter of the fastener or slightly larger. If you are installing a self-tapping screw into a wooden surface, then you can use a drill, and the diameter of the drill should match the diameter of the rod.
When working with sheets of drywall, first make markings with a pencil. You can use a screwdriver for installation. First you will need to screw in at the highest possible speed, then it should be reduced slightly. If you don’t have such a tool, you can take a regular screwdriver. To create a strong and even connection, you can additionally secure a metal bracket. When working with screws, you can put a special magnetic bracelet on your hand to fasten metal parts. It will allow you to keep all the elements at hand, without them getting lost or rolling away. After fixing the screws, you can paint them with powder pigment.
How and what to fix self-tapping screws with
Among the variations of tools with which self-tapping screws work well, the first place, naturally, is occupied by a screwdriver.
Many types of screws can be screwed in using a regular Phillips screwdriver. In this case, it is better not to make unnecessary efforts, but to screw in evenly and carefully. Remember, oxidized screws are very fragile.
Safety precautions when working with the tool
Let's consider a short set of rules for working with the tool:
| Illustration | Description of action |
| When working with a screwdriver, you should never put your hand under the tool. Even if you think you have control over the situation, leaning slightly can cause the tool to slip and cause injury. | |
| Never try to drill a self-tapping screw into a knot. Such areas are often the densest. In addition, the mounting location cannot be called durable. It is better to choose a place a little to the left or a little to the right. | |
| Always keep the tool firmly in line with the screw you are turning, whether you are working at an angle or not. In relation to each other they must create a single line. |
What are roofing screws?
A roofing screw is a screw of a complex design. It is equipped with a hexagonal wrench head and a drill bit. The package also includes a metal washer with an elastic gasket attached.
All metal parts are coated with anti-corrosion coating or made of stainless steel.
Technical characteristics of roofing screws
Self-tapping screws are distinguished by:
- cap shape - round with a slot for a screwdriver, hexagonal, with a cap recessed into the surface
- size – from 16 to 150 mm long, 4.8, 5.5, 6.3 mm in diameter
- purpose - fastening roofing materials to the sheathing or installing the sheathing to the rafters / etc.
- material of manufacture – carbon steel, stainless steel
- the material to which the fastening is made - wood or metal.
Purpose of fasteners
The self-tapping screw serves to firmly fasten structural elements together:
- The tip in the form of a drill helps to penetrate into the base material without pre-drilling and unnecessary damage to parts;
- Solid thread provides a durable and reliable grip;
- A large diameter washer guarantees good adhesion to the material being fastened and reduces the load on it at the fastening point;
- An elastic gasket, tightly clamped between the washer and the roof, ensures the waterproofness of the fastener;
- The self-tapping head gives the connection an aesthetic appearance and provides the builder with ease of installation.
Types of roofing screws
There are two main types of roofing screws - for metal and for wood, which differ greatly in tip, diameter, and type of thread. To fasten roof elements that are not in direct contact with water, self-tapping screws with a press washer can be used.
When installing rafters or other elements with a large distance between the surface to be installed and the wooden base, self-tapping screws with incomplete threads can be used. When purchasing from technically identical self-tapping screws, you can choose galvanized or painted in the desired color.
How to choose high-quality fastening material
When selecting fastening material, first of all it is necessary to calculate its quantity and type for each type of work. For rafters, nails or galvanized self-tapping screws are most often used; for sheathing, self-tapping screws with a press washer, and special roofing screws are used.
After determining the necessary characteristics of the screws - size, color, diameter, type of base, it remains to check the quality of the potential purchase:
- The manufacturer puts a stamped mark on the head of the self-tapping screw; if there is none, you should be wary of a cheap counterfeit made from low-quality steel;
- The thickness of the galvanization must be indicated on the box; the permissible value is more than 12 microns. The complete absence of a box with the specified characteristics is a clear indication of low quality;
- the gasket must be firmly attached to the washer, be at least 2 mm thick, and withstand test compression of the washer with pliers without peeling;
- if the self-tapping screw is painted, then the paint coating on the washer should not crack when it is bent with pliers;
- among other things being equal, it pays to buy branded European products, with a manufacturer’s guarantee for the highest quality of the steel used and with a test for resistance to temperature changes and long-term exposure to variable loads.
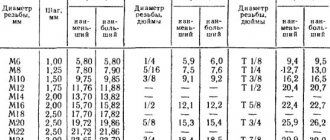
Correspondence tables between fastener diameter and screwdriver size (bits)
For high-quality and confident work with fasteners that have an internal slot, it is important to choose the right tool - a hand screwdriver or a screwdriver bit.
The size of the working profile of the tool must exactly correspond to the size of the working profile in the hardware head.
The most common self-tapping screws, screws and bolts most often have a straight or Phillips slot, the size of which is directly related to the diameter of the fastener leg.
Below are tables of correspondence between the diameter of the hardware and the size of the screwdriver (bit).
Screws
1. Screws with low cylindrical head and straight slot DIN 84, GOST 1491-80, EN ISO 1207.
Table 1
| Screw diameter, d , mm | M1,2 | M1.4 | M1.6 | M1.8 | M2 | M2.5 | M3 | M3.5 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M8 | M10 |
| Head diameter, dk , mm | 2,3 | 2,6 | 3 | 3,4 | 3,8 | 4,5 | 5,5 | 6 | 7 | 8,5 | 10 | 13 | 16 |
| Slot width, n , mm | 0,3 | 0,3 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,5 | 0,6 | 0,8 | 1,0 | 1,2 | 1,2 | 1,6 | 2,0 | 2,5 |
| Screwdriver size SL , mm | 0.3x2.0 | 0.4x2.5 | 0.5x3 | 0.6x3.5 | 0.8x4 | 1x5.5 | 1.2x6.5 | 1.2x8 | 1.6x10 | 2x12 | 2.5x14 |
2. Straight slot screws with cylindrical rounded head DIN 85, GOST 17473-80, EN ISO 1580.
table 2
| Screw diameter d , mm | M1.6 | M2 | M2.5 | M3 | M3.5 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M8 | M10 |
| Head diameter dk , mm | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 20 |
| Slot width n , mm | 0,4 | 0,5 | 0,6 | 0,8 | 1,0 | 1,2 | 1,2 | 1,6 | 2 | 2,5 |
| Screwdriver size SL , mm | 0.4x2.5 | 0.5x3 | 0.6x3.5 | 0.8x4 | 1x5.5 | 1.2x6.5 | 1.2x8 | 1.6x10 | 2x12 | 2.5x14 |
3. Countersunk and semi-countersunk head and straight slot screws: GOST 17475-80, DIN 963, EN ISO 2009, DIN 964, EN ISO 2010, GOST 17474-80.
Table 3
| Screw diameter d , mm | M1,2 | M1.4 | M1.6 | M1.8 | M2 | M2.5 | M3 | M3.5 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M8 | M10 |
| Head diameter dk , mm | 2,3 | 2,6 | 3 | 3,4 | 3,8 | 4,7 | 5,6 | 6,5 | 7,5 | 10 | 9,2 | 14,7 | 18 |
| Slot width n, mm | 0,3 | 0,3 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,5 | 0,6 | 0,8 | 0,8 | 1,0 | 1,2 | 1,2 | 2 | 2,5 |
| Screwdriver size SL , mm | 0.3x2 | 0.4x2.5 | 0.5x3 | 0.6x3.5 | 0.8x4 | 1x5.5 | 1.2x8 | 1.6x10 | 2x12 | 2.5x14 |
4. Set screws for a slotted screwdriver with a cylindrical end (trunnion) and a flat end: DIN 417, EN ISO 7435, DIN 427, EN ISO 2342.
