Device and design features
An oxy-fuel cutter is used to mix a mixture based on fuel (acetylene, propane) and cutting gases (oxygen) to produce a cutting jet.
Structurally, a gas cutter for cutting metal consists of the following elements:
- special head with two replaceable mouthpieces;
- tubes for supplying oxygen and gas;
- mixing chamber for forming a mixture of fuel and cutting gases;
- 3 valves – for flammable gas, supply and regulation of the amount of oxygen supplied;
- lever.
These are the main components of an oxy-fuel cutting tool as there are many other parts to its design.
Figure 1. Diagram of an oxy-fuel torch
Principle of operation
Gas cutting technique refers to the technology of gas flame processing of metals , in which the flame of a burning gas-air mixture heats the workpiece to a high temperature to perform cutting, surface hardening, surfacing or other technological operations.
The basic principle of gas cutting is the ability of metal to ignite in an environment of chemically pure oxygen. For the technical implementation of this complex physical and chemical process, a special metal cutter is used, which performs the following functions:
- mixing in a certain proportion of flammable gas (acetylene, propane, natural gas) with oxygen to form a heating gas-oxygen mixture;
- ignition of the heating mixture and heating it with a metal flame along the cut line;
- separate supply of a flow of heating mixture and a stream of oxygen to the cutting site.
The gas cutting operation, which is provided by the cutter with burning gas, consists of two technological stages:
- Preparation for cutting, which consists in heating the local zone of the workpiece to the ignition temperature of the metal. Heating is carried out by a flame torch of the burning heating mixture. At the site of the start of the cut, the metal is heated to white heat, which corresponds to heating to a temperature within 1100 degrees. C.
The local preheating mode is necessary so that the metal of the workpiece ignites in a stream of oxygen along the cut line without the use of an external ignition initiator.
- Direct gas cutting of a workpiece, which consists of burning the metal in a stream of oxygen supplied under pressure and blowing out the resulting combustion products in the form of hot particles from the working area. The cutting process proceeds in the following sequence:
- an oxygen stream under a pressure of 5-12 atm is supplied to the heated zone;
- upon contact with a heated surface, oxygen ignites;
- under the influence of an oxygen jet, the metal in the cut zone burns;
- combustion products - oxides - are blown out of the cutting zone in a stream, leaving behind a narrow groove.
Oxidation of the material of the cut workpiece occurs only in the area of action of the oxygen jet, so the penetration of oxides into the metal is excluded.
Gas cutter for metal: types
The tool is classified according to various criteria, but the main ones are the type of combustible gas used and the principle of mixing the gas with oxygen. They are also divided by purpose (universal and special) and type of cutting (separation, surface, oxygen-flux).
According to the method of mixing gas and oxygen, cutters are of the following types:
- Injection - equipped with intra-nozzle mixing of gases, which ensures high reliability and safe operation of the devices. This is due to the fact that the gases pass separately along the entire length of the channels and are mixed into a combustible mixture in a special mixing chamber.
Photo 2. Appearance of an oxygen injection burner
- Injectorless - the design does not imply the presence of a mixing chamber. Oxygen is supplied through two tubes, gas through a third. They mix inside the head. Such a tool requires significantly higher hot gas pressure compared to an injection tool.
Photo 3. Appearance of a non-injector gas cutter
According to the flammable gas used, cutters are propane, acetylene and universal.
Acetylenic
Acetylene acts as the working gas, providing a high flame temperature (within 3300 °C). It is used for cutting thick metal workpieces and is equipped with additional valves for setting a high gas supply speed.
Propane
Designed for the use of propane as a cutting gas. They are characterized by higher reliability and long service life, and are safe to use.
Universal gas cutter
The universal tool provides the ability to use different types of flammable gas. Moreover, they are not much more expensive than a classic acetylene or propane cutter.
