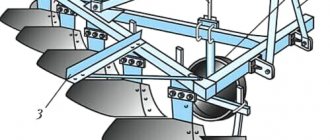
The tool for plowing the soil is the plow. The purpose of the equipment is to deeply loosen the soil, which provides the basis for preparation for sowing crops and the further process of cultivating them. This land-cultivating device is characterized by working with the highest energy consumption among all other types of loosening devices (harrows, cultivators) as part of units.
High-performance trailed reversible arable unit
Types of plows
Among the loosening devices, depending on the nature of soil cultivation, there are the following types of plows:
- Dump
- Dumpless
- Special
The first two categories relate to agricultural devices and are used for basic soil cultivation. The devices differ from each other in the nature of loosening, where the first ones provide plowing with the rotation of the soil layer, and the second (non-moldboard) cultivate the fertile layer without turning it over.
Plow body
Working paw of a bladeless flat cutter
Chisel rippers
The category of special plows includes devices designed for reclamation operations or wandering in the development of areas after logging. The working bodies of such devices correspond to the nature of the tasks performed. The example below shows a universal device that provides, during readjustment: uprooting, cutting fire furrows, hilling.
Working parts of a universal forestry plow
Blade
The plow moldboard cuts off the soil layer from the wall of the furrow, turns it over and dumps the layer to the bottom of the formed furrow. The front of the blade is its chest, and the back is the wing. The chest wears out more intensively, so plows that are used for plowing heavy soils have a removable chest. The wing is subject to a constant bending moment, which can cause its deformation and subsequent failure.
Read also: IN COLOR BALANCE Color selection
The moldboard and ploughshare are attached to the plow stand with bolts with a countersunk head that does not protrude above the surface. When attaching, it is important that the blade fits tightly to the ploughshare along their joint line and does not protrude above the surface of the ploughshare.
Aggregation of plows
According to the nature of the connection with the tractor, plows differ in:
- mounted
- semi-trailer
- semi-mounted
- trailed
Mounted - attached rigidly to the three-point hitch of the aggregated machine, the entire mass of which in the transport position falls on the tractor chassis. The implement is transferred to the working and transport position by a hydraulic cylinder of the linkage as part of the hydraulic linkage system of the tractor. All mounted plowing implements have a small working width with no more than 8 ripper bodies in their design.
Semi-trailed and semi-trailed plows are connected through the tractor hitch hitch. To move the unit in the transport position, the plows are equipped with running wheels. Part of the plow's mass is distributed to the tractor's coupling device, and the other part is distributed to the running support wheels as part of the equipment.
Trailed plows are equipped with a chassis that carries the full weight onto its support wheels without exerting force on the tractor coupling.
Semi-mounted arable unit
Semi-trailer arable unit
Trailed arable unit
The translation of trailed and semi-trailer (semi-mounted) devices into the working position is carried out by hydraulic cylinders built directly into the design of the land-cultivating equipment. Such plows are characterized by high productivity and have from 6 to 12 working bodies. Considering the significant traction force required for the operation of such devices, arable units are formed with powerful energy-rich tractors of at least the 5th traction class.
Manufacturers
On the agricultural machinery market you can find many different types of tractors and plows. Manufacturers such as Caliber and Dongfeng create tools for mini-tractors.
Dongfeng tools are distinguished by their strong mounts. The working mechanism produces neat dumps. The cost of such a unit from official representatives of the company can vary from 30 to 40 thousand rubles.
The Caliber company is a domestic production company that produces tools with a disk base. Their main feature is that the mass of the working unit is small, and due to this, a less powerful traction force is needed. The price of units from this manufacturer can range from 20-27 thousand rubles.
Mouldboard and plowshare plows
Plows that perform plowing with formation turnover have a loosening body design in the form of a body with a cutting blade and a blade that turns the formation. Such devices are the most common and are widely used for basic soil cultivation.
Types of moldboard plows
Moldboard plows are divided into two categories:
1 General agricultural devices used for basic soil cultivation. This category includes mounted and semi-trailer and trailed devices, both single-body and multi-body tillage devices.
PLN-3-35 with angle marks on dumps
2 Planting plows are used for deep cultivation (from 50 cm to 100 cm) when restoring soil fertility, plowing before planting orchards and vineyards, and when carrying out reclamation activities. The design of the device is a powerful hinged body with a blade for deep loosening. The operation of such devices is characterized by mixing the upper and lower soil horizons, opening access to moisture from the lower layers.
Planting PPN-100
In addition, there are cultivator plows with disc bodies, which have several universal functions in use. Such devices provide plowing with partial rotation of the formation, where the depth of processing is regulated by changing the angle of attack of the cutting discs.
Moldboard disc plow
Form of dumps
To achieve good quality plowing, depending on the physical condition of the cultivated soil, plow bodies for basic cultivation can be equipped with moldboards of various types and shapes. So, for equipping moldboard plows, there are four main types of moldboards:
- Cylindrical - in relation to the flow of the cut formation, the dump is placed steeply, as a result of which the formation bends sharply and crumbles when falling. Such a dump does not provide a complete rotation of the formation, but crumbles the soil well.
