Types of road markings
Highway lines are divided into two main categories:
- horizontal markings;
- vertical marking;
Let's consider each type separately.
Horizontal marking
This includes everything that is “drawn” on the asphalt. Such lines indicate the order of movement along this section of the roadway. Horizontal markings on the road are useful not only for car owners, but also for pedestrians.
To decipher the meaning of the lines, use the following table:
| Numbering in the rules | Applicability |
| 1.1 | "Solid." Used to create a boundary between two traffic flows in opposite directions. |
| 1.2 | Used to mark the edge on the roadway. For example, roadsides. Called "edge" |
| 1.3 | Drivers are familiar with this type of marking. They call it “double solid”. The purpose is the same as one. However, it is used on wider roads, for example, with 4-lane traffic. |
| 1.4 | Prohibits stopping on the selected section of the route. Apply to the edge of the road. |
| 1.5 | "Intermittent." Separates traffic flows, but allows overtaking or turning left. |
| 1.6 | The same intermittent one, but longer and notifies the car owner that he is approaching a “solid” one. |
| 1.7 | Indicates a lane in which you can move through an intersection. Simply put, this is a route map. |
| 1.8 | Such intermittent markings indicate separate rows intended for exiting the highway or braking. |
| 1.9 | It is used on roads where reverse traffic operates. |
| 1.10 | "Yellow dotted line." Also applied to the edge of the road. It does not prohibit stopping, but parking in this place will be prohibited. |
| 1.11 | Allows any lane changes, advances and even turns, but only on the side on which the intermittent one is located. |
| 1.12 | Refers to a boundary used to stop before an intersection, pedestrian crossing or railway crossing. |
| 1.13 | The “Triangle” marking on the road indicates that you need to give way on this section of the road. As a rule, there are several triangles |
| 1.14.1, 1.14.2 | Designations of various types of pedestrian crossings. |
| 1.15 | Such markings inform the driver that the road is crossed by a path intended for bicycle traffic. |
| 1.16.1–1.16.3 | Safety islands for pedestrians who did not have time to cross the road. |
| 1.17 | Informs the driver that minibuses stop at this location. |
| 1.18 | Show directions of movement along the lanes. |
| 1.19 | Indicates a narrowing of the road. The direction of the arrow indicates in which direction the roadway will narrow. |
| 1.20 | Warns you when approaching an intersection where you will have to give way. |
| 1.21 | Warning markings indicating that you are approaching a marking marked “STOP”. |
| 1.22 | These numbers indicate the route number. |
| 1.23.1 | The letter “A” indicates a lane for minibuses and buses. "Bus Lane". |
| 1.23.2 | Footpath. |
| 1.23.3 | Bike path coverage area. |
| 1.25 | Placed in areas with low traffic speeds or in front of a pedestrian crossing. In the rules, such markings are prescribed as “artificial unevenness”. |
| 1.26 | "Waffle iron" If there is a traffic jam at the intersection, then you cannot drive into the waffle iron. |
There are certain types of horizontal markings that are not used in all cities. Eg:
- 24.7 – looks like a rectangle and the letter D. Allows parking only for diplomatic vehicles.
- 24.3 – designates parking spaces allocated for disabled people of any group.
- 24.5 – only electric vehicles may park or move in this location.
All other types of markings only duplicate road signs.
Vertical marking
This type of marking according to traffic regulations is used exclusively on vertical surfaces and structures. It indicates areas of dangerous structures and structures so that the driver can visually navigate and correctly direct the vehicle. There are few types of such markings.
