The use of fasteners is standard practice when assembling most modern products used in the household or industrial sphere. An important factor is a competent choice taking into account the technical characteristics. Fastenings must withstand not only the mechanical load that occurs after final installation, but also cope with the influence of external factors, ensuring strength, safety and reliability of operation. To make it easier to navigate the variety of existing types, there are markings of bolts - deciphering the designations allows you to clarify the properties of the hardware.
General overview
Metal fasteners manufactured in accordance with GOST standards differ in many parameters - from diameter and thread size to material class. The information necessary to understand the specifics of a particular product is applied to the head or cap. Before choosing, you need to calculate strength indicators, clarify the chemical composition and resistance to certain categories of substances, and also take into account special requirements related to operating conditions.
Bolt classification
There are many different types of bolts. The choice is made depending on what performance qualities the product being created should have. Bolts can be classified according to several criteria:
- Strength class. If we consider the most common tables, the strength class becomes the main criterion. It determines the possibility of using the product in certain cases. Special bolts can have high strength and are used in the construction of bridges or other critical structures. The strength class of fasteners is indicated by almost all manufacturers. This is due to the fact that the strength class determines the possibility of using products in certain conditions.
- Size classification is important. This is because as the cross-sectional area increases, the torsional resistance increases. However, larger fasteners require larger diameter holes. As for the length of the rod, it is selected depending on the thickness of the elements to be connected and the required length of the threaded connection.
- There are different types of heads. An example is a product with a hexagonal head or in the form of an octagon. It is worth considering that this indicator only determines which tool is most suitable for the job.
Types of bolts
Other indicators may be used to classify fasteners. For example, in some cases, the most attention is paid to surface hardness. However, the choice is often made taking into account the accuracy class. That is why the classification is carried out according to the accuracy class, which is indicated in regulatory documentation and during design.
How are bolts marked?
Symbols are regulated by the state standard, first adopted back in 1977. The last update of the regulations dates back to 2006, however, as practice shows, there are still quite a lot of old-style fasteners in circulation - which means that full-fledged operation requires the ability to read not only new, but also previous markings.
The basic codification of hardware involves the use of digital and letter designations. For products manufactured by domestic manufacturers, the following algorithm is considered a characteristic feature: the letters are located at the top, while the numbers on the bolts are printed directly below them.
The first GOST, No. 22353-77, provides for a special decoding procedure. First, as a rule, comes the manufacturer's mark - each plant has its own identification symbol, which uses elements of the Latin or Cyrillic alphabet. The number series, in turn, begins with the resistance indicator. After the digital combination, the HL marking may also be indicated, indicating that the hardware belongs to the category of products that can withstand low-temperature conditions without loss of strength characteristics. On models with non-standard threads, a small arrow is applied, directed counterclockwise.
The changes contained within the framework of GOST R 52644, approved in 2006, provide for the indication in numbers of bolt strength parameters - in accordance with the updated table of standards - as well as the climatic area of operation, batch number, strength and dimensions. To designate the latter, the standard metric system is used - for example, a marker 16x32 means that the cross-section of the hardware is 16 and the length is 32 mm.
Basic requirements according to GOST
- The part must be completely free of traces of metal corrosion, large defects and cracks. The presence of the latter means that the product does not meet the quality standard.
- Stamping cracks on the surface of the part are allowed, provided that the length of the crack is less than the bolt diameter, and the width and depth are not more than 4% of the bolt diameter. Otherwise, the product cannot meet the state quality standard and should be discarded.
- According to GOST, there may be bubbles on the bolt, but their size cannot be more than 3% of the diameter of the product.
- A bolt that has lacerations that extend into the threads or supporting part is also rejected.
- According to the quality standard, products with defects on the end of the head may be acceptable provided that the defect does not exceed the circumference of the limit value.
- A slight spot change in the color of the alloy in the form of ripples is allowed.
Ready-made solutions for all areas
Stores
Mobility, accuracy and speed of counting goods on the sales floor and in the warehouse will allow you not to lose days of sales during inventory and when receiving goods.
To learn more
Warehouses
Speed up your warehouse employees' work with mobile automation. Eliminate errors in receiving, shipping, inventory and movement of goods forever.
To learn more
Marking
Mandatory labeling of goods is an opportunity for each organization to 100% exclude the acceptance of counterfeit goods into its warehouse and track the supply chain from the manufacturer.