Table 4
| Thread diameter d , mm | M2.5 | M3 | M3.5 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M8 | M10 | M12 |
| Slot width n , mm | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 0,6 | 0,8 | 1,0 | 1,2 | 1,6 | 2 |
| Bit size SL , mm | 0.4x2 | 0.4x2 | 0.4x2.5 | 0.6x3 | 0.8x4 | 1.0x5 | 1.2x6.5 | 1.6x8 | 1.6x8 |
Self-tapping screws for metal
1. Self-tapping screws (screws) for metal with a semicircular (cylindrical) head and a straight slot DIN 7971, EN ISO 1481.
Table 5
| Self-tapping screw diameter d , mm | 2,2 | 2,9 | 3,5 | 3,9 | 4,2 | 4,8 | 5,5 | 6,3 |
| Head diameter dk , mm | 4,2 | 5,6 | 6,9 | 7,5 | 8,2 | 9,5 | 10,8 | 12,5 |
| Slot width n , mm | 0,6 | 0,8 | 1 | 1 | 1,2 | 1,2 | 1,6 | 1,6 |
| Bit size SL , mm | 0.6x3.5 | 0.8x4 | 1x5.5 | 1x5.5 | 1.2x8 | 1.2x8 | 1.6x10 | 1.6x10 |
2. Self-tapping screws for sheet metal with countersunk and semi-countersunk heads and straight slots: DIN 7972, EN ISO 1482, DIN 7973, EN ISO 1483.
Table 6
| Self-tapping screw diameter d , mm | 2,2 | 2,9 | 3,5 | 3,9 | 4,2 | 4,8 | 5,5 | 6,3 |
| Head diameter dk , mm | 4,3 | 5,5 | 7,3 | 7,5 | 8,4 | 9,5 | 10,8 | 12,4 |
| Slot width n , mm | 0,5 | 0,8 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,2 | 1,2 | 1,6 | 1,6 |
| Bit size SL , mm | 0.5x3 | 0.8x4 | 1.0x5.5 | 1.0x5.5 | 1.2x8 | 1.2x8 | 1.6x10 | 1.6x10 |
Self-tapping screws for sheet metal
1. Self-tapping screws with a semicircular head for a Phillips screwdriver (bit) PH and PZ: DIN 7981, GOST 10621-80, EN ISO 7049.
2. Countersunk screws for a Phillips screwdriver (bit) PH and PZ: DIN 7982, GOST 10619-80, EN ISO 7050.
3. Semi-countersunk screws under the cross PH and PZ: DIN 7983, GOST 10620-80, EN ISO 7051.
Table 9
| Self-tapping thread diameter, mm | 2,2 | 2,9 | 3,5 | 3,9 | 4,2 | 4,8 | 5,5 | 6,3 |
| Phillips screwdriver size (number) | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
Wood screws
1. Round head screws, slotted PH, PZ: DIN 7996.
2. Screws with countersunk and semi-countersunk heads, slot PH, PZ: DIN 7997, DIN 7995.
Table 10
| Screw thread size, mm | 2 | 2,5 | 3 | 3,5 | 4 | 4,5 | 5 | 5,5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Phillips screwdriver size (number) | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
3. Universal screws for wood, drywall with PH and PZ slots (black, yellow, galvanized)
Table 11
| Thread diameter, A , mm | 2,5 | 3,0 | 3,5 | 3,8 | 4,2 | 4,5 | 4,8 | 5,0 | 6,0 |
| Screwdriver size (bits) Ph/PZ, number | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
How to read the markings of bits and screwdrivers?
The type and size of the tip of the bit (screwdriver) is indicated by two numbers, for example, PH1, PZ2. This tool marking contains information about what size fastener it is intended to work with.
For example, consider the PH2
.
PH
— working profile Phillips cross
2
— screwdriver number
The number indicates a certain range of fastener diameters with which the bit can work. In this example, these are self-tapping screws of size 3.1 - 5 mm
.
Table 12. Correlation between the bit number and the external thread of the fastener.
| Screwdriver no. PH and PZ | Diameter of fastener, mm |
| 0 | up to 2 |
| 1 | 2,1 — 3 |
| 2 | 3,1 — 5 |
| 3 | 5,1 — 7 |
| 4 | from 7.1 |
Slotted screwdrivers are marked with the letter SL
indicating the width and thickness of the slot. Some manufacturers indicate only the width.
For example: SL 0.6x3.5
or
SL 2.0
Table 13. Typical sizes of spline bit tips.
| Tip width, mm | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 | 4 | 4.5 | 6 | 5.5 | 6, 6.5, 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Tip thickness, mm | 0.3-0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5-0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8-1.0 | 1.0-1.2 | 1.2-1.6 | 1.4-1.6 |
If the size of the screwdriver or screwdriver attachment is selected correctly, then the tool sits tightly in the slot and without play. The tight fit eliminates the risk of licking off the working edges, promotes better transmission of torque and guarantees an excellent final assembly result.
Articles about products 01/31/2020 09:20:31
What types are there?
The production of wood screws is carried out in three main versions. The only difference between them is in appearance.
You can learn how to use façade dowels for thermal insulation by reading the article.
Phosphating (black)
The first most popular option is phosphating the product. They are characterized by a black color. They are used for rough work and do not have an anti-corrosion coating. When using such self-tapping screws in the bathroom or kitchen, after a while they begin to rust and collapse.
Galvanized and yellow-passed
The next two types of wood screws are called galvanized and yellow-passed.
The first type is characterized by coating the product with a thin layer of zinc, but yellow-passivated screws require treating their surface with a special yellow-tinged solution.
These self-tapping screws are corrosion resistant. Of course, such products are more expensive, but they are not afraid of the influence of moisture. Galvanized self-tapping screws are characterized by a silver color. The last two options are actively used for installing fasteners for hinges, furniture elements, as well as other work.
How you can use nails for a used air gun is described in this article.
Size and price table according to GOST
Such fasteners can have a variety of sizes, making it possible to carry out a through installation of a metal profile to a wooden base. Also, a similar product is widely used for mounting parts of wooden structures. The presence of a cross-shaped slot on the head of the self-tapping screw allows the connection to be made using a screwdriver or screwdriver for this purpose. Phosphate-coated self-tapping screws can secure sheets of drywall to wood framing. Such elements do not require pre-drilling. They are produced with a wide thread pitch.
Construction nails GOST 4028 80 can be used for the intended purpose described in the article.
