Why do you need chrome plating?
Using chrome plating you can make the part more durable. This way you can protect it from external damage that occurs during operation. The chromium layer improves reflective properties. The processed part acquires a metallic shine and looks more aesthetically pleasing. By adding dyes to the reagent, you can achieve the desired shade.
Chrome can be used to cover not only plastic, but also metal elements. Car owners chrome rims, interior plastic elements, and sometimes even the entire car body.
Coverage options
Various dyes are added to chrome paint, which creates a unique special effect.
Classic
The composition with the natural white-silver color of aluminum is considered classic. The surface looks mirror-like, as if covered with white foil. Classic white imitation chrome can be found in the design of furniture parts for living rooms, bedrooms and kitchens, as well as on curtain rods and jewelry.
Black chrome
A translucent black dye is added to the aluminum powder. Dark paint looks impressive on car rims and grilles. A more discreet option is matte chrome. It lacks an eye-catching shine. The surrounding objects are only reflected in muted colors. Matte finishes are more often used in interiors.
Colored chrome plating
Of the colored paints, golden compositions are the most popular. They contain yellow metallic powder. Using yellow shades, they create an imitation of gold or brass. Like classic silver, gold plating is found on lamp shades and stands of lamps, floor lamps, curtain rails, door handles, and home decor.
Expert opinion
Zakharova Irina Yurievna
Cleaning professional with 15 years of experience. Our best expert.
How to prepare for work
Chrome plating of plastic requires preparation. In order to do chrome plating, you will need to purchase special equipment, which is quite expensive. Therefore, if you are planning a one-time procedure, then it is better to turn to specialists, it will be much cheaper. If you plan to carry out chrome plating often, then you can take on this matter personally.
It should be kept in mind that chrome plating of plastic is carried out using caustic, volatile chemicals. Therefore, the room in which the work will be carried out must be well ventilated. A living space is absolutely not suitable for such a procedure; it is better to do chrome plating in a garage, basement or workshop. Volatile acidic substances evaporated during the procedure settle on interior items and can react with them and destroy them. You should also take care of personal hygiene products and stock up on the following items:
- respirator;
- rubber gloves;
- safety glasses;
- oilcloth apron.
During work, you need to protect your skin from contact with reagents, as chemicals will cause burns. There is also no need to inhale toxic acid fumes, this will negatively affect the condition of the body.
Technological features
Not only plastic products, but also metal parts can be chrome-plated. It should be borne in mind that this procedure uses chemicals that may pose a hazard to human health, so it should only be performed in a well-ventilated area. Chemical reagents can not only have a detrimental effect on the respiratory system, leading to poisoning, but also cause burns when they come into contact with the skin.
As a place for chrome plating plastic, it is best to choose a non-residential premises - a garage or a home workshop. To ensure personal safety, such an operation must be performed in a respirator, thick rubber gloves, safety glasses and an oilcloth apron.
Homemade electrolytic bath
To chrome plating plastic parts with your own hands, you need to prepare the following tools and devices:
- a container made of glass or plastic, the internal volume of which is selected depending on the size of the product being processed;
- a wooden box, the walls of which must be insulated with fiberglass and then insulated with sand;
- a heating element, with the help of which the temperature of the electrolyte will be brought to the required value (a conventional heating element can be used as such an element);
- thermometer capable of measuring temperatures up to 100 °
; - plywood sheet;
- clamp;
- bracket on which the workpiece will be fixed.
What tools are needed?
Before you start chrome plating, you need to stock up on everything you need. Tools and materials should be at hand. To work you will need:
- glass or plastic containers for dielectric solution, the container must be resistant to acids;
- electrolyte solution;
- plastic bucket or basin;
- you will need to make a plywood box, trim it with fiberglass and insulate it with sand or mineral wool to achieve a thermal insulation effect;
- brush for applying the solution;
- heating element or other heating device;
- car battery or other electrical power source;
- a thermometer that allows you to measure the temperature of a liquid up to 100 degrees Celsius;
- an anode plate connected to an electrical source;
- bracket for hanging the elements being processed;
- a lid with which to cover the container, you can take a plywood sheet;
- clamp
When all the necessary materials and tools are ready, you can begin chrome plating plastic at home.
