It is possible to prepare oil or water-soluble coolant with your own hands at home. To do this, you need a little free time and a simple set of components.
Do-it-yourself coolant is potentially dangerous to your equipment and health! We are not responsible for negative consequences. Using the recommendations from this article, you act at your own peril and risk!
The popularity of cutting fluids (coolants) is explained by their wide spectrum of action. They extend the service life of the machine by cooling the cutting tool, improve the quality of processing, increase speed and productivity, and make operations safer and more comfortable. Buying a ready-made liquid is not always the easiest or most obvious way to get these benefits. Sometimes it’s easier to prepare coolant for machines with your own hands.
Does homemade coolant have a right to life? You can replace expensive components with more affordable ones, but you cannot guarantee that the liquid obtained at home will “work” correctly.
DIY coolant
It is possible to prepare oil or water-soluble coolant with your own hands at home.
To do this, you need a little free time and a simple set of components. Do-it-yourself coolant is potentially dangerous to your equipment and health! We are not responsible for negative consequences. Using the recommendations from this article, you act at your own peril and risk!
The popularity of cutting fluids (coolants) is explained by their wide spectrum of action. They extend the service life of the machine by cooling the cutting tool, improve the quality of processing, increase speed and productivity, and make operations safer and more comfortable. Buying a ready-made liquid is not always the easiest or most obvious way to get these benefits. Sometimes it’s easier to prepare coolant for machines with your own hands.
Does homemade coolant have a right to life? You can replace expensive components with more affordable ones, but you cannot guarantee that the liquid obtained at home will “work” correctly.
Lubricant replacement technology
Before carrying out the coolant replacement procedure in the equipment, it is necessary to clean the system.
For this, a special composition is used. It allows you to prepare the system for filling with new lubricant. The cleaner removes traces of contaminants and removes remnants of the old composition from the system. At the same time, it has an antiseptic effect on internal surfaces.
Processing takes a minimum amount of time.
The procedure is carried out in several stages:
- 8 hours before the planned refilling of the lubricant, you need to pour a cleaner into the system. In this case, the old emulsion remains in the equipment. The concentration of the cleaner should be 3% (3 liters of cleaner will be required per 100 liters of emulsion).
- The machine operates for an entire shift (8 hours) in normal mode until the coolant is replaced.
- After this, you need to completely drain the old emulsion from the equipment. In this case, it is necessary to remove dirt, deposits and chips. They are washed out along with the lubricant.
- All equipment elements accessible for manual cleaning must be wiped with a rag. It is recommended to flush the system with liquid under pressure using a pump.
- The system is filled with water to the minimum level. You can prepare a weak emulsion (0.5%). This composition should circulate in the equipment for about an hour.
- The flush needs to be drained. The condition of the tank must be visually assessed. If there are contaminants, they are removed. They can be washed out of the system after flushing.
- If dirt and deposits have been washed out of the equipment, the washing is repeated several times until the tank is clean.
- Next, the emulsion is prepared. It is filled to the maximum level in the unit. The concentration of the composition is checked using a refractometer. The readings are recorded in a table. This allows for regular monitoring in accordance with existing requirements, comparing subsequent indicators with initial data.
How to make oil-based coolant
It’s easy to make coolant yourself, especially if it contains mineral oils. To prepare the base you will need oil, water and a surfactant.
The simplest recipe looks like this: mix 200 ml of surfactant (liquid soap will do), purified vegetable oil, kerosene and soda ash. Add 50 ml of laundry bleach, 25 ml of concentrated dishwashing detergent. Bring the resulting volume to 10 liters using plain water, and then heat to 90 °C, stirring constantly. The output will be do-it-yourself coolant for a lathe. Before use, dilute it in a ratio of one to three.
In some recipes you can see industrial oil - replace it with motor oil, the result will be the same. For example, another popular recipe involves preparing a mixture of industrial (motor) oil, water and a surfactant, which again can be any detergent or liquid soap.
