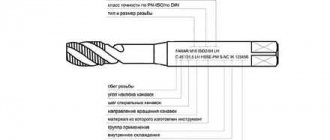
A manual die for thread cutting is a mechanism that allows you to create external threads on pipes, bolts, studs, bends, and barrels. The device is also used to regenerate ready-made but slightly worn cuttings. The tool consists of a holder and cutters. The latter are made of high-strength metal, which guarantees the durability of the entire device and the creation of high-quality threads. There are two types of manual thread-cutting die: the first type is capable of cutting threads with a diameter of 0.5″ to 1 1/4″, and the second – 1 1/2″ and 2″.
Using a hand clamp you can cut or renew threads on workpieces of small diameter
What is a thread and why is it needed?
Threading is one of the most popular types of fastening parts or mounting structures. It is used to connect several parts, such as pipes, into one structure. To do this, grooves are cut out on their side or inner part, which have a certain shape, angle of inclination and distance between the recesses (turn pitch).
Also, the notch can be on connecting parts, for example, taps or tees. Using this installation method, you can make collapsible or permanent structures, such as water supply, sewerage and other types of pipe systems. You can cut threads only on round or conical parts, since for other surfaces it will be inconvenient and impractical.
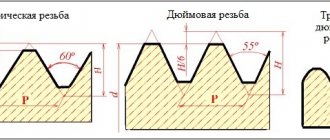
The most common thread profile option is triangular. It is very simple and affordable, but is not suitable for frequent system disassembly. If you need to frequently disconnect pipes or other parts, a round profile is used. It is most often used in plumbing. Other types of profiles are used in kinematic systems (for example, transmissions), but are not used in plumbing.
A type of kinematic cutting Source findpatent.ru
Application
The cutting die is used wherever there is a pipe, there is a thread and there is access to a place to work. These are the gas industry, sewerage, heat supply and water supply. In addition, they are used in the following industries:
- For the manufacture of prefabricated structures, as an option, prefabricated structures of greenhouses, gazebos, light stairs and other areas.
- When installing a water supply system. In this case, threads can be cut on pipes made of cast iron, copper, stainless steel and other metals.
- For parts in heating systems, if necessary, combine polypropylene and metal.
- In places where wells are drilled and wells, when arranging sewerage systems.
Before use, it is important that the metal is free of paint and rust. Before cutting pipes, an assessment is made to see whether the clamp can be placed between the wall and the pipe. The cut is made using a grinder, having previously completed the markings. At home, marking a perfect circle on a pipe can be done with a sheet of paper, wrapping it around the pipe and connecting the two ends together.
Having completed the markings, make two cuts of the tube, having previously calculated the distance for future installation. Then they clean both edges, chamfering them a little so that the clamp is put on evenly. Having aligned the tool evenly, they begin to rotate it to the right.
Types of thread
Thread cutting greatly depends on the surface on which it will be turned and for what purposes it will be used. For example, a conical one is good for sealing a joint, but it is difficult to make. There are 2 types of thread direction: right and left. The first one is the most common. It can be seen on bolts, screws, pipes and other connection elements. To screw a part onto such a notch, you need to turn it clockwise, and for the left - in the opposite direction.
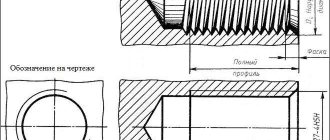
Also, the thread can be single-start or consist of several parallel threads. In such connections, in addition to the pitch (P), the Ph parameter is used, which shows the distance between the grooves that are cut in one go. This is necessary in order to understand whether another turn will fit between the adjacent notches. You can see what thread cutting on pipes with several turns looks like in the picture below.
Example of the distance between turns Source https://ng.sibstrin.ru/wolchin/umm/in_graph/ig/004/000.files/102.jpg
There are several types of threads that perform different functions and are suitable for specific tasks:
- Metric (M) is its most common type in everyday life, but is completely unsuitable for pipes, since it is not standard. When cutting such a notch on a pipe yourself, problems may arise with the installation of additional modules or connection with a standard product due to a mismatch in pitch, angle and profile. The metric notch has a triangular profile with an angle of 60°, and the pitch is from 0.5 to 2 mm. The dimensions of the thread in the marking indicate its outer diameter, for example, M10 is 10 mm.