What you need
To chrome plating plastic at home you will need:
- a container made of dielectric material, which can be glass (or plastic);
- anode plate connected to the positive contact of the electric current source;
- electrolytic solution into which the anode and the workpiece will be immersed.
The electroplating bath must correspond to the dimensions of the product
Progress
First of all, you will need to make an electrolytic solution. It is prepared as follows:
- Distilled water is heated to 60 degrees Celsius. The volume of liquid depends on the size of the part.
- Chromic anhydrite is added to the heated liquid and stirred well. Anhydrite is taken in a ratio of 250 grams per liter of liquid.
- Then pour in sulfuric acid and stir again. Take 2.5 grams of acid per liter of water.
You need to run an electric current through the prepared solution; this will take about three hours. The substance should acquire a dark burgundy color.
The current strength is calculated taking into account that 6.5 A is required per liter of solution. The current strength should not be exceeded, this can lead to stains and uneven distribution of the mass. After this, the solution is left for a day. The prepared solution can be stored for several months, but only if the container with the liquid is tightly closed with a lid.
Preparation rules
To chrome plating plastic at home, you need to make a special brush. The handle of such a brush, into the hollow inner part of which the electrolyte will be poured, can be made from a tube made of plexiglass. The bristles of the brush must be conductive, so it can be made from a bundle of copper wire, having first removed the insulation from it.
Brush design for chrome plating large plastic parts
An important element of the installation for chrome plating plastic is a current source, which can be a powerful transformer or a car battery. The operating diagram of such an installation will have some differences when using different current sources.
In the case of using a transformer as a current source, a diode is additionally connected to the hand prepared in advance, and when using a battery, this element is not used in the electrical circuit. The anode is connected to the step-down winding of the transformer using a cable, and the cathode is fixed to the workpiece.
Components for preparing the electrolyte: sulfuric acid, distilled water and chromic anhydride
After you have selected and prepared the container in which chromium will be applied to plastic, it must be filled with an electrolytic solution. The composition of such a solution, as well as the temperature to which it will be heated before chrome plating, depends on what characteristics the finished coating should have.
Compositions of various electrolytes for chrome plating
In addition, the plastic must be degreased before processing. To do this, perform the following steps.
- The following chemicals are taken in equal quantities - caustic soda, soda ash, silicate glue.
- All prepared components are dissolved in water and mixed.
- The resulting solution is brought to a boil, then the product to be treated is placed into it.
When the plastic is degreased, you can begin chrome plating, but before that you need to put on all the above protective equipment.
Chrome plating of plastic: stages of work
At the first stage, the part is prepared. It is treated with a degreasing solution, which is prepared from the following components:
- soda ash;
- sodium hydroxide;
- silicate glue.
The ingredients are mixed in equal parts and diluted with water, then put on fire and brought to a boil. When the solution is ready, the part to be chromed is lowered into it.
After the part is degreased, proceed to the next stage - chrome plating. This can be done using a galvanic bath or a special brush. Everyone chooses the method that they consider most convenient.
Chrome plating with a brush
You can make a brush yourself. You will need a hollow tube made of plexiglass. A bristle is fixed to one end of it, which can be made from a bundle of bare copper wire. The brush is wrapped with a thin lead wire. The brush and the part are connected to the battery. A transformer can act as a power source, then the hand is connected to it with a diode, while the anode goes to the transformer winding, and the cathode is connected to the part. The diode is not useful for the battery.
Next, a reagent is applied to the part with a brush, which is poured into the glass handle of the brush before work. The procedure is carried out carefully, with smooth movements, you need to ensure that the solution spreads evenly. The solution is constantly added to the brush. The substance is applied in several layers. Each area is processed up to 35 times. As a result, the coating should be a thick, uniform layer.
Chrome plating using a galvanic bath
If chrome plating of plastic is carried out in a galvanic bath, the electrolyte is heated to 60 degrees and left for about three hours. The anode is lowered into the container, and the cathode is connected to the transformer. Then the part is lowered into the bathtub. It must be hung on a bracket so that the object in no case touches the walls of the bathtub, so as not to damage the uniformity of application of the substance.