Replacement procedure without industrial cleaner
If the enterprise does not have a special system cleaner on its balance sheet, the equipment can be prepared according to a different scheme.
It includes several stages:
- The old emulsion must be drained from the system. Chips, other contaminants and deposits are removed, which will be washed away along with the lubricant.
- Using a rag, manual cleaning of all accessible elements of the unit is carried out.
- The system is filled to the minimum level with a just prepared two percent solution of water and soda. 0.01% furatsilin is added to it. The liquid should be heated to a temperature of about 65ºC. The liquid circulates under the action of the pump for 3-8 hours. The duration of washing is selected in accordance with the level of bactericidal damage.
- The rinse flows out of the unit. Next, the system is wiped again with a rag. You can clean surfaces using a jet of liquid supplied by a pump.
- Next, water or a weak (0.5%) emulsion solution is poured into the system. The liquid circulates in the equipment for an hour. Then you need to drain it from the unit and wipe all accessible surfaces.
- After this, the emulsion is poured inside to the maximum level. The concentration is checked with a refractometer. The result is recorded in a table.
Do-it-yourself coolant - how to prepare an emulsion for a lathe?
WARNING: USING HOMEMADE COOLANT CAN BE DANGEROUS TO THE EQUIPMENT AND YOUR HEALTH! THE SITE ADMINISTRATION IS NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR POSSIBLE CONSEQUENCES!
The use of cutting fluids (coolants) during turning operations:
- extends the service life of the tool and machine;
- increases the cleanliness class of treated surfaces;
- allows for high-speed metal processing.
There is a wide selection of coolant in stores, but you can prepare an emulsion for a lathe with your own hands, using simple recipes.
Homemade coolant analogues are made on the basis of oil (if better lubrication of the workpiece and tool is required) or water (if higher cooling properties are required). There is no clear answer to the question of what is the best material to use to prepare coolant for a machine yourself. For example, expensive WD-40 lubricant for drilling aluminum can be replaced with a mixture of kerosene (70%) and turpentine (30%). When making emulsions for processing ferrous metals, you need to remember that they must contain corrosion inhibitors.
How to replace coolant
Cooling lubricants are not unique in composition and principle of action. If you have a small amount of work to do, you can get by with the closest home-made analogues with similar characteristics.
Let's say you need to prepare coolant for aluminum with your own hands. At home or in the garage, you can get by with kerosene or turpentine, but this will not be the best solution for many reasons (the main ones are a strong unpleasant odor and toxicity). Ethyl and isopropyl alcohol are good alternatives. They do not require a high degree of purification, but you need to monitor their water content. If its mass fraction exceeds 0.1, you risk causing corrosion on the metal surfaces of the cutting or grinding tool.
How to make your own oil-based coolant
To prepare an oil-based emulsion with your own hands, just thoroughly mix three components - oil, water and surfactant (surfactant).
Metalworking forums also offer more complex recipes for making homemade coolant for lathes. For example:
- mix one faceted glass of flavored liquid soap, unrefined sunflower oil, kerosene and soda ash + half a stack of laundry bleach + a quarter stack of Fairy, add warm water to a volume of 10 liters and heat to 90 ° with continuous stirring. Dilute the resulting concentrate with water in a ratio of 1:3.
- 65 liters of water + 7 liters of diesel fuel + 1 piece of grated 60% laundry soap + 1 pack of Pemos Automatic washing powder + 200g of Feri dishwashing liquid (Fairy) + 2 tablespoons of soda ash. After pouring into the coolant tank, run the pump for 10 minutes - and the homemade emulsion is ready.
Industrial oil is often found in recipes for homemade emulsions. It can be replaced with a motor one.
How to lubricate a drill when drilling metal?
It is possible to prepare oil or water-soluble coolant with your own hands at home. To do this, you need a little free time and a simple set of components.
Do-it-yourself coolant is potentially dangerous to your equipment and health! We are not responsible for negative consequences. Using the recommendations from this article, you act at your own peril and risk!
