Gas cutting seems to be a simpler process than gas welding work, and therefore even a person who does not have special skills can cope with it.
For this reason, almost any of us can master working with a cutting torch. The main thing here is to understand the essence of gas cutting technology. In modern conditions, propane cutters are increasingly used. Working with them requires the use of both propane and oxygen, since the combination of such substances provides the maximum combustion temperature.
The designs of different types of cutters may differ from each other in size or in some components, but the principle of operation is the same for all.
Operating principle and types of cutters
Regardless of the size of the autogen and the types of heating gas mixture, cutting can occur using the process of metal combustion in a stream of oxygen of a pure mixture, pumped through a special nozzle in the head of the working zone.
The main and fundamental feature of gas cutting is the combustion temperature, which must be no less than the melting temperature. Otherwise, the metal, without having time to flare up, will melt and flow all the time. Low-carbon fats must meet these conditions, but non-ferrous metals and cast iron do not.
A large number of alloy steels will also not be amenable to the gas cutting process - there are significant restrictions on the maximum indicator and permissible dosages of alloying components, carbon, impurities, the process of exceeding the combustion of which inside oxygen will become the most unstable or will cease to occur at all.
The cutting itself should be divided into two stages:
- Heating one part of a part to a temperature at which the metal begins to burn. In order to obtain a heating flame, part of the technical oxygen in a certain ratio is mixed with gas .
- The process of combustion (oxidation) of heated metal in a stream of oxygen and the general removal of the combustion product from the cutting zone.
If we start to consider the classification of only hand-held cutters, then this value will have the following features:
Type of fuel, power and method of producing a mixture of gases for a heating-type flame.
- Classification by type of flammable gas: propane-butane, methane, universal MAF, and acetylene.
- Power feature: small (cutting metal with a thickness of 3 to 100 mm) - marking P1, medium (up to 2-0 millimeters) - marking P2, higher (about 300 millimeters), marking - P3. There are special samples with a cutting thickness of about 500 millimeters.
- And if the first feature will only affect the overall temperature of the heating flame, as well as the power - the maximum thickness of the metal, then another feature will determine the design feature of the cutter.
Flame temperature of propane torch and acetylene torch
And this rule must be strictly observed. After all, kerosene poured into a gasoline “soldering iron” will turn it into a tool like a flamethrower. Once in the burner, it will not have time to completely evaporate, therefore, it will not be the vapor that will burn, but the kerosene itself.
Such a tool will not work normally.
It is even more dangerous to pour gasoline into a kerosene blowtorch.
Gasoline evaporates much faster than kerosene, and its vapor pressure in the burner will be 6 times greater than the calculated one. If you try to light it, the fumes will explode, turning the useful tool into a dangerous bomb.
Features of gas cutters: acetylene and propane
Today, various types of torches are used for cutting metal, which differ in type of processing, purpose, design, oxygen supply, power, type of mouthpiece, and type of fuel.
This ensures very high productivity, low formation of oxidation processes, which guarantees high cutting quality.
As for the operating principle, it is not very original. Oxygen from the cylinder is supplied to the injector and cutting tube. In the injector, this gas is mixed with acetylene, heated and ignited.
It is with this flame that sheets of metal are cut. Such models use a combination of oxygen and propane during the cutting process, and the cut is less clean than when using acetylene units. By adjusting the gas supply power using an inductor, it is possible to process fairly thick materials.
You should buy a propane gas cutter due to the following advantages:
- convenience when creating curved cuts;
- light weight;
- affordable price;
- high performance;
- possibility of creating blind holes.
It is worth emphasizing that this type of equipment is not used for all materials. It can be used exclusively for cast iron (malleable), as well as steels with low or medium carbon content.
This is an indispensable tool for working according to a template when it is necessary to cut out a part of a certain shape. If you need to buy cutters running on or, you should contact the Avant online store.