| Numbering according to the rules | Where is it used? |
| 2.1.1–2.1.3 | Such markings can indicate structures, for example, supports of bridges and tunnels, which can create a danger for drivers. The direction of the lines indicates the detour direction. Similar markings can be applied to temporary road signs that are installed in the middle of two lanes. |
| 2.2 | Also shows the boundaries of the bridge and tunnel, but from above. Necessary for truck owners who know the dimensions of the vehicle. |
| 2.3 | Boundary lines that indicate safe zones on expressways and highways. |
| 2.4 | Denotes various street lamps or poles. |
| 2.5 | It is used on bump stops to mark the edge of the road before dangerous areas, for example, cliffs. Currently, it is completely replaced by reflective elements. |
| 2.6 | Necessary for marking the side parts of various dangerous structures. |
| 2.7 | Sometimes islands are created on roads, raised above the road. It is for such structures that this type of vertical marking is used. |
If a highway passes under a bridge or overpass, the upper part of which, as well as the supports, are not marked with vertical markings, then this structure is placed in violation of safety standards. The road authorities are responsible for this. This is GOST.
Marking. Purpose and types of markings.
Marking is the operation of applying lines and dots to a workpiece intended for processing. Lines and dots indicate processing boundaries.
There are two types of markings : flat and spatial.
Marking is called flat when lines and points are applied to a plane, spatial - when marking lines and points are applied to a geometric body of any configuration.
Spatial markings can be made on a marking plate using a marking box, prisms and squares. When marking in space, prisms are used to rotate the workpiece being marked.
For flat and spatial marking, a drawing of the part and a workpiece for it, a marking plate, a marking tool and universal marking devices, a measuring tool and auxiliary materials are required.
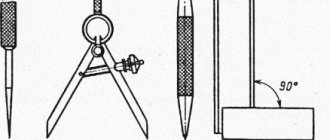
Marking tools include: scriber (with one point, with a ring, double-sided with a curved end), marker (several types), marking compass, punches (regular, automatic for stencil, for circle), calipers with a conical mandrel, hammer, center compass , rectangle, marker with prism.
Marking devices include: a marking plate, a marking box, marking squares and bars, a stand, a thicknesser with a scriber, a thicknesser with a moving scale, a centering device, a dividing head and a universal marking grip, a rotating magnetic plate, double clamps, adjustable wedges, prisms , screw supports.
Measuring tools for marking are: a ruler with divisions, a thickness gauge, a thickness gauge with a moving scale, a caliper, a square, a protractor, a caliper, a level, a control ruler for surfaces, a feeler gauge and standard tiles.
Auxiliary materials for marking include: chalk, white paint (a mixture of chalk diluted in water with linseed oil and the addition of a composition that prevents the oil from drying out), red paint (a mixture of shellac with alcohol with the addition of dye), lubricant, washing and etching materials, wooden blocks and slats, a small tin container for paints and a brush.
Simple marking and measuring tools used in plumbing work are: a hammer, a scriber, a marker, an ordinary center punch, a square, a compass, a marking plate, a graduated ruler, a caliper and a caliper.
Planar or spatial marking of the part is carried out on the basis of the drawing.
Before marking, the workpiece must undergo mandatory preparation, which includes the following operations: cleaning the part from dirt and corrosion (do not do it on a marking plate); degreasing the part (do not do it on a marking plate); inspection of the part in order to detect defects (cracks, cavities, bends); checking overall dimensions and processing allowances; determination of the marking base; covering with white paint the surfaces to be marked and lines and dots applied to them; determination of the axis of symmetry.
If a hole is taken as a marking base, then a wooden plug should be inserted into it.
A marking base is a specific point, axis of symmetry or plane from which, as a rule, all dimensions on a part are measured.
Penciling is the operation of applying small dots-indentations on the surface of a part. They define the centerlines and hole centers required for machining, certain straight or curved lines on the product. The purpose of marking is to mark persistent and noticeable marks on the part that define the base, processing boundaries or drilling location. The punching operation is performed using a scriber, a center punch and a hammer.
Marking using a template is used in the manufacture of a significant number of identical parts. A template made of tin 0.5–2 mm thick (sometimes stiffened with a corner or wooden strip) is placed on the flat surface of the part and traced along the contour with a scriber.