Table 1 – Dimensions and price of wood screws GOST 1145-80
Read also: A machine that breaks down and is reassembled
| Dimensions, mm | Weight, kg | Price, rubles |
| 3.5x16 | 1 | 155 |
| 3.5x19 | 1 | 158 |
| 3.5x25 | 1 | 184 |
| 3.5x32 | 1 | 233 |
| 3.5x35 | 1 | 244 |
| 3.5x41 | 1 | 287 |
| 3.5x45 | 1 | 315 |
| 3.5x51 | 1 | 357 |
| 3.5x55 | 1 | 616 |
| 3.8x25 | 1 | 626 |
| 4.2x65 | 1 | 629 |
| 4.2x70 | 1 | 684 |
| 4.2x75 | 1 | 782 |
| 4.2x90 | 1 | 1109 |
| 4.8x95 | 1 | 1129 |
| 4.8x100 | 1 | 1211 |
How to choose the right one
To select the correct furniture screw, you should consider what material it will be installed in. The choice of head will depend on the force applied and the space available when screwing
It is also important to choose not only the type of head, but also the pattern for the tool used
With proper selection of bits, a strong grip of the fastening element with the screwing tool is ensured. Only in this case, the screws smoothly and evenly enter wooden boards, drywall, laminated chipboard, MDF.
Some important nuances that will help buyers of fasteners much better navigate their diversity, as well as make the right choice:
- color - screws from the same batch must be in the same color scheme. This indicates that all products have undergone the same processing under similar conditions, and also have the appropriate strength and corrosion resistance;
- parameter - the sizes of one batch of products should not be visually different from each other, and also comply with standards;
- pitch - the load between the threads should be distributed evenly;
- hole - the slot must be clear, symmetrical, and be deep enough;
- marking - the standard designation of screws - is a number in which the first number is the size of the thread diameter, the second is the length of the product from its very head to the sharp tip.
In order to efficiently assemble and install furniture elements, you need to use such a convenient, accessible assistant in fastening work as a screw. This type of furniture screed will not only simplify the assembly and installation procedure, but will also be invisible after the installation process is completed, thanks to its unique structure. All structures and foundations fixed with such fasteners will retain their shape, appearance, and properties for a long time.
Peculiarities
The popularity of such products is directly related to the trend due to which ordinary slate is giving way in popularity to the latest generation of roofing products. And they need special parts for fastening. Self-tapping screws for roofing are screws, the main function of which is to securely fix roofing materials to a specially constructed base made of metal or wood.
The high quality characteristics of roofing screws greatly expand their range of applications.
- The main area of use is the creation of roofs of various configurations, where during the work corrugated sheets, metal tiles and others can act as roofing materials.
- Finishing the walls of buildings used for industrial purposes.
- Construction of fencing and fencing made of metal, the construction of which involves installation to a wooden frame.
In addition to the features associated with the operating conditions of roofing screws, their important quality is a certain design, due to which the elements will be in harmony with the overall appearance of the roof.
The product has certain advantages, among them the following:
- raw materials for manufacturing are distinguished by their ability to withstand heavy loads;
- the products have an anti-corrosion coating, due to which the service life of the product increases - on average it is about 50 years;
- the presence of a rubber gasket, which ensures reliable waterproofing of the roof at the joints;
- the washer allows you to evenly distribute the load on the roofing material, and also increases the sealing properties in the area of the screw holes;
- wide choice of colors.
Selection principles
When choosing fasteners, you need to consider some factors:
- Quantity, dimensions of fastening elements. The longer the screws, the more they weigh. This is not noticeable when connecting small parts, but if there are a lot of fasteners, the weight of the finished product will increase.
- There is no point in using the longest screws. It is enough for the fasteners to pierce through the metal sheet.
- The type of coating for fasteners must be selected depending on the conditions of use.
- To securely fasten profiled sheets, you need to choose self-tapping screws with a special gasket. It should be secured under the hardware cap. There should be a marking on the cap itself. A high-quality gasket is made of EPDM, a low-quality gasket is made of rubber.
- It is better to choose galvanized fasteners. This is reliable protection against rust formation.
- On sale you can find fasteners of different colors. The shade is selected depending on the color of the profiled sheets.
Construction store (Photo: Instagram / kubmaster1)
Self-tapping screws for fastening “seed” profiles
These products are better known under the popular name “seeds” because of their external similarity to sunflower seeds. There are both black, phosphate coated, and galvanized. Due to the very sharp tip and small size, they are ideal for fastening profiles up to 0.9 mm thick.
These hardware are available in a version with a drill - for screwing into metal up to 2mm thick. All self-tapping screws have slots for the PH2 bit.
| Size | Llength, mm | Head diameter, mm | Head height, mm | D1 outer diameter, mm | D2inner diameter, mm | Weight 1000 pcs, kg |
| Sharp tip3.5×11 | 10,45-11,55 | 7,39-8,00 | 2,45-2,92 | 3,42-3,58 | 2,76-2,92 | 1,13 |
| Drill 3.8×11 | 10,20-11,80 | 7,60-8,00 | 2,70-3,00 | 3,75-3,95 | 2,76-2,92 | 1,13 |
Try turning your phone to landscape position or changing the browser zoom. To display the table, you need a screen resolution of at least 601 pixels in width!
Dimensions of wood screws - table
Wood screws are available in various types and sizes, here are the main ones:
| Nominal diameter, mm | Length, mm | Outer thread diameter, mm | Internal thread diameter, mm | Cap width, mm |
| 2,5 | 12-25 | 2,25-2,55 | 1,1-1,5 | 5,1 |
| 3 | 12-45 | 2,75-3,05 | 1,5-1,8 | 6 |
| 3,5 | 12-50 | 3,2-3,55 | 1,75-2,15 | 7 |
| 4 | 16-70 | 3,7-4,05 | 2-2,5 | 8 |
| 4,5 | 25-80 | 4,2-4,55 | 2,22-2,7 | 8,8 |
| 5 | 30-120 | 4,7-5,05 | 2,52-3 | 9,7 |
| 6 | 40-240 | 5,7-6,05 | 3,22-4,05 | 11,6 |
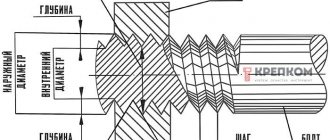
What is the diameter of the drill bit for the self-tapping screw?
What materials are commonly used at home? Items made of wood, metal, plywood, drywall - their installation is not complete without the use of self-tapping screws. Of course, without practice, you can bend the screws and break them, all due to lack of knowledge on how to work with these fasteners. Therefore, it is better to learn in advance how to screw in self-tapping screws.
Fastening elements are divided into many types. Most often there is a division into “for metal” and “for wood”. They differ from each other even in appearance. The difference lies in the thread ball, that is, the distance between the threads. The thread of self-tapping screws for wood has a larger distance between the turns of the thread (for metal there is a smaller distance).
If you confuse the screws and screw the screw into wood, for example, into a sheet of metal, the fastening will either bend or even break. A self-tapping screw for metal in wood will not hold at all, since the wood will not penetrate between the turns and actually does not hold.
As for self-tapping screws for metal, you can find 2 varieties - with a drill at the tip and without.
Drill diameter for wood screws
It is quite easy to identify a self-tapping screw for wood - it has a large distance between the turns (than a self-tapping screw for metal). Why is that? The reason is quite simple - wood is a less dense material than iron.
Such screws can be of different colors - black, white, gold. The color does not affect functionality, that is, this is not some kind of special marking, but simply different colors for selecting fasteners to match the color. Of course, if you have white furniture, then it is better to use a white screw.