Great Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
Air-acetylene flame (temperature 2300 C) is the most widely used. The reducing flame prevents the formation of heat-resistant oxides in a number of metals, which prevent atomization.
The air-acetylene flame has a lower temperature, which reduces the risk of solder burnout. The air-acetylene flame of the UPN apparatus burner is regulated in such a way that the fluoroplastic-3 powder, passing through it, does not melt, but only heats up and partially softens.
Using an acetylene air flame, plastics can also be sprayed. An air-acetylene flame (extended burner, flame length 11–12 cm and cut width 0 07 cm) and a medium dispersion quartz spectrograph were used. Light from a lamp with an Fe cathode was passed through a flame into which solutions containing iron in concentrations ranging from 7 to 500 μg/ml were sprayed.
The temperature of the air-acetylene flame is 2100 - 2400 C; the temperature of the oxygen-acetylene flame reaches 3300 - 3400 C. The minimum ignition temperature of the oxygen-acetylene mixture ranges from 416 to 440 C; the ignition speed of this mixture is 90 - 200 m/sec, depending on the oxygen content in it.
The speed of explosion propagation (detonation) is 3000 m sec.
For air-acetylene flames, burners without external air intake are usually used, and the air necessary for combustion is supplied by a sprayer. For these burners to operate properly, the amount of air passing through the atomizer must be just enough to produce a stable flame; therefore, the diameter of the tube supplying air to the atomizer and the size of the burner outlet depend on the air pressure in the atomizer.
It is almost impossible to determine aluminum in an air-acetylene flame due to insufficient dissociation of its monoxide. The stoichiometry and operating height of the flame greatly influence the signal-to-noise ratio and various matrix effects. It is almost impossible to determine aluminum in an air-acetylene flame due to insufficient dissociation of its monoxide.
It is almost impossible to determine aluminum in an air-acetylene flame due to insufficient dissociation of its monoxide. The stoichiometry and operating height of the flame greatly influence the signal-to-noise ratio and various matrix effects.
If an aqueous solution of aluminum is fermented into a reducing air-acetylene flame, the absorption will be very small.
However, David reports [75] that acidic aqueous 8-hydroxyquinoline aluminum slave solutions provide a strong absorption signal in an air-acetylene flame. This is probably explained by the fact that the organic complex prevents the formation of an aluminum-oxygen bond in aerosol particles entering the flame, and the complex itself easily dissociates at the flame temperature. Pages: 1
Highest burner flame temperature.
Adjusting the burner flame.
It is impossible to cut with such a flame, since in addition to obtaining a poor-quality cut, productivity is noticeably reduced.
Flame adjustment is to create a normal or slightly oxidizing flame of the required power, symmetrical with respect to the cutting oxygen stream. The flame power is set depending on the thickness of the metal being cut.
Typically, with the pressure set correctly and the oxygen and acetylene valves (on the torch) fully open, there will be some excess acetylene in the ignited preheat flame. By gradually closing the acetylene valve, a normal flame is achieved. A normal flame must be created with the valves not fully open to allow further adjustment.
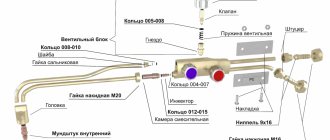
Design Features
A two-pipe, as well as an injection, gas cutter is the most common type of this design. Technical oxygen in the cutter will be distributed into two formats at once.
One portion of the top tube flow will pass through the tip head and exit at high velocity through the center nozzle of the inner mouthpiece. This part of the structure will begin to be responsible for the cutting phase of the process. A control valve or lever valve located outside a specific housing.
The next part will begin to flow into the injector itself. The principle of operation of this device will be that the injected gas (oxygen), entering the mixing chamber under strong pressure and at a high speed, creates a rarefaction area in this place and through the peripheral holes is drawn independently into the flammable (injected gas). Using the process of such mixing, the overall speeds are equalized, and at the exit of the chamber a special flow of a mixture of gases begins to occur at a speed much lower than that of the injected oxygen, but much higher than that of the electrified combustible gas.