The accuracy of the applied contour on the part depends on the degree of accuracy of the template, the symmetry of the scriber's tip, as well as on the method of advancing the scriber's tip (the tip must move perpendicular to the surface of the part). The template is a mirror image of the configuration of parts, lines and points that must be applied to the surface of the part.
The accuracy of marking (the accuracy of transferring dimensions from the drawing to the part) depends on the degree of accuracy of the marking plate, auxiliary devices (squares and marking boxes), measuring instruments, the tool used to transfer dimensions, on the degree of accuracy of the marking method, as well as on the qualifications of the marker. The marking accuracy is usually from 0.5 to 0.08 mm; when using standard tiles - from 0.05 to 0.02 mm.
When marking, you should handle sharp scribers with care. To protect the worker’s hands before marking, it is necessary to put a cork, wooden or plastic cover on the tip of the scriber.
To install heavy parts on the marking plate, you should use hoists, hoists or cranes.
Spilled oil or other liquid on the floor or marker board may cause an accident.
Purpose and types of markings.
The main purpose of marking is to indicate the boundaries to which the workpiece must be processed. Depending on the shape of the blanks to be marked for parts, markings are divided into planar and spatial (volumetric).
Planar marking is carried out on the surface of flat parts, on the surface of flat parts on strip or table material and consists of applying contour and parallel perpendicular lines, circles, arcs, geometric figures according to zonal dimensions or contours of various holes to the workpiece.
To mark individual spatial parts located at different angles to each other in different planes, the markings of these individual surfaces are linked to each other. Devices for planar marking are marking plates, pads, rotating devices, jacks. Tools for spatial marking: scriber, farmers, compasses, marking rod - compass, ruler, squares.
Before marking, you need to do the following: clean the workpiece from dirt, traces of corrosion, carefully inspect the workpiece to identify holes and cracks. Study the drawing and mentally place the marking plan, determine the bases (surface) of the workpiece from which dimensions should be set aside, prepare the surfaces for painting. For painting, various compositions of chalk diluted in water, a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4), alcohol varnish, and quick-drying varnishes and paints are used. To save time, simple workpieces are often processed without preliminary marking.
For example, in order for a toolmaker to make an ordinary key with flat ends, it is enough to cut off a piece of square steel from a bar of a certain size, and then saw it to the dimensions indicated on the drawing.
Blanks are received for processing in the form of castings (produced from metal poured into pre-prepared molds - earthen, metal, etc.), forgings (produced by forging or stamping), or in the form of rolled material - sheets, rods, etc. (obtained by passing metal between rollers rotating in different directions, having a profile corresponding to the resulting rolled product),
Yellow markings
It is important to differentiate between yellow and orange markings, as they mean completely different things. For example, yellow markings indicate the following:
- Prohibition on stopping or parking. As mentioned earlier, a yellow single solid line along the roadway prohibits stopping at the indicated location. And intermittent does not prohibit stopping, but introduces a ban on parking.
- Places and sections of the road intended for stopping route vehicles. As a rule, it is made in the form of a zigzag. Does not prohibit ordinary drivers from stopping, but on the condition that they do not create any interference for buses.
solid line
Very often, when driving through a certain area, you can see a solid one. In the driving school, starting from the first lessons, they indicate that such a road element cannot be crossed. Even a normal collision with this line can result in a fine. Traffic police officers are well aware of this and therefore often patrol sections of roads where a solid line is drawn.
Solid is usually used in 4 situations:
- to separate flows of different directions in areas with 2 lanes;
- on roads with sharp turns, where oncoming cars become invisible;
- in urban conditions before an intersection or other dangerous area;
- to designate minibus lanes.
This type is also applied in the parking lot to make it easier for drivers to park their car.
In some cases, a solid road indicates an area where you cannot enter. This is usually done on the highway, outside the city. On the roads, and especially in the city, there are also double solid lines. It is used in other situations, but its essence is the same.
You cannot cross or run into it. This should not be done, not even to avoid a fine, but also for personal safety. As you can see, a solid one is usually applied in dangerous areas so that there are no collisions with it.
Orange markings
This type of lines on the road is temporary. That is, its effect will not be permanent. As a rule, orange markings are applied on those sections of roads where repairs are being made. To do this, it’s worth considering a trivial example:
The road surface was cut off on a section of the road. The new one will not be installed soon, so new orange markings are quickly being made for car owners. Where it was intermittent will now become continuous.
Temporary markings always take precedence over permanent markings. Therefore, even if both types of lines are available at the same time, drivers should rely on the orange ones. However, this type of line is rarely present with white markings. And even if this happened, the situation can be considered as a violation on the part of the road services.
Vertical marking
When driving, vertical objects are usually visible as well. They become more pronounced due to vertical markings. It is also numbered.
So, the vertical marking is presented:
2.1.1 – 2.1.3 – usually applied to poles and other high vertical objects on the road.
2.2 – used on the lowest edge of structures if they are located above the road.
2.3 – necessary to designate rounded objects. They are usually located in the middle of the road to separate traffic going in different directions.
2.4 - also used on small rounded posts, but to determine the direction.
2.5 - often found on rounded bridges, as well as when driving in the mountains and other dangerous areas.
2.6 – used on fences that are installed on straight sections of roads.
2.7 – applied on curbs to make them easier to see.
Of course, there are fewer vertical markings, but their role is very important, especially at night. Thanks to it, many objects become better visible. So that it does not harm motorists, but, on the contrary, is useful, when applying it, GOST Road markings must be observed.
What has priority – road signs or markings on the asphalt?
Many car owners are interested in what they should do when dealing with contradictions on the road? For example, there is a road sign on the road prohibiting overtaking, but the line in the middle is broken.
The traffic rules say that in any case, the road sign will have priority. Moreover, if the markings are temporary, but the road sign is permanent, then this is a violation of road services. With orange markings, appropriate signs must be used.
How to mark in a warehouse
In warehouse complexes and other industrial premises, markings serve to prevent any actions and draw attention to dangerous areas. The main types of markings are arrows, lines, signs, shading.
In order to improve logistics processes and ensure safety in warehouses, the following is used:
- marking areas of movement of equipment and personnel. In this case, pedestrian zebra crossings, arrows, signs, boundary lines are actively used, and shelving is outlined;
- marking of floor storage cells with codes, shading, alphanumeric numbering.
What's the difference between one and two solid ones?
Many car owners are interested in what is the difference between these two markings. On some sections of roads they use one solid road, and on others, even double ones. There is an explanation for this.
- Double solid is used on roads that have several lanes for traffic in one direction. However, this rule is not the only one. Not only the number of stripes determines the appearance of a solid line. If the width from the edge of the roadway to the middle is more than 3.75 meters, then such a road will have a double continuous road.
- One solid one is used in places where this width is smaller or where one lane is used for one-way traffic.
Such types of markings not only delimit sections of roads, but also introduce restrictions on overtaking, ahead, changing lanes, turning left or making a U-turn. For such violations there are very strict penalties, including deprivation of rights.
Markings in traffic rules
Painted elements on the road are very common and come in different forms. They look different, and each option is designed to regulate movement or limit it in some situation.
However, the traffic rules indicate only 2 types of markings:
- Horizontal. It is used directly on the road and is represented by lines, arrows, and inscriptions. This type is necessary to establish the order of movement, and sometimes restrictions;
- Vertical. It is usually used on poles and other structures on the road. Such markings are intended to protect drivers from possible dangers, since some objects are not visible at night, and with its help the dimensions become clear. Most often, this look looks like an alternating combination of reflective black and white stripes.
It happens that white stripes are applied, and on top of them there are yellow stripes and their directions differ. In this case, you must continue driving based on the direction of the yellow markings, even if they have a different meaning than white stripes.
Yellow road signs are temporary and are usually found in areas where repairs are being carried out and in other situations. After a certain period they are removed.
Fines for violations of road markings
If you do not obey the requirements of road markings, you may receive a fine. Its size and degree of punishment depend on the severity of such a violation. The list of penalties is as follows:
- Driving along the median strip. Only special and operational vehicles can enter it, however, as in any other conditions. The fine for such a violation is 500 rubles.
- Row-related disorders. In simple terms, this is a banal violation of the rules of maneuvering. For example, at an intersection there is a stripe indicating the place of passage. If you don’t drive along it, you can run into a fine of 500-1500 rubles. In exceptional cases, a traffic police inspector may punish the driver with a simple warning.
- Intersection of a solid line. This violation is gross, and therefore the punishment will be appropriate. For the first time, the driver faces a fine of 5,000 rubles. But for systematic violations, he may lose his license for 4-6 months. Moreover, if the offense was recorded not by a police officer, but by a camera, then they will only be punished with a fine. However, there are mitigations. For example, if there is an obstacle on the road, then driving around a solid road will not be such a serious violation. For this, the driver will be fined 1,500 rubles.
- Waffle iron. If a driver enters this marking when there is a traffic jam there, he will face a fine of 1,000 rubles. The exception is when turning right. In this case, the punishment for the driver will apply only after stopping.
- STOP line. If a driver stops behind a line designated for stopping before an intersection, he will face a fine of 800 rubles.
Marking equipment
The expediency of using machines is justified when there is a large volume of work. If the area is small, you can limit yourself to manual application.
Manual marking devices
The equipment is intended for small and medium volumes of work. This is a small-sized equipment with low weight, which makes it easier to transport and use in limited areas and cramped conditions.
Most devices operate using the airless method of spraying paint . The main operating mechanism is high-pressure piston pumps. They are powered by gasoline engines. This method, based on the action of high pressure, helps to use any marking paints, including high-viscosity ones.
Material savings when marking by machine reaches 20%, solvent consumption is reduced
The machines produce durable markings with clear edges. To improve the quality of marking, equipment of this type provides for double cleaning of the paint using filters .
Another plus is the possibility of equipping with additional devices for marking with reflective glass beads. The work uses second spray guns, which is convenient when applying a double marking line.
Manual marking machines for hot thermoplastics
The equipment is designed for hot thermoplastic marking on concrete and asphalt concrete surfaces . The operation of the machines is based on the “drawing box” principle. Hot thermoplastic is loaded into the hopper. The material is fed by gravity into a special carriage. The machine operator adjusts the length of the stroke. The operating temperature of the hot thermoplastic is maintained by gas burners located at the bottom of the equipment.
The kit includes a gas cylinder, the capacity of which depends on the manufacturer. In general, the equipment benefits from its compactness, light weight, and ease of use. Marking work can be completed quite quickly.
Automatic marking machines
Marking machines are used to apply thermoplastic markings using an extruder. The set of equipment is located on the base of GAZ vehicles . The kit includes: a hopper for thermoplastic, a control unit, a power unit, electrical equipment, an extruder for feeding thermoplastic.
In such kits, the tanks are designed for a volume of 1000 liters. There is a heating system that maintains the required temperature using a thermostat. For high-quality mixing of thermoplastic, a mixer with a hydraulic drive is used.
From the tank, the finished material is transferred to an automatic extruder mechanism. Additionally, the loading platform is equipped with a bunker for balls, capacity from 100 l.
Trailed vehicle units for marking
Equipment of this type is placed on the body of any truck. The only limitation is that the load capacity should not be lower than 1.2 tons. Trailed units are used to perform medium and large volumes of airless spray marking work. The use of reflective balls is acceptable.
Main features of the units:
- simultaneous use of two colors;
- all types of lines are drawn automatically;
- horizontal marking is applied at a speed of 3-19 km/h;
- The width of the marking line can reach 1 m inclusive.
Boilers for thermoplastics
Autonomous operation of the boiler is ensured by its own power unit
The equipment is used to heat thermoplastics. The material reaches operating temperature and is fed into the marking machine. The unloading height varies using hydraulic lifts and can be 1200-1500 mm . Thermal plastic is fed by gravity.
The boiler is mounted in the body of a car with a load capacity of at least 8 tons (for example, Kamaz, Maz).
Demarkers
The machines are used to remove lines and markings from concrete and asphalt surfaces.
Such equipment is a walk-behind tractor on wheels, on which are installed:
- engine;
- belt drive with tension device;
- working body with casing;
- transportation and control handle (changes the angle of inclination according to the height of the worker);
- mechanism for measuring the depth of processing.
The ignition switch is located on the control handle of the machine. Demarkers are equipped with replaceable cutters for thermoplastics and paints. To ensure that the removal of markings is safe and the worker is protected from fragments of old markings, a special protective casing with a splash guard is provided. This device further reduces noise.
Floor dryers (heaters)
These are high-performance devices designed for drying concrete and asphalt concrete surfaces. The equipment works to solve any problem where drying is required during the process of marking in any weather.
Drying units are used for drying temporary road markings made on the basis of polymer tape . This will allow you to quickly and easily dismantle such markings upon expiration.
Operating principle of drying equipment:
- a powerful fan is driven by a gasoline engine;
- an intense air flow is created - up to 27 thousand l/min;
- the air flow is heated by a gas burner (powered by propane);
- the burner and fan are adjustable, which helps to choose the optimal operating mode;
- A gas cylinder with a volume of up to 50 liters is mounted on the machine;
- the heated flow comes out of the socket and completely dries a section of the coating 30 mm wide;
- After warming up, you can apply markings with any selected material.
Table for selecting equipment for marking:
| Marking material | Equipment |
| Paints | Air spray machines . Used for applying solvent-based, water-based materials. The equipment provides a marking width of 5-50 cm in parking lots, parking lots, and limited areas |
| Airless spray technology . Suitable for water-based paints. The paint goes on smoothly, even with wide lines, with crisp edges. When spraying, a slight mist is formed. Marking widths greater than 50 cm are possible | |
| Universal marking machines . Option for large volumes of work with high productivity. Suitable for working with any type of paint and any type of marking | |
| Vehicles based on truck chassis | |
| Cold plastic (smooth/profile/structural lines) | Machines for laying cold plastic . The equipment ensures rational application of the material. Finished marking – smooth lines up to 3 mm thick. The standard line thickness is 12-30 mm. Can be equipped for drawing wider lines up to 50 mm |
| Universal marking machines | |
| Equipment based on truck chassis | |
| Thermoplastic (smooth lines) | Universal marking machines Equipment based on truck chassis |
| Thermoplastic (profile lines) | |
| Thermoplastic (structure lines) | |
| Hot spray |
For large volumes of work, truck-mounted equipment is used
Noise marking
Noise marking
In some cases, to attract the attention of drivers, noise markings in the form of stripes are used, which are especially relevant at pedestrian crossings in emergency zones. Also, such markings are used when you need to mark the boundaries of stripes or divide them. This type of marking is striking even to tired drivers, reminding them of the need to reduce the speed limit. There are several types of noise markings:
- milled (shallow recesses are cut in the asphalt with special cutters);
- raised (it is applied to the canvas);
- pressed;
- molded.
The last two options are applied only during road construction, when the asphalt concrete is still hot.
New markup
New standards were introduced in 2022, starting from the first day of summer by Rosstandart according to GOST R 51256–2018. Such a standard was already considered valid, and how quickly drivers learned about it depended on the quality of the work of regional heads. However, no one canceled the old markings, especially its main lines.
Among other things, markings have appeared indicating the zone only for turns (even now in some places this place is indicated simply by an arrow, disorienting those sitting behind the wheel), as well as the boundaries of electric vehicle charging zones.