The procedure is repeated several times until the chrome layer lies perfectly even. On average, the main process takes about half an hour.
The next step is to wash the part under the tap and boil it in three liters of water for half an hour. The treated element must be dried well for two hours. Do not touch the part until it is completely dry. To make the surface shine, it is polished with a soft cloth. At this point the work can be considered completed.
At the end of the work, care should be taken to dispose of the waste substance. Electrolyte should not be poured down the drain, much less splashed into the yard, since it contains harmful chemical compounds and acids.
Chrome plating: technologies, methods, photos, videos, process, types, composition
For practical purposes, electrolytic chromium plating is carried out exclusively from electrolyte solutions based on hexavalent chromium oxide. Numerous attempts to create an industrially useful electrolyte based on trivalent chromium compounds, which makes it possible to obtain chromium coatings with the same technical and operational properties, especially for the production of thick-layer hard wear-resistant coatings, have not led to positive results.
All chromium plating electrolytes contain free acid radicals, which, acting as non-consumable catalysts, promote the deposition of chromium on the cathode. In addition, all chromium plating electrolytes based on hexavalent chromium necessarily contain trivalent chromium ions .
The permissible content of trivalent chromium ions for each chromium plating electrolyte is, as a rule, determined in accordance with the technological features of the process and the requirements for the quality and functional characteristics of the chromium coating (brilliance, hardness, wear resistance, etc.). However, it is usually recommended to maintain the concentration of trivalent chromium in the chromium plating electrolyte in the range of 3-5 g/l.
Electrolytic chromium plating, carried out on the basis of hexavalent chromium salts, is a highly toxic process, and the electrolytes used for this are aggressive liquids, even in dilute solutions. In addition, during the electrodeposition of chromium, increased gas formation occurs and a large amount of aggressive substances enters the air along with the gas in the form of an aerosol. Therefore, when working with chrome plating electrolytes, safety regulations must be strictly observed and all necessary precautions must be taken, and the chrome plating baths used must be equipped with powerful suction devices and ventilation units that purify the air from harmful aerosol impurities.
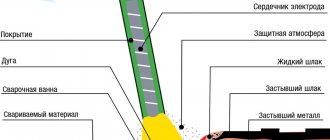
Depending on the conditions of the electrolysis process, there are three types of chrome coatings encountered in practice: these are shiny protective and decorative coatings, characterized by a small thickness of the coating and allowing one to obtain shiny deposits of chromium, then hard wear-resistant protective coatings, allowing one to obtain chrome coatings of great thickness, with high values hardness and wear resistance, and milky non-porous coatings, used mainly as an underlayer to improve the corrosion resistance of coatings. According to their functional purpose, chrome coatings can be divided into protective and decorative, wear-resistant and milky. In this article we will touch only on shiny protective, decorative and milky wear-resistant chrome coatings.
Shiny protective and decorative chrome coatings have a small thickness, in the range of 0.2 - 0.7 microns, are usually applied over a sublayer of copper and nickel, and are used to increase the mechanical and corrosion resistance of the coating, to give the surface of the product improved decorative properties. Milky protective chrome coatings are deposited on steel, aluminum, titanium and some other metals and alloys. The resulting coatings are thick, on the order of 10-100 microns, and are used to protect working tools, optical equipment, to cover the shafts of printing machines, turbine blades, etc.
Chromium plating electrolytes have the lowest dissipative power of all electrolytes known today. Chromium deposition and chrome plating require very high current loads in the bath, much higher than other plating processes. This in turn determines the choice of a current source for chrome plating or a power converter, which is also much more powerful than for other electroplating processes.
