Group G23 STANDARD
INTERSTATE
GOST
24996-81
TURNING CUTTERS WITH MECHANICAL FASTENING OF REPLACEABLE PLATES. SECURED BY ROCKING PIN
Types and main sizes
Turning tools with mechanical clamped changeable polyhedral plates fixed by swing pin.
Types and basic dimensions
M KS 25.100.10
By Decree of the USSR State Committee on Standards dated November 18, 1981 No. 4988, the introduction date was set
from 01/01/84
1. This standard applies to turning tools with mechanical fastening of replaceable polyhedral inserts, secured by an oscillating pin, intended for use on numerically controlled machines and universal machines.
2. Cutters must be made of the following types:
1 - with triangular plates bent at an angle <р = 45°, right and left;
2 - the same. with an angle <р ■ 60°;
3 - the same. with angle <р - 90°;
4 - with square plates, straight lines with an angle <р = 45°;
5 - with square plates bent at an angle (p ■ 45°, right and left;
6 - the same. with angle <р = 60';
7 - with square plates, straight lines with an angle <р = 75°, right and left;
8 - with rhombic plates with an angle of 80° with an obtuse angle at the apex, straight, with an angle Ф ■ 75°, right and left;
9 - with rhombic plates with an angle of 80′, bent with an angle <р ■ 95°, right and left;
10 - with rhombic plates with an angle of 55°, straight with a corner <р ■ 63°, right and left;
11 - with rhombic plates with an angle of 5512, bent with an angle <р ■ 93°, right and left;
12 - straight with round plates;
13 - with round plates, bent, right and left.
3. The main dimensions of the cutters must correspond to those indicated in the drawing. 1 - 13 and in table. 1 - 13.
Type I
Types of turning tools with replaceable inserts
The following types of cutting tools with replaceable inserts are distinguished:
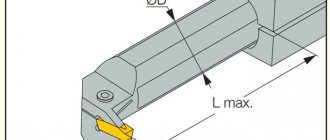
- Boring cutters: have a cone-shaped holder and mechanical fastening for making through and blind holes in parts. They can also be used for cutting internal and external threads in cylindrical products. When making blind holes, the cutting edge should be positioned at an angle of 90°, for through holes - at an angle of 60°.
- Pass-through: used during external processing of metal parts. Their cutting edge is located at an angle of 45°.
- Shaped: necessary for processing shaped surfaces. These cutting tools are capable of ensuring the identical shape and dimensional accuracy of the processed workpieces. Shaped cutters are made from high-quality high-speed steels.
- Parting cutters: used for cutting workpieces into several parts. They are used when processing small and large bar parts. The main cutting edge of the tool is at an angle of 90°.
- Multi-faceted carbide cutters: equipped with polyhedron-shaped inserts.
- Grooving: intended for cutting grooves in cylindrical and conical products. They are characterized by high structural rigidity and high productivity. These tools are able to withstand high loads during turning operations.
The choice of the type of thread cutters with replaceable inserts depends on the type of technical operations performed during the processing of metal parts. The quality of the instrument depends on the precision of manufacturing and the professional skills of the craftsman.
How to choose the right cutter?
When choosing a cutter, you must be guided by the following basic recommendations:
- Determine what metal the cutter will work with, what processing operations you will carry out and what loads it will experience
- It is necessary to decide what is the priority criterion - the accuracy of the geometric dimensions of the finished product or the quality of its surface treatment. Depending on this, the type of cutter is selected according to classifying characteristics and geometric parameters.
- Determine how important it is to comply with the wear resistance conditions of the cutter and for how long it should be maintained.
If you find it difficult to choose the tool you need, our company’s specialists will help you professionally implement it in a matter of minutes. In our company's warehouses there is a large assortment of different cutters that will satisfy any of your requests.
Nuances of choosing a cutter
When purchasing cutting tools, you need to pay attention to the following criteria:
- A type of cutting tool. Different types of cutters differ in profile shape, determined by the technical features of carbide inserts.
- Dimensional characteristics. The different dimensions of products processed on a lathe determine the dimensions of the cutting tool. For modern types of cutters, you can select workpieces with distinctive dimensional characteristics.
- Back angle value. This indicator affects the accuracy of finishing of the material. The surface cutting cleanliness is directly proportional to the clearance angle. This parameter is taken into account when turning metal workpieces with soft surfaces.
- Accuracy class. This parameter is used to calculate the accuracy of the cutting performed. According to GOST 9253-59, 3 main accuracy classes are established for plates. When measuring this parameter, it is possible to cut workpieces with tools with different tolerance values.