After the mixture of gases begins to circulate through the lower tube into the tip head itself, exits through the nozzles between the inner and outer mouthpiece, and also creates a torch of a heating flame. Each channel has its own valve, which will regulate the supply of oxygen, current and combustible gas to the injector.
A non-injector or three-pipe cutter , which contains a more complex design - two oxygen gas flows will begin to flow to the head through separate tubes.
The displacement of the entire heating mixture will occur inside the head itself. But it is the absence of a chamber in which mixing occurs that provides a stronger safety indicator, and also does not create conditions for creating a backlash (the process of spreading burning gases into the channel of the cutters themselves and the pipes in reverse motion).
In addition to more developed structural designs and inflated costs, the disadvantage of a three-pipe gas cutter is considered to be that for its stable operation it is necessary to use a higher pressure of combustible gas (there is no ejection effect here, as well as an increase in the speed of general flows).
Device and parameters
An apparatus for cutting metal parts using gas consists of several elements. The master needs to know its structure in order to take certain measures in case of breakdown or jamming. Main details:
- handle;
- frame;
- channels for supplying flammable gas and oxygen;
- mouthpiece;
- a nozzle responsible for the formation of a burning jet.
In addition to the key elements, the metal cutter has gas supply regulators, a system of channels through which they pass through the body and reach the outlet openings. The dimensions of the apparatus for cutting metal parts are smaller than that of a grinder, however, the burner requires the connection of cylinders with consumables, which complicates the delivery of the equipment to the workplace.
Overall size and weight
The parameters of a manual injection gas cutter will be contained in GOST 5191−79 standards and will directly depend on its power indicator:
- P1 has about 500 millimeters.
- For P2 and P3 they are within a certain limit of 580 millimeters. But more extended models are also being produced to carry out work in appropriate conditions.
- There are special restrictions on the weight of any such power category: 1.0 and 1.3 kilograms in the ratio for P1 and P2-P3.
The same standards from GOST will determine that the P3 variety is an oxygen-propane cutter, and also P1 and P2 can perform work on absolutely any type of combustible gas. There is also a separate group of manual injection tools for oxygen cutting - insert cutters, which have a special marking PB.
According to GOST standards, they will be defined as tips for cutting on a welding torch. The main differences in such designs are that the process of separating oxygen, as well as a mixed type of combustible mixture, will occur on the tips themselves, which have a smaller weight and size than the cutter. So the weight indicator of PB1 has a special upper limit of 0.6 kilograms, and PB2 and PB3 are about 0.7 kilograms.
But this type of gas cutter cannot be called complete in terms of its metal - in the working position during the assembly process with the main body of the burner, its overall size and weight will be no less than that of special equipment. Its main advantage is that you can purchase a torch together with various types of tips (cutting and welding), and the complete complex can be easily placed in a small case. Or buy a portable backpack specially designed for the burner.
But in this case there is one peculiarity. Propane will be much cheaper in cost than acetylene. It is for this reason that the cost of using an acetylene torch will be much higher than an oxypropane torch. To weld metal, it is better to use an acetylene torch, whose total flame temperature will be as much as 300-400 degrees higher than that of an oxygen- propane torch (with an all-propane torch the total temperature will be less than 2 thousand degrees Celsius).
The compactness of the entire post for manual cutting can be ensured using the capacity of all gas cylinders.
Advantages and disadvantages
The gas burner is designed for cutting products in production conditions, with a large volume of tasks. Before using the device, it is important to understand what key features metal cutting with propane and oxygen has:
- The mechanism of action is convenient when making curved cutting lines. Stable power allows you to separate metal products of various thicknesses into parts. In situations where it is impossible to use a tool such as an angle grinder, a gas torch is used. The task of making a round product or a blind hole is performed with a gas torch without requiring much effort.
- A gas cutter has an advantage over gasoline models. In addition to being lightweight, the mechanism does not produce excessive noise during operation and is also compact.
