When operating a car, its owner is invariably faced with the need to maintain and replace the battery. Such a battery is subject to increased load, so over time the battery begins to hold a charge worse, requiring appropriate replacement. The efficiency of such a car battery is directly influenced by the density of the electrolyte. It is necessary to regularly check the density of the electrolyte, which will ensure trouble-free engine starting, and the battery itself will last as long as possible without causing any trouble. In this article we will tell you how to check the battery density.
Battery device
Before talking directly about how to check the density of the electrolyte in a battery, let's talk about the structure of standard car batteries. This battery consists of:
- A body consisting of six cans.
- Plus and minus lead plates located inside each can.
- The positive and negative buses that connect each sealed compartment.
- Serial connection, which allows you to obtain the required charging power at the output.
The battery owes its ability to release and accumulate electrical charge precisely to the electrochemical properties of the electrolyte. This electrolyte is poured into each of the sealed jars and has certain density indicators. During the operation of the car, the density indicator may change, so the car owner needs to know how to check the battery density at home and, if necessary, increase or decrease this indicator.
Review of popular hydrometer models
Car owners who are faced with measuring acidity for the first time are wondering what kind of hydrometers there are for measuring electrolyte density and what their prices are. Modern manufacturers offer several varieties of these devices, which differ in cost, appearance, and functionality.
The most popular are:
- Sparta 549125. A model with compact dimensions, a durable glass body and low cost.
- SKYBEAR 623000. Inexpensive Chinese equivalent, according to reviews, a good thing for the money.
- Orion AR-02. Density meter for electrolyte of domestic production (NPP Orion, St. Petersburg). The flask is glass, but, according to the owners, the float constantly sticks to it, which makes you a little nervous during the measurement process.
- Refractometers (digital hydrometers). These are tools for professional use. They can measure the characteristics of many different liquids, of which motorists will find the acidity of the electrolyte and the temperature of the antifreeze (antifreeze) useful. They are expensive, but they can be adjusted using distilled water, which allows you to always correctly determine the parameters, regardless of external conditions. You can order a digital hydrometer from the Chinese.
Read also: Installation of an intercom calling panel
Budget density meters can be purchased at prices ranging from 100 to 600 rubles. Professional tools cost from 800 rubles.
How to properly maintain your battery
The trouble-free operation of such a car battery depends on the timeliness and correct maintenance of the battery. Such work includes:
- Visual inspection.
- Electrolyte level analysis.
- Checking battery density.
- Voltage level measurement.
- Checking the battery with a load fork.
This battery check must be performed twice a year - in spring and autumn. This will ensure high-quality battery operation both in summer and in cold winter. Maintenance and proper care of the battery is not particularly difficult. If the density of the electrolyte is higher than normal, it is necessary to add distilled water. If low density is noted, then you should simply charge the battery.
When and what to top up the battery with?
The need to add working fluid to the battery occurs infrequently, but it is sometimes necessary. What, how much and in what cases should I add? There are two such cases: low electrolyte level and abnormal acidity of the working fluid.
We recommend: Ista battery: types of car batteries
Low level in sections
This situation occurs often because during battery operation the water evaporates or, as they say, boils away. In this case, the level of solution in the sections decreases, and the edges of the plates turn out to be dry. This can be determined visually by simply unscrewing the plugs from the sections and looking into the filler necks. The normal liquid level in the section should be approximately 1 cm above the cut-off level of the plates. Some batteries even have a special mark stamped on the case. If the level is low, then the situation, although serious, can be easily eliminated. For this operation you will need:
- a medical syringe without a needle or a car hydrometer;
- distilled water;
- protective equipment (glasses and rubber gloves).
Distilled water is drawn into a syringe and poured into the appropriate sections to the required level. After adding liquid to the battery, it is placed on charge. In this regard, an autohydrometer is much preferable, since by adding water, you can immediately control the density of the solution.
Be careful not to work with acid unless your eyes are protected.