If these criteria are not taken into account, then the thread cutters will not be able to be firmly fixed on the lathe and produce precise processing of metal parts.
When purchasing cutting tools, it is important to choose the right inserts. These parts are made of hard metal alloys. The ratio of metals determines the operating characteristics of the cutting tool. There are 2 main types of plates:
- With increased strength. They are resistant to vibration, shock and other physical stress that occurs during cutting. It is recommended to purchase this category of plates if you need to cut a large amount of metal from the workpiece.
- With increased heat resistance. They can withstand high temperatures that arise during long-term processing of workpieces and exposure to frictional forces. Heat-resistant plates are fixed mechanically. They are used when working at high speeds.
Materials of manufacture are indicated on the markings of carbide inserts. Each alloy has a unique image. In the manufacture of cutting parts, tungsten is used, which has high strength and resistance to large temperature changes. Additionally, titanium carbide or cobalt can be used. Plates made of ceramic materials are used during finishing or semi-finishing of metal products. They can be used for cutting workpieces made of heat-resistant alloys. The percentage of these components determines the category of replacement plates. On the marking, titanium is designated by the letter “T”, cobalt by the symbol “K”. Example of marking: T14K7 (percentage of titanium carbide - 14%, cobalt - 7%).
For large volumes of turning work, it is recommended to purchase a set of turning tools with replaceable inserts, which will allow you to quickly adjust the tool during various technological operations. When choosing sets, it is important to consider the manufacturer's brand. The most popular replacement plates on the market are from the following companies:
- LLC “Instrument-Service”: a Ukrainian company that produces parts for cutting tools.
- Interpipe: is the largest organization for the production of pipe and threaded connections in Eastern Europe. The products are manufactured at the Novomoskovsk pipe plant, located in the Ukrainian city of Dnepr.
- BDS-Machinen: German company producing devices and parts for magnetic drilling machines.
- Proxxon: an organization that develops parts for cutting small workpieces. Production takes place in Germany.
- Ceratizit: a company producing metal-cutting tools and their main components. The headquarters is located in Luxembourg.
The cost of a set of turning tools depends on the manufacturer's costs and the financial policies of suppliers. Imported parts have the highest price. The average price of a set is 15,000 rubles. Additionally, you can purchase certain types of plates. Their average price is 164 rubles.
Design features of cutters.
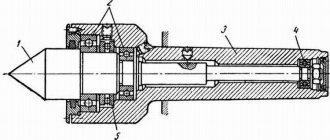
The cutter conventionally consists of two parts: a rod (holder) and a head. The holder is designed to secure the cutter in the tool holder of a metal-cutting machine. The profile of the rod has the shape of a square or rectangle.
To unify the use of cutters, the following range of rod section sizes, mm, has been established:
- for square sections (square side) - 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40;
- for rectangular sections - 16x10; 20x12; 20x16; 25x16; 25x20; 32x20; 20x25; 40x25; 40x32; 50x32; 50x40; 63x50.
The cutter head is its working part and contains a number of edges and planes sharpened at certain angles for various metal processing methods.
Sharpening angles:
- α is the main relief angle;
- β is the sharpening angle;
- γ — front angle;
- δ—cutting angle;
- φ is the main plan angle;
- φ1—auxiliary plan angle;
- ε—cutter apex angle;
- α1—auxiliary clearance angle;
- λ is the angle of inclination of the cutting edge.
Main rear corner. The angle formed between the main flank surface of the cutter and the cutting plane. Reduces the friction force that occurs between the flank of the cutter and the workpiece. Affects the quality of surface treatment and its wear (they decrease as the angle decreases). The value of the angle is inversely proportional to the hardness of the metal being processed.
Point angle. The angle formed between the front and main back surfaces of a cutter. Affects the strength of the cutter and its sharpness.
Front corner. The angle formed between the rake surface of the cutter and the normal to the cutting plane at the point of contact of the rake surface with the workpiece. Reduces deformation of the metal being cut, facilitates chip flow, reduces cutting force, and improves heat dissipation. The value of the angle is inversely proportional to the hardness of the metal being processed.
Cutting angle. The angle formed between the rake face of the cutter and the cutting plane.
Principal angle in plan. The angle formed between the main cutting edge and the workpiece plane (or feed direction). Determines the quality of the machined surface of the workpiece while maintaining the cutting depth and feed rate. The quality of the surface is inversely proportional, and the resistance of the cutter to breakage and the occurrence of vibrations is directly proportional to the angle. Standard angle values are: 10, 20, 30.35, 45, 50, 60, 65, 75 and 90 degrees.
