Left hand thread. Features of application
If you have questions about fasteners with left-hand threads, call us and we will advise you!
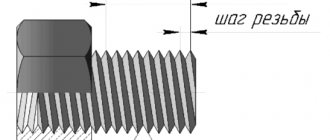
One of the main characteristics of the thread is the direction of rotation of the profile. There are two main types of fasteners that correspond to this feature - with right-hand and left-hand threads. The thread is right-handed if, with clockwise rotation, the projections move away from the observer. On a left hand thread with clockwise rotation the lugs get closer. Right-hand thread is considered standard. The lion's share of fasteners are produced with just this. In what cases is left-hand thread used?
In coupling structures, multidirectional threads are provided on the rotating part. On one side is left, and on the other is right. By rotating such a device, the attached parts will either move closer or move away. A striking example of such a device is a lanyard. The lanyard body (it can be open or closed) has a left-hand thread on one side and a right-hand thread on the other. As it rotates, the mating parts—this can be a screw with a hook, ring, or eye—either move closer together or move away. So, with the help of a left-hand thread, cables are tensioned, masts or canopies are installed, and equipment or equipment is secured to the platform. Another example is a nipple for a sectional radiator. Having multi-directional threads on both sides, they use a special wrench to tighten sections of aluminum, bimetallic, and cast iron radiators.
– to prevent self-unscrewing
The nut or screw that secures a part to a rotating shaft must be tightened in the direction of rotation of the shaft. Otherwise, the likelihood of self-unscrewing of the fasteners increases sharply. Therefore, threaded fasteners with left-hand threads are often in demand for completing such products or equipment. Examples include mounting bicycle pedals, fan blades, angle grinder discs (some models), wheels of some bus models, and many other devices.
– protection from standard operations
Often, fasteners with left-hand threads are used on similar equipment that poses an increased danger. If there is a possibility of a mistake in connecting the products, then one of them is made with a right-hand thread, and the other with a left-hand thread. The connecting threads for the compressed gas cylinder reducer are designed using this principle. The propane tank has a left-hand thread, the oxygen tank has a right-hand thread. Thus, it is impossible to attach a reducer from a flammable gas cylinder to an oxygen cylinder.
Many manufacturers, especially in the automotive industry, use fasteners with left-hand threads to protect against the installation of non-original products. Such a marketing move, firstly, makes the product more individual. Secondly, it guarantees that during repair or replacement only original fasteners from the manufacturer will be used.
In branding
To protect against the use of counterfeit parts in the automotive industry, manufacturers resort for commercial purposes to the marketing ploy of using left-hand cutting, from which their products acquire uniqueness and individuality.
This idea ensures that customers will only buy spare parts for repair or replacement from the official manufacturer.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Types of threaded connections
pkmetiz.ru
The most common method of joining elements of various structures is a threaded connection. It is widely used in construction, pipeline installation, mechanical engineering and many other industries. The popularity of this method is due to the following advantages:
- high reliability and long service life;
- creation of detachable connections, ease of installation and dismantling using publicly available tools;
- control of tightening force during assembly;
- low weight and dimensions of fasteners compared to the structural elements being connected;
- wide availability, large selection of fastener sizes.
Left and right hand thread. Differentiating, application
There are two types of fasteners, divided according to the direction of rotation of the profile: with a right-hand thread and a left-hand thread. The most widely used products are those with screws directed clockwise, that is, with right-hand threads. But there are a number of elements and parts that are equipped with threads in the opposite direction.
How to distinguish right-handed from left-handed threads
There are several methods that can help in solving this problem, but the simplest, “everyday” one that most modern craftsmen use is the following:
Place the product whose thread direction you want to determine on your palm with the chamfer facing up (thread facing you) and pay attention to the end of the spiral. If you trace the rotation of the thread from its base to the “tail”, and this “tail” will be directed to the right, then you have a right-hand thread (clockwise)
Accordingly, if it’s the other way around, then it’s left.
Right-hand threads are most often found in the industrial sector, however, it is not always advisable to use it. Let's consider several options when a right-handed thread cannot satisfy all design requirements, and it would be more rational to use a left-handed thread.
Preventing self-unscrewing and loosening of connections
The rotating shaft or any other rod on which nuts and bolts are screwed determines the direction of rotation of the hardware used: the screws or nuts must be tightened according to the direction of movement of the shaft. This is done so that during operation the fastening does not weaken or unwind.
