08/13/2020 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- The essence of any type of metal bending
- Basic methods and types of metal bending
- Application areas of various types of metal bending
Various types of metal bending are used in cases where it is simply impossible to process or manufacture products using a conventional vice. For example, a small diameter pipe can be bent, but for larger ones this method will not work. Metal bending allows you to do this without deformation or damage to the material, while maintaining the required radius of curvature.
There is manual and automated metal bending. However, there are other types, the choice of which is determined not only by the type of metal workpiece, but also by the technical specifications. Each type has its own nuances and features that are worth knowing before choosing and starting work.
The essence of any type of metal bending
During the bending process, sheet metal is affected in a certain way, giving it the desired shape in accordance with the drawings. This metalworking operation does not require additional welding or other methods of joining parts that change the structure of the metal and reduce its strength characteristics and service life. During bending, the outer layers of the metal are stretched, and the inner layers are compressed.
The essence of this method of processing material is to bend the sheet at a predetermined angle. The workpiece is deformed during the process, and the degree of deformation is affected by the thickness of the metal, the bending angle, the fragility of the material and the bending speed.
VT-metall offers services:
For the bending operation, special equipment is used, with the help of which the necessary processing of the workpiece is carried out, while the finished product has no defects. Improper bending leads to the formation of many microcracks, weakening of the material in the bending zone, and, as a consequence, to the likelihood of the part breaking in this place.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
There are different types of metal bending depending on the thickness of the metal sheets being processed. It is necessary that the bending stress is above the elastic limit. In order for the finished part to retain its given shape after removing the load experienced during the bending process, the deformation must be plastic.
The advantages of different types of metal bending in metalwork include:
- high performance;
- automation of locksmith operation;
- seamless finished product;
- corrosion resistance of the part;
- strength of the obtained parts.
If welding is used during the processing process, then over time corrosion occurs in the welded area, which cannot be completely prevented even with the help of special protective coatings. When bending, the metal structure remains intact, which protects it from corrosion.
Not all workpieces can be processed using different types of metal bending in a vice and other equipment. The following points are subject to preliminary clarification:
- the value of the maximum bending radius, its comparison with the actual thickness of the workpiece;
- rolling fiber direction;
- initial value of the metal's yield strength;
- possible deviations in the shape of the finished part after processing.
These data must be taken into account when working with thin-sheet workpieces. When processing pipes and certain types of profiled metal products (circles, hexagons, angles, etc.), the permissible relative deformation of the workpiece after bending must also be taken into account.
Subtleties of the process of bending metal pipes
Curved metal pipes are widely used in the oil and chemical industries, mechanical engineering, architecture and construction.
The angle that the pipe should form can be obtained through the use of various fittings. However, such a solution can lead to leaks. And in some cases, aesthetic considerations oppose fittings. A better, more reliable and attractive option for producing curved pipes is bending them, since in this case the integrity of the workpiece is not affected.
To obtain high-quality bending, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the materials.
The deformed pipe is exposed to:
- radial forces changing the cross-section of the workpiece;
- tangential forces due to which folds appear.
When bending metal pipes, it is important to leave their cross-section unchanged. In addition, the formation of corrugations on the walls must not be allowed. Pipe bending technology eliminates the need for welding during pipeline laying.
- Methods for bending pipes.
The choice of technology for bending metal pipes - manually or using special equipment - depends on parameters such as the required bending angle, material of manufacture, and workpiece diameter. In addition, bending can be:
- hot;
- cold;
- using pipe filler;
- without one.
At the end of the pressure on the workpiece, a springing phenomenon occurs, which is directly proportional to the degree of elasticity of the metal. The amount of deformation is influenced by the bending method and the configuration of the product.
- Specifics of the hot metal bending process.
The hot metal bending process is chosen when the diameter of the workpiece exceeds 10 cm. Deformation can be done either manually or using special equipment. However, in any case, the minimum bending radius must be taken into account.
The length of the heated part of the pipe is calculated depending on its diameter and the required bending angle. The rounding must be greater than the diameter multiplied by 3.
To determine the length of the pipe that should be thermally treated, the formula is used:
L = α × d / 15,
where L is the required length in mm;
α – bending angle in degrees;
d – outer diameter of the pipe in mm;
15 – coefficient.
For example, a pipe with a diameter of 200 mm needs to be bent at an angle of 60°, then L = 60 × 200 / 15 = 800 mm, i.e. four diameters.
Before starting the metal bending process, the pipe is heated to a temperature of +900 °C. At the beginning of processing the temperature should be +760 °C, at the end – +720 °C. Higher temperatures negatively affect the strength of the metal.
During the process of hot bending of metal, the following operations are performed:
- make a template;
- the pipe cavity is filled with sand;
- mark the bending zone;
- heat the workpiece;
- bend it.
The pipe cavity is filled with quartz sand to prevent deformation of the section and to avoid the appearance of folds on the inside of the workpiece.
The sand must be pre-dried and calcined at a temperature of +150...+500 °C (this is necessary to remove organic impurities from it), and then passed through a fine sieve with fractions of 3.3x3.3 mm. A plug is installed at one end of the pipe, after which its cavity is filled with sand.