It is impossible to determine by the colors what this self-tapping screw is for wood or metal, only by the distance of the thread.
Self-tapping screws can be of different lengths and you need to choose according to your tasks; there are the smallest ones - a little more than a centimeter long and there are long ones, more than 20 centimeters long.
Black screws are usually 3.5 and 4.2 millimeters in diameter. And yellow ones - from 2.5 to 5.5 millimeters.
Of course, there should be no problems with soft wood, but with oak or acacia there may be difficulties (plus do not forget that the wood can split). Therefore, in order not to spoil the entire structure, it is better to first drill a hole of a smaller diameter in the material. The cap needs to be sunk flush into the material (to do this, pre-drill a recess with the same diameter as the cap).
If the diameter of the self-tapping screw is small, pre-drilling is not necessary, but if the diameter is more than 4 millimeters, then you need to pre-drill with a drill 0.5 - 1 millimeter smaller than the self-tapping screw itself.
Read also: Circulation pump in the heating system of a private house
Diameter of drill for metal self-tapping screw
If the metal that needs to be drilled or screwed into metal is less than 0.5 millimeters thick, then there are no problems, you don’t even need to pre-drill it. But if the metal thickness is greater, for example 0.8 millimeters or 1 millimeter, then you must first drill a hole for installing a self-tapping screw. Typically, the thickness of the hole being drilled depends on the thickness of the material. If you guess the size of the drill, then you can tighten the self-tapping screw even with a regular screwdriver.
Below is a table of recommended drill diameters for a certain metal thickness.
The most common drill diameter is 3.4, the others are less common.
In the case of self-tapping screws (+ press washer) up to 1.5 mm of metal thickness, you don’t have to drill a hole, but above that you can’t do without it, since the drill itself made from a self-tapping screw can’t do the job, it’s almost useless.
Correspondence table between drill diameters for sharp self-tapping screws and metal thickness
The table data may change a lot due to:
- The quality of the material itself;
- Quality of self-tapping screws;
- Screwdriver power;
- What kind of reliability is needed for fastening?
So, in general, if you have thick, dense wood or a thick sheet of metal, you first need to drill it (smaller in diameter than the diameter of the screw) and then screw it in.
Reading time: 7 minutes No time?
Self-tapping screws for wood are hardly inferior in popularity to any other fastener. Without them, durable wooden furniture, frame supports, doorways and many building structures, including drywall, would not exist (by the way, if you have ever looked for special fasteners for these purposes, there are none). A self-tapping screw is a reliable, but at the same time simple and affordable tool. Today, in a review by the HouseChief.ru editors, we will talk about how to choose the right wood screws, and tables with sizes and prices will help you navigate their diversity and choose the right option for a specific type of work.
Read in the article
Hole in metal for self-tapping screw
There are self-tapping screws for metal with a sharp tip and with a drill. Both types of fasteners are characterized by a small interridge distance, or, more simply, a small thread. This allows you to improve the adhesion of the hardware to the solid material, and hence the fastened unit.
The sharp tip of the product produces the same self-tapping action, which significantly simplifies the fastening process. In other words, we take a tool, a screwdriver or a screwdriver, in one hand, a self-tapping screw in the other, and screw it into the structure. Even a metal surface will give in under such pressure if... the thickness does not exceed 0.5 mm. For thicker metal flooring, it is necessary to drill a hole, the diameter of which will directly depend on the thickness of the metal.
The basic principle is to go through the fastening point with a drill with a diameter smaller than the diameter of the selected screw. Lubricate the resulting hole with machine oil before screwing in the hardware and the process will be done without much effort.
Here is the following table of recommended drill diameters for a certain thickness of a metal surface:
| Metal thickness, mm | 0,5 | 0,7 | 1,0 | 1,5 | 2,0 | 3,0 | 4,0 |
| Drill diameter, mm | — | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,5 | 3,6 | 3,7 | 3,8 |
Since the thickness of the most commonly used metal decking is 1mm, the most common drill diameter is 3.4mm.
In the assortment of self-tapping screws, you can often find black hardware. Having the same design with a sharp end, they are capable of piercing metal 1.5 mm thick without additional preparatory work. The diameter of black screws starts from 3.5 mm; A phosphate or oxide coating contributes to the mechanical protection of the fastener and gives it excellent adhesive properties. Unlike yellow ones, they do not have electrochemical protection. These products are made from carbon and low-alloy steels, and the phosphate film adheres tightly to the base metal at the molecular level. When the fastener is deformed, this protective layer is not destroyed due to its high ductility. Therefore, if you need to secure a metal structure up to 1.5 mm thick, with further application of paints, putty or plaster, you can safely use black self-tapping screws. For thicker metal surfaces, hole preparation will again be required, but in different proportions:
| Metal thickness, mm | 0,5 | 0,7 | 1,0 | 1,5 | 2,0 | 3,0 | 4,0 |
| Drill diameter, mm | — | — | 2,5 | 2,7 | 2,9 | 3,0 | 3,1 |
The above data in the tables was derived empirically and the following factors will play an important role: the quality of the fastener and metal of the working deck, the force with which the hardware is screwed in and the required reliability of fastening.
1) The metal from which the self-tapping screw is made must comply with the stated GOST or DIN. Otherwise, preparatory work should be carried out earlier than indicated in the tables. As for the black self-tapping screws, they should not cause black stains on the working surface - the phosphate coating remains on the product under the influence of water, and does not flow down the wall like black tears. You can distinguish a high-quality product by a feature characteristic of self-tapping screws for metal: the thread should not fit close to the head. That is, there must be a gap equal to the diameter of the rod between the head and the turns, which ensures the strength of the entire fastener.
2) If the metal surface does not meet the stated requirements, then it may not be worth doing additional drilling, but screwing in the screw directly. Then the coupling will be tighter and sufficient structural density will be achieved.
3) Sometimes you can pierce 2 mm of metal with a high-quality black self-tapping screw without drilling, if you use good manly force using a screwdriver. And on a corded screwdriver, it’s important to choose the mode wisely so as not to strip the threads. In addition, it is important to prevent the screw from overheating, otherwise it will quickly become dull.
4) If you first make a hole for the self-tapping screw a little smaller than indicated in the tables, then installing the fasteners will be more difficult, but screwing small threads into the metal will be more penetrating, and therefore the connection will be more durable.
There are also metal screws equipped with a drill end. They are applicable without preliminary preparation of holes for metal up to 2 mm thick. When screwed into a joint, the drill end of the hardware tears and squeezes out the metal, making a passage for itself. For them, the quality of both the product itself and the working surface will also play a huge role.
To select the drill diameter for a hole in metal for a self-tapping screw, you can use the reference matching table below. If you have to work with metal more than 4 mm thick, you probably cannot do without a hole.
| Self-tapping screw diameter, mm | Drill diameter, mm |
| 3,5 | 2,76 — 2,92 |
| 4,8 | 2,8 — 3,0 |
| 5,5 | 2,8 — 4,7 |
| 6,3 | 5,4 — 5,55 |
As for the length of the hole, it should extend far into the structure being fastened or correspond to it. If the self-tapping screw goes right through, protruding far beyond the structure, then this is a waste of the length of the hardware. The larger the product, the more high-quality and expensive material is spent on its production, and therefore more expensive. It turns out that with an irrational approach to the matter, part of the product will not work.