Operating principle and types
The principle of operation is based on supplying a pure stream of oxygen through the nozzle of a gas cutter. Regardless of the design features of the autogen, execution occurs due to the combustion of metal under the influence of a propane-oxygen environment. The main requirement for using the device is that the combustion temperature must be higher than melting, otherwise the material will melt and drain, which interferes with high-quality work.
Most steel alloys are not susceptible to the action of an oxygen-propane cutter, due to restrictions on the maximum proportion of alloyed impurities. The presence of carbon in the element can lead to unstable functioning or stop the process. The impact on metal occurs in several steps:
- The temperature rises to the point where the steel begins to burn. To obtain the required flame, pure ozone is mixed with the combustible mixture in the required proportions.
- After the zone is heated, both the heated steel is oxidized by the oxygen environment and materials are released from the processing area.
The classification of hand cutters is divided according to several parameters, depending on the type of work. Main characteristics:
- a type of flammable gas, methane, propane - butane, acetylene and others are used;
- power, parameter for obtaining a mixture for heating;
- The nozzle design, which affects the production of gas, is used both with injection systems and without injection.
Injection cutter-burner
Power is divided into several types, from low to high cutting power. With low power, products with a thickness of 3 to 100 mm are affected; with the medium type of installation, it is possible to cut materials up to 200 mm thick, and with high power – 300 mm. There are varieties capable of processing products up to 500 mm thick; such installations are used both in industry and in domestic settings. Some components of the characteristics depend not only on the power, but also on the design of the cutting torch.
Advantages and disadvantages
Any tool has its pros and cons, and a gas cutter is no exception. Among the advantages of modern devices with intra-nozzle gas mixing, the following should be noted:
- The relatively large thickness of the metal being cut is up to 300 mm, depending on the modification and operating parameters (gas used and oxygen pressure).
- Stable flame burning without pops or backfires.
- Possibility of cutting steel in any direction, regardless of thickness.
- High performance.
- Easy to maintain and long service life.
Photo 4. Oxygen gas cutting process
However, it has no less disadvantages:
- As a result of strong heating, the cut parts may become deformed (especially those made of thin sheet metal).
- The cutting width is quite large, which requires compliance with certain allowances during marking work.
- Low quality of cut - uneven edges with oxides and scale. Therefore, before welding or other work, pre-treatment of the edges is required.
- Quite a high cost of the oxy-fuel cutting process.
Varieties
The welding cutter, used for gas cutting of metals, is presented on the welding equipment market with dozens of modifications from various brands, however, almost all offered models are structurally identical and differ slightly from each other in appearance .
The design of manual autogens requires the presence on the body of two or three valves for regulating the supply of combustible gas, oxygen and a heating mixture to the cutting line, as well as a nozzle (nozzle) that forms the metal combustion flame. Unlike a gas welding torch, a manual iron cutter is equipped with an oxygen cutting jet supply tube with corresponding shut-off and control valves.
Numerous modifications of autogens are classified according to the following main characteristics.
By type of flammable gas:
- acetylene cutter;
- propane;
- methane.
By purpose:
- universal, capable of cutting workpieces in all directions, including curved cuts, up to 300 mm thick;
- special units designed for individual specific work (cutting parts up to 700 mm thick, underwater cutting, profiling, etc.).
According to the method of mixing oxygen and combustible gas:
- injection;
- non-injector.
By oxygen supply pressure - low, medium and high pressure.
In terms of power - in accordance with GOST 5191-79 “Injection cutters for manual oxygen cutting...” cutters are divided into three types:
- Type P1 – for cutting products with a thickness of no more than 100 mm;
- Type P2 – for working with products with a thickness of no more than 200 mm;
- Type P3 – for cutting workpieces up to 300 mm thick.
Features of choice
To avoid mistakes, before purchasing a gas cutter, it is important to familiarize yourself with some of the design features of the device. This will allow you to understand what primary factors you need to pay attention to when choosing it.
Selection rules:
- Nipples - made of brass and aluminum, the former are considered more durable.