The popularity of cutting fluids (coolants) is explained by their wide spectrum of action. They extend the service life of the machine by cooling the cutting tool, improve the quality of processing, increase speed and productivity, and make operations safer and more comfortable. Buying a ready-made liquid is not always the easiest or most obvious way to get these benefits. Sometimes it’s easier to prepare coolant for machines with your own hands.
Does homemade coolant have a right to life? You can replace expensive components with more affordable ones, but you cannot guarantee that the liquid obtained at home will “work” correctly.
How to make oil-based coolant
It’s easy to make coolant yourself, especially if it contains mineral oils. To prepare the base you will need oil, water and a surfactant.
The simplest recipe looks like this: mix 200 ml of surfactant (liquid soap will do), purified vegetable oil, kerosene and soda ash. Add 50 ml of laundry bleach, 25 ml of concentrated dishwashing detergent. Bring the resulting volume to 10 liters using plain water, and then heat to 90 °C, stirring constantly. The output will be do-it-yourself coolant for a lathe. Before use, dilute it in a ratio of one to three.
In some recipes you can see industrial oil - replace it with motor oil, the result will be the same. For example, another popular recipe involves preparing a mixture of industrial (motor) oil, water and a surfactant, which again can be any detergent or liquid soap.
Replacement procedure without industrial cleaner
If the enterprise does not have a special system cleaner on its balance sheet, the equipment can be prepared according to a different scheme.
It includes several stages:
- The old emulsion must be drained from the system. Chips, other contaminants and deposits are removed, which will be washed away along with the lubricant.
- Using a rag, manual cleaning of all accessible elements of the unit is carried out.
- The system is filled to the minimum level with a just prepared two percent solution of water and soda. 0.01% furatsilin is added to it. The liquid should be heated to a temperature of about 65ºC. The liquid circulates under the action of the pump for 3-8 hours. The duration of washing is selected in accordance with the level of bactericidal damage.
- The rinse flows out of the unit. Next, the system is wiped again with a rag. You can clean surfaces using a jet of liquid supplied by a pump.
- Next, water or a weak (0.5%) emulsion solution is poured into the system. The liquid circulates in the equipment for an hour. Then you need to drain it from the unit and wipe all accessible surfaces.
- After this, the emulsion is poured inside to the maximum level. The concentration is checked with a refractometer. The result is recorded in a table.
How to prepare water-based coolant
The composition of coolant for do-it-yourself machines can be different. Along with oil-based ones, water-soluble lubricating fluids are popular. They have a simple composition, and preparation consists of dissolving the main components in warm water. The composition of such coolant may include:
| Main component | Auxiliary Component |
| Soda Ash | – |
| Soda Ash | Sodium nitrite |
| Trisodium phosphate | – |
| Trisodium phosphate | Sodium nitrite |
| Potassium soap | Trisodium phosphate + sodium nitrite |
| Potassium soap | Soda Ash |
An aqueous solution with soda and sodium nitrite is often used. This mixture prevents corrosion on metal workpieces. If the composition includes trisodium phosphate, the coolant is suitable for turning workpieces.
If you make coolant yourself, the composition may change. But the safety rules for their preparation must remain unchanged. Use personal protective equipment, and carry out work in a non-residential area: workshop, garage, etc.
Types, composition and characteristics
There are dozens of types of coolant, which differ in composition and characteristics. The functions performed are the same, but each type increases the efficiency of a particular action when working with the machine in a different way.
Oily
The main component of the coolant is mineral oil, which is mixed with mineral elements. The coolant contains the following substances: anti-wear, anti-friction and extreme pressure additives. Inhibitors and agents against oxidation and the appearance of nebulae are also present.
Characteristics of substances:
- Anti-wear additives - reduce wear of working tools.
- Antifriction additives - technical oils.
- Anti-Seize - Protects tools from overheating and wear under severe conditions.