To learn more
E-commerce
Speed, accuracy of acceptance and shipment of goods in the warehouse is the cornerstone in the E-commerce business. Start using modern, more efficient mobile tools.
To learn more
Institutions
Increase the accuracy of accounting for the organization’s property, the level of control over the safety and movement of each item. Mobile accounting will reduce the likelihood of theft and natural losses.
To learn more
Production
Increase the efficiency of your manufacturing enterprise by introducing mobile automation for inventory accounting.
To learn more
RFID
The first ready-made solution in Russia for tracking goods using RFID tags at each stage of the supply chain.
To learn more
EGAIS
Eliminate errors in comparing and reading excise duty stamps for alcoholic beverages using mobile accounting tools.
To learn more
Certification for partners
Obtaining certified Cleverence partner status will allow your company to reach a new level of problem solving at your clients’ enterprises.
To learn more
Inventory
Use modern mobile tools to carry out product inventory. Increase the speed and accuracy of your business process.
To learn more
Mobile automation
Use modern mobile tools to account for goods and fixed assets in your enterprise. Completely abandon accounting “on paper”.
Learn more Show all automation solutions
Reading the markings
The order of arrangement of numeric and letter values is determined by the norms of the standard. Thanks to this, deciphering the technical specifications used in the implementation of construction, installation and production projects becomes much easier. A specialist who understands what the numbers on the head of the bolt mean can easily understand what specific fasteners we are talking about and what criteria should be used to select the material.
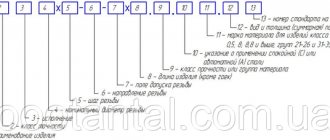
For clarity, it is worth examining the designations of fasteners, the technical characteristics of which are expressed using the following markings: A2M12x1.50 LH-4gx60.66. C.097. It is important to emphasize that, in accordance with the given sequence, the actual name must be indicated first. This applies to all marked products of the category in question, so in our case the word “bolt” will be placed before the alphanumeric combination.
The rest of the reading principle will look like this:
- The first in order is the letter A, which determines the accuracy class of the hardware. The existing gradation involves division into three groups (A, B, C), so in this example we are talking about the best possible option.
- Number 2 characterizes the performance format. The standards include 4 possible varieties, the first of which is not used for labeling.
- The letter M indicates the type of thread applied to the rod part of the fastener. There are three varieties - conical, trapezoidal and metric, which is discussed in this example.
- The number 12 is the millimeter diameter of the rod. It is curious that the combination of M12 markers is typical only for A-class products.
- 1.50 is a value characterizing the thread pitch. Moreover, in cases where the combination of dimensions is typical, inclusion in the description is not considered a mandatory condition.
- Similar to the previous point, the LH mark, indicating that a left-hand cut has been applied, belongs to the special category. If processing is carried out in a standard manner, the designation is excluded from the general list.
- The 4g marking on the bolt head indicates that the thread accuracy is at a basic level. The maximum possible indicator on the scale used is 8.
- The number 60 is the length of the hardware in millimeter terms.
- The number 66 is a strength characteristic, a dot is used to separate it from the previous value.
- C - grade of steel alloy selected during manufacturing. This particular marker is used in the production of fasteners made of “quiet” steel, while the letter A denotes “automatic” products.
- 097 - element coating. There are thirteen possible options, of which nine is galvanized. 7 in this case is the thickness of the outer layer in microns, equal to seven microns.
A designation on the bolt head that complies with a unified standard is a practical and convenient way to quickly and accurately select the required products. It is worth noting that the products of European and American manufacturers have a different description, including one that uses inches as the base measurement, so to read it you will need to use a conversion table.
Types of studs
Studs are another fastener made from a male threaded rod that forms a connection using a nut or threaded hole. Unlike a bolt or screw, a stud does not have a head, but instead has two threaded ends, or even a continuous thread along the entire length of the rod.
Studs are widely used for blind landings. Naturally, the length of the screwed end is strictly regulated. In accordance with GOST, it can only be 1; 1.25; 2; 2.5 from the thread diameter. The length of the second end in addition to the length of the threadless section can vary within wide limits.
In addition, studs are manufactured with equal thread lengths at the ends, as well as with continuous threads.