For the process of bright decorative chrome plating, electrolytes containing a high concentration of chromic anhydride are mainly used. The advantages of such electrolytes include their higher electrical conductivity, and therefore the ability to carry out chromium deposition at lower current densities, as well as less sensitivity to contamination, compared to diluted electrolytes used for milky chromium plating. The disadvantages of concentrated electrolytes include, first of all, their “non-environmental friendliness” (due to a higher concentration of hexavalent chromium ions, a greater amount of toxic chromium compounds that are carried into wastewater, greater problems with wastewater treatment, etc.). The advantages of dilute electrolytes used for satin chrome plating are, first of all, lower costs for wastewater treatment, lower costs for neutralizing spent electrolytes, as well as higher current efficiency. In addition, in dilute electrolytes, the chrome plating process is carried out at a significantly higher current strength (up to 150 A/dm2), which makes it possible to increase the deposition rate and reduce the duration of the chrome plating process. The disadvantages of diluted electrolytes include their low electrical conductivity, which requires the use of higher-voltage current sources than usual, which accordingly leads to higher energy consumption.
Shiny protective and decorative chrome coatings are not recommended to be deposited directly onto a copper, brass or bronze base, or a sublayer of these metals or alloys. This is due to the fact that when used in atmospheric conditions, copper interacts with atmospheric gases to form carbon dioxide and other copper salts. The resulting salts, accumulating in the pores, sharply worsen the appearance of the chrome coating. In cases where chromium must be deposited directly on parts made of copper, brass or bronze, the thickness of the chromium coating must be at least 4-5 microns. A three-layer decorative chrome coating in a Cu-Ni-Cr (copper-nickel-chrome) bond has fairly high protective and anti-corrosion properties. The first thin copper sublayer ensures the adhesion strength of the coating to the base. The second, thick layer of copper increases the corrosion resistance and protective ability of the coating, and makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the expensive nickel deposit, while maintaining the necessary corrosion properties of the entire coating. It is important that, in addition to leveling additives, the copper plating electrolyte also includes effective brightening additives, which make it possible to obtain not only smooth, but also shiny copper deposits. A shiny nickel coating is deposited onto such a shiny layer of copper from nickel plating electrolytes, which also contain brightening and leveling additives. An important role in the protective and decorative properties of the Cu-Ni-Cr coating belongs to the last layer of shiny chrome. Since, unlike nickel, which passivates over time and has a yellowish tint, shiny chrome does not fade and has a beautiful bluish tint, and the chrome coating itself has better decorative properties. In addition, in Western countries, nickel is generally prohibited from being used as a final decorative coating if direct human contact is possible, as nickel has been found to be a strong allergen.
The most common chrome plating electrolytes are electrolytes consisting of chromium oxide and sulfuric acid. They come in diluted, standard and concentrated.
| Bath number | CrO3, g/l | Catalyst or additive, g/l | Temperature, °C | Current density, A/dm2 | Current output, % |
| 1 | 130-175 | 1.3 - 1.75 H2SO4 | 40-70 | 15-105 | 16-18 |
| 2 | 220-250 | 2.2 - 2.5 H2SO4 | 40-70 | 15-105 | 12-14 |
| 3 | 275-300 | 2.75 - 3.0 H2SO4 | 40-70 | 15-105 | 8-10 |
Dilute electrolytes have the best dissipative power, but the electrolyte is not very stable in composition, and the chromium deposits are prone to roughness. The most commonly used standard chrome plating electrolyte is... has a wider range of current densities, and variations in composition are not significant. Concentrated chromium plating electrolyte has the lowest dissipative ability, and the deposits have the lowest hardness, but are highly decorative.
In some cases, zinc cations are added to the electrolyte. Such electrolytes are used for applying wear-resistant coatings on parts operating under conditions of exposure to highly aggressive environments. To increase the dissipative ability of the electrolyte and improve the physical and chemical properties of chromium coatings, organic additives are introduced into the electrolyte. The disadvantage of organic substances is their interaction with chromic acid, which leads already at the beginning of the electrolysis process to the accumulation of an excessive amount of trivalent chromium in the electrolyte.
In all technical electrolytes containing chromic acid, to ensure stability of the chrome plating process, it is important to maintain the correct ratio between the concentrations of chromic acid and the catalytic additive. The ratio of the concentration of chromic acid to the total concentration of catalytic acid radicals must be maintained in the range from 50:1 to 200:1, but a ratio of 100:1 is best (concentrations here are expressed in grams of CrO3, H2SO4).