Battery operating principle
The battery in a car works cyclically, that is, the battery first accumulates a charge, and then releases it when you need to start the engine. During such cycles, a chemical reaction occurs inside the battery, when various salts fall out of the sulfuric acid, which settle on the lead plates, and water is released from the electrolyte in the jars. Over time, the concentration and density of the electrolyte changes, which leads to improper operation of the battery. Periodic density measurements will help avoid battery discharge, which will last as long as possible. Let's talk in more detail about how to check the density of a battery with a hydrometer.
Attention. If the density indicator is below normal, then electrolyte should not be added to the battery. It is necessary to recharge the battery, which will ensure the required density.
What does irresponsibility lead to?
When the driver constantly adds only water to the battery level, the normal density of the electrolyte drops; in winter, such a battery will simply burst with ice. There is more water in it than acid, which means that when the temperature drops, it will turn into ice. And ice, as you know, expands, which is why the battery case ruptures.
In the summer, such a battery is quickly discharged, despite a working generator and constant stationary recharging. When it gets colder, at temperatures around zero, the car will not start. Since the density also decreases as the temperature decreases. The charge level drops automatically.
How and why is the density of an electrolyte measured?
Many car owners simply do not know why they should measure the density of the electrolyte in the battery. As you know, the electrolyte consists of 35% sulfuric acid and 65% distillate. This ratio makes it easy to accumulate a charge without causing any harm to the lead plates. During operation, the density of the electrolyte may change, which is explained by the evaporation of distilled water and chemical reactions during battery operation. As a result, the content of sulfuric acid increases, which in turn degrades the charge and can harm the lead plates, up to the complete deterioration of the battery.
Checking the density of the working fluid
To measure the density of liquids, there are special instruments - hydrometers or density meters. There is one for car batteries as well. It is made in the form of a large syringe, inside of which there is a float with a specially graduated scale.
The autohydrometer float is equipped with a special “syringe” for working in narrow-necked sections of batteries.
In order to measure the density in the battery, plugs are rolled off from all its sections. Next, the hydrometer bulb is compressed, and its needle is immersed in the section. After releasing the bulb, draw electrolyte into the syringe. In this case, the float of the device floats up. The density of the liquid is read from the scale according to the level to which the float floats.
The float rose to level 1.200. Electrolyte density is 1.2 g/cm. cube .
After the measurement, the bulb is squeezed again, and after draining the electrolyte back into the battery, the hydrometer is washed with running water and dried. We should not forget that each section is a separate, independent part of the battery, so the density must be measured in each.
Checking the electrolyte level
Before checking the battery density without a hydrometer, you need to set its level. If the battery itself is made of translucent plastic, then checking the electrolyte level is not difficult. If the battery is made of opaque dark plastic, then to check the electrolyte level you will need a special glass tube with a diameter of about 5 millimeters. Such a tube is lowered into the jar until it stops, after which its upper hole is closed with a finger. The tube is carefully removed from the battery. Electrolyte will remain in it, which is poured into the flask and the level is checked. It is believed that the amount of liquid in the flask will be 10-15 millimeters. If the level is higher or lower, it is necessary to level it, and then measure the density of the electrolyte.
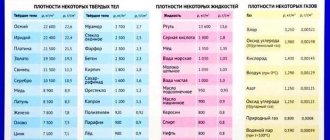
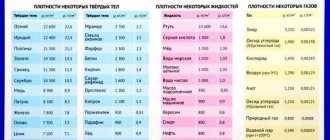
Parameter – density (p)
A scalar physical quantity, which is determined by the ratio of the mass (m) of a body to its volume (V), is the concept (p). For lead-based battery electrolyte, this value will be expressed in grams per cubic cm.
It is impossible to determine (p) an acidic substance by eye. To accurately measure it, you will need a special “unit”.
How to measure electrolyte density
If you are wondering how to properly check the density of a battery, we can say that such work is not particularly difficult. Just remember that the banks inside the battery are not connected to each other, so you should check the density in each of the containers. It is prohibited to turn the battery over and mix electrolyte with each other to equalize the density. The battery cover and plugs must be clean and free of any contamination. The density check is performed exclusively on a charged battery, otherwise the measurements will be incorrect.