- Mouthpieces - the outer one is usually made of chrome bronze or pure copper (distinguished by a reddish tint). For acetylene devices, it is also desirable for the internal one to be copper; for others, the use of brass analogues is allowed.
- Connecting tubes are made of brass. At the same time, they should not have a decorative coating that can hide minor defects.
- Valve spindles are made of stainless steel; brass spindles have a short service life.
- Handle – aluminum is considered the best material, plastic is less wear-resistant. Its size must be at least 40 mm to have a comfortable girth.
- Cutter length – for cutting thick metal, as well as painted or oily materials, it is better to choose devices up to 1000 mm in size. In other cases, you can buy 500 mm burners.
Photo 5. Basic consumables for gas cutters
Also, when purchasing, it is recommended to take the tool in your hands and check it for ease of use. The productivity and time the master can work with a cutter without fatigue directly depends on this.
Correct setting of the cutting torch
Before you start working with a new gas cutter for metal, you need to properly connect and check the functionality of the tool. The device is directly configured by the manufacturer in the factory and is the final stage of its assembly. Individual intervention in the burner design is prohibited.
Sequence of work:
- Study the operating instructions and follow all steps according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Connect the device to cylinders with flammable and cutting gases. At the same time, they must be equipped with gearboxes: oxygen – blue, propane – red. Rubber gas supply hoses are screwed onto the threads of the gearboxes and tightened with clamps.
- Check the integrity of the tool, the presence of all gaskets, and the absence of oil traces near the oxygen valve.
- Adjust the gas and oxygen supply, blow out the hoses. When working with acetylene, open the supply valve 1 turn, and the pressure of the substance should be up to 1 atm, but it is better to set it to 0.54 atm. To purge, you need to open the valve on the cutter, and after the sound changes, close it. When setting up the oxygen supply, the pressure is set to 2 atm. Then the hoses are purged using valves on the gearbox and cutter.
You should also remember that it is forbidden to change the hoses for supplying oxygen and propane (acetylene) with each other, or to blow the hose for propane (acetylene) with oxygen.
Photo 6. The process of separation cutting of thick rolled metal with a gas cutter
How to use a gas cutter correctly: preparatory stage
First, we will ensure security and prepare everything necessary. You will need:
- Carbon dioxide fire extinguisher. Metal cutting with a cutter is carried out at temperatures above 1800 degrees, so we need protection. Carbon dioxide will be most effective compared to powder. By the way, a bucket of sand won’t hurt either.
- Fireproof suit. In principle, the usual equipment of a gas welder will do. It is made of tarpaulin impregnated with a fire-resistant compound. You will also need protective gloves and boots.
- Glasses. It’s easy to get a “bunnies” effect from the brightness of hot gases, so you need regular filter glasses, preferably level 3.
- Marking tool.
- Ear protection. Construction headphones or earplugs.
- Lighter for cutter. Ordinary matches or lighters are not suitable - your hands are too close to the torch. You can buy what is sold in the store under the name “household lighter.”
We prepare the workplace separately. Ideally, buy or make a welding table with an exhaust hood. But a base of fireclay bricks is a good place to start. There should be no flammable objects for 2-3 meters around the work site: paper, solvents, fuel, oils.
Necessary equipment
Now let's assemble the necessary equipment. All we need is:
- Cylinders. To assemble a propane oxygen cutter , we simply buy the appropriate cylinders. This can be done at any shop with welding equipment. They are refillable and can be refilled at the same retail outlet or gas station.
- Sleeves. For propane you will need a class 1 hose with a diameter of 1 to 2 centimeters. It is desirable that it be red for convenience. Oxygen has the same diameter, but strength class 3.
- Gearboxes. They are purchased for each gas separately. We need propane (for example, BPO-5DM) and oxygen (BKO-50DM). By the way, it is impossible to confuse them, since propane has a reverse thread.
- Check valves. At the entrance to the burner, fire arresters are installed, which also have a gas gradation. It is not worth starting the cutter without them, since if there is a bang, the combustion will spread to the sleeve and may reach the cylinder.