Studs according to DIN 975 and DIN 976 are the most common options. Essentially these are just long studs with a solid thread: their length is usually 1 or 2 m (but there are also 3 and 4 meters). The main difference is that DIN 976 can be of different lengths, and DIN 975 is only 1 or 2 m. More information about studs and their features can be found on our blog. Please note that for ease of operation, the rods are marked by coloring the ends depending on the material and strength class. Below is a table of the colors used.
| Strength class | Color |
| 4.8 | no color |
| 5.6 | brown |
| 5.8 | blue |
| 8.8 | yellow |
| 10.9 | white |
| 12.9 | black |
| A2-70 | green |
| A4-70 | red |
Did you like the material?
Features of marking high-strength hardware
Fasteners belonging to class 8.8 (or higher) represent a group of durable elements for which special requirements are imposed. This also applies to alphanumeric designations - for example, in accordance with GOST of 2006, the marking on the head of carbon steel bolts will look like W11.14 8.8S HL, where:
- W - manufacturer's mark.
- 11.14 - heat batch number.
- 8.8 is a parameter in which the product of the first number and 100 gives the maximum load for the thread, while the second number indicates a tenfold increase in the ratio of yield strength and strength.
- S - Compliance with the category of high-strength fasteners with a large hex head.
- HL - permissibility of operation at low temperatures.
Thus, deciphering the meanings used in labeling is also not particularly difficult - even taking into account the differences between the old and new standards.
Bolt GOST 7798-70 high-strength with hex head: bolt m6, m8, m10, m12, m16, m20, m24
| Catalog / high-strength bolt GOST 7798-70: bolts m8, m10, m12, m16, m20, m24, m27, m30 |
Bolt GOST 7798-70 with a hexagonal head of accuracy class B with a thread diameter from 6 to 48 is most often used in mechanical engineering, industry and construction as connection parts.
The high-strength bolt GOST 7798-70 works reliably in aggressive environments, under high-temperature loads and at low temperatures. May have a thread with a fine or large pitch.
BSR bolts are used to secure parts of building structures, pipelines, and equipment to concrete, reinforced concrete and brick structures of buildings and structures.
The most widely used bolts are M6, M8, M10, M12, M16, M20, type 1. Types 2 and 3 are made to order.
The material for the manufacture of bolts in accordance with GOST 7798-70 using the cold heading method on machines with thread rolling uses steel wire with increased manufacturing precision. Requirements for wire diameter depend on the model of the press machine and the design of the bolt.
Hole bolts having a tensile strength of 800MPa and above are called high-strength. They perceive high static and dynamic stresses. The material for this fastener is 40X steel. It is used in metallurgy, in the chemical, pharmaceutical industries, for work in the Far North and in all cases where it is necessary to ensure high joint strength.
Bolt size range: bolt M6, M8, M10, M12, M16, M20, M24, M27, M30, M36, M42, M48, M52.
Bolt GOST 7798-70 is a foreign analogue of GOST 7805-70 or DIN 931, ISO 4014.
DIN 933 - full thread.
Bolt drawing GOST 7798 70:
Steel grade and main bolt dimensions. Bolt GOST 7798-70 m6, m8, m10, m12, m16, m20, m24 with hex head.
| NTD | GOST 7798-70 |
| Size range | bolt M6 - M48 |
| Accuracy class | IN |
| Thread tolerance field | 6g |
| Strength class | 3.6 4.6 4.8 5.6 5.8 6.6 8.8 10.9 |
| steel grade | 10kp 20kp 10,20,35 20G2R |
Hex bolt GOST 7798-70. Buy a construction bolt.
| d | M8 bolt | M10 bolt | M12 bolt | M16 bolt | M20 bolt | bolt M22 | bolt M24 | M27 bolt | bolt M30 |
| Thread pitch | 1,25 | 1,5 | 1,75 | 2 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 3 | 3 | 3,5 |
| k | 5,3 | 6,4 | 7,5 | 10 | 12,5 | 14 | 15 | 17 | 18,7 |
| b* | 22 | 26 | 30 | 38 | 46/52 | 50/56 | 54/60 | 60/66 | 66/72 |
| S | 13 | 17 | 19 | 24 | 30 | 32 | 36 | 41 | 46 |
| e, min | 14,2 | 18,7 | 20,9 | 26,2 | 30 | 35 | 39,6 | 45,2 | 50,9 |
| L | 20-70 | 25-90 | 25-90 | 30-120 | 50-150 | 60-150 | 60-150 | 80-200 | 80-200 |
Hex bolt GOST 7798-70. Bolt weight GOST 7798 70. Theoretical weight of 1000 pieces of bolts (in kg).