Screed
There are a number of tightening devices, such as lanyards, the design of which implies the presence of a part with a right-hand thread and a part with a left-hand thread. Rotation of the element body allows you to loosen the tie or, on the contrary, load it, depending on the direction of rotation.
As a way to protect against dangerous operations
In some of the most critical operations, the incorrect implementation of which can result in casualties or pose a threat to health, it is recommended to use left-handed threads. Thus, the likelihood of dangerous actions is reduced. For example, working with cylinder equipment requires careful monitoring of the gas in the container. Therefore, propane cylinders are produced with a left-hand thread, and oxygen cylinders with a right-hand thread, in order to prevent emergency situations of improper use of this cylinder.
Branding
Some manufacturers produce products with counterclockwise threads in order to uniqueize their product and protect the buyer from purchasing non-original products.
Tags
Standard right-hand thread Which thread is for Thread for Thread in Thread in Thread of a turn thread is subdivided by a left-handed thread has with a thread directed left-handed thread such a right-hand thread or Right-hand thread with a right-hand thread. from the right to distinguish a right-hand thread from a right-hand thread to distinguish a right-hand thread to distinguish a right-hand thread a left-hand thread from a left-hand thread to the left with a left-hand thread with a left-hand thread with a left-hand thread threads with left direction threads left. The differences between left threads make threads right hand threads left hand threads right hand threads from left hand threads mark
taps be cut trapezoidal formed osirisdin
Why (why) do you need a left-hand thread, where is it used, how and with what to cut a left-hand thread?
Why do you need a left-hand thread at all, where a left-hand thread is used.
There are quite a few examples of the use of left-hand threads; left-hand threads are mainly used in lanyards and other various ties. The principle is quite simple, take a tube (nut), cut a left-hand thread at one end and a right-hand thread at the other, screw in the corresponding bolts, and when the tube is rotated in one direction, the product is lengthened and shortened in the other.
The same system is used when assembling cast iron batteries; the coupling has 2 threads at once and, when twisted, tightens the rubber gasket.
An exception to the rule, so to speak, is the use of left-hand threads on the left side of the wheel mounts on heavy-duty GAZ, ZIL, MAZ vehicles.
You can cut left-handed threads only on a lathe; maybe there are tap dies, but I haven’t seen them.
It is needed in those units and parts that rotate to the right and can unwind, that is, it prevents the unit from unscrewing itself.
As an example, we can give a drill chuck; it rotates to the right and is secured with a screw (to the shaft) with a left-hand thread to prevent it from unwinding.
Also, left-hand threads are used in various tie-down structures, as an example of a lanyard, a device with the help of which the slack of rigging (cable), cables, etc. is removed.
In this device, there is a left-hand thread on one side and a right-hand thread on the other.
Grinder circular saws (angle grinders), various machines (lathes, for example) and here fasteners with left-hand threads are used.
Bicycle pedals (from the mount) of the fan blades (they rotate to the right) and here a fastener with a left-hand thread is used.
Some (but not all) gas cylinders have valves with left-hand threads, or the mounting of the reducer to the cylinder has a left-hand thread.
In automobile construction, left-hand threads are often used.
Entire units are assembled on fasteners with left-hand threads, the goal is one, when repairing a car, use only original fasteners from a specific manufacturer.
There are simply a huge number of types of threads, in addition to the fact that the thread can be external or internal.
In which areas are left-handed threads used?
To prevent connections from loosening
Here are simple examples when the use of such non-standard fasteners is necessary:
- In units and parts that rotate to the right, the parts may unwind when the mechanism operates. The powerful rotational force of the mechanism unscrews the nut, therefore, to prevent unwinding, left-handed fasteners are used in the direction of shaft rotation.
- The nipple of the radiators of the heating system is equipped with multi-directional threads. The coupling, when twisted with a special wrench, causes the rubber gasket in the radiator sections to tighten.
- The wheels of GAZ, MAZ, ZIL trucks use left-hand mounts.
- The drill chuck with the drill rotates to the right. To prevent loosening of the connection of parts, the chuck is attached to the shaft with a left-hand thread.
- Home fan blades.
- The gearbox transmits torque from the engine to the blades of the brush cutter.
- Bicycle pedals.
- Fastening the cutter to the shaft, discs of grinding machines.
- Some details in miter saws and circular saws.