All of the above metal screws are available in an assortment in our online store. Thanks to sorting, you will quickly select the necessary equipment for the tool if, during the work process, you consider it necessary to make a hole in the metal before installing the hardware.
How to attach?
All sheets of metal tiles should be secured to the roof sheathing at the bottom of the sheet, since only there is a tight fit between the washer and the rubber gasket and the sheet. It is preferable to carry out this work using special roofing screws for metal. They need to be screwed in two centimeters below the so-called step, which acts as a guide.
When the fastener is tightened, the rubber gasket should be slightly deformed and reliably hide any gap between the roofing material and the screw head.
Rubber made using vulcanization technology will ensure tight installation. Such work is performed with self-tapping screws no less than 28 mm long.
Self-tapping thread
The thread is also varied, and which screws to use depends on the type of material being fastened:
Large carving. Self-tapping screws with a rare thread pitch allow you to fasten soft materials - gypsum, asbestos, plastic and soft wood. The diameters of such screws are from 3.5 to 5 mm, length – from 16 mm to 150 mm;
Medium thread. These are universal self-tapping screws, suitable for almost all types of fastened materials. The diameters of medium self-tapping screws are from 3 mm to 6 mm, lengths are from 12 mm to 220 mm;
Medium thread, herringbone profile. Designed for fastening to concrete and brick surfaces, driven into a dowel. The diameters of the screws are from 3 mm to 8 mm, the length is from 12 mm to 200 mm;
Frequent carving in two passes. Self-tapping screws designed for fastening to metal sheets up to 0.9 mm thick have this type of thread. Available with or without a drill at the tip (in this case, pre-drilling is required). The diameters of such screws are from 3 mm to 8 mm, length - from 12 mm to 200 mm;
Asymmetrical thread. This type of thread is intended for self-tapping screws used in furniture production; it is used for fastening furniture elements made of wood, plywood or chipboard. Pre-drilling is required, screw diameters are 5 mm and 7.5 mm, lengths are from 40 mm to 70 mm;
Variable knurled thread. The purpose of construction screws with such threads is to fasten to concrete or brick surfaces without dowels. The diameter of the self-tapping screw is 7.5 mm, length from 70 mm to 200 mm.
Types and classification of self-tapping screws
The key difference between wood screws is the wide thread pitch. It is this feature that distinguishes these fasteners from those intended for metal structures.
This feature significantly reduces the friction force, which allows you to screw in the screws without much effort using a simple screwdriver. There are many classifications of wood screws, depending on the characteristics of the surface being fixed, their shape and type of thread. Let's consider each of them in turn.
Interesting fact! There are extremely small hardware. They received an interesting name - “seeds”, since their appearance resembles the shape of sunflower seeds. In some variants they are also called “bugs” due to the cap being relatively large in relation to the length of the stem.
Due to the fact that not everyone knows about the different types, and, consequently, the purpose of “consumables”, a lot of problems arise: screws break, the work process is complicated and delayed.
Depending on the nature of the outer surface treatment
It doesn’t matter what size the hardware is, short or long, it is necessarily covered with a special surface that protects the metal from oxidation and further strengthens it.
Read also: DIY mini gearbox
Black (oxidized) wood screws
Sometimes they are called GD self-tapping screws - plasterboard-wood. Thanks to the hidden cap, they are used for interior finishing work. After screwing in, such fasteners are practically invisible and lend themselves well to puttying and leveling work.
Such self-tapping screws have a countersunk head, which allows you to “drown” the hardware by a couple of millimeters
Design features of self-tapping screws:
- Sharp tip . This feature allows you to save time during installation work.
- Rare thread pitch. They are most often used on soft rocks, which allows screws to be screwed in easily and effortlessly.
- Hidden hat.
- Hardened metal.
There are two subtypes of black self-tapping screws:
- Phosphated . This is a special coating that gives it a matte black color. These are the most brittle self-tapping screws; they are used for simple types of work with a low degree of pressure. They have low corrosion resistance, so should be used in areas with low humidity.
- Oxidized . These self-tapping screws are subject to additional treatment with magnetic oxide, making them more wear-resistant. They look glossy rather than matte.
Important! There is a type of GM screws - plasterboard-metal; on the contrary, they have a frequent pitch, which makes the wood surface more loose and sloppy. Under the influence of loads, a shelf with such an incorrectly selected screw may break.
Moreover, the thread can be applied along the entire length or cover the product partially. There are certain parameters: self-tapping screws up to 55 mm long come with a full screw thread, from 65 to 75 - in this case the thread length is 50 mm, and if the self-tapping screw is more than 90 mm, this figure reaches 60 mm.
Most often, black self-tapping screws are used in conjunction with dowels. Among the disadvantages, experts call their low resistance to moisture.
Yellow-passivated and galvanized wood screws
This type of hardware is resistant to corrosion. They are most often used as decorative fasteners. Among the disadvantages are the rather high cost and softness of the metal, due to which they can bend during careless operation with a screwdriver.
Universal self-tapping screw, galvanized
Galvanized fasteners can most often be found in furniture structures. They have a silver tint and are also not hardened. But they are practically invisible in any design.
Depending on the shape
Fasteners of this type differ not only in the composition of the coating and the width of the screw “pitch”, but also in the shape of the head and its design. Depending on the characteristics of the work, there are several types of its execution.
Wood screws with press washer
The press washer provides precise and strong fastening of thin sheets, for example, wooden or plastic panels; most often, such screws have a slot for a Phillips screwdriver. Most often, self-tapping screws with a press washer for wood have a sharp tip and do not require additional drilling. The length of screws of this type varies from 13 to 76 mm, and the nominal diameter is 4.2 mm.
Wood screws with hexagon head
In appearance, such self-tapping screws resemble a regular hexagon screw. This self-tapping screw is sometimes called a "grouse".
Such self-tapping screws have a thickened rod; a hole must be drilled for it.
They are used where sufficient force is required, for example, for assembling and fastening rafters.
Furniture self-tapping screws – confirmed
Confirmat is a type of self-tapping screw that is familiar to anyone who has ever assembled furniture from an IKEA supermarket. This hardware has a flat head and a concave hole for a special hex key.
Confirmat is a fairly strong fastener that can be screwed in without special power tools.
Depending on thread type
Depending on the type of thread, such self-tapping screws come in several variations:
- Fully threaded . The simplest type of fastener. The thread in this case is located along the entire length of the screw. This type of fastener creates the maximum possible and strong adhesion to the wooden structure. Allows you to withstand large longitudinal loads. Such screws can easily be screwed into wood at different angles.
- Self-tapping screws with ribs. There is a cutter in the head of the screw; during the screwing process, it increases the diameter of the hole and allows you to effortlessly sink it into the wood. Sometimes self-tapping screws are equipped with a middle cutter.
- Adjustment screws . They are used for the installation of doorways, frames and window structures. They are distinguished by countersunk heads with special notches and a sharp tip. Self-tapping screws of this type allow for adjustment of structures.
- Insulation screws . Such screws allow you to fasten the sheathing to rafters, beams, and screw the mesh to the batten. Most often they have two types of heads: semicircular with a press washer or cylindrical.