Before checking the density of a maintenance-free battery, it must be removed from the car and kept for several hours at room temperature. The optimal temperature range when measuring density is 20-30 degrees.
To measure density, you will need to use a hydrometer, also called a densimeter. On sale you can find a variety of hydrometers that have a similar design, but at the same time differ in their cost. When choosing such a device for measurement, it must be tested on a calibration liquid, which will allow you to be completely confident in the accuracy of such measurements.
Most hydrometers have the same design and provide the required accuracy. And yet you should not purchase the cheapest Chinese samples, since their quality and measurement accuracy will correspond to the cost.
Measuring the density of an electrolyte using a hydrometer is not difficult. The following must be done:
- The tip of the hydrometer is being wiped.
- It is lowered into a flask for measurement.
- Using a pear, collect the electrolyte and fill the flask with it.
- They wait a few minutes and then check the readings.
- Drain the electrolyte back.
- Similar work is carried out with each of the cans in the battery.
Optimal electrolyte density
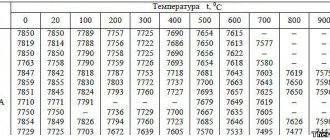
When operating the battery and measuring the density of the electrolyte, you should remember that the indicators may fluctuate depending on the climate in the region.
- For southern Russia, the optimal density indicator is 1.25.
- For the middle band - 1.27.
- For the north - 1.29.
When making batteries, a standard electrolyte is poured into the battery, which freezes at temperatures below 60 degrees and has a density of about 1.26-1.27 grams per cubic centimeter.
If the measurement showed an increased density of the electrolyte, distilled water must be added to the battery. You can purchase such a distillate at gas stations or in specialized stores. Do not use regular tap water. Add distillate by eye, and then check the density of the electrolyte again.
Important. The lead plates of the battery must be completely immersed in the liquid. Based on this, you should add distillate or additionally charge the battery.
Changes in the density of the electrolyte inside the battery occur for natural reasons. However, if you notice that the battery quickly loses charge, and the density readings change literally a week after they are leveled and topped up with distillate, this indicates serious problems with the battery, which will soon require replacement.
Design and principle of operation of the battery
In order to properly service the battery and ensure its proper operation, it is necessary to at least approximately understand what is inside it and how it all works. Therefore, before moving on to questions about the electrolyte, it is necessary to understand how a car battery works and on what principle it works.
Battery design
Almost all lead-acid batteries have the same design. They consist of separate sections (cans), each of which has a set of positive and negative plates. The first are called cathode and are made of metal lead. The second, anode, are made of lead dioxide. The plates are collected in a bag and placed in an acid-resistant container, into which the working fluid is subsequently poured - an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid or the so-called electrolyte.
Lead-acid battery section design:
- 1 – jar lid;
- 2 – can body;
- 3 – ribbed settling tank;
- 4 – plates collected in a package;
- 5 – negative (anode) terminal;
- 6 – negative (anode) plates;
- 7 – dielectric gasket – separator;
- 8 – positive (cathode) terminal;
- 9 – positive (cathode) plates.
The finished sections connected in series are the battery. There are three such sections in six-volt batteries, and six in 12-volt batteries.
How it works
So, the design of the battery is quite simple, but how does voltage appear at its terminals? Indeed, if you take a battery straight from the store and connect a voltmeter to it, the device will show “0”. The lack of current is due to the fact that the electrolyte is not poured into the battery immediately after manufacture, and the plates in the battery standing on the store shelf are dry. The working fluid is poured into the battery after purchase.
It's time to find out what the electrolyte is for . Since the positive and negative plates have different chemical compositions, a potential difference arises between them when immersed in an acid solution (about 2 V per section, which determines the number of sections in the battery). When a load is connected to the battery terminals, current begins to flow between the plates due to the high electrical conductivity of the electrolyte. At the same time, the chemical process of converting lead dioxide into lead sulfate begins with the participation of sulfuric acid. As soon as the amount of dioxide and sulfuric acid drops to a certain level, the process will stop and the battery will stop producing current - it will be discharged.