In tension structures
Let's imagine this picture: housewives hang wet laundry on a line to dry. The rope begins to sag from constant use. The tension for the laundry has to be adjusted frequently. In such cases, bolts with double-sided threading are used here. One side of the bolt goes to the right and the other goes to the left. That is, in this case, the left-hand thread is used to adjust the degree of tension.
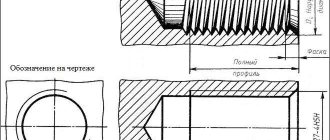
Designation on the drawing of a left-hand thread
The principle of operation can be represented as follows: a right-hand thread is cut at one end of the nut, and a left-hand thread at the other, and the bolts are screwed in. When the nut is rotated in one direction, it lengthens, and in the other direction, it shortens.
The use of left-handed fastening in tie-down structures is a prime example.
Such a device used in rigging work - a lanyard is a type of screw tie. This design features a pair of load-handling elements. One of them has a standard thread, the other, respectively, a left-hand thread. When the structure rotates during operation, the element body rotates, the tie is weakened, and a change in the direction of rotation leads to loading (tension). That is, when rotating, the parts of the mechanism move away from each other or move closer together.
Masts on ships are installed by pulling cables.
To protect against dangerous activities
Some operations require careful monitoring of work equipment to protect against increased hazards. In the gas industry, the reducer valve of a compressed propane cylinder is equipped with a left-hand thread, and the oxygen cylinder is equipped with a right-hand thread. Therefore, it is not possible to attach a propane tank to an oxygen tank. Using this method helps reduce the likelihood of dire consequences.
Metric and imperial
Metric threads are manufactured based on the standards prescribed in GOST 8724–2002. Often this type is used to create fasteners. This type can be used as a chassis if certain conditions have been met.
The basis for the metric type is an equilateral triangle, the angle of which at the base is 60 degrees. The manufactured thread can have from one to several starts. The second option is used when it is necessary to increase the strength of the joint.
Now they produce products with a cross-section of up to 600 mm and a pitch of turns up to 6 mm. Small ones are used in cases where you need to make a detachable mount on the thin walls of the device. This type is very common in the automotive industry.
The thread can be left or right. First, the letter M is indicated, which indicates that the product is made in accordance with the metric system. After this, the size and pitch in millimeters are indicated.
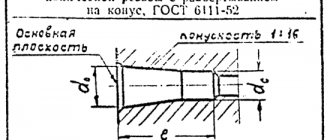
The inch system is mainly used in the manufacture of pipeline fittings and fittings. Marking is applied to both plastic and metal products. All requirements are specified in GOST 6111–52. This regulatory document contains tables with dimensions and pitch for a specific type. All designations are in inches.
Making pipe threads
The methods for making pipe threads depend on the equipment available, the production volume and the required accuracy. Thus, knurling is used mainly for the production of large series of products, since it guarantees high productivity and low cost of the operation.
Thread cutting methods
- Cutting on a screw-cutting lathe is characterized by high accuracy and very low productivity. Used in individual and small-scale production.
- Cutting with dies and taps also has low productivity and is usually carried out in several passes using tools of varying degrees of accuracy.
- Knurling is the main industrial method; the formation of a profile occurs not due to the removal of chips, but as a result of plastic deformation of the metal by rolling dies. High productivity is ensured by automating the operation of removing and placing the part on the machine.
- Thread milling is performed on specialized thread milling machines.
- Casting. Advanced casting methods - high pressure casting and powder metallurgy - make it possible to obtain an accurate and durable thread profile directly from the casting, without subsequent machining
In construction and repair conditions, as a rule, only the manual method is available.
Subtleties of applying external threads with dies and clamps
External threads, unlike internal threads, are cut according to a different principle. The part is processed on the outer surface, it is ground until the required diameter is reached . This figure should not exceed the internal diameter of the die, but should be 0.1-0.4 mm larger than the required final diameter. To facilitate the thread cutting process, you need to chamfer the edge of the workpiece - this will make it easier for the tool’s cutters to make the first notches. Different thread cutting tools are used for different cylindrical workpieces.
Dies are used for almost any product: mounting studs, towing eyes, pipes, bolts, etc. With their help you can cut standard metric threads with a diameter of 4 to 20 mm.
The shape of the die resembles a nut, only it has cutting edges inside, and special holes are provided for removing chips. There are split dies and solid ones. The latter fix the workpiece more reliably and cut threads more accurately, so the completed elements can be used in critical connections.