- The use of a device based on the influence of flammable gas makes it possible to double the speed of execution, which is beyond the power of mechanical tools.
- Propane, as a liquid gas, has a low price. Therefore, it is used not only when processing products for production needs, but also when recycling metal and other activities.
- The use of propane as a flammable mixture allows for high-quality cutting. Cutting is carried out along a narrow line, which is the main factor in quality work.
The disadvantages are that some materials cannot be processed with a propane cutter, such as cast iron and high-alloy steels.
Advantages of portable gas burners
Recently, on the market you can see offers for the purchase of portable gas burners, which include an attachment to a small collet cylinder filled with gas.
The flame temperature in such a device usually does not exceed 1300 degrees Celsius. And although there are professional collet portable cutters with a total torch temperature from 2000 to 2500 degrees Celsius (for example, Kovea KT -2610 when working with a MAPP US gas mixture), which is already closest to the temperature of the flaring flame of an oxygen-propane cutter - 2700 -2800 degrees Celsius.
In any case, in order to establish certain conditions for combustion, there is no main cutting component - a stream of oxygen, with the help of which the general oxidation of the metal occurs.
These portable cutters can be used to cut low-melting metals, as well as alloys: aluminum, bronze, copper, brass, and tin. But even in this case, we will not be talking about cutting, but about the melting process. It is for this reason that they are most often used during the repair of refrigerators or air conditioners, and cutting can be done using manual or electrical equipment.
Preparing for work
Before you start working with gas cutting equipment, you need to prepare. It includes actions that reduce the risk of damage to the device, workpiece, and injury. Preparation stages:
- Inspect the cylinders, connecting hoses, fasteners, and burner for damage. They must be intact, without visible defects.
- Sniff the surrounding air. This way you can detect a gas leak. Initially, you need to connect the hoses to the cylinders and the burner, clamp them with clamps. The flammable mixture should not burst out.
- Rubber seals must be intact. If cracks appear on them or their shape changes, it is necessary to immediately replace the gaskets with new ones.
- Before opening the oxygen valve, it is necessary to check the equipment for grease stains and oil leaks. Even small amounts of these substances can cause an explosion.
It is important to connect the hoses correctly without confusing the gas supply.
Preparing to use a cutting torch
Choosing an Oxygen Torch
If we consider the device from the hose to the head, it is important to highlight the following features:
- The valves must rotate with the least effort.
- Nipples made from brass last much longer than aluminum devices.
- The material on the handle must be of the aluminum type; in this case, plastic linings will last less and may soon float.
- The best diameter of the handle in the cutting oxygen valve is at least 40 millimeters.
- Lever varieties are considered the most attractive to use and allow the user to significantly save gas.
- Spindles on valves: stainless steel - these are the most reliable varieties (up to 15 thousand cycles), brass - can fail in a short time (about 500 cycles), combined types - have average performance.
- The material for the body in the tubes is brass, copper, and stainless steel.
- Acetylene cutters , in which parts in contact with flammable gas before the mixing chamber, should in no case be made of copper or alloys, and its total content should not exceed 65 percent.
- The collapsible model helps to repair the cutter, as well as clean the entire injection unit, tubes and the tip itself.
- The outer mouthpiece should be created using only copper.
- The internal mouthpiece of an acetylene cutter is copper, while an oxygen-propane cutter can be made of brass.
- The manufacturer must include spare parts for the selected device, as well as additional parts for consumption.
Differences
The main difference between a propane burner and an acetylene burner is based on the different calorific values of the gases and different proportions when creating the working mixture . The proportions of oxygen and acetylene are 1:1, oxygen and propane are 3.5:1. In an acetylene burner, the combustion rate of the mixture is significantly higher.
Accordingly, the cross-section and shape of the injection channels, working chamber and nozzle differ.