- Inhibitors - used to protect instruments from corrosive reactions.
- Anti-fog additives - reduce the risk of oily fog.
Emulsol is an oily liquid made from spindle oil and several additives. The main advantage is excellent corrosion protection. When combined with water, it becomes a universal liquid that does an excellent job of protection and cooling.
But also, the oily solution has disadvantages - a low degree of cooling, in comparison with other types of liquids.
The use of oily liquids increases the risk of fire.
Synthetic
The product is used for abrasive processing of metal workpieces. It consists of several additives that have a balanced composition. If you mix synthetic liquid with water you will get a transparent microemulsion.
Synthetic coolant is an excellent coolant for lathes, since cooling is its main advantage.
Synthetic coolant reduces the risk of smoke in the workplace. Used in various water compositions.
The composition is formed from stable minerals that cope with foaming.
This liquid is not always used. It is used when working with certain metals: steel, cast iron, glass and aluminum alloys, stainless steel.
Semi-synthetic
Unlike the previous type of liquid, it not only perfectly cools the machine, but also lubricates the parts.
It contains a small amount of mineral oils, which are mixed with a small amount of other mineral additives.
Emulsol, which is the main component, allows you to effectively lubricate and cool equipment parts.
Emulsol is better suited for lathes that specialize in working with heavy metals.
The emulsion is used for some types of work, best for abrasive machining of cast iron. But this is not the only type of work; this includes blade and sharpening of complex metals.
Water based
Water-based fluids have one function - lubricating parts. Although they are not coolers, they are the best at lubricating prepared materials and equipment.
There are many watery solutions, but we’ll tell you about one of the main ones:
- An aqueous solution with a small content of soda (0.8%) and sodium nitrate (0.25%). Protects workpieces and tools from corrosion.
- Boiled water containing trisodium phosphate - 1.5%. Used for turning workpieces.
- A solution of water with 2-3% emulsol and a small amount of calcined salt (1.5%). Used for accelerated processing, but has low cleaning quality.
Feeding watery coolant on a lathe helps speed up the processing of materials.
Efficiency of using lubricant-cooling mixtures
Tests have shown that the economic effect of using refrigerants reaches 15-45%. The research was carried out by the German plant Karnasch. Two core drills with a diameter of 25 mm were taken as a basis, and a sheet of metal 10 mm thick served as the workpiece. In the first case, a 7% emulsion solution was supplied to the working area, in the second - water. Result: the first drill made 1500 holes, the second - 850. The difference is significant - 45%.
When using coolants and spending on them, the economic effect ranges from 15-20%, and the machine lasts longer, which is also important.
Which is better: homemade or factory coolant?
Many people wonder how to make coolant for a machine with their own hands. But at the same time they think little about the consequences. Experts say that the best option is to purchase a ready-made cooling lubricant.
Homemade products have many disadvantages:
- it is difficult to achieve stable fluid characteristics;
- alternative components do not always perform the stated functions;
- there is a high probability of damage to the coolant due to the development of fungus or rotting of individual components during storage.
If you prepare the liquid and coolant pump with your own hands, you will have to come into contact with chemically active components that can be dangerous to the skin and mucous membranes, and inhale toxic fumes. The result may be dizziness, nausea and other signs of poisoning, which should promptly consult a doctor. Therefore, it is better not to experiment, but to immediately purchase ready-made concentrated coolant for specific tasks.
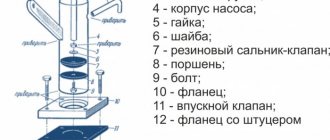
Lubricant replacement technology
by product Lubricant replacement technology
Before carrying out the coolant replacement procedure in the equipment, it is necessary to clean the system.
For this, a special composition is used. It allows you to prepare the system for filling with new lubricant. The cleaner removes traces of contaminants and removes remnants of the old composition from the system. At the same time, it has an antiseptic effect on internal surfaces.
Processing takes a minimum amount of time.