Cluppies are shaped like a die, only they have additional elements: faceplates, clamping rings and clamping bolts. In them, the workpiece is fixed very reliably, and it is possible to achieve high-precision threads. These tools are used to cut inch threads on water pipes.
To cut a thread with a die or die, you need to secure the tool in a special holder. It is then centered on the workpiece and screwed onto it, the rotation being created by rotating the handle of the holder. The first cutting edges cut the “rough” thread, and the rest bring it to finishing. Screwing should be smooth, without sudden movements and excessive effort, then the thread turns will be neat.
Pipe thread. Classification, designation
04.09.2017
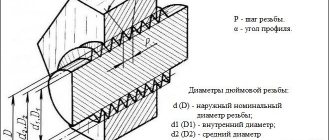
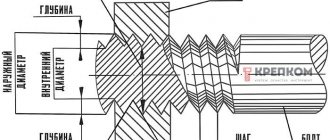
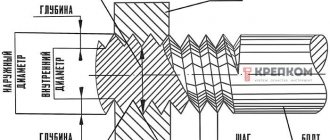
Thread refers to the main elements of a threaded connection and has the form of a spiral, formed along a helical line on a conical/cylindrical surface and having a constant pitch.
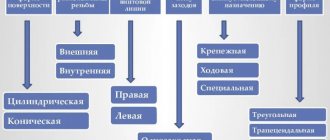
Pipe threads are divided into classes:
1.According to surface shape: conical and cylindrical
2.By unit of diameter: inch and metric
3. According to the location of the thread: external and internal
4.According to profile shape: round, triangular, rectangular, trapezoidal
5. By purpose: chassis, fastening, fastening and sealing, etc.
6.Thread direction: right and left
7. By number of passes: single and multi-pass
Designation on drawings
Designation of pipe tapered thread:
- R - external conical;
- RC - conical grooves of internal type;
- RP - internal conical with a cylindrical profile;
- LH - left;
- RH - right;
- MK - conical metric;
- M - metric;
- K - inch conical;
- reproach. — shortened profile;
- pov exact — increased cutting accuracy.
In the drawing, the designation is placed using a leader on the shelf, the arrow points to the main line. Cutting lengths are not indicated as this is standard. Tapered threads are indicated as a fraction: the numerator is the marking of the internal thread, and the denominator is the external thread.
The main plane of the thread is indicated by a solid thin line.
Slicing principles
When slicing, you need to take into account a number of features:
- cutting accuracy is determined by the parameters of the holes: diameter, perpendicularity of the center line to the surface of the workpiece, length;
- inch is cut with a profile angle of 60 degrees, and metric - 55;
- the tops and bottoms of inch threads, unlike metric threads, have more bluntness and have better tightness;
- to simplify the process, drilling a hole with a cylindrical drill is required; it is selected according to the smallest diameter;
- chamfering is required;
- When working, the tool must be lubricated to prevent overheating;
- when cutting, 2 turns are made forward, and then 1 turn back;
- the force on the cutting tool can be weakened after driving to the middle of the calculated length;
- Once the desired length is reached, the die can be removed by rotating in the opposite direction;
- Before finishing cutting, you need to do a rough cut.
Conical taps are distinguished by an elongated shape of the intake part and an incomplete thread, which additionally plays a calibrating role. In the upper part they have a square cross-section; longitudinal grooves are made on the cutting part to remove chips.
Cutting:
- The workpiece is vertically fixed in a vice.
- Lubricant is applied to the tool.
- The tool is applied perpendicular to the center line for cutting threads, that is, strictly in a horizontal plane.
- Several turns are cut.
- The correctness of the work is checked. In case of misalignment, you need to remove the cutting tool, tap the part and repeat steps 3–4.
- Further cutting is carried out provided that the first turns are correctly positioned. You can check with a regular level.
- A thread is formed to the required length.
- At the end of the work, remove the chips and clean the tool from lubricant.
For cutting on lathes, heads with thread-cutting dies are used. A special design feature of the tool is the automatic spreading of the dies during operation. This ensures high machining precision and optimal productivity.
In some cases, knurling rollers are used. The cutting accuracy is lower than when using heads, and the complexity of the work is higher.
To set up a lathe, it is enough to set the spindle rotation speed to low and associate the caliper offset with it. Setting rule: one revolution of the spindle must correspond to the movement of the caliper by the distance of the thread pitch.