- Cultural - more curved than cylindrical, satisfactorily crumbles and turns over the layer. It is used in well-groomed areas with light soil composition.
- Half-screw - used in old arable and soddy areas; it wraps well around a layer with partial coloring.
- Screw - characterized by good turnover of the formation with poor crumbling, used in soddy areas.
Types of dumps for plowing with formation turnover
Among the innovative modifications of moldboard plows, one can note the introduction of feather-shaped moldboards in the form of a split plane, which makes it possible to improve the crushing of a moving soil layer, or the equipping of dumps with “angle skimmers”, in the form of metal plates, which ensure crushing of the layer and the formation of an even plowing topography. As well as the use of moldboard bodies made of a wear-resistant polymer composite, which are less susceptible to sticking of moistened soil and facilitate the overall design of the plow.
Three-furrow moldboard plow with feather mouldboards
Mounted PLN-4-35 with angle signs
Additionally, for effective incorporation of crop residues and good crushing of soil clods, moldboard plows can be equipped with skimmers in the form of a separate cutting plowshare installed in front of each body at ⅓ of the working depth of the main body. In the classification of plows, equipment with skimmers is called cultural plows.
Cultural plow
Reversible moldboard plow
To increase the productivity of arable units, the design of moldboard plows includes redundant bodies with a reverse direction of operation. If it is necessary to turn the unit, the hydraulically controlled turning mechanism in the plow changes the direction of plowing by changing the bodies. This design makes it possible to avoid the formation of stall and camber furrows in the plowing horizon, reduce fuel consumption and time for turning the unit, since with the function of changing the direction of operation of the bodies, it is unnecessary to divide the field into pens, and the movement of the unit is carried out according to a shuttle pattern.
Reversible five-furrow plow with feather mouldboards
Six-furrow reversible moldboard plow at work
Models of moldboard plows
Among the models of moldboard plows, there are devices for machines from the smallest traction class (walk-behind tractors and mini-tractors) to high-performance ones, when coupled with energy-rich heavy-duty tractors.
Examples of deciphering the abbreviations of moldboard plow models:
PLN 5-35 – mounted ploughshare plow, 5-hull, with a body grip width of 35 cm. PNO 3-35 (PON 3-35) – mounted reversible 3-hull, body grip 35 cm PLP 7-30 – trailed ploughshare, 7- mi cabinet, with a body grip width of 30 cm.
PLONU 8-40 is a mounted, reinforced 8-hull plowshare, with a body grip of 40 cm. PPO 9-35 is a trailed reversible 9-hull, with a body grip of 35 cm.
Additionally, in the designations of moldboard plows, the manufacturer may indicate the type of installed moldboards or an additional letter indicating the specialization in the use of the device. For example:
PBN-3-50A - swamp mounted 3-hull, with a body width of 50 cm, PLB-1 - swamp-shrub single-hull plowshare
Table of main models of moldboard plows
| Plow model | Working width, m / Capacity, ha per hour | Tractor traction class, t.p. |
| PLN 1-35 | 0,35/0,2-0,3 | 0.2-0,6 |
| PLN 2-35 | 0,7/0,35-0,65 | 0,9-1.4 |
| PLN 3-35 | 1,05/ 0,74-1,05 | 1.4 |
| PNO 3-35 | 1.05/O.72-0.94 | 1.4-2 |
| PLN 4-35 | 1,4/ 0,98-1,26 | 2-3 |
| MON 4-35 | 1,4/1-1,3 | 3 |
| PLN 5-35 | 1,75/1,22-1,57 | 3 |
| MON 5-35 | 1,75/1,28-1,6 | 3 |
| PLN 6-35 | 2.1/ to 1.9 | 3 |
| PLN 7-35 | 2,45/2,45 | 4-5 |
| PLN 8-35 | 2.8/ up to 2.8 | 4-5 |
| PPO 7-35 | 2,45/2,2-2,5 | 4-5 |
| PLP 8-35 | 2,8/2,8 | 4-5 |
| PLNU 8-40 | 3,2/3,2 | 5 |
| PLP 9-35 | 3,15/3,15 | 5-6 |
| PP 9-35 | 3,15/3,15 | 5-6 |
| PP 10-35 | 3,5/3,5 | 6-9 |
| PP 11-35 | 3,85/3,85 | 6-9 |
| PP-12-35 | 4,2/4,2 | 6-9 |
| PPO-12-35 | 4,2/4,2 | 6-9 |
Classification by hitch types
There is no clear opinion about the advantages of each model based on the type of hitch. You should choose a design based on individual parameters. In small areas, the minimum turning radius and maneuverability of agricultural equipment are important, while in large fields, productivity and plowing width per pass come to the fore.
The following types of equipment exist:
- mounted plows - they are the most maneuverable, they depend entirely on the tractor’s mounted mechanism, but at the same time their productivity is quite low;
- semi-mounted plows – characterized by greater productivity, as they are driven not only by the tractor’s mounted mechanism, but also by their own wheels;
- trailed structures are less popular because they have too large a turning radius, but are able to show a larger plowing width in one pass.