The procedure is carried out in several stages:
- 8 hours before the planned refilling of the lubricant, you need to pour a cleaner into the system. In this case, the old emulsion remains in the equipment. The concentration of the cleaner should be 3% (3 liters of cleaner will be required per 100 liters of emulsion).
- The machine operates for an entire shift (8 hours) in normal mode until the coolant is replaced.
- After this, you need to completely drain the old emulsion from the equipment. In this case, it is necessary to remove dirt, deposits and chips. They are washed out along with the lubricant.
- All equipment elements accessible for manual cleaning must be wiped with a rag. It is recommended to flush the system with liquid under pressure using a pump.
- The system is filled with water to the minimum level. You can prepare a weak emulsion (0.5%). This composition should circulate in the equipment for about an hour.
- The flush needs to be drained. The condition of the tank must be visually assessed. If there are contaminants, they are removed. They can be washed out of the system after flushing.
- If dirt and deposits have been washed out of the equipment, the washing is repeated several times until the tank is clean.
- Next, the emulsion is prepared. It is filled to the maximum level in the unit. The concentration of the composition is checked using a refractometer. The readings are recorded in a table. This allows for regular monitoring in accordance with existing requirements, comparing subsequent indicators with initial data.
Simple rules
To avoid unpleasant moments associated, for example, with overheating of the drill, strong heating of the drilling site, and others, you need to follow a few simple rules, which will allow you to make perfectly even holes without additional time and material costs. It must be taken into account that stainless steel has a viscous structure, therefore, in order to avoid overheating of the drill, stainless steel must be drilled only at low speeds. The drills should be as sharp as possible. In addition, to avoid severe overheating of the drilling site, which will significantly complicate further drilling of the material, it is necessary to reduce the temperature of the drill every 10 seconds.
If during the drilling process the chips become increasingly fine and dark, this indicates that the drill is dull and the hole in the stainless steel is overheating. Before continuing work, the drill must be sharpened or replaced with a new, sharper one. Drilling into stainless steel usually starts with small diameter drill bits, such as size five or four. Next, you can use drills of the required diameter to achieve the required hole size. As a result of such actions, you can significantly reduce drilling time and make the hole as smooth as possible.
Very few basics at the beginning.
Before work, you must select the cutting mode. What it is? Elements of the cutting mode when drilling
There are 3 main parameters: Cutting speed
when drilling, it is conventionally the peripheral speed (the speed of a point located on the surface) of the drill relative to the workpiece.
(In simple terms: "how fast the drill rotates", or the number of revolutions per minute depending on the diameter of the drill.) For example, the same cutting speed of 20 m/min is achieved if a drill with a diameter of 1.0 is rotated 6366 times per minute (rpm), and a drill with a diameter of 10.0 - 637 times per minute. Feed
– the amount of movement of the drill in the direction of the drilling axis per revolution in mm/rev (how quickly the drill immerses into the material).
Torque
perceived by the drill when cutting (what torsional load the drill experiences during operation).
These three parameters are mutually determining and their choice depends on: - the material being processed; - the material of the drill itself; -equipment on which work is performed and type of cooling; - other factors (surface roughness, contamination, etc.).
About
the features of drilling stainless steels
The main feature (difficulty) when working with stainless steel is related to its ductility. As a result, a kind of sticking occurs on the working surface of the drill, which leads to overheating of the tool and its failure. Therefore, it is important: – to ensure heat removal using cooling; – use drills that are more resistant to heat and allow better chip removal.
Made from high speed steel HSSCo (M35) or similar designations (HSSCo5, HSSE, P6MK5), these drills are specially designed and recommended for drilling difficult-to-cut and stainless steels.