Metric notch Source upload.wikimedia.org
- Cylindrical (G) - referred to as BSPP and was invented in Britain. Because of this, all measurements for its standardization are carried out in inches, which is why it received the corresponding name. This notch is used in more than 90-95% of all systems that are connected to pipes and it is cut on all fittings that are used in plumbing, common in our market. The size marking of such a thread shows the diameter of its nominal bore, not the outer circle, and can range from 1/16 to 6 inches. This notch has rounded cuts at the tops and a profile angle of 55°.
Video description
This video shows how to make inch cutting with a die and die:
- Conical (R) - designated as BSPT and also has British roots. It has a pitch and profile angle similar to cylindrical threads. It is used for cutting notches into cone-shaped parts. In some cases, it is possible to connect parts with R and G notches. By creating additional tension on the turns during the joining process, the conical notch provides additional reliability of the docking units.
- Round (R) is a very rare type of pipe connection, which is used in places where it is necessary to frequently assemble and disassemble the joint. Even after frequent dismantling, such a mount does not lose its shape, reliability and tightness. The disadvantage of such a thread is that it cannot be combined with other types of notches. The round variety has a profile in the form of a circular arc with an angle of 30°.
There is an American standard for conical and cylindrical parts, which is labeled NPSM or NPTF. It has an angle not of 55°, but of 60°, similar to the metric one. This type of thread has its own thread size and profile height, but is found almost nowhere, since it is being replaced on the market by the British standard.
Example of American NPSM Source www.staniosind.com
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in the installation of utilities: water supply, sewerage and heating
Why is this even required?
Despite the fact that the 21st century has arrived relatively long ago, and store shelves are full of various modern materials for gas and water pipes, carving as such is still relevant. It has been used for quite a long time, but still there is no reason to refuse its use.
On a note! Of course, polyethylene pipes are connected to each other using compression fittings, while polypropylene pipes are generally soldered. It is not only easy, but also convenient and fast.
However, all plastics (including composites made on their basis) are characterized by two significant disadvantages.
- Firstly , high temperatures are contraindicated for them. For example, the “ceiling” for polypropylene is only +90 degrees. This is true, you will notice, but in accordance with the standards and requirements, there should not be a higher temperature in the pipelines of residential buildings; That’s right, but in many northern regions, due to cold winters, heating systems have to exceed these standards, otherwise people may simply freeze. And if the temperature in the plumbing/heating system exceeds +100 degrees, that is, the boiling point of water, then polypropylene in this case cannot be used at all. As for PE pipes, the maximum permissible temperature for them is only +40 degrees.
- Secondly , the mechanical strength of plastics/composites is low. And if the pipeline needs to be laid, say, under a popular road or in a restaurant toilet, where it can be damaged by drunken visitors, then the use of plastic must be abandoned altogether! The same applies to metal-plastic pipes, which can easily be deformed or removed from the fitting.
Important information! If you need a heat-resistant pipeline, we recommend paying attention to copper. Pipes made from it can be used at temperatures from 0 (if the temperature is lower, the water will simply turn into ice) to +250 degrees. However, copper is quite expensive, and due to the fact that pipes made from it have thin walls, its strength under lateral loads is unsatisfactory.
What options are left? Unfortunately, only steel. Preference, of course, is better to give galvanized ones, since there is definitely too much rust in the pipeline.
Note also that there are two ways to achieve a tight connection between steel pipes:
- use a threaded connection;
- use welding.
At the same time, not everyone can boast of having a welding machine; in addition, after welding, the protective zinc layer is damaged. And this leads to rusting of the welds. Consequently, such a water supply system will initially have vulnerable spots.
Tools
There are different pipe threading tools that can make notches inside or outside the structure:
- A tap is a device for cutting internal threads. In appearance, it resembles a rod or drill on the outer surface of which there are notches and grooves applied in order to retract the handle. Taps are used for cutting or calibrating threads. Most often, their working part consists of 3 sections, which perform the functions of rough, intermediate and final cutting. Some manufacturers make a set consisting of 2-5 taps, which perform the notching separately. The tap can also be made for manual cutting or for processing parts on a machine. They are most often used for cutting metric threads, but there are varieties for cutting internal notches for pipe standards.
Set of different taps Source prosto-instrumenty.ru
Video description
This video shows the features of thread cutting with a die:
- A clamp is a device for cutting threads in hard-to-reach places. In appearance, it resembles a wrench, but instead of attachments for bolts, it has a hole for attaching replaceable cutters. The principle of operation of the clamp is similar to a die, only instead of a whole washer it uses its cutting edge, and for turning it uses a mechanism similar to a wrench. There are devices that, instead of a solid body, use adjustable or open-end wrenches for turning. Such a device will cost less than a solid socket with a ratchet, but when using them you can get injured, since the key sometimes jumps off.