| Length, mm | Theoretical weight 1000 pcs. bolts kg with nominal thread diameter d , mm | ||||||||||||||
| M6 | M8 | M10 | M12 | M14 | M16 | M18 | M20 | M22 | M24 | M27 | M30 | M36 | M42 | M48 | |
| 8 | 4,306 | 8,668 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 10 | 4,712 | 9,394 | 16,68 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 12 | 5,118 | 10,120 | 17,82 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 14 | 5,524 | 10,850 | 18,96 | 27,89 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 16 | 5,930 | 11,570 | 20,10 | 29,48 | 43,98 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 18 | 6,336 | 12,300 | 21,23 | 31,12 | 46,21 | 65,54 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 20 | 6,742 | 13,020 | 22,37 | 32,76 | 48,45 | 68,49 | 95,81 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 22 | 7,204 | 13,520 | 23,51 | 34,40 | 50,69 | 71,44 | 99,52 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 25 | 7,871 | 14,840 | 25,22 | 36,86 | 54,05 | 75,87 | 105,10 | 133,3 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 28 | 8,537 | 16,330 | 26,92 | 39,32 | 57,40 | 80,29 | 110,60 | 140,2 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 30 | 8,981 | 17,120 | 28,52 | 40,96 | 59,64 | 83,24 | 114,30 | 144,8 | 193,0 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 32 | 9,426 | 17,910 | 29,43 | 42,59 | 61,87 | 86,19 | 118,00 | 149,4 | 198,6 | 237,0 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 35 | 10,090 | 19,090 | 31,28 | 45,34 | 65,24 | 90,62 | 123,60 | 156,3 | 207,0 | 246,9 | 340,6 | — | — | — | — |
| 38 | 10,760 | 20,280 | 33,18 | 48,00 | 68,59 | 95,04 | 129,20 | 163,2 | 215,4 | 256,9 | 353,3 | — | — | — | — |
| 40 | 11,200 | 21,070 | 34,36 | 49,78 | 71,25 | 97,99 | 132,90 | 167,8 | 221,0 | 263,5 | 361,8 | 474,8 | — | — | — |
| 45 | 12,310 | 23,040 | 37,45 | 54,22 | 77,30 | 105,70 | 142,10 | 179,4 | 235,0 | 280,1 | 373,0 | 500,9 | — | — | — |
| 50 | 13,420 | 25,020 | 40,53 | 58,67 | 83,35 | 113,60 | 152,40 | 190,9 | 249,0 | 296,7 | 404,1 | 526,9 | 834,5 | — | — |
| 55 | 14,530 | 26,990 | 43,62 | 63,11 | 89,39 | 121,50 | 162,40 | 203,7 | 263,1 | 313,3 | 425,3 | 553,0 | 872,1 | 1304 | — |
| 60 | 15,640 | 28,970 | 46,70 | 67,55 | 95,44 | 129,40 | 172,40 | 216,0 | 278,9 | 329,9 | 446,5 | 579,0 | 909,8 | 1356 | — |
| 65 | 16,760 | 30,940 | 49,79 | 71,99 | 101,50 | 137,30 | 182,40 | 228,4 | 293,8 | 348,8 | 467,7 | 605,1 | 947,4 | 1407 | 2009 |
| 70 | 17,870 | 32,910 | 52,87 | 76,44 | 107,50 | 145,20 | 192,40 | 240,7 | 308,8 | 366,5 | 491,1 | 631,1 | 985,0 | 1458 | 2076 |
| 75 | 18,980 | 34,890 | 55,96 | 80,88 | 113,60 | 153,10 | 202,40 | 253,0 | 323,7 | 384,3 | 513,6 | 659,7 | 1023,0 | 1509 | 2143 |
| 80 | 20,090 | 36,860 | 59,04 | 85,33 | 119,60 | 161,00 | 212,40 | 265,0 | 338,6 | 402,1 | 536,1 | 687,5 | 1061,0 | 1561 | 2211 |