1. The composition of R6M5K5 includes 5% cobalt, which significantly increases the red-hardness of the drill - the ability to maintain high hardness and wear resistance obtained as a result of heat treatment when heated to red-hot temperatures. 2. The drill is made using more expensive grinding technology - i.e. The drill bit is not twisted into a spiral (like rolled drills), but the flutes are formed on a grinding machine. As a result, there is no internal tension in the drill, and the surfaces are smooth, which significantly improves chip yield (important when drilling stainless steel). 3. The apex angle is 135 degrees with a cross-shaped point. This is the angle between the working edges of the drill (i.e., unlike conventional metal drills, cobalt drills look more “blunt”). This angle reduces the area of the drill’s working area, which reduces the load on it, and the cross-shaped point at the top reduces the dead zone (in this place the drill bears the greatest load) between the working edges.
How to drill ordinary stainless steel with a cobalt drill
If you can provide the correct cutting conditions,
i.e.
If you have a machine on which you can accurately set the speed, feed and provide cooling
, then we simply choose for stainless steel:
Cutting speed
V = 10 m/min is recommended by most manufacturers for working with stainless steels and is necessary for selecting speed.
Then the revolutions can be calculated using the formula: n=3180/D for a drill with a diameter of 1.0 - 3180 rpm, for a drill 5.0 already 636 rpm Feed:
0.005-0.01d mm/n, where d is the diameter of the drill .
This means that in one minute a drill with a diameter of 5 mm should drill a hole with a depth of about 3 mm, and a hole with a diameter of 10 mm is already 1.6 mm. Cooling: It is recommended to use oleic acid as a coolant .
Read also: Capacitor for starting an electric motor
If you work with an ordinary drill in “field conditions”
For cooling, you can take olive oil (it contains 81% oleic acid) or sunflower oil - up to 40%, and if it is absolutely impossible to use liquid, then you can use lard or fat - they contain up to 44% oleic acid. Drill at minimum speed (100-200 rpm). If the drill does not allow you to set the speed, use the on/off method and drill by inertia. Only the minimum feed (pressure on the drill), while trying to ensure a uniform feed.
1. It is a grave mistake to cool the drill by dipping it in water or something else (i.e., drill “dry” and then dip it, etc.). By these actions you instantly damage the drill. Rapid heating and cooling leads to unpredictable consequences, a kind of uncontrolled tempering or hardening. 2. Cobalt drills do not have to be yellow (bronze), cobalt is not a coating, it is part of the high-speed steel from which the drill is made. The coating is either: additional protection against corrosion, or it improves gliding, or it is just an image move by the manufacturer. 3. The given recommendations are valid when working with ordinary stainless steel; they have additional features when drilling thin-sheet stainless steel.
To prevent oil paint from drying out during storage and to prevent a film from forming on it, place a circle of thick paper on the surface of the paint and fill it with a thin layer of drying oil.
"The polyethylene film covering the balcony or greenhouse is protected from being torn off by the wind by a string stretched on both sides at intervals of 10-15 cm. "
» To make it easier to work with a concrete mixture, clay is usually added to it, but clay reduces the strength of the mixture. Add a spoonful of washing powder to it per bucket of water. "
“To prevent the screw, the head of which is hidden behind the obstacle, from rotating together with the tightened nut, you need to throw several turns of thread or thin wire over it and lightly tighten the ends. Due to friction, the screw is held well in place. The ends of the thread can be trimmed after tightening. "
» You can cut out the birdhouse entrance without a brace. It is enough to split the front side of the board in the center and cut out half-holes of the required size with a chisel or hatchet, and then connect the halves again. "
Coolant - do-it-yourself video
You can see how to make coolant for a machine yourself in this video. Its author needed a simple set of ingredients for the work: 72% laundry soap, waste oil, warm water. Tools include a convenient knife for grinding soap, two separate containers for mixing and heating the items listed above, plus an electric stove. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the preparation process:
If you prefer to use high-quality products with a predictable effect in your work, we recommend purchasing coolant for a lathe from a trusted manufacturer at Loc-Line. We will offer the optimal cutting fluid for your operating conditions, and advise on its use and replacement. For detailed information, call number 8 in St. Petersburg or write by e-mail