On lathes, adjustments are easy because there are many clutch combinations available on the gearbox. If necessary, it is possible to cut threaded grooves of non-standard sizes.
All the news, hurry up to visit us.
New on the site
- Dynamic well level
- How long can the suction line be?
- How to test a pump on a bench.
- Secrets of dry running of household pumps
Well parameters. Start…
Latest reviews
- Senovad : Hello, Ilya. If you think so, then yes, please.
- Senovad : Greetings, Igor. Why is the pressure weak? Maybe it's time.
- Ilya : Hello. I have a question. Is it possible in reverse?
- Igor : Hello dear Senovad. In fact of the matter. that water.
- Senovad : Hello, Nikolay. If the battery is connected, then.
About the site
I created this site to tell you about my mistakes, to share my experience, my knowledge, my past, present and future projects, my ideas - not only about plumbing. Do not judge strictly. Here I am also learning, and mistakes are inevitable. Ask, I will definitely answer. Share your experience, it will be interesting to everyone.
Sizes of grinders
A grinder is an angle grinder used for processing and cutting durable materials. It is used in construction, dismantling and repair work. The popularity of the tool is due to its relatively low cost and wide capabilities. The grinder is considered one of the most popular tools due to its versatility. It is popular among both professional builders and ordinary users. This instrument received recognition due to the huge variety of types, sizes and their price category.
How do you unscrew the candles?
The answer is simple - the candles are unscrewed counterclockwise and twisted clockwise. This question is very relevant when the spark plug is jammed and does not turn.
Interesting materials:
What is the level of urbanization in Africa? What is the weight of a piglet at 1 month? What is the weight for a height of 173 for men? What sport develops flexibility? How tall should a desk be? What gland produces somatotropin? What is the most common zodiac sign? Which zodiac sign comes first? What is the procedure for sending on a business trip? What are the rules for picking mushrooms?
Cutting tools
A tap is used to cut internal threads. This is a special screw that has hard cutting edges. This tool consists of a working part and a shank designed for fixation in the driver. The device can be manual or machine.
Locksmith kit contents:
- Tap. Its diameter can vary and reaches 18 mm.
- Two rough working parts.
- Rough tap of a different diameter, medium and finishing.
Before you start cutting, you must first make a hole that will have a slightly smaller diameter. During operation, the tool must be held perpendicular and lubricant added to the cutting area. The tap should be unscrewed every few turns to remove accumulated metal shavings. This is very convenient to do with a small special brush.
On an industrial scale, external threads are made on a machine. For household needs, dies are used, which are:
- Split. The tool is made of two halves, which is why it is not as rigid as other types. Can be used for undemanding connections.
- Whole round. With this die you can cut high-quality threads.
- Sliding. Used in clamps. You can make pipe threads.
The die itself looks very similar to a regular nut, inside of which there are cutting edges. The tool can be designed for cutting metric or inch threads.
Content:
- 1. Making internal threads with a tap
- 2. Subtleties of applying external threads with a die and a die
- 3. 5 tips for successful completion of work
From fasteners to working units such as a screw pair, all these connections are threaded. Over time, it wears out, especially if the fasteners are under load, for example, car hub studs, nuts, bolts, etc. Then the worn part needs to be replaced, but it is not always possible to find a new one that matches the parameters. In such cases, many craftsmen cut threads manually using special thread-cutting tools - taps, dies and clamps.
Thread-cutting tools are made from high-speed steel or carbide metals and have sharp cutting edges of a special shape and size, resulting in a thread that exactly fits the parameters. Tools vary in pitch, length and direction of the thread being cut. But their main difference is that some are designed for making internal threads, others for external threads. We will tell you more about each type.
Taper thread cutting technology
In the industrial production of npt, threading is performed on a specialized threading machine using a swordsman mounted on a rotating spindle, which automatically forms threads on a stationary pipe.
Design and types of taps
The tap consists of parts:
- shank;
- working part;
- fence element;
- calibration.
Using a shank, the tap is secured in the machine spindle or in a chuck when cutting a threaded connection inside a pipe. The cutting is done by a working part that resembles a screw with spiral grooves. The front part of the tap is often called the fence element, which has the shape of a cone. It is the intake element that begins cutting the thread, then calibration continues. The carving is made by teeth called cutting feathers, which form recesses - grooves through which chips are removed. Sharpening of teeth is subject to technology requirements for cutting parts.