- Oxygen-propane burner. You can buy it at any online tool store. For example, GZU 228, G2 Mini 273, R1 142.
That's all that is needed to start the propane-oxygen cutter .
When everything is prepared, you can proceed to working with metal.
How to use an oxypropane torch
Preparing for work
And so, let’s assemble our cutter and check for functionality. By the way, a preventive inspection should be carried out before each start-up to avoid leaks. Especially if the equipment has been idle for a long time or there is a suspicion of a leak.
Begin:
- First, let's connect the sleeves to the cylinders. The oxygen hose is connected to a nipple with a fitting to the gearbox with a right-hand thread. The propane hose is installed in the same way. We pass all connections with a sealant (anaerobic sealant, tow, fuser).
- We release the gas a little to remove dirt from the hoses.
- Nipples are attached to the reverse side of the sleeve for transferring to fire-retardant valves.
- The burner itself is already attached to them. There should be color markings on it so as not to confuse oxygen with gas.
By the way, it would be a good idea to check the air leaks. To do this, the oxygen hose must be connected to the cylinder, and the propane nipple must be left free. We set the oxygen supply to 5 atmospheres. Touch the free nipple with your hand. If it “sucks in”, everything is fine, you can work. If not, you will need to bleed the injector.
Don't forget to seal all connections.
Let's get started
Now we will look at how to properly cut metal with a cutter . It's not difficult, but you'll have to get used to the angle of the cut. To begin with, we set the oxygen reducer to 5 atmospheres. On propane we set it to 0.5. The proportion of 1 to 10 was chosen because we have gas combustion in an oxygen environment.
Let's start by igniting the propane. Open the valve on the burner slightly and light it. We rest the nozzle against the metal at an angle of 90 degrees. Now we open the regulating oxygen a little. Now we open the valves one by one until we get a torch of the required size. Its length depends on how thick a piece of metal we need to cut through.
We start heating from the point from which cutting is planned. We are waiting for the metal to melt. On average, it takes about 10 seconds to warm up. When the metal is hot enough, let in cutting oxygen. It looks like a thin needle. Then we just slowly move it along the cutting line.
The cutting oxygen valve must be opened slowly.
The pressure difference can cause the flare to backfire, called a “pop.” If there is no fireproof check valve, flames will flow to the cylinders and cause an explosion.
How to use a cutter correctly? The correct angle must be maintained. We start with 90 degrees, then slightly tilt the cutter 5-6 degrees in the opposite direction from the cut. If the metal is more than 9 centimeters, you can tilt it up to 10.
When the metal has already been cut by 20 millimeters, set the angle of inclination to 20 degrees.
Cutting nuances
The cutting speed largely influences the work. You can tell if it is chosen correctly by the sparks. If it is chosen correctly, their angle of incidence will be in the range of 88-90 degrees.
If the sparks noticeably deviate in the direction opposite to the cutting line, you need to increase the speed; on the contrary, slow down.
Before cutting with a cutter , measure the thickness of the metal. If it is more than 6 centimeters, there will be problems with the outflow of waste. To prevent this, just tilt the sheet to one side.
According to technology, it is not recommended to stop the cutting line.
If work needs to be interrupted, there is no need to start from the same place. You need to start a new line from the back of the marking.
When the work has been completed, first the cutting oxygen is turned off, then the regulating oxygen and only then the propane.
You can learn more about how you need to hold your hands while cutting so that the lines are obtained from the video:
Precautionary measures
Before using a gas cutter, remember safety precautions. First of all, be sure to have the full equipment described above. It cannot be neglected, since metal heated to 2000 degrees can cause severe skin burns.
Before each cut, inspect the hoses for integrity. Joints, cracks, and breakthroughs will lead to gas leakage, which can easily lead to an explosion. It is also not recommended to seal them - it is better to change them.
By the way, rubber hoses do not like frost and often crack after working outside in winter. Because of this, many people change them to metal ones, which is prohibited due to safety regulations.
Remember the properties of gas.