Auxiliary plan angle. The angle formed between the minor flank surface of the cutter and the workpiece plane (or feed direction). Affects the quality of workpiece surface treatment (as the angle decreases, roughness decreases and cleanliness improves). Angle at the tip of the cutter. The angle formed between the main cutting edge and the secondary flank surface of the cutter. The strength of the cutter is directly proportional to the angle.
Angle at the tip of the cutter. The angle formed between the main cutting edge and the secondary flank surface of the cutter. The strength of the cutter is directly proportional to the angle.
Auxiliary back angle. The angle formed between the minor flank surface and a plane perpendicular to the plane of the cutter and passing through the minor cutting edge. Reduces the friction force that occurs between the secondary flank of the cutter and the workpiece.
Angle of inclination of the cutting edge. Controls the direction of chip flow and determines the geometry of contact between the cutting part of the cutter and the workpiece. The angle values determine the purpose of the cutter: a negative value for finishing, 12-15 degrees for roughing, 25-35 degrees for processing hardened steel. Universal cutters have a cutting edge angle of zero.
Cutting modes
Cutting modes are a set of parameters that determine the conditions for processing parts using a turning tool. The cutting process is influenced by the following factors:
- Cutting speed is the path of movement of the machined surface of the workpiece relative to the cutting edge per unit time. Measured in m/min or m/s. In the drawings it is designated by the Latin letter V.
- Feed is the path traveled by the cutting edge in 1 stroke or revolution of the workpiece being processed. Measured in mm/rev. In the drawings it is marked with the Latin symbol S.
- Depth of cut is the distance between the machined and machined surfaces. It shows the amount of metal layer being removed. In the diagrams it is denoted by the Latin letter t.
- The cross-sectional area of the cut layer is the product of the cutting depth and the feed. It is a nominal value and affects the presence of roughness. In the diagrams it is indicated by the Latin symbol f.
These parameters are tabular values and are specified in GOST 25762-83.
Download GOST 25762-83
Each type of cutting tools with mechanically fastened inserts has additional cutting modes. Cutting cutters carry out transverse movements, boring tools move longitudinally relative to the surface of the workpiece. During operation, the average speed of the cutting edges is tenths of mm. The feed is 0.1 mm/rev.
Design
A turning cutter consists of two structural parts: a holder, with the help of which the tool fits into the mounting groove of the machine, and a cutting head. The holder is made in a rectangular or square shape and is the main part of the device.
The head consists of an edge sharpened at the required angle and several planes; it is the working part of the device; during processing it gives the workpiece the required shape. The sharpening angle affects how the cutter removes metal from the workpiece.
By design, cutters are divided into several types:
- straight: the holder and the working head are located on one axis, or on two parallel ones;
- curved: when viewed from the side, a curved holder is visible;
- bent: viewing the tool from above, the bend of the working part is clearly visible;
- drawn: the width of the holder is greater than the working head, drawn to the left or right. The axes of both parts of the part coincide or are shifted.
Advantages and disadvantages of incisors
Thread cutters with replaceable inserts have the following advantages:
- low cost: cost less than solid type incisors;
- allow you to save a large amount of time resources during the preparation of cutting tools for various technological operations;
- the plates are able to withstand high loads because they are made of carbide materials;
- cutting cutters can be used to process parts with small dimensions and uneven terrain;
- the cutting tool can be readjusted if necessary;
- high service life of the holders, which allows the tool to be firmly secured to the lathe;
- do not require additional sharpening or soldering;
- during processing, reduce cutting force and temperature by 35 - 40%;
- provide the ability to change cutting modes on the fly;
- unification of all cutter models: allows you to select the right insert for processing workpieces made of certain types of metals.
Experts highlight the following disadvantages of cutters with replaceable inserts:
- due to the presence of many fasteners for carbide inserts, the total weight of the cutting tool increases;
- cutters are not able to provide optimal geometric parameters of the cutting edge due to the different shapes of the plates and the peculiarities of their fastening;
- high complexity of manufacturing cutting tools.
The quality of a thread cutter depends on the type of processing and cutting mode. The cutter retains its benefits longer at low cutting speeds and during internal cross turning. The cutting tool wears out faster during external longitudinal turning. To increase its durability, lubricating and cooling media are used. You can also increase the rigidity of the tool by increasing the area of the holder.