| 85 | 21,200 | 38,840 | 62,13 | 89,77 | 125,70 | 168,90 | 222,40 | 277,7 | 353,6 | 419,8 | 558,6 | 715,2 | 1098,0 | 1612 | 2278 |
| 90 | 22,310 | 40,810 | 65,21 | 94,20 | 131,70 | 176,80 | 232,40 | 290,1 | 368,5 | 437,6 | 581,0 | 743,0 | 1141,0 | 1663 | 2345 |
| 95 | — | 42,790 | 68,30 | 98,64 | 137,80 | 184,70 | 242,40 | 302,4 | 383,4 | 455,4 | 603,5 | 770,8 | 1181,0 | 1715 | 2412 |
| 100 | — | 44,760 | 71,38 | 103,10 | 143,80 | 192,60 | 252,40 | 314,7 | 398,3 | 473,2 | 626,0 | 798,5 | 1221,0 | 1766 | 2479 |
| 105 | — | — | 74,47 | 107,50 | 149,90 | 200,50 | 262,40 | 327,1 | 413,3 | 490,9 | 648,5 | 826,3 | 1261,0 | 1826 | 2546 |
| 110 | — | — | 77,55 | 112,00 | 155,90 | 208,40 | 272,30 | 339,4 | 428,2 | 508,7 | 671,0 | 854,1 | 1301,0 | 1880 | 2614 |
| 115 | — | — | 80,63 | 116,40 | 162,00 | 216,30 | 282,30 | 351,8 | 443,1 | 526,5 | 693,5 | 881,8 | 1341,0 | 1934 | 2690 |
| 120 | — | — | 83,72 | 120,90 | 168,00 | 224,20 | 292,30 | 364,1 | 458,1 | 544,2 | 716,0 | 909,6 | 1381,0 | 1989 | 2760 |
| 125 | — | — | 86,80 | 125,30 | 174,00 | 232,10 | 302,30 | 376,4 | 473,0 | 562,0 | 738,5 | 937,4 | 1421,0 | 2043 | 2831 |
| 130 | — | — | 89,89 | 129,70 | 180,10 | 240,00 | 312,30 | 388,8 | 487,9 | 579,8 | 761,0 | 965,2 | 1461,0 | 2098 | 2903 |
| 140 | — | — | 96,06 | 138,60 | 192,20 | 255,80 | 332,30 | 413,5 | 517,8 | 615,3 | 806,0 | 1021,0 | 1541,0 | 2207 | 3045 |
| 150 | — | — | 102,18 | 147,50 | 204,30 | 271,60 | 352,30 | 438,1 | 547,6 | 650,8 | 850,1 | 1076,0 | 1621,0 | 2315 | 3187 |
| 160 | — | — | 108,38 | 156,40 | 216,40 | 287,40 | 372,30 | 462,8 | 577,5 | 686,4 | 895,9 | 1132,0 | 1701,0 | 2424 | 3329 |
| 170 | — | — | 114,58 | 165,30 | 228,50 | 303,20 | 392,30 | 487,5 | 607,4 | 721,9 | 940,9 | 1188,0 | 1780,0 | 2533 | 3471 |
| 180 | — | — | 120,68 | 174,20 | 240,60 | 319,00 | 412,30 | 512,2 | 637,2 | 757,5 | 985,9 | 1243,0 | 1860,0 | 2642 | 3614 |
| 190 | — | — | 126,88 | 183,10 | 252,70 | 333,80 | 432,30 | 536,9 | 667,1 | 793,0 | 1031,0 | 1299,0 | 1940,0 | 2751 | 3756 |
| 200 | — | — | 133,08 | 191,90 | 264,70 | 350,60 | 452,20 | 561,5 | 697,0 | 828,6 | 1076,0 | 1354,0 | 2020,0 | 2860 | 3898 |
| 220 | — | — | — | 209,70 | 228,90 | 382,20 | 492,20 | 610,9 | 756,7 | 899,6 | 1166,0 | 1465,0 | 2180,0 | 3077 | 4182 |
| 240 | — | — | — | 227,50 | 313,10 | 413,80 | 532,20 | 660,3 | 816,4 | 970,8 | 1256,0 | 1576,0 | 2340,0 | 3295 | 4466 |
| 260 | — | — | — | 245,20 | 337,60 | 445,40 | 572,20 | 709,6 | 876,1 | 1042,0 | 1346,0 | 1687,0 | 2500,0 | 3513 | 4751 |
| 280 | — | — | — | — | 361,50 | 476,90 | 612,20 | 759,0 | 935,9 | 1113,0 | 1436,0 | 1798,0 | 2660,0 | 3730 | 5035 |
| 300 | — | — | — | — | 385,70 | 508,50 | 652,20 | 808,3 | 995,6 | 1184,0 | 1526,0 | 1910,0 | 2820,0 | 3948 | 5319 |
The thread length indicated in the denominator is for bolts with a length greater than 120.