Propane is an explosive gas that can ignite from any spark. Oxygen is more dangerous because it is a powerful oxidizing agent. When it comes into contact with oil (especially natural oil: teak, tung, linseed), it oxidizes it, leading to fire. The cylinder should not be touched with oily hands or gloves. There should be no oil rags or stains nearby, especially near the place of work.
The cylinder must be located at least 10 meters from the workplace. Between each other - 5 meters.
You can learn more about safety precautions when working with a cutter from the video:
Preparing the tool for work
Before work, it is necessary to properly prepare the gas cutter. The preparation process consists of several stages that minimize the risks of tool failure and injury:
- Inspection of cylinders, rubber hoses for supplying fuel and cutting gases, connecting and fastening elements, burners for defects or damage.
- Check all connections for gas leaks.
- Inspect the condition of the seals - if there are cracks, they change shape and require immediate replacement.
When working with injection cutters, you also need to check that they are working correctly. This is done until the flammable gas supply hose is connected. Initially, an oxygen hose is connected to the corresponding fitting on the burner, and the valve on the reducer of the oxygen cylinder is opened. Then the oxygen and flammable gas supply valves on the cutter open - if you put your finger against the flammable gas fitting, you will “suck it in.” In this case, the injection is OK.
Design
The most common type of device used in machining steel structures is the double-tube injection cutter. The combustible mixture is divided into several streams, which allows you to adjust the flame power to suit the work. The adjustment mechanism is located on the outer part of the body; there are lever-type devices.
The flow moves through the tube to the tip through the head, releasing at high speed through the central nozzle. The mouthpiece is responsible for the main functionality of the cutter, the cutting part of the process. Part of the gas is transferred to the injector, which, when released under high pressure, creates a vacuum, thereby connecting the combustible mixture. The mixing process determines the equalization of the flow rate by which the action is performed.
The formation of the mixture is carried out by the head of the tip, into which it enters through the lower tube. A torch is formed between the outer and inner mouthpiece, as a result of the formation of a flammable mixture. The two-channel system is equipped with control valves that allow you to adjust the supply of both oxygen and auxiliary gas to the injector.
Cutting torch design
The design without an injection type is more complex, since there are tubes for two flows of oxygen and separately for gas. The mixture of the flammable composition occurs directly inside the head; this design is considered safer. Operations will require higher supply pressures of both oxygen and flammable gases.
The dimensions of the cutters are fixed by GOST standards; for production with small parts, P1 models with a total length of no more than 50 cm are used. More powerful designs are produced longer in shape, there are specific elongated designs designed to perform tasks with difficult access to the cutting site.
Instructions for use
The cutting technology involves initially setting the ratio of oxygen and propane at 1 to 10 – i.e. at an oxygen pressure of 6 atm. The flammable gas pressure is set to 0.6 atm.
Opening and closing the gas supply is carried out in a strict sequence:
- The oxygen and flammable gas valves open 0.5 turns (strictly in that order).
- The flammable mixture is ignited.
- The torch is brought to the metal being cut and by opening the valve, the supply of oxygen is added until a cutting jet appears.
- After completion of the work, the supply of flammable gas is initially shut off, and then oxygen.
Figure 7. Scheme of the process of oxygen cutting of metal
The cutting technique after igniting the torch involves the need to heat up the metal area in the cutting area. If the heated area becomes red, the oxygen supply can be increased a little more. After completely cutting through the workpiece, the torch moves along the cutting line. The speed of movement of the cutter depends on the thickness of the rolled metal being cut, the operating characteristics of the process, and therefore is determined individually.
The following video shows how to properly use a gas cutter:
Necessary equipment
To perform various steel processing tasks, it is necessary to prepare equipment and appropriate tools. Operation is carried out using:
- oxygen and propane cylinders;
- cutting tool;
- mouthpiece of a certain size;
- hoses.