The plugs can be wooden or metal with a hole for gases to escape.
Not suitable for stuffing pipes:
- fine sand, because when heated it sinteres and sticks to the walls;
- wet sand, as steam is generated during the heating process, which can knock out the plug.
There should be no stones in the sand that could damage the walls.
Due to the complexity of the stuffing process, the pipe is first moved to the tower, where it is installed vertically or at an angle. Since the quality of bending directly depends on the density of the packing, the pipe must be constantly tapped during the process. A dull sound indicates that it is filled with sand correctly.
VT-metall offers services:
After filling the workpiece, bending zones are marked on it according to a template. Furnaces or furnaces are used to heat the pipe. The metal bending process can be either manual or using special equipment.
With the mechanized method, the heated section of the pipe is fixed on a special plate with thrust posts and a clamp that holds the end of the workpiece. A cable is put on the opposite end of the pipe, which is pulled with a winch or capstan, bending the workpiece.
To avoid metal deformation, straight or curved gaskets are placed between the pipe and the stand. To secure the free end with the cable, use a stand. During the metal bending process, the geometry of the workpiece is controlled using a template.
Basic methods and types of metal bending
There are two types of metal bending depending on the orientation of the workpiece:
- Longitudinal, in which the metal is only bent.
- Transverse (for example, the sides are bent, bent, blanks are planted, etc.), in which the metal is also upset and pulled out.
For longitudinal bending, appropriate machines are used that work with cold metals. Cross bending is possible:
- in cases of small curvature radius, if cold working will lead to excessive stresses;
- when working with thick metal workpieces.
Heating large-area workpieces increases the likelihood of curvature appearing along spherical and helical surfaces. When working with cold parts, it does not form due to the fact that the metal is springy, preventing the appearance of curvature.
For transverse bending, the metal is always heated. The edges of straight sheets (ship hull blanks) are bent in a cold state without upsetting on special machines or presses.
If edge processing and hole formation are necessary, the workpiece is bent while hot, because when heated, the distance between the holes changes, and the edges lose their correct shape during the process of drawing or upsetting.
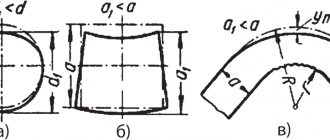
Classification of types of bending according to the contour of the finished product
There are several types of bending that make it possible to obtain sheet metal blanks with different contours:
- V-shaped, it is also called single-angled;
- U-shaped, also known as arc;
- curvilinear;
- multi-angle;
- bending, which results in a workpiece similar in shape to a pipe.
To obtain the desired contour, two different methods are used:
- Free bending method. When performing this, you do not need to fix the center of the workpiece. The punch, which is the working tool of the machine, acts on the workpiece. As a result, its finishing shape is determined by the configuration of the punch.
- Bending method using a calibrating blow. The workpiece is preliminarily placed in the matrix, and it is the shape of the matrix that determines its final configuration.
If roller dies are used, the axis of the workpiece is formed by rotating the moving part of the punch.
Bending has a feature that distinguishes it from other methods of metal processing: the macrostructure mesh can be different and depends on the direction in which the bending was made. If metals and alloys with low or medium ductility are processed, the direction of the fibers is especially important. When it coincides with the direction in which the workpiece axis moves, the risk of destruction during processing will tend to zero. This risk is very serious: delamination is considered a defect that cannot be corrected.
Application areas of various types of metal bending
Different types of metal bending are used in small enterprises, as well as in everyday life, when the production of profiles of different sizes, prefabricated partitions, cabinet products, corners, channels, slopes, gutters, metal frames, suspended building systems, etc. is required.
Pipe bending is also carried out both on an industrial scale and at home. In some cases, the configuration of their connections can be complex. To reduce the number of elements and threaded connections used, the pipes are given a certain shape, for which they are bent at the desired angle. In this way, sewer, water and gas pipes of the desired configuration are obtained with minimal costs, while ensuring minimal resistance inside the networks.
Stages and sequence of technology
In the future, we will talk about the processes of processing rolled metal in a cold state. The development of a technological process for bending sheet metal is carried out in the following sequence:
- analysis of the part design;
- calculation of effort and process work;
- selection of standard size of production equipment;
- preparation of a drawing of the original workpiece;
- calculation of deformation transitions;
- design of technological equipment.
Testing the suitability of the starting material is an important process that must be performed to determine the suitability of the metal for stamping according to the specific dimensions indicated on the drawing of the finished part. This stage includes:
- studying the plastic abilities of the material and checking whether the result corresponds to the level of stresses arising during bending. For low-plasticity alloys and metals, it is necessary to split the process into several transitions and use interoperational annealing, which is designed to increase ductility;
- the possibility of obtaining a bending radius at which the risk of material cracking is reduced to zero;
- determination of possible distortions in the profile or thickness of the workpiece upon completion of pressure treatment with complex contours of the product.