It is possible to supply high-strength bolts in accordance with GOST 7798-70 in sizes from M6 to M24, strength classes 8.8, 10.9, made of steel 20G2R.
Example of a symbol:
Bolt GOST 7798-70 version 1 with thread diameter d
=8 mm, with a turnkey size
S
=13 mm, length
l
=60 mm, with a large thread pitch with a tolerance range of
6g
, strength class 5.8, uncoated:
Bolt M8 - 6gx60.58 (S13) GOST 7798-70
Bolt 7798-70 version 2 with thread diameter d
=10 mm, with a turnkey size
S
=16 mm, with a fine thread pitch with a tolerance range of
6g
, strength class 10.9, made of steel grade 40X, with coating 01 6 microns thick:
Bolt 2М10х1.25 - 6gх60.109.40Х.016 GOST 7798-70
Bolt GOST 7798-70 version 3 with thread diameter d
=12 mm, with a turnkey size
S
=18 mm, length
l
=60 mm, with a large thread pitch with a tolerance range of
6g
, strength class 5.8, uncoated:
Bolt 3M12 - 6gx60.58 (S18) GOST 7798-70
Bolt 7798 version 1 with thread diameter d
=16 mm, with turnkey size
S
=24 mm, with fine thread pitch with a tolerance range of
6g
, strength class 10.9, made of steel grade 40X, with coating 01 6 microns thick:
Bolt M16x1.25 - 6gx60.109.40X.016 GOST 7798-70
Bolt GOST 7798 version 2 with thread diameter d
=20 mm, with a turnkey size
S
=30 mm, length
l
=60 mm, with a large thread pitch with a tolerance range of
6g
, strength class 5.8, uncoated
Bolt 2M20 - 6gx60.58 (S30) GOST 7798-70
Sale of bolts: M6, M8, M10, M12, M16, M20, M24, M27, M30, M36, M42, M48, M52 of various lengths from 0.05 tons.
How to buy bolts GOST 7798-70: bolts m8, m10, m12, m16, m20, m24 at low prices:
- fill out the simple “Place an order” form at the top of the page;
- call on the phone +7;
- send your application by email;
Delivery of GOST 7798-70 bolts throughout the Russian Federation: Moscow, St. Petersburg, Arkhangelsk, Astrakhan, Barnaul, Belgorod, Bryansk, Vladimir, Volgograd, Vologda, Voronezh, Yekaterinburg, Ivanovo, Izhevsk, Yoshkar-Ola, Kazan, Kaluga, Kirov, Kostroma , Krasnodar, Kurgan, Kursk, Lipetsk, Omsk, Orenburg, Penza, Perm, Pskov, Rostov-on-Don, Ryazan, Samara, Saransk, Saratov, Sevastopol, Simferopol, Smolensk, Stavropol, Tambov, Tver, Tomsk, Tula, Tyumen , Ulyanovsk, Ufa, Chelyabinsk, Yaroslavl, etc.
The information presented on this website contains a catalog of reference information on more than 3,000 types of metal products, is for informational purposes only, and can be used in various areas of enterprise activity.
| Steel wire Welding electrodes Steel rope Fasteners | Metal mesh Hex bolts Nut GOST, DIN Steel rivets | Adjustable cotter pins GOST, DIN washers Threaded rods Calibrated rolled products | Slings, rigging Construction nails Steel cable Screws GOST, DIN |
What markings are applied to stainless bolts?
But in the case of hardware, for the manufacture of which austenitic steels are used, the alphanumeric code will differ from the previous version. Such products are usually marked as A2-50 or A4-60, with the possible addition of the manufacturer's mark at the beginning. The letter A and the number after it characterize the specific grade of the alloy, while the second group of numbers represents a value equal to one tenth of the tensile strength established for carbon-type models. Thus, the A4-80 marker applied to the fasteners will indicate that they are made of stainless material with the addition of molybdenum, and are capable of withstanding mechanical loads of up to 800 MPa, corresponding in their characteristics to elements made of carbon steel of category 8.8.
Bolt strength
In addition to the material, the main quality of a fastener is its reliability. After all, everyone who deals with various types of bolts and nuts hopes that such a connection will withstand the load.
