Properties of aluminum alloys and their applications
Aluminum alloys are widely used in aircraft construction and automobile production. Adding magnesium to the alloy improves the strength of the resulting metal. Finished products are easy to shape, since this property is practically not lost. In this case, the result of the work is not deformed. This material does not rust. This property makes it indispensable in shipbuilding. Anti-corrosion resistance is very necessary in the marine environment. Aluminum-magnesium alloys are used to make structures that are intended to be used in harsh weather conditions. For example, this material is indispensable in the construction of sea vessels and oil platforms. The properties of aluminum alloys make it possible to produce high-strength parts.
Machining aluminum: what problems can you encounter?
Soft and ductile aluminum lends itself well to machining, but sometimes you can encounter negative effects. Some alloys have high viscosity. In this case, when milling or drilling, long chips may be formed, which will wrap around the working tool, causing it to break. To minimize the risk of such a problem, tools for machining aluminum alloys should be selected with large chip flutes - although this will limit the maximum number of teeth on the cutter, it will facilitate the flow of chips, partially solving the problem. We also do metal bending and metal laser cutting.
How are aluminum alloys classified?
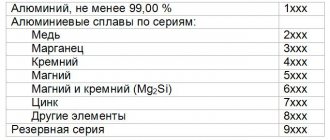
The classification of aluminum alloys occurs depending on the metal additives and is divided into:
The most common element in the earth's crust is aluminum. This is the thirteenth element of the periodic table. It is widely used in industrial production.
Other metals are added to an aluminum alloy in addition to the main element. Impurities are called alloying. This means that additional components are introduced into the alloy to give it some properties. Alloying elements can improve the physical or chemical properties of a material. An alloy is a mixture of aluminum-based metals with the addition of other elements. The content of the predominant metal should not exceed 99%.
- silicon (Si);
- magnesium (Mg);
- manganese (Mn);
- copper (Cu);
- zinc (Zn)
Iron can be considered an undesirable impurity because it reduces the strength of the alloy. But sometimes it is added specifically, for example, to make aluminum foil.
In addition to the main alloying elements discussed above, others are added to the alloy. They are included in small quantities up to 0.5%. These elements can add anti-corrosion, strength, and castability to the alloy.
Another basis for classifying aluminum alloys is the processing method. Alloys are distinguished:
- foundries;
- deformable.
In the first case, ready-made aluminum products are cast by filling out special molds. The alloy must have good fluidity in order to completely occupy the volume of the workpiece.
Wrought alloys are processed under pressure. They can be rolled, stamped or pressed.
Alloys using manganese have good strength. They are resistant to corrosion. This metal is easy to weld and is called duralumin, whose properties are highly durable.
Alloys with the addition of copper and silicon have a ductile structure, but are susceptible to corrosion. Therefore, they need to be coated with a protective metal. The use of aluminum alloys with copper occurs mainly in sleeve bearings and cylinder blocks.
Device cases are cast from alloys containing silicon, since the metal has little shrinkage.
What determines the quality of the surface formed during machining?
The quality of surfaces formed during the machining of aluminum is determined by three parameters:
- kinematic roughness - theoretical roughness depth, calculated from the movement of the metal-cutting tool and the workpiece relative to each other;
- roughness of a surface that has been machined - the reaction of the metal to its mechanical separation. This indicator directly depends on the microstructure of the material;
- influence of external factors - system stability, sharpness of the tool blade, etc. The listed parameters play a special role when processing aluminum at high speeds.
The quality of the machined surface of a part is determined by the same factors as the shape of the chip. As the strength characteristics of aluminum increase, the smoothness of new surfaces formed during machining improves.
In cast aluminum alloys, the quality of the surfaces formed depends on the microstructure of the metal.
Hard inclusions of the alloy, penetrating into the soft matrix, are capable of breaking out, resulting in the formation of a rough surface. If we consider cast alloys in general, they are processed quite simply, and the quality of mechanical surface treatment is at a good level. Go to list of articles >>
Types and methods of processing aluminum
Aluminum alloys can be used to make products of any shape. There is a chance to achieve any length and dimensions of the product.
When working with aluminum, you must follow the cutting mode, as the cutter may wear out unnecessarily. Aluminum workpieces can clog the grooves of cutting tools.
Types of aluminum processing include welding. This metalworking has its own characteristics. Aluminum products can be welded using argon gas. With this connection, the craftsman can make practically jewelry joints without seams.
Types of corrosion
Aluminum oxidizes quickly in the atmosphere, but to a shallow depth. This is prevented by a protective oxide film. Oxidation accelerates above the melting point of aluminum. If the integrity of the oxide film is compromised, aluminum begins to corrode. The reasons for the thinning of its protective layer can be various factors, from exposure to acids, alkalis and ending with mechanical damage.
Aluminum corrosion is the self-destruction of metal under the influence of the environment. According to the flow mechanism, they are distinguished:
- Chemical corrosion - occurs in a gas environment without the participation of water.
- Electrochemical corrosion – occurs in humid environments.
- Gas destruction - but accompanies heating and hot processing of aluminum. As a result of the interaction of oxygen with metals, a dense oxide film appears. This is why aluminum does not rust, like all non-ferrous metals.
On video: electrochemical corrosion of metals and methods of protection.
Processing technology for aluminum and its alloys
Aluminum processing methods include chemical polishing, electrochemical grinding and oxidation. Using chemical polishing, defects are eliminated from the surface of the product. The parts are dipped into a container with a special chemical composition that smoothes the surface.
Features of aluminum processing using electromechanical grinding: the part is immersed in a heated liquid. First, the part is placed for a few seconds. The top oxidized layer is removed. The object is then placed into the solution again. With the help of a discharge, polarization is created. Both aluminum processing technologies are designed to improve the appearance of products.