Example of a die with different heads Source otk-instrument.ru
Advantages of a die over a simple die
Typically the die is made of expensive tool steel. In this case, only the cutters must be especially strong, because they form the thread. And the die, as we noted earlier, is also a die, but without expensive and non-functional elements. An inexpensive holder, as well as durable cutters, is all that is required in this case.
It would seem illogical to consider the tool as a budget alternative to a die: on the market you can find dies whose cost is measured in thousands of dollars. But do not forget that the cutters here are replaceable elements.
What are the savings anyway? On consumables. As for the tool, its cost is so high for the reason that it makes the thread cutting process less tedious and more convenient.
Video - Pipe clamp: what is it?
How to cut threads
Before cutting a thread, you should decide on its size, pitch and standard used. If you need to make a cut on a part that should fit an already finished element, then it is recommended to first understand its dimensions. To do this, look for the appropriate marking next to the finished thread.
If it is not there, then for measurement you can use a caliper or a special set with templates for notches of different standards. You can also use marked plumbing fixtures for this if there are no other options. With its help you can understand the diameter of the pipe.
To determine the notch pitch, you can mark 10 turns with a marker, measure the length of the entire section and divide it by 10. The resulting number will be the pitch. The thread cutting tool should also be selected based on the diameter of the pipe and the pitch of the notch on the part with which the connection is required.
Before working with dies or dies, you should clean the surface of the pipe on which the notch will be made using a file, sandpaper or a grinder with a grinding wheel. The end part of the part also needs to be turned and an entrance chamfer made on it to start working.
Example of an entrance chamfer Source upload.ecvv.com
Gutter cutting machine
Special machines are often used in production. In terms of design features, they are in many ways reminiscent of vertically oriented machines. Among the features we note:
- The diameter and thread pitch are adjustable.
- If necessary, you can carefully adjust the number and speed of rotation of the cutting element.
- Almost all models are characterized by the ability to process external and internal surfaces.
Modern machines can be used even when cutting thin-walled products. Difficulties can only arise if the workpiece cannot be removed and installed vertically.
Video description
This video shows how to cut an internal thread using a machine and a tap:
Tapping with an electric die is similar to the conventional process, but this tool requires more space and additional fixation to operate. Its advantage is that the labor intensity of the process for the mechanic is reduced. For any type of cutting, it is recommended to add lubricant during operation to the places where the cutting edge is located.
Thread cutting can also be done using a lathe. This type of work is most often used for large volumes of production. Using such a device, you can make both external and internal threads, but you need a trained specialist to work with them. Without proper knowledge, operating the machine can cause injury.
Example of plumbing fittings with thread Source static-eu.insales.ru
Key varieties of klupp
We should start with the fact that pipe clamps are divided into several groups depending on ease of use and, of course, price. Let's take a closer look at these groups.
Group No1. Simple hand tools
Let's not beat around the bush - we are talking here about the simplest die in a simple holder. Visually there is no difference at all. The round frame is a guide that has clamps for the cutters and a pair of handles necessary for its rotation.
Group No2. Hand tools with ratchet
This design is a slightly more complicated version of the previous one - the frame is equipped with a ratchet, thanks to which it becomes possible not to intercept the handles. You just need to make reciprocating movements with one handle (like pumping water with a pump).
Important information! If you find both the first and second variants of the clutch in the store, but their cost is the same, then it is certainly better to give preference to the first. After all, a ratchet in tandem with cheap Chinese production (read: the use of low-quality metals) is a very dangerous combination, which you should definitely stay away from.
Group No3. Electrical tools
But in this case, all the work with the device consists of correctly installing the pipe and pressing the appropriate button. The electric drive will handle everything else perfectly. Having a fairly modest power (estimated at only a few hundred watts), such tools are capable of developing great force, which is possible due to the significant transmission coefficient on the gearbox.
Briefly about the main thing
Threading is a convenient and reliable way to fasten parts and mount various structures.
There are different types of threads, but for pipes the most commonly used standard is cylindrical or tapered.
The simplest and most accessible tool for cutting external threads is a die, and for internal threads, a tap.
With the help of a die, you can save time and effort when cutting threads in hard-to-reach places, for example, near walls, and the electric device can make the notch independently.
Ratings 0