When propane is supplied to an acetylene burner, unstable combustion is observed, the torch power decreases, and backfire is possible. This type of use is unacceptable and may result in a serious accident.
Using the cutter
Rules for general use:
- When working with a cutter, you should wear a special mask (or special glasses).
- You should first put on gloves and work clothes with fire-resistant (that is, non-flammable) properties.
- The autogen flame must face away from the supply hoses, and the hoses must not negatively affect the work of the entire cutter.
- Cylinders together with gas should be placed at a distance of no closer than five meters to the workplace. Metal cutting should be done either in open air or in a well-ventilated place.
After a long break or during the first launch of a new injection cutter, it is worth making sure that such channels are completely clean and that the oxygen inside the injector can create the required level to dilute the suction of combustible gas .
From the very beginning, when closing the valves on the cutter itself and on the cylinders with cutters, you should remove the hose along with the propane. Afterwards, you should install a special working division on the oxygen cylinder, and also open the valve on the cutter; this valve will begin to actively heat the oxygen and gas. The functionality of the injector should be checked by placing a finger on the flammable gas nipple - at this time the person should feel air being sucked into the nipple hole.
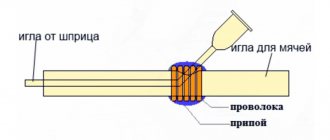
Do-it-yourself cutting torch
You can make a mini-torch for small jobs (for example, melting and cutting copper wires) yourself. For this you will need:
- 2 large droppers;
- a can of gas for refilling conventional lighters;
- a needle used to inflate balls;
- nipple;
- compressor;
- aquarium pump;
- copper wire;
- soldering iron with consumables;
- needle file
Assembly instructions:
- The needle from the dropper is bent at an angle of approximately 60°, the sharp end is sharpened.
- A hole is made in the side of the ball needle, into which a bent needle from a dropper is passed with the end protruding by about 2 mm.
- The remaining hole is wrapped with copper wire and sealed well.
- Tubes from droppers are attached to the ends of the needles.
- A gas cartridge is connected to the thick needle, and a compressor is connected to the thin one.
Photo. Appearance of a homemade mini-cutter
The gas supply is regulated by plastic jumpers installed on the tubes from the droppers.
Basic methods of cutting metal with gas
Spear cutting - this operation is used to process stainless steel, cast iron and low-carbon steel of large diameters. The essence of cutting is that the spear is heated to the melting temperature and pressed against the workpiece being cut. The method is common in the field of mechanical engineering and metallurgy. Oxygen-flux cutting is used to work with high-alloy chromium and chromium-nickel alloys. This method is characterized by the fact that powdered flux is introduced into the gas (oxygen) stream; it serves as an additional source of heat.
Air arc cutting is based on melting metal using an electric arc. When using this method, gas is supplied along the entire electrode.
Propane cutting is performed when it is necessary to cut titanium, low-alloy and low-carbon steel alloys. Equipment of this type cannot cut metal thicker than 300 mm.
| Material thickness, cm | Penetration, sec. | Cutting width, cm | Propane consumption, m3 | Oxygen consumption, m3 |
| 0,4 | From 5 to 8 | 0,25 | 0,035 | 0,289 |
| 1,0 | From 8 to 13 | 0,3 | 0,041 | 0,415 |
| 2,0 | From 13 to 18 | 0,4 | 0,051 | 0,623 |
| 4,0 | From 22 to 28 | 0,45 | 0,071 | 1,037 |
| 6,0 | From 25 to 30 | 0,5 | 0,071 | 1,461 |
Necessary equipment
To perform various steel processing tasks, it is necessary to prepare equipment and appropriate tools. Operation is carried out using:
- oxygen and propane cylinders;
- cutting tool;
- mouthpiece of a certain size;
- hoses.
Safety precautions require the presence of a control valve on each cylinder. The propane cylinder has a reverse thread, so installing an additional reducer is impossible. The equipment has similar designs, both for home use and for industrial purposes. Before cutting metal, it is necessary to check the functionality and presence of all adjustment elements.