Aluminum can be anodized. This means that the oxidative protective film formed on the surface of the metal is compacted. Anodizing also makes the surface of aluminum products smoother.
Aluminum cutting is done using different techniques. The choice depends on the material and the desired result, as well as the amount of work. If the sheets are thin, they can be cut with ordinary scissors. If the sheets are thick or there are too many of them, use a cutter or grinder. For high precision, a machine based on numerical control is used.
Aluminum weighs little but has high strength. Therefore it is easy to process. By means of chemical and mechanical action, as well as the addition of impurities, its organoleptic properties can be improved. This is why aluminum is so widely used in industry.
Anodizing of aluminum parts
Anodizing is a process, also known as folk oxidation, that creates an oxide coating on the surface of an aluminum workpiece. In this case, aluminum is oxidized, but an oxide film protects it from oxidative processes.
This processing has a number of undeniable advantages:
- increases the protective and decorative properties of metal;
- provides surfaces with dullness and uniformity;
- eliminates mechanical damage such as chips, scratches, cracks;
- increases the thickness of the protective layer.
There are several types of processing of aluminum blanks by anodizing.
- Thermal anodization has a fairly simple technology; it is carried out at room temperature and allows you to obtain a beautiful color coating. In this case, only organic dyes are used. A skilled specialist can obtain several color schemes for the same part. Among the disadvantages, it should be noted that a high degree of protection against corrosion cannot be achieved.
- Cold anodizing of aluminum billets is characterized by the strength and hardness of the anode layer, excellent wear resistance, and high quality. Each part used within this technology must be well cooled. This treatment has the only drawback - it is impossible to use organic dyes during the cold anodizing process.
- A sufficiently strong and hard film can be obtained by hard anodizing. The peculiarity of the technology is the use of one of several electrolytes: in addition to sulfuric acid, oxalic, acetic, tartaric or boric acid is also used. During the process, the current density increases, and, accordingly, the film of increased density also increases.
For the anodizing process, several aluminum baths of different diameters are used (plastic or polypropylene can also be used). The main condition is compliance with the thermal insulation properties of the bath.
Methods for removing scale from aluminum cookware
Aluminum cookware is susceptible to scale formation. This is due to the high content of heavy metal salts and lime deposits in tap water. To fix the problem and return the kettle, saucepan or can to shine and cleanliness, you need to properly clean and wash the products in a timely manner.
Vinegar
Algorithm for cleaning an aluminum kettle:
- Pour 1/2 bottle of vinegar, 9%, into the container.
- Close the kettle with a lid and boil.
- After boiling, shake the liquid to coat all sides of the dish.
- Drain the solution, add clean water and boil the kettle twice.
To get rid of the unpleasant vinegar aroma after cleaning, place an orange/lemon peel in a bowl, cover with water and leave for 15 minutes. This trick will create a pleasant aroma and freshness.
Lemon acid
Instructions for descaling aluminum:
- Dissolve 25 g of citric acid in warm water (1.5 l).
- Pour the solution into the container, close the lid and put on fire.
- After boiling, boil the liquid for 5 minutes with the lid open.
- Leave the dishes to cool completely.
- Rinse the product with running water.
Citric acid or natural citrus juice will gently clean limescale from aluminum surfaces
Method 2
To paint aluminum at home you will need:
- primer for aluminum, stainless steel and galvanized coatings - fine sandpaper - acrylic or epoxy zinc-aluminum paint for metal - white spirit, acetone or kerosene for degreasing the surface
Instructions for painting aluminum without anodizing
1 Thoroughly sand the surface of your aluminum product with fine sandpaper.
The less grainy sandpaper you use, the better. Size 600, 800 or 1200 is suitable 2 Degrease the surface using white spirit, acetone or a special degreaser 3 After complete cleaning and degreasing, coat the surface with a primer for aluminum and stainless steel as quickly as possible. If you leave aluminum treated with sandpaper in the air for a long time, then after a short time it will begin to darken - this is the result of the oxidation process, and primer and paint do not adhere well to oxidized aluminum. This is why it is so important to apply the first coat of primer as soon as possible. A few minutes later, after the first layer of primer has dried, you need to apply a second layer of primer for better adhesion of the paint to your product 4 Let's move on to painting. How to paint aluminum treated with primer? To do this, you will need a special zinc-aluminum metal paint containing zinc and aluminum. It is best to use paint in an aerosol can, since when applying paint from an aerosol can, it goes on much more evenly and smoothly than when applied with a brush. Before you start painting, shake the can thoroughly; paint should be applied from a distance of 25-30 centimeters. Painting should be done from top to bottom to avoid drips. After the first coat of paint has dried (20-25 minutes is enough), apply the next coat of paint. As a rule, for good and high-quality painting of aluminum, 3-4 layers of paint are enough. 5 After painting is completed, let your aluminum product dry completely. This requires 4 - 6 hours 6 You can additionally coat the product with varnish, this will add depth to the color and additionally protect the painted surface from damage. If you have followed all the steps of the instructions exactly, the new paint on your aluminum product will last for many years and look like new !
Manifestation of aluminum corrosion
The following types of corrosion of aluminum and its alloys are distinguished:
- Superficial – the most common, causes the least harm, is easily noticeable and can be quickly eliminated.
- Local – destruction is observed in the form of depressions and spots. A dangerous type of corrosion due to its invisibility. Found in hard-to-reach parts and assemblies of metal structures.
- Thread-like, filigree - observed under organic coatings, on weakened areas of the surface.
Any type of corrosion of aluminum structures causes destruction.
This shortens the life of the products. In a galvanic couple, aluminum can corrode while protecting the other metal.
The natural anti-corrosion properties of aluminum and its alloys are not enough. Therefore, mechanisms, assemblies, structures and metal products need additional protection.