- Self-tapping flugel . Used for installation of wooden sheathing. There is usually a drill at the end of the screw, which eliminates the need to drill a hole in advance.
Read also: Conventionally graphic designation of electrical elements GOST
Self-tapping screw with full thread is considered one of the simplest and most reliable
Adjustment countersunk screws for windows
Dimensions
Selecting self-tapping screws should be done with special responsibility, and it is important to consider the following rules:
- the length of the threaded part should be selected so that it is greater than the total thickness of all materials being connected;
- purchasing fasteners that are too long is considered irrational, since the cost of hardware is directly affected by their length;
- masters say that the optimal length will be the tip, which passes right through the materials.
The table will help you learn more about the sizes of the smallest and largest metal screws with a sharp tip:
| Marking | Length | Cap diameter, mm | Press washer diameter, mm | Int. Base diameter, mm | External diameter of the base, mm | Weight, kg per 1000 pieces |
| 4, 2*13 | 13 mm | 7,1 | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4, 05–4,3 | 1,66 |
| 4,2*14 | 14 mm | 7,1 | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4, 05–4,3 | 1,73 |
| 4,2*16 | 16 mm | 7,1 | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4, 05–4,3 | 1,89 |
| 4,2*19 | 19 mm | 7,1 | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4, 05–4,3 | 2,04 |
| 4,2*25 | 25 mm | 7,1 | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4, 05–4,3 | 2,45 |
| 4,2*32 | 32 mm | 7,1 | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4, 05–4,3 | 2,87 |
| 4,2*41 | 41 mm | 7,1 | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4, 05–4,3 | 3,6 |
Table of sizes of self-tapping screws for metal with a drill:
| Marking | Length | Press washer diameter, mm | Int. base diameter, mm | Ext. base diameter, mm | Drill length, mm | Drill diameter, mm | Weight 1000 pieces, kg |
| 4,2*13 | 13 mm | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4,08–4,22 | 4,5–5,8 | 3,35–3,5 | 1,85 |
| 4,2*14 | 14mm | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4,08–4,22 | 4,5–5,8 | 3,35–3,5 | 1,87 |
| 4,2*16 | 16 mm | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4,08–4,22 | 4,5–5,8 | 3,35–3,5 | 2,05 |
| 4,2*19 | 19 mm | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4,08–4,22 | 4,5–5,8 | 3,35–3,5 | 2,26 |
| 4,2*25 | 25 mm | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4,08–4,22 | 4,5–5,8 | 3,35–3,5 | 2,61 |
| 4,2*41 | 41 mm | 10,6–11,4 | 3,2 | 4,08–4,22 | 4,5–5,8 | 3,35–3,5 | 3,05 |
Installation conditions and diameters of preliminary holes for self-tapping screws BEST-Fixtures
Experienced craftsmen also remember those times when several self-tapping screws were used at once to create just one fastening using a self-tapping screw! The installation method was simple, but required a mandatory technological sequence. The first screw was screwed in 2/3 of its length and, to avoid licking the slot on the head, was unscrewed and thrown out. The second was to cut a thread in the base to the full depth of the fastening and again, unscrew it and throw it away. The concerns were quite serious - the licked slot on the head of the screw prevents its unhindered unscrewing if necessary (Fig. 7). Those. The first two self-tapping screws served as a kind of tap - a tool for cutting threads. And only the last, third, screw served its intended purpose: to form a threaded fastener. In everyday life, they often avoided the advice of “experienced” people and, applying considerable pressure on a screwdriver, screwed a self-tapping screw into the base. In this case, the slot on the head was indeed damaged, but with sufficient effort this did not interfere with installing the self-tapping screw in the designed position. As a result: after 2-3 years of use, even indoors, the hardware sometimes became covered with rust and when replacing it, it was almost impossible to unscrew them without the help of pliers and a drill.
Currently, against the backdrop of the widespread use of threaded fasteners, they have a serious responsibility. The requirements for fasteners have also become significantly stricter. New technologies for the production of steel and their processing make it possible to produce hardware for use in completely different operating conditions. For example, fasteners made of A2 and A4 steel in accordance with GOST R ISO 3506 can be used even when exposed to aggressive environments without the formation of corrosion or at extremely high and low temperatures without fear of destruction of the fastener. For various installation methods and materials with different properties, special spline shapes have been developed: Philips, Pozidrive, Torx, etc.
All this is implemented in a line of self-tapping screws, the so-called self-tapping screws, BEST-Fasteners. Which are made of high-alloy chromium-nickel stainless steel. The correct choice of head slot from a wide range of models ensures smooth installation of our self-tapping screws into all kinds of bases using a power tool or manually. The high strength of these hardware allows the product to cut a landing thread when screwing them into a pre-drilled hole in the base. Depending on the base: wood, plastics, composite materials, metals, etc., the design of the thread of BEST-Fixture screws also differs significantly. Self-tapping screws, the threads of which are made in accordance with GOST R ISO 1478-93 (or ISO 1478) are intended for installation, primarily in metals and other hard materials. As can be seen from the name of the regulatory documents, they are completely identical. According to them, the thread of self-tapping screws is designated ST and the numerical value of the nominal (external) diameter of the thread of the product, as well as its length, for example:
ST4.8 x25,
Where:
ST – thread type, the parameters of which fully comply with GOST R ISO 1478-93 (or ISO 1478),
4.8 – nominal (external) thread diameter in mm,
25 – thread length in mm.
Screwing screws into metals and other solid materials is carried out using powerful torques with a significant load on the head of the hardware or its slots. Acceptable fastenings of sheet materials using self-tapping screws are shown in Figures 1-6. Their installation requires compliance with strict technical regulations. Failure to comply with which can lead to undesirable results, for example: “licking” of the slots on the head (Fig. 7), bending of the thread (Fig. 8) or deformation of the entire self-tapping screw (Fig. 9).
When installing self-tapping screws BEST-Fasteners with threads in accordance with GOST R ISO 1478-93, we recommend following the German standard DIN 7975 Self-tapping screws. Pre-hole and installation guide.
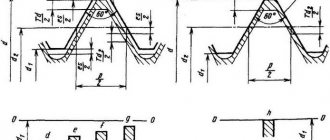
DIN 7975 provides 6 types of fastening:
| Fig.7 “Licking” the slot on the head of a self-tapping screw. Occurred as a result of screwing a screw into plywood without a preliminary hole | |
| Fig.8 Collapse of the thread of a self-tapping screw. The cause of the defect was the screwing of an A2 steel screw into a carbon steel profile. Shelf thickness 4 mm. | |
| Fig.9 Deformation and breakage of the self-tapping screw. The cause of the defect was the screwing of an A2 steel screw into a carbon steel profile. Shelf thickness 4 mm. |
In this case, the permissible thickness of the fastened materials specified in Table 1 of DIN 7975 must be observed:
| Thread size | ST 2.2 | ST 2.9 | ST 3.5 | ST 3.9 | ST 4.2 | ST 4.8 | ST 5.5 | ST 6.3 | ST 8 |
| Minimum permissible sheet thickness*, mm | 0.35 | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| Minimum thickness of materials to be bonded, mm | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 2.1 |
| Maximum thickness of materials to be bonded, mm | 1.8 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 3 | 3.5 | 4 | 4.5 | 5 | 6.5 |
* - which is capable of ensuring that the sheet engages the thread of a self-tapping screw with the types of fastening shown in Fig. 3-5
For the types of fastenings shown in Fig. 1 and 2, holes are pre-drilled. The diameters, depending on the thickness and strength of the materials being fastened, are indicated in Table 2 for each size of self-tapping screws.