Safety precautions require the presence of a control valve on each cylinder. The propane cylinder has a reverse thread, so installing an additional reducer is impossible. The equipment has similar designs, both for home use and for industrial purposes. Before cutting metal, it is necessary to check the functionality and presence of all adjustment elements.
Hoses for oxy-propane cutter
The supply of ozone is marked in blue; the valves are located both directly on the cylinder and on the cutter. The propane stream is marked like all other gases and explosive substances, in red or yellow.
After connecting the torch, a process begins in which oxygen and propane merge in the mixing chamber, resulting in the formation of a flammable mixture. The design provides for the replacement of units for scheduled repairs and maintenance; if one of the units fails, it is possible to replace it and continue working. The mouthpiece is selected depending on the type of tasks performed, has different indications and differs in numbers.
Do-it-yourself cutting torch
You can make a mini-torch for small jobs (for example, melting and cutting copper wires) yourself. For this you will need:
- 2 large droppers;
- a can of gas for refilling conventional lighters;
- a needle used to inflate balls;
- nipple;
- compressor;
- aquarium pump;
- copper wire;
- soldering iron with consumables;
- needle file
Assembly instructions:
- The needle from the dropper is bent at an angle of approximately 60°, the sharp end is sharpened.
- A hole is made in the side of the ball needle, into which a bent needle from a dropper is passed with the end protruding by about 2 mm.
- The remaining hole is wrapped with copper wire and sealed well.
- Tubes from droppers are attached to the ends of the needles.
- A gas cartridge is connected to the thick needle, and a compressor is connected to the thin one.
Photo. Appearance of a homemade mini-cutter
The gas supply is regulated by plastic jumpers installed on the tubes from the droppers.
Homemade for household needs
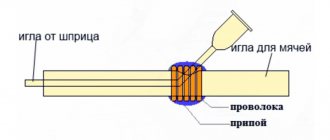
If it is necessary to carry out a small amount of work related to cutting thin sheets of metal (thickness within 1.0 mm) or melting copper wires, home craftsmen are able to make a compact portable gas cutter of simple design with their own hands. The cutter diagram is shown in Fig. below
Diagram of a homemade gas cutter.
To make such a simple product you need:
- dropper;
- needle for inflating nipple soccer balls;
- gas cartridge used in lighters;
- aquarium air compressor or plastic bottle.
The sequence of manufacturing a mini-cutter is as follows:
- A cut is made on the nipple ball needle.
- The needle from the dropper is bent at an angle of 45 degrees. And a ball needle is inserted into the incision.
- Both needles are tied together with wire, then the wire tie is fixed with solder.
- Dropper tubes are placed on the ends of the needles, acting as gas hoses.
- The protruding end of the dropper needle acts as a nozzle.
- The air supply will be provided by an aquarium compressor or a plastic bottle slightly modified to match an external air source (tube, tire, etc.).
- Gas will be supplied from a gas cartridge.
- To regulate the outlet gas and adjust the flame, dropper limiters are used, acting as valves.
With proper flame adjustment, the temperature can exceed 1200-1300 degrees. C. Users of this mini-cutter claim that it can successfully serve for several years.
Tips from experts on working with a cutter
Experienced carvers advise always using high-quality personal protective equipment:
- special glasses;
- gloves (mittens), jacket and pants with fire-resistant properties;
- special work shoes.
The workplace must also be properly equipped. The location of gas cylinders is at a distance of 5 m from hot work. The workshop should be well ventilated, the floor should be concrete or earthen. The flame of the gas-oxygen burner should be located frontally relative to the gas supply hoses. Hoses must not interfere with work.
It is also important to have auxiliary tools and devices for marking work - pencil (chalk), tape measure, square, ruler. To ignite the flame, you will need a special lighter, which the carver should always have at hand.
At the end of the work, you need to carefully inspect the workplace so as not to accidentally step on a piece of molten metal, which can burn through even the thick sole of your shoes. The cut metal blanks are usually left to cool in natural conditions, but if necessary, forced cooling with water is allowed - this must be done carefully so that hot splashes do not get on the skin.