Based on the results of this analysis, a decision can be made on:
- replacing the original material with a more plastic one;
- heating the workpiece before deformation begins;
- performing preliminary softening heat treatment.
An extremely important point in the development of the technological process is the calculation of the minimum permissible bending angle, its radius and the springing angle.
The bending radius (rmin) is calculated based on the level of plasticity of the workpiece metal, the ratio of its dimensions and the rate of deformation. As the rmin value decreases, all metals experience a decrease in the initial thickness of the workpiece. This process is called thinning. Its intensity determines the thinning coefficient λ, the percentage of which determines how much the thickness of the finished product will decrease. If this value is higher than critical, then it is necessary to increase the initial thickness of the workpiece metal (s). Correspondence between the above parameters:
It is also important to determine the minimum bending radius, which depends on the ductility, thickness and location of the rolled metal fibers. This is necessary if the bending radius is small, since in this case the outer fibers of the steel may break, resulting in the integrity of the finished product being compromised. For this reason, the minimum radii should be calculated based on the greatest deformations of the extreme parts of the workpiece based on the relative narrowing (ψ) of the metal subjected to deformation. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the amount of deformation of the workpiece.
The effect of possible springback is taken into account using data on the actual springback angles (β):
Sheet metal bending
Sheet metal bending is one of the leading areas in mechanical engineering today. This method of metal deformation is used everywhere to produce various parts. Bent parts have gained such popularity due to their high strength and minimized corrosion. After all, such parts do not have welding seams or significant defects. All parts are monolithic, but with a complex configuration.
Where are parts using bending technology used?
Bent sheet products are used in all industries and their relevance is in great demand. By bending, parts are made for: cars, ships, airplanes, tanks and other products.
Metal bending equipment
For bending metal, various bending equipment is used, from the simplest, which allows you to produce channels and angles even at home, to high-tech.
Types of industrial equipment:
- rotary - in it the sheets are bent while moving between the rolls. They are stationary and mobile. The main area of application is the production of long and voluminous parts, where the minimum bending radius is equal to the radius of the machine roller. Most often, shells are produced in cylindrical and conical shapes, but it is also possible to obtain completely different configurations of the rolled sheet.
Technological capabilities of the equipment
The market offers a huge number of various devices and machines for carrying out the process of bending steel materials. They make it possible to obtain profiles of complex shapes from steel sheets.
All types of metal bending equipment can be classified as follows:
Recommendations from experienced professionals
Cold deformation is accompanied by the appearance of a huge number of dislocations, which leads to the appearance of significant stresses. For products that do not experience significant loads during operation (roofing, tin pipes and other elements) this is not critical. But for critical products and assemblies, such stresses can serve as a concentrator of destructive forces. Therefore, products of this type must necessarily undergo recrystallization annealing, which normalizes the structure and relieves harmful stresses.
The magnitude of stresses and voids and pores formed between metal grains directly depends on the radius of curvature, and therefore on the tool used for bending the metal. This parameter belongs to the category of reference data and depends on the chemical composition of the steel, as well as on the thickness of the sheet material. If the radius of curvature does not exceed the permissible value, then the product is allowed to work after testing the strength of the control sample.
Process technology: main stages
In order to bend rolled products, it is necessary to prepare special bending dies. In the press of the machine, the entire sheet of steel or alloy is placed until it stops. After this, it will be secured with clamps. Movement of sheets from side to side during the bending process is unacceptable. The bending itself occurs under the influence of the press.
The technology itself is not particularly complex. If rolled steel has sufficient ductility, it can be used to make one-piece structures of various types. The technology itself has become an excellent alternative to welding metal sheets. The absence of seams on the body parts guarantees them a greater degree of strength.
It is worth noting that modern bending equipment makes it possible to obtain bent sheets of excellent quality, which, due to their integrity, have a good appearance, are characterized by durability and reliability.
Bending at home
To give the metal the desired shape, the presence of complex and expensive equipment is not at all necessary. If the thickness of the steel is relatively small (up to 3 millimeters) and it contains a little carbon, then it can be used to produce a product of complex shape in a home workshop. As a machine for bending metal, you can use an ordinary bench vice with a hammer, and to curl spirals from a rod or thin strip, use the so-called snail. The design of the snail is not complicated. You can make it yourself.
Determination of bending force
Bending strength directly depends on the plasticity of the metal and the intensity of its hardening during deformation. These parameters have the direction of rolling of the original workpiece. Upon completion of rolling, the material acquires the property of anisotropy (in the direction of the rolling axis, the residual stresses are less than in the opposite direction). Thus, if you bend the metal along the fibers, then with the same degree of deformation, the risk of destruction of the part is significantly reduced. For this reason, the bending rib is positioned so that the angle is minimal between the location of the workpiece in the sheet and the rolling direction.
To obtain a high-precision calculation of force parameters, it is necessary to clarify how the deformation will be carried out. There are two options:
- bending element - the workpiece is laid on the stops, followed by free deformation;
- force - at the final moment of the process, the part rests on the working surface of the matrix.
The first method is the simplest and less energy-intensive, the second allows you to obtain more accurate parts.