Table 2.1 Diameters of preliminary holes (mm) for self-tapping screws ST 2.2
| Total thickness of fastened products, mm | Material strength, Rm, N/mm2 | ||||||||
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | |
| 0,8 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 |
| 0,9 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 |
| 1,0 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,8 |
| 1,1 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 1,8 |
| 1,2 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,8 |
| 1,3 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,8 |
| 1,4 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,9 |
| 1,5 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,9 | 1,9 |
| 1,6 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,9 | 1,9 | 1,9 |
| 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,9 | 1,9 | 1,9 | 1,9 |
| 1,8 | 1,7 | 1,7 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,8 | 1,9 | 1,9 | 1,9 | 1,9 |
Table 2.2 Diameters of preliminary holes (mm) for self-tapping screws ST 2.9
| Total thickness of fastened products, | Material strength, Rm, N/mm2 | ||||||||
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | |
| 1,1 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 |
| 1,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 |
| 1,3 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,3 |
| 1,4 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,3 | 2,4 |
| 1,5 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,3 | 2,4 | 2,4 |
| 1,6 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,3 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 |
| 1,7 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 |
| 1,8 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,3 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,5 |
| 1,9 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,5 | 2,5 |
| 2,0 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,3 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 |
| 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,2 | 2,3 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 |
Table 2.3 Diameters of preliminary holes (mm) for self-tapping screws ST 3.5
| Total thickness of fastened products, | Material strength, Rm, N/mm2 | ||||||||
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | |
| 1,3 | 2,6 | 2,6 | 2,6 | 2,6 | 2,6 | 2,6 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 |
| 1,4 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,8 |
| 1,5 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,8 | 2,9 |
| 1,6 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,9 | 2,9 |
| 1,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,8 | 2,9 | 2,9 |
| 1,8 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,8 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 |
| 1,9 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 3,0 |
| 2,0 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 3,0 | 3,0 |
| 2,2 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,8 | 2,9 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 |
| 2,5 | 2,7 | 2,7 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,1 |
| 2,8 | 2,7 | 2,8 | 2,9 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,1 |
Table 2.4 Diameters of preliminary holes (mm) for self-tapping screws ST 3.9
| Total thickness of fastened products, | Material strength, Rm, N/mm2 | ||||||||
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | |
| 1,3 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 |
| 1,4 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 2,9 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,1 |
| 1,5 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,2 |
| 1,6 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,2 | 3,2 |
| 1,7 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 |
| 1,8 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,3 |
| 1,9 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,3 |
| 2,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,3 |
| 2,2 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,1 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,4 |
| 2,5 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,4 |
| 2,8 | 3,0 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,4 |
| 3,0 | 3,0 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,5 |
Table 2.5 Diameters of preliminary holes (mm) for self-tapping screws ST 4.2
| Total thickness of fastened products, | Material strength, Rm, N/mm2 | ||||||||
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | |
| 1,4 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,1 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,4 |
| 1,5 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,4 |
| 1,6 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,4 |
| 1,7 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,4 |
| 1,8 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,5 |
| 1,9 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,5 |
| 2,0 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,5 | 3,5 | 3,5 |
| 2,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,5 | 3,5 | 3,5 | 3,6 |
| 2,5 | 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,4 | 3,4 | 3,5 | 3,5 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 |
| 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,3 | 3,4 | 3,5 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 |
| 3,0 | 3,2 | 3,4 | 3,5 | 3,5 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,7 |
| 3,5 | 3,3 | 3,5 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,7 | 3,7 | 3,7 | 3,7 |
Table 2.6 Diameters of preliminary holes (mm) for self-tapping screws ST 4.8
| Total thickness of fastened products, | Material strength, Rm, N/mm2 | ||||||||
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | |
| 1,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,7 | 3,8 | 3,9 | 3,9 |
| 1,7 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,7 | 3,8 | 3,9 | 3,9 | 4,0 |
| 1,8 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,8 | 3,8 | 3,9 | 4,0 | 4,0 |
| 1,9 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,7 | 3,8 | 3,9 | 3,9 | 4,0 | 4,0 |
| 2,0 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,8 | 3,9 | 3,9 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,1 |
| 2,2 | 3,6 | 3,6 | 3,7 | 3,9 | 3,9 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,1 | 4,1 |
| 2,5 | 3,6 | 3,7 | 3,9 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,1 | 4,1 | 4,1 | 4,2 |
| 2,8 | 3,6 | 3,8 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,1 | 4,1 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 |
| 3,0 | 3,7 | 3,9 | 4,0 | 4,1 | 4,1 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 |
| 3,5 | 3,8 | 4,0 | 4,1 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,3 |
| 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,1 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,3 | 4,3 | 4,3 |
Table 2.7 Pre-hole diameters (mm) for ST 5.5
| Total thickness of fastened products, | Material strength, Rm, N/mm2 | ||||||||
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | |
| 1,8 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,3 | 4,4 | 4,5 | 4,6 | 4,6 |
| 1,9 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,4 | 4,5 | 4,6 | 4,6 | 4,7 |
| 2,0 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,3 | 4,4 | 4,5 | 4,6 | 4,6 | 4,7 |
| 2,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,3 | 4,4 | 4,5 | 4,6 | 4,7 | 4,7 | 4,8 |
| 2,5 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,4 | 4,6 | 4,7 | 4,7 | 4,8 | 4,8 | 4,8 |
| 2,8 | 4,2 | 4,4 | 4,6 | 4,7 | 4,7 | 4,8 | 4,8 | 4,8 | 4,9 |
| 3,0 | 4,2 | 4,5 | 4,6 | 4,7 | 4,8 | 4,8 | 4,8 | 4,9 | 4,9 |
| 3,5 | 4,4 | 4,6 | 4,7 | 4,8 | 4,8 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 |
| 4,0 | 4,6 | 4,7 | 4,8 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 5,0 | 5,0 |
| 4,5 | 4,7 | 4,8 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 |