There are eleven strength classes in total: starting from 3.6 and ending with 12.9. More information about this can be found in GOST R 52627-2006 or its analogue ISO 898/1-78.
High-strength bolts are considered to be products that belong to strength classes 6.8, 8.8, 9.8, 10.9 and 12.9. Such bolts are often used in the production of parts for agricultural machinery, machine tools, railway fastenings, as well as in bridge construction.
Fasteners below class 6.8 are considered weak and are used to create structures that are not subject to heavy loads. For example, such products are used in the production of small-sized equipment and furniture.
Modern requirements
The updated standards, which determine what the numbers and letters mean in the markings on the bolt heads, are not much different from the previous edition, both in terms of meaning and in terms of the location of the elements. The addition of strength characteristics, as well as other nuances related to operational properties, is not considered by experts as a radical change - however, for those whose professional activities are closely related to design and assembly, it is important to be able to read not only the old, but also the new format.
Markings
The class indicator - two numbers written through a dot, or sequentially - is one of the most significant characteristics. The first number is used to describe 1/100 of the nominal strength limit of the fastener, measured in MPa, the second shows the ratio of the yield and strength limits, which must be multiplied by 10 to obtain the final value. This, in fact, is the maximum working load of the hardware used - when calculating connections, a coefficient of 0.5-0.6 is used, which excludes exceeding the permissible norm.
What do the numbers on stainless steel bolts mean?
Austenitic products are marked indicating the specific type of alloy (A2, A4), as well as one tenth of the limit value (50, 60, 70) characteristic of carbon compositions.
Nut markings
In the case of elements of this category, a similar designation principle applies, however, due to limited space, the information is located on the side and is presented in an abbreviated format. To read completely, you will need the original packaging and accompanying specifications.
The marking order remains unchanged - name, accuracy level, thread type, diameter, pitch and direction (for non-standard cutting), strength characteristics and coating thickness in microns. At the same time, at the end of the description, GOST is indicated, which corresponds to the manufacturing technology of a specific model, which is why not all of the specified points are necessarily included in the designation.
M20 bolt wrench dimensions (conditions for the possibility of tightening the nut)
For prefabricated keys
Turnkey location according to GOST 2839-80 – stroyone
For keys according to GOST 2839-80
Prefabricated space – stroyone.com
Dimensions in mm
| Dimensions | For keys according to GOST 2839-80 | For prefabricated keys |
| Dmin | 55 | 26 |
| Amin | 35 | 36 |
| Bmin | 40 | 32 |
| Cmin | 45 | 22 |
| Emin | 28 | 30 |
| Fmin | 16 | — |
| Gmin | — | 39 |
Ready-made solutions for all areas
Stores
Mobility, accuracy and speed of counting goods on the sales floor and in the warehouse will allow you not to lose days of sales during inventory and when receiving goods.
To learn more
Warehouses
Speed up your warehouse employees' work with mobile automation. Eliminate errors in receiving, shipping, inventory and movement of goods forever.
To learn more
Marking
Mandatory labeling of goods is an opportunity for each organization to 100% exclude the acceptance of counterfeit goods into its warehouse and track the supply chain from the manufacturer.
To learn more
E-commerce
Speed, accuracy of acceptance and shipment of goods in the warehouse is the cornerstone in the E-commerce business. Start using modern, more efficient mobile tools.
To learn more
Institutions
Increase the accuracy of accounting for the organization’s property, the level of control over the safety and movement of each item. Mobile accounting will reduce the likelihood of theft and natural losses.
To learn more
Production
Increase the efficiency of your manufacturing enterprise by introducing mobile automation for inventory accounting.
To learn more
RFID
The first ready-made solution in Russia for tracking goods using RFID tags at each stage of the supply chain.
To learn more
EGAIS
Eliminate errors in comparing and reading excise duty stamps for alcoholic beverages using mobile accounting tools.
To learn more
Certification for partners
Obtaining certified Cleverence partner status will allow your company to reach a new level of problem solving at your clients’ enterprises.
To learn more
Inventory
Use modern mobile tools to carry out product inventory. Increase the speed and accuracy of your business process.
To learn more
Mobile automation
Use modern mobile tools to account for goods and fixed assets in your enterprise. Completely abandon accounting “on paper”.