Hoses for oxy-propane cutter
The supply of ozone is marked in blue; the valves are located both directly on the cylinder and on the cutter. The propane stream is marked like all other gases and explosive substances, in red or yellow.
After connecting the torch, a process begins in which oxygen and propane merge in the mixing chamber, resulting in the formation of a flammable mixture. The design provides for the replacement of units for scheduled repairs and maintenance; if one of the units fails, it is possible to replace it and continue working. The mouthpiece is selected depending on the type of tasks performed, has different indications and differs in numbers.
Cutting metal with an oxygen-propane cutter: pros and cons, technology, features
Gas cutting seems to be a simpler process than gas welding work, and therefore even a person who does not have special skills can cope with it. For this reason, almost any of us can master working with a cutting torch.
The main thing here is to understand the essence of gas cutting technology. In modern conditions, propane cutters are increasingly used.
Working with them requires the use of both propane and oxygen, since the combination of such substances provides the maximum combustion temperature.
Features of use
Such tools are not suitable for cutting high-carbon steels for the reason that they have a fairly high melting point, which is almost the same as the flame temperature.
This leads to the fact that instead of the release of scale, which looks like a column of sparks, from the back side of the sheet, it mixes with the molten metal along the edges of the cut.
As a result, oxygen cannot reach the thickness of the metal, which is why it fails to burn through the material.
Difficulties when cutting cast iron are created by the shape of the grains, as well as the graphite between them. True, this does not apply to malleable cast iron. It is impossible to solve the problem if you have to deal with aluminum, copper and their alloys.
It is important to dwell on the following point: the category of low-carbon steels is represented by grades from 08 to 20G, medium-carbon steels - grades from 30 to 50G2. A characteristic feature of carbon steel grades is the presence of the letter U in front of their names.
Let's get started
First, you need to move the oxygen reducer to the position corresponding to 5 atmospheres, the gas reducer to 0.5. You also need to make sure that each valve is in the closed position.
After that, you need to take a propane torch and open the propane slightly, and then light it. The cutter nozzle must be positioned so that it rests on the metal, after which you need to slowly open the oxygen control. Next, you should adjust these valves one by one, thereby ensuring the required flame supply force. During such a setup, you need to sequentially open gas, oxygen, gas, oxygen.
When choosing the flame strength, you need to focus on the thickness of the metal. As the thickness of the sheet increases, the strength of the flame will have to increase, which will lead to an increase in the consumption of oxygen and propane. After adjusting the flame strength, you can start cutting metal.
The nozzle must be held in relation to the edge of the metal so that it is removed from the object being cut at a distance of 5 mm, and it itself must be located at an angle of 90 degrees. In some cases, it may be necessary to cut through the sheet or product in the center.
In this case, the starting point is chosen to be the place from which the cut will go.
The essence of the procedure is to heat the top edge to a temperature of 1000-1300 degrees Celsius. The exact temperature is determined taking into account the metal. In practice, such work will look like the surface appears to be “wet.” The heating itself will take no more than 10 seconds. After waiting for the metal to ignite, you need to open the cutting oxygen valve, after which a powerful, narrowly directed jet will begin to flow.
Cutting Features
When opening the valve of a propane cutter, do not rush. In this case, the ignition of oxygen will occur naturally as a result of interaction with the heated metal. By acting this way, you will eliminate the risk of a flashback of the flame, during which you may see a pop. It is necessary to slowly guide the oxygen stream strictly parallel to the given line
It is important not to make a mistake with the angle of inclination.
First, it is maintained at 90 degrees, after which it is necessary to create a slight deviation of 5-6 degrees in the direction opposite to the movement of the cutter. If you have to deal with metal whose thickness is more than 95 mm, then it is allowed to increase the deviation to 70 degrees. After the cut in the metal reaches 15-20 mm, the angle of inclination begins to increase to 20-30 degrees.