The so-called driven plows are popular because they allow you to plow a fairly wide strip of soil in one pass. The advantages of using such equipment are a reduction in fuel consumption for plowing the field, as well as faster completion of assigned tasks.
Moldless plows
The category of moldless plows includes subsoilers-flat-cutters and chisel rippers. Plowing with such devices is characterized by deep loosening of the fertile layer with minimal disruption of its upper part. This treatment helps protect the soil from wind erosion and drying out.
Mounted flat cutter KPG-2-150
The working parts of the flat cutter are made in the form of powerful pointed paws, ensuring loosening over the entire thickness of the horizon without disturbing the surface. Chisel plows are equipped with chisel-shaped rippers, which allow, together with effective loosening, at maximum depth, to destroy the compacted layer of the arable sole, ensuring the deepening of the arable layer and the supply of moisture from the lower layers.
Mounted chisel PCHN-4
The majority of models of moldless rippers require the creation of a significant traction force from the tractor for the unit to operate. Among the non-mouldboard devices on the market, the lowest traction force, as part of such an arable unit, requires a tractor of at least 2nd traction class and higher.
Trailed chisel wide-cut subsoiler
It should also be noted that there are models of plows with universal use, where, when converting working bodies, the ripper device can be used as a moldboard plow and a moldboardless ripper. An example of such a land-cultivating mounted machine is the high-speed combined universal plow - PSKu-5(6), which in the moldboard mode is equipped with screw blades, and in the non-mouldboard mode the blades are dismantled.
Mounted PSKu-5
Brands of flat cutters
Decoding the brands of flat cutters
KPG-2-150 cultivator flat-cutter deep-ripper with 2 working parts, with the grip of one lancet share 150 cm PGN-5 mounted flat-cutter-subsoiler with 5 cutting paws PGP-7 trailed flat-cutter-subsoiler with 7 cutting tines
Moldboard-less flat cutter ripper PGN 5
| Brands of flat cutters | Working width, m/productivity, ha per hour | Required traction force of the tractor, t.p. |
| KPG-250 | 2,5/1,08-1,35 | 3-4 |
| KPG-2-150 | 3.2/ up to 3 | 3-4 |
| PGN-3 | 3,2/3 | 3-4 |
| PGN-5 | 5,3/5,3 | 5-6 |
| PGN-7 | 7,4/7,4 | 5-6 |
| GGP-7 | 7,4/7,4 | 5-6 |
Chisel brands
Examples of deciphering the abbreviation of subsoiler chisels:
PCHN-4.5 mounted chisel plow with a working width of 4.5 m PCHG-3 chisel deep-ripper plow with a working reach of 3 m GCh-4 chisel deep-ripper with a working reach of 4 m PCH-3/1-6 – chisel plow with a working reach of 3 m, one row of working tools with 6 rippers PCH-4.5/2-9 – chisel plow with a grip of 4.5 m, two rows of working tools with 9 rippers
| Brands of chisel subsoilers | Working width, m/productivity, ha per hour | Required traction force of the tractor, t.p. |
| GRZ-1.5 | 1,5/0,8-1,2 | 2 |
| PCH-2/1-4 | 2/1,5 | 2-3 |
| PCH-2,3 | 2,3/1,5 | 2-3 |
| PCHN-2.5 | 2,5/1,8 | 2-3 |
| PCh-2.5/2-5 | 2,5/1,8 | 3-4 |
| PCHG-3 | 3/1,5-3 | 3 |
| PCH-3/1-6 | 3/1,5-3 | 3-4 |
| PCH-3.5 | 3,5/2,5 | 4-5 |
| PCh-3.5/2-7 | 3,5/2,5 | 4-5 |
| PCH-4/2-8 | 4/3-4 | 5 |
| PCHG-4.2 | 4,2/2-4,2 | 5 |
| PCH-4.5 | 4,5/3,5 | 5-6 |
| PCH-4.5/2-9 | 4,5/3,5 | 5-6 |
| GC-4 | 4/3,2-4,8 | 5-6 |
| PCHG-5.4 | 5,4/2,5-5,4 | 5-6 |
Furrow tool
Grain cannot simply be thrown on the ground - it will germinate only if it falls into loose soil, through which its tender sprouts and roots will break through. Loosening and digging up the soil also eliminated weeds that interfered with the growth of cultivated plants. People have noticed that it is easier to loosen the top layer of soil by dragging a pointed stick. So, along with the hoe, a furrow tool - a stick with a sharp branch pointing downwards, which was dragged while plowing the ground. This stick was the predecessor of the plow drawbar , and the branch on it was a prototype of the ploughshare (coulter) .
Egyptian at the plow. Painting of the 2nd millennium BC.
Special plows
This category of devices includes plows intended not so much for cultivating the soil, but for performing technological operations related to the formation of relief or soil cleansing, such as:
- uprooting roots and stumps
- hilling crops
- cutting irrigation, planting and fire furrows
Universal mounted forestry plow
In the design of these devices, there is no specific underlying system and nature of the work of the working body and processing. The cutting and loosening organs of special plows have a different appearance, with a shape and design that meets the specifics of the work being performed.
Rooter
PKL-70D forest uprooter-furrow cutter
Rooter