Learn more Show all automation solutions
Strength classes of threaded fasteners
According to the standard classification, there are seven categories for nuts (4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12), which, as in the case of hardware, indicate 1/100 of the total limit value determined when calculating the pressure on the structure. However, there are also differences - in particular, these categories apply only to parts with a standard and high profile, while the designations 04 and 05 are applied to the sides of low models, indicating that this option is not suitable for operation under high load conditions.
Strength
Strength is strictly regulated by GOST, since in some cases this affects human safety and the safety of equipment or buildings. To achieve accurate strength characteristics, high-strength bolts are calculated. The production of high-strength bolts is regulated by GOST 7798-70.
Based on their strength characteristics, bolts are divided into 11 classes. Each category has its own labeling, based on which you can clearly determine which class it belongs to and what load it can withstand. It should be noted that each hardware has a certain margin of safety to the indicators indicated in the marking. Therefore, you should not worry that the safety margin of the bolt will be used for future use.
The strength of bolts depends not only on the type of material used, but also on the manufacturing technology. Based on the strength characteristics of fastening elements, we can distinguish the classification of bolts by strength:
- 3.6 – fasteners made of non-alloy steel, without additional hardening;
- 4.6 – products made of carbon steel (carbon less than 0.55%);
- 5.6 – from steel without tempering (carbon more than 0.15%);
- 6.6 and 6.8 – bolts made of carbon steel without additional additives;
- 8.8 – steel with additional components (chrome, manganese, boron) is used, which after hardening is tempered at a temperature of more than 400 degrees;
- 9.8 - practically no different from class 8.8, having an increased strength index;
- 10.9 - steel with additives is used, which is tempered in the temperature range from 340 to 425 degrees.
- 12.9 – alloy steel with a minimum content of phosphorus and sulfur is used for the manufacture of fasteners.
The importance of choosing the right fasteners
The products offered by modern manufacturers differ from each other in terms of technical and functional characteristics. Bolts, studs, screws, nuts - to solve each specific problem, the appropriate equipment is required. The main indicators depend on the grade of steel used for manufacturing - when selecting a suitable option, it is worth paying special attention to the parameters that a particular alloy provides, as well as the conditions and the maximum load that can arise during the use of fasteners.
Nuances associated with labeling
The generally accepted norms on which state standards are based correspond to the system developed by the International Organization for Standardization. In addition to the features and requirements already discussed, there are several more rules that must be taken into account by manufacturers of fasteners:
- Bolts and screws with a diameter of more than 6 mm are required to be marked, while for products with a smaller cross-section the procedure is voluntary.
- The alphanumeric designation is not applied to hardware with a cross-shaped or straight slot, as well as to fasteners made without stamping, while hexagons with any head shape must be designated in all cases.
- For marking, the end or side of the cap is used, while in the second option the method of applying in-depth marks is used. Convex elements are subject to restrictions directly related to the thread diameter - the maximum permissible value is 0.3 mm.
The geometry of various types of threaded fasteners is regulated by separate standards that require strict compliance.
Pros and cons of threaded connections
The advantages that determine the demand in everyday life and industry for products with applied threads include:
- Versatility and reliability.
- Strength characteristics.
- Resistant to axial and lateral loads.
- Ease of installation and disassembly.
- Affordable cost of organizing work.
Among the shortcomings, one can note only the increased stress in the section of the depression profile, which necessitates the need for a competent choice of marking technique. Matching loads reduces the risk of accidental loosening or tearing.
Types of threaded fastening
The considered principle of connecting elements is based on the use of at least two parts, the first of which has an external thread, and the second - an internal thread. The following types of configurations are distinguished:
- Bolted - the formation of through holes with the subsequent insertion of a rod tightened from the reverse side.
- Screw - in this case, the base itself acts as a retainer, the channels in which are prepared in advance, or - when using self-tapping screws - are formed during the integration process.
- Using studs, one of the ends is screwed into the component part, and the corresponding nut is screwed onto the second in a special way.
Quality control
All products are controlled according to two parameters: visual compliance with the standard and metallographic examination. During visual quality control, the product is inspected for deviations from the state standard in size and diameter, the presence of mechanical damage and defects, as well as the presence of corrosive changes. Metallographic evaluation involves magnetic examination. For a more detailed study of the composition of the part, the metal etching method can be used. These techniques make it possible to accurately determine the amount of impurities in alloys and the nature of the material from which the product was made. If a part does not meet the standards, it is rejected.