The chromium deposition process and the properties of the resulting chromium coating largely depend on the chromium deposition mode, i.e., on the cathode current density and electrolyte temperature. The clearest idea of the approximate boundaries of electrolysis modes that ensure the production of gray, shiny and milky chromium deposits is given by the diagram of current density and temperature (DK-t), shown in Figure 1.
A gray chromium deposit appears on the cathode at low electrolysis temperatures (35...50°C) and a wide range of current densities. Bright chromium deposits have high hardness (6000... 9000 N/mm2), high wear resistance and are less brittle.
Rice. 1. Zones of chromium deposits.
Milky chromium is obtained at a higher electrolyte temperature (above 70°C) and a wider range of current densities. Milk sludge is characterized by reduced hardness (4400.. 6000 N/mm2), but has plasticity and increased corrosion resistance.
Supersulfate chromium plating electrolyte
Supersulfate chrome plating electrolyte is recommended for high-speed deposition of thick-layer, shiny and wear-resistant chrome coatings (up to 500 microns).
Composition of supersulfate chrome plating electrolyte, g/l:
Chromic anhydride (CrO3) 250-300 g/l
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) 8-10 g/l
Trivalent chromium (in terms of Cr203) 20-22.
The electrolyte temperature must be no lower than 500C, and the current density during the chrome plating process must be more than 55 A/dm2
.
resistant, hard chrome coatings are deposited from a supersulfate electrolyte over a wide range of temperatures and current densities (up to 300 A/dm 2
Recommended electrolysis modes:
Supersulphate chromium plating electrolyte has extremely low dissipation ability. Therefore, it is recommended only for applying chrome coatings to cylindrical parts: rods, shafts, cylinders, etc., when using special equipment that ensures a concentric (coaxial) arrangement of the part and the anode. Recommended anode composition: Pb 7986%; Sb 4-6%; Sn 10-15%
Self-regulating sulphate electrolyte chrome plating
Self-regulating sulphate electrolyte is similar to standard chrome plating electrolyte in that it contains only one anion catalyst - sulfate. The only difference is that sulfates are introduced into the electrolyte not in the form of sulfuric acid, but in the form of a sparingly soluble salt - strontium sulfate. The sulfate content in the electrolyte is regulated due to the limited solubility of this salt. Composition of self-regulating sulfate electrolyte for chromium plating, g/l
:
Chromic anhydride (Cr03) 250;
Strontium sulfate (SrS04) 6-8;
Silicon dioxide (SiO;) 10-15.
Electrolyte operating mode:
Shiny hard coatings
: Current density 60-95 A/dm2. Temperature 60-650C.
Dairy thick coatings
: Current density 20-50 A/dm2. Temperature 78-800C.
Self-regulating sulfate-silica fluoride electrolyte chrome plating
In a self-regulating sulfate-silica fluoride electrolyte, the catalyst anions are S04 ions2
- and SiF6
2
-.
The main advantages of this electrolyte compared to the sulfate electrolyte are greater composition stability, slightly higher dissipative power, higher current efficiency and a wider range of permissible temperatures and current densities, ensuring the production of shiny chromium deposits. When using this electrolyte, the problem of obtaining a strong adhesion of chromium to a shiny nickel coating or stainless steel is more easily solved .
This is explained by the fact that fluorine-containing electrolytes have a significantly greater activating ability than electrolytes without fluorine. The chromium plating process in these electrolytes is less sensitive to current interruptions.
The main disadvantage of self-regulating silicofluoride electrolytes for chrome plating is their increased aggressiveness compared to standard electrolytes, especially in relation to copper alloys, steel and lead anodes. The rate of dissolution of metals in a self-regulating chromium plating electrolyte, and therefore the rate of accumulation of iron or copper ions in it, is higher than in sulfate. With poor dissipative ability of the electrolyte, areas of chrome-plated parts where a lower current density is realized are more slowly coated with chromium and are subjected, on the one hand, to etching with the electrolyte, and on the other, to strong hydrogenation.
Composition of self-regulating sulfate-silica fluoride electrolyte, g/l:
chromic anhydride (CrO3) - 250-300:
strontium sulfate (SrSO4)— 5.5 -6.5
potassium silicofluoride (K2SiF6) - 18-20
Tetrachromate chromium plating electrolyte
The