Table 2.8 Diameters of preliminary holes (mm) for self-tapping screws ST 6.3
| Total thickness of fastened products, | Material strength, Rm, N/mm2 | ||||||||
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | |
| 1,8 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 5,0 | 5,2 | 5,3 | 5,3 | 5,4 |
| 1,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 5,0 | 5,1 | 5,2 | 5,3 | 5,4 | 5,4 |
| 2,0 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 5,1 | 5,2 | 5,3 | 5,4 | 5,4 | 5,5 |
| 2,2 | 4,9 | 4,9 | 5,0 | 5,2 | 5,3 | 5,4 | 5,5 | 5,5 | 5,6 |
| 2,5 | 4,9 | 5,0 | 5,2 | 5,4 | 5,4 | 5,5 | 5,6 | 5,6 | 5,6 |
| 2,8 | 4,9 | 5,2 | 5,3 | 5,5 | 5,5 | 5,6 | 5,6 | 5,7 | 5,7 |
| 3,0 | 4,9 | 5,3 | 5,4 | 5,5 | 5,6 | 5,6 | 5,7 | 5,7 | 5,7 |
| 3,5 | 5,2 | 5,4 | 5,5 | 5,6 | 5,7 | 5,7 | 5,7 | 5,7 | 5,8 |
| 4,0 | 5,3 | 5,5 | 5,6 | 5,7 | 5,7 | 5,7 | 5,8 | 5,8 | 5,8 |
| 4,5 | 5,5 | 5,6 | 5,7 | 5,7 | 5,8 | 5,8 | 5,8 | 5,8 | 5,8 |
| 5,0 | 5,5 | 5,7 | 5,7 | 5,8 | 5,8 | 5,8 | 5,8 | 5,8 | 5,8 |
Table 2.9 Pre-hole diameters (mm) for ST 8
| Total thickness of fastened products, | Material strength, Rm, N/mm2 | ||||||||
| 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | |
| 2,1 | 6,3 | 6,3 | 6,3 | 6,3 | 6,5 | 6,6 | 6,7 | 6,8 | 6,9 |
| 2,2 | 6,3 | 6,3 | 6,3 | 6,5 | 6,6 | 6,8 | 6,8 | 6,9 | 7,0 |
| 2,5 | 6,3 | 6,3 | 6,5 | 6,7 | 6,8 | 6,9 | 7,0 | 7,0 | 7,1 |
| 2,8 | 6,3 | 6,4 | 6,7 | 6,8 | 6,9 | 7,0 | 7,1 | 7,1 | 7,2 |
| 3,0 | 6,3 | 6,5 | 6,8 | 6,9 | 7,0 | 7,1 | 7,1 | 7,2 | 7,2 |
| 3,5 | 6,4 | 6,8 | 7,0 | 7,1 | 7,1 | 7,2 | 7,2 | 7,3 | 7,3 |
| 4,0 | 6,7 | 6,9 | 7,1 | 7,2 | 7,2 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,3 |
| 4,5 | 6,8 | 7,1 | 7,2 | 7,2 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,4 |
| 5,0 | 7,0 | 7,1 | 7,2 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 |
| 5,5 | 7,1 | 7,2 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 |
| 6,0 | 7,1 | 7,2 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 |
| 6,5 | 7,2 | 7,3 | 7,3 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 | 7,4 |
However, when using Tables 2, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of chromium-nickel alloys. Steel grades A2 and A4 according to GOST R ISO 3506 are in demand due to their high corrosion resistance. This is explained by the low carbon content (C ≤0.1%) and high content of alloying elements, primarily chromium (Cr ≈18%) and nickel (Ni ≈10%). For the same reason, austenitic alloys are softer than general purpose carbon steels. Their strength limit is almost comparable to each other, but alloys A2 and A4 do not have a so-called yield plateau. What causes the low values of the yield strength of austenitic alloys:
| steel grade | Strength class | Tensile strength Rm1, N/mm2, not less | Conditional yield strength Rp0.21, N/mm2, not less |
| A1, A2, A3, A4, A5 | 50 | 500 | 210 |
| 70 | 700 | 450 | |
| 80 | 800 | 600 |
When screwing self-tapping screws made of soft austenitic alloys into shaped rolled products made of carbon steels, the strength of which is significantly higher, damage to the hardware shown in Fig. 8 and 9. Therefore, in Tables 2, data for materials whose strength exceeds the yield strength of steels A2-70 and A4-70 are highlighted in gray.
DIN 7975 takes into account the characteristics of austenitic steels.
Clause 5.4 says: “In cases of fastening steel elements with self-tapping screws made of corrosion-resistant steel using the methods shown in Fig. 1-3, the low strength of the screws can cause deformation of the thread when screwing in.
In such cases, installation conditions must be determined experimentally.”
Taking this into account, when installing steel structures, BEST-Fixtures recommends:
— preliminarily determine the steel, assortment profile and strength characteristics,
— compare the strength of the base with the capabilities of hardware made from corrosion-resistant alloys,
— if necessary, select experimentally the most suitable type and conditions for fastening production,
- strictly adhere to the technical installation regulations.
If necessary, BEST-Fixture specialists are ready to come to your facility or production area to conduct a full technical consultation.
They will help you select and calculate the most suitable mounting method for your project.
How to unscrew?
To remove the self-tapping screw from the material, you can use thin pliers. Using the tool, you need to grab the end of the fastener and gradually turn it counterclockwise to unscrew it. If the self-tapping screw is at too great a depth and it is impossible to get it out with pliers, then you should take a chisel. When removing a part from a concrete surface, you should first make small cuts using a grinder in order to grab the element with another tool.
When removing self-tapping screws from metal structures, you will have to make additional small holes next to the seat. After this, grab the screw with pliers and pull it out with rotational movements. If the slot is torn off, but the cap itself is intact, then take a small piece of rubber. It is placed on the head of the self-tapping screw, then a screwdriver is pressed against it and they begin to gradually unscrew the part.
To learn how to properly tighten and unscrew a self-tapping screw, see the following video.
Determining quality
Quality is an important characteristic of any material. Self-tapping screws for metal with a drill are no exception. Before purchasing, be sure to check:
- The presence of a stamp on the head of the self-tapping screw with the name of the manufacturer.
- Compliance of actual sizes with standard ones.
- The thickness of the zinc coating. It must be at least 12 microns.
- The tightness of pressing the gasket to the washer. When compressed with pliers, it should not come away.
- Paint quality (for painted fasteners).
The simplicity, reliability and practicality of self-tapping drills contribute to the fact that such hardware is widely used in finishing work and in the installation of various metal structures.
Tip 3. How to choose the diameter of the screw
When deciding on the diameter of a self-tapping screw for woodworking, many people make the same mistake. It lies in the fact that to connect individual parts, they try to use fasteners with the greatest possible thickness. It is believed that a screw with a large diameter makes the connection as reliable as possible. This is not entirely true - a long and thin self-tapping screw will do the job much more efficiently than a thick and short one. In addition, it is more convenient to work with thin products - the chance of splitting the workpiece in this case is significantly reduced.
On concrete
When choosing self-tapping screws for concrete, the following characteristics of hardware are taken into account:
- Non-standard thread.
- Cink Steel.
- Sharp end.
- Length from 50 to 200 mm.
- Nominal diameter 7.5 mm.
- Head with an asterisk or cross.
During installation, preliminary drilling of the material is not required if the concrete is loose. A solid base requires drilling a shallow hole. With the help of such hardware you can make fastenings not only in concrete, but also in brickwork.
Having become familiar with the types of self-tapping screws, as well as their purpose, you can qualitatively connect parts made of any materials: metal, wood, install drywall, corrugated sheets or sandwich panels. You can see the selection of hardware more clearly in the video, which shows self-tapping screws for construction and repair work
How to choose wood screws - recommendations from the HouseChief.ru editors
First of all, choose a self-tapping screw based on the density of the surface being fastened or drilled.
The harder the wood, the smaller the screw pitch
Consider the width of the surface and the size, as well as the expected load. When attaching drywall, follow the required step - the screws should be fastened no further than 7 cm from each other. It is better to choose self-tapping screws with anti-corrosion treatment. If necessary, do not be lazy and pre-drill.