During the discharge process, sulfuric acid and lead dioxide are consumed to form lead sulfate
We recommend: Comparison of batteries from the top car batteries
But batteries, unlike galvanic cells (batteries), can restore their chemical properties. If you connect the battery to a DC source, then under its influence the sulfate will begin to decompose into lead dioxide and sulfuric acid. The battery will begin to charge, converting electrical energy into chemical energy. As soon as the amount of dioxide and acid reaches the initial values, the battery can be considered charged.
Chemical processes that occur in a battery when it is discharged and charged
Sulfuric acid, which is part of the electrolyte, plays one of the main roles in the operation of the battery. The quality and long-term operation of the battery as a whole will depend on its properties.
How to measure density in maintenance-free batteries?
If checking the density and level of electrolyte in maintained batteries is not difficult, then how to check the density of the electrolyte in a maintenance-free battery. Such batteries have a small peephole in the top cover, which can be unscrewed and through the hole that appears, the density of the car battery can be checked. Just remember that in maintenance-free batteries it will be possible to measure the density of the electrolyte in one jar, so you will get an average reading. You will not be able to take accurate measurements for each of the cans.
What is a hydrometer
A device for measuring the concentration of various solutions is called a hydrometer. The operation of the density meter is implemented on the basis of a well-known physical law.
Archimedes' principle states that if a body is immersed in a liquid, a hydrostatic or lifting force will begin to act on it. In modulus it will be equal to the weight of the liquid that the body displaced, but opposite in direction.
For practical use, the hydrometer scale is graduated to the concentration of the dissolved substance. Car enthusiasts will find a useful device for checking the density of electrolyte and antifreeze.
Antifreeze density measurement
A significant characteristic of antifreeze is its freezing temperature, which is important when operating the cooling system in winter. This indicator directly depends on the density of the liquid, or more precisely on the specific gravity of the substance (ethylene glycol or propylene glycol) contained in the coolant. Using a hydrometer, you can find out the density of antifreeze and determine its freezing point.
It is important to remember that most antifreezes contain ethylene glycol, which is toxic to humans and animals. All work with it, including measurements, should be carried out in a well-ventilated room or in the open air.
Prolonged exposure to the substance causes skin irritation.
When carrying out work, observe safety precautions - use gloves and safety glasses.
Antifreeze density readings do not say anything about its quality. Such a measurement is necessary only to determine its freezing temperature. This is most often done if you dilute antifreeze with distilled water before pouring it into the cooling system.
Reduced solution density
If the hydrometer test reveals low acid concentration in one section, the battery will need to be monitored. It is likely that a short has occurred between the plates and the power supply has reached the end of its service life. Option two is sulfation of the plates, which occurs due to deep discharge or insufficient charging voltage on the car.
You can make the electrolytic liquid denser in three proven ways:
- evaporation of excess water through prolonged charging and slow boiling;
- replacing part of the acidic solution with a more concentrated one;
- adding sulfuric acid.
To implement the first method, you will need a charger whose current is manually adjusted. The procedure looks like this:
- Determine the charging current by taking 3% of the initial battery capacity. Example: a 60 A*h battery needs to be charged with a current of 60 x 0.03 = 1.8 A.
- Place the autonomous power supply on charge and wait for bubbles to appear.
- Adjust the charge current and measure the density as the water evaporates. When it reaches the norm, turn off the “charger”.
If during the boiling process the liquid level drops significantly, you will have to buy a ready-made electrolyte with a standard density of 1.27 g/cm3 and add the required amount to the jars.
Replacement of the acid solution is carried out by analogy with adding distilled water. The liquid is sucked out of the well with a pear, and a denser solution purchased at the store is poured in its place. Electrolytes with values of 1.34–1.41 g/cm3 are commercially available. Then the density is checked, if necessary, adjustments are made and the battery is fully charged.
The difficulty of the third option lies in the absence of a high concentration sulfuric acid solution - it is almost impossible to find and buy it. If you managed to get the specified chemical, add it to the jars in small portions, literally 1 cm3, using a syringe
Proceed with caution and use personal protective equipment - sulfuric acid is very aggressive