How to cut external threads using a die
To cut external threads manually, a special tool is used - a die holder with dies of various diameters.
Die holder with dies for different diameters
In hard-to-reach places, for example near walls, a die holder with a ratchet is used.
Selection of dies
Nominal thread diameter is the diameter at the vertices of the thread triangles. The die cuts the metal, forming depressions and leaving the tops intact, thus both the rod and the die must be the same diameter. The diameter of the thread, for example, is M3 - this is “M” - metric thread, and the number is the nominal diameter of the thread in mm. Accordingly, to cut a thread on a 3 mm rod, we take an M3 die. Measurements of the rod are made with a caliper.
To make the die cut better into the rod, a chamfer is cut off from its end.
Principle of thread cutting with a die
To secure the workpiece you will need a vice. The workpiece is firmly fixed in a vice and lubricated with machine oil for easier movement of the die, reducing friction and tool wear.
When cutting threads with a die, you must avoid large accumulations of chips in the chip removal holes.
The die is installed on the end of the part perpendicularly. With slight pressure, they begin to rotate the die holder clockwise if the thread is right-handed, respectively, if it is left-handed, then counterclockwise.
Cut the thread as follows:
- First make 2-3 turns.
- Then half a turn back to remove chips.
- Lubricate after every 3-4 turns, using a syringe.
- Etc.
I recommend: Foundation bolt: characteristics, dimensions, types, scope of application and selection tips
The thread is checked with a nut or ring gauge. You can buy nuts for your thread here → https://rus-metiz.com/categories/gaiki (RusMetiz).
Ring gauge
Cutting a thread with a die with your own hands (video)
Taps, dies and heads for thread cutting
The most widely used hand tools are for thread cutting. They can be used in industry and everyday life.
The most widely used versions are:
- Similar tools are used to make bolts and studs. Such a product is a round washer, inside of which several ribs protrude. External threads can be formed and calibrated in just one pass. There are various versions of tools on sale; hardened tool steel is used in manufacturing.
- Taps are used to produce internal threads. It is also manufactured using hardened tool steel, which is characterized by high wear resistance. The tap has the shape of a rod, the working part of which has several depressions and protruding edges. Due to this, the thread cutting process is significantly simplified.
- Special heads can also be used to carry out the work in question. They can have different sizes and are used in conjunction with a special holder.
The cost of hand tools is low, but they are characterized by high efficiency in use.
Tapping internal threads
Using a tap, cut the internal thread in the pre-drilled hole. The hole should be smaller by approximately the thread size (the thread size is indicated on the tap). Approximately as in the table:
Hole diameter for internal thread with tap
It is worth remembering that the drill will not give an absolutely accurate diameter; it will be larger by a few fractions of a mm. This is especially noticeable on diameters up to 3 mm. This should be taken into account and take a drill less than a tenth of a mm.
Just like with dies, there is a tap holder.
There are rough and finishing taps. Sometimes they cut first with a rough tap, then with a finishing tap, but mostly they use finishing taps straight away.
Manual cutting of internal threads with a tap (video)
The process is almost identical to thread cutting with a die. The tap is attached to the holder and installed perpendicular to the hole. The part with the hole must be securely fastened.
The tap and hole are lubricated and this is done periodically, after several turns. Just like with a die, you need to make 1-2 turns and 0.5 turns back to remove chips.
To check the accuracy of thread cutting, use a square, checking the verticality of the tap after several turns.
Pitch thread
Pitch metal carving ensures motion transmission. It is used to organize worm and gear drives used in jacks, presses, extruders and lifts.
Pitch connections have a 40-degree inclination of turns, which ensures reliable engagement with mating elements. Threads differ in the geometry of the turn, the pitch, and the dimensions of the inner, outer and middle circle.
The unit of thread measurement is pitches, each of which is equal to 3.14 in.
The thread turns are made in the form of an involute, trapezoid or Archimedean spiral. Their size depends on the purpose of the connection. Thread cutting is performed using cutters, modular and finger cutters. Products are subject to high demands on precision and workmanship.
The typical designation of a pitch thread contains information about its type, size, direction and tolerance parameters. The article “Pitch Thread” posted on our website will help you obtain more detailed information about connections of this configuration.
DIY thread cutting on a metal pipe
When installing metal pipes for water supply or heating, they have to be threaded. The threaded connection of pipes is quite reliable and can withstand significant pressure (if done correctly), so let's look at how to cut threads on metal. pipe with your own hands.
First of all, we cut off the required section using a grinder or a hacksaw, making sure to control the evenness of the cut so that one part of the pipe is not larger than the other - the cut must be perpendicular to the walls of the pipe.
The pipe must be cleaned of rust, old paint, etc., if there is anything on it. Next, we cut a chamfer from the pipe (internal or external, depending on what thread you are cutting) for easier movement of the cutting tool. The chamfer can be cut with a grinder with a metal disc (→ how to work with a grinder) or with a flap disk or file.
Beveled metal pipes
Cutting external threads on a pipe using a die (die)
Everything is the same as with the rods described above, but now with a larger diameter, which most likely will require some practice and you should practice or be extremely careful the first time. Also, to obtain high-quality threads and subsequent good pipe connections, you need to work first with a rough die, then with a finishing die (such kits are sold).
I recommend: Collection and delivery of scrap ferrous and non-ferrous metals - how to make money on it
The choice of die metal is also important. To work with hard alloys, you should use the appropriate dies made of certain alloys; please check this when purchasing.
But, a die is not such a good and powerful tool for cutting threads on pipes with your own hands; it is much more convenient to use clamps.
The die holder is practically the same die holder, only with a guide for smooth movement and thread cutting. The clamp is placed on the pipe of this particular guide.
We put on and attach the clamp to the pipe, screwing it in a little by hand, then you need to use either a special tool - a ratchet, which is convenient for twisting the clamp, but for household needs a large adjustable wrench or gas wrench is also suitable.
One part of the pipe must, of course, be fixed in a vice. If the pipe is cut locally, then make sure that it is not torn out somewhere due to the force applied to the clamp. The pipe can be fixed using a second gas wrench, but it is better for a second person to do this, because cutting threads with one hand is problematic.
What is a clamp and how to use it (video)
Cutting internal threads on a pipe with a tap
Sometimes you have to cut into meth. pipes and internal threads. This is done in the same way using a tap, only with a larger diameter.
To cut a good thread, you should use at least 2 taps - roughing and finishing. It is important to select the correct tap for the pipe diameter. So, the internal diameter of the pipe should be larger by the length of the tap turn (more precisely, by the thickness of the cut), this is indicated on the tap itself.
Cutting is done first with one tap, then with a second.
The main thing is to strictly observe the perpendicularity of the tap stroke and control it. That's all, good luck with your threading! Leave your tips and comments below. Subscribe to our newsletter. Good luck to you and good luck to your family!
Additional Threading Techniques
Regarding manual work, threads of only initial standard sizes . The larger the thread diameter is cut, the more force must be applied to the cutting tool.
In the past, serial and mass production of metal products did not exclude manual labor in the manufacture of threaded surfaces. Today, threads are almost completely cut using specialized equipment. Thread-cutting and thread-rolling units have become widespread.
There are even compact machines that make it possible to cut threads by machine on site.
screw cutting machines do this job well . Of course, you can trust the creation of threaded surfaces to an ordinary lathe. When using machine turning equipment, dies and taps are often used for manual cutting. But threads, internal and external, can be made even with an ordinary turning tool.
Marking
The markings, which are usually placed on the shank, help the specialist to distinguish between different types of taps and quickly find the right one. For example, a metric type will be marked with the letter M, and its size will be measured in millimeters. Manufacturers offer a wide range of this device, so you can find a tap on sale that allows you to achieve almost any thread.
Pipe taps are recognized by the letter G, but are measured in inches. There are both common sizes and rare ones. The master selects them based on the specifics of the work. The conical type of tap is designated by the first letter of the name - K.
Rules of procedure
When working with pipes, it is important to stock up on dies with a pipe clamp and a wrench. The die is selected taking into account the type of thread required
This can be determined by checking the stamp or inspection. The dies must be marked. The data on them will give an idea of what brand the tool is made from.
Most pipes require straight threads. Also, before working, you need to determine its direction: right or left. To do this, a letter indicator is depicted on the dies: “L” is left, and “P” is right. The die also indicates what grade of steel it belongs to, this makes it possible to choose the right tool for cutting stainless steel pipes.
The cutting rules are quite simple:
1). Prepare the pipe for cutting. To do this, the chamfer is removed with a file, and the area is treated with an oil solution.
2). Insert the die into the holder, securing it with screws.
3). Bring the die to the product and make several circular rotations in the required direction of the thread.
4). Lightly press down the die to embed it into the material.
Scrolling algorithm:
- 2-3 turns in one direction;
- half a turn to the other.
And so on until the end of cutting
In this case, it is very important to keep the pipe and die strictly perpendicular. Otherwise, the thread will “walk”, which will affect the quality of the connection.
The arrangement of elements, as well as thread cutting, is demonstrated on video and photo materials for better results. Checking thread quality is easy. To do this, it is enough to screw the nut if it is screwed along the outer diameter of the pipe. The most accurate cut is obtained with a sliding die. It will help out if you urgently need to replace a piece of pipe that has a threaded connection.
Also, when choosing dies, it is important to consider what kind of thread will be made, external or internal. High-quality work will allow you to make a sealed threaded connection even in pressure water pipes
Let's sum it up
As you can see, making your own carving using dies is not at all difficult. To do this, it is enough to choose the right tool, put in a little effort and accuracy. Probably, many representatives of the male half of humanity remember how similar problems were solved in labor lessons at school. Therefore, for the majority, it will only be necessary to remember the acquired skills and apply them in adulthood. It’s like riding a bicycle: you only need to learn once to feel confident in the saddle even after a long break.
Other types of thread
The types of threads are not limited to pitch, metric and inch. There are other types of threaded connections used to solve certain technical problems.
Round thread
Round threads are in demand when creating pipeline fittings. It has a smooth rounded profile and is cut according to GOST 13536-68. The angle of inclination of the threaded protrusions does not exceed 30 degrees.
Round thread
Trapezoidal thread
Running self-braking thread with a trapezoidal profile. The extensive contact area of the connected elements contributes to an exponential increase in the friction force as they move. This creates a braking effect that prevents arbitrary weakening of the knot.
Trapezoidal threads are widely used in robotics. With its help, elements of assembly lines and injection molding plants are fixed. Cutting and quality control of trapezoidal threads is regulated by GOST 24738-81.
Trapezoidal thread
Thrust thread
A type of trapezoidal thread, characterized by an inclination of the working side at an angle of 3 degrees. The thread is cut in accordance with GOST 10177-82 and is used in critical components with increased axial load.
Thrust thread
Die holder with electric drive
It can already be considered as an intermediate model for thread cutting between a hand-held mechanical tool and a machine. An electric thread-cutting die holder greatly facilitates the work of thread cutting and is more productive. There are different delivery options depending on the set of accessories and fixtures.
In their work, they use the same heads as manual models (of course, within the same brand and restrictions on thread diameter). The guide jaws in the head are not enough to ensure a stable position of the tool. Still, the “weakest” of them has a power of 750 Watts, but models from 1000 Watts are more often used.
If we consider that the transmission of rotation takes place with a powerful reduction gearbox, and 1 hp is equal to 735.5 watts, then holding a working tool in your hands is already problematic. Therefore, the kit includes a clamp-retainer. As an additional option, an oil pump can be supplied to supply special oil to the working area.
There are certain restrictions on using an electric clamp. And the point is not even that it is not always possible to connect to the network on the site. An electric manual die holder has a weight of 5 kg and quite significant dimensions compared to a mechanical one (especially with a clamp). Therefore, when cutting threads during repair of an existing pipeline, its use is simply impossible.
The main purpose is the laying of new routes and work on site or use in the preparation of pipes in a workshop (although portable threading machines can already be used for this).
As a continuation of the topic, there are compact portable thread cutting machines.
This is an ideal solution for a workshop or procurement area if you have to work with significant volumes. Their power in watts is no different from a household vacuum cleaner or hair dryer (from 1.5 kW), but it is enough to provide high performance when working with a pipe up to 4 inches. They are already equipped with a pipe cutter, deburring device, automatic oil supply (more precisely, its circulation from the pan through a filter system) and can be installed on a workbench or on removable legs. a pipe bender yourself.
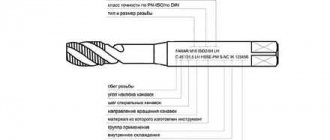
All about dies
A die or die is a device used to cut external threads of various types. It is represented by a small nut on which there is an edge and a chip outlet. The threaded device can have thread pitch sizes from eight to ten.
Thread pitch is the distance between adjacent threaded threads.
The working area of dies is iron pipes and rods. Threads come in conical and cylindrical shapes. To obtain a high-quality thread, you need to cut in one pass. The die has a cutting edge. To make cylindrical threads, dies with two parts of the working area are used - calibrating and cutting. The calibrating part forms the final diameter and thread profile.
Classification of dies
Ledgers are divided into: tubular, square, round and hexagonal.
They are also divided by structure:
- solid;
- sliding (prismatic);
- cut.
The round lecher is the most widely used. It is threaded in one pass, and not in several, like sliding ones. These dies can cut threads at different pitches. They can also be used to cut pipe and inch threads. The working part of round dies is not subjected to grinding. The outside diameter will depend on the size of the chip guards and the size of thread required.
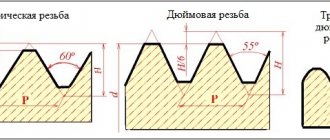
Characteristics of thread types
When determining thread characteristics, the following parameters are taken into account:
- diameter between the top cutting points;
- diameter between the lowest points of the depressions;
- pitch between turns;
- units of measurement (inches, millimeters);
- profile configuration.
Indicators taken into account when classifying threads:
- measurement scale;
- location of the working surface (outside or inside the element);
- direction of turns;
- appointment;
- number of cutting passes.
The type of profile is also taken into account, which can be triangular, trapezoidal, spherical, etc. The main types of threads are presented in the diagram.
Main types of fastening and running threads
Advantages and disadvantages of threaded connections
Among the advantages of threaded connections it is worth highlighting:
- the possibility of obtaining a high-strength detachable unit;
- unified design of hardware and thread-cutting tools;
- ease of connection of threaded components;
- long service life of the created connections;
- the ability to perform work with moderate load on the tool.
The disadvantages of threaded connections include a tendency to “sour”, as well as the need for special tools for installation and dismantling operations. When working with certain types of connections, groovers are used to prevent arbitrary unwinding of the components, as well as large washers that distribute clamping forces.
Thread designation
Each type of thread has its own designation:
- pitch thread - p”;
- inch thread - G
- metric thread - M;
- tapered thread - K;
- round thread - Rd;
- trapezoidal thread - Tr.
The thrust thread is designated by the letter S. More detailed information on the types and designations of threads is presented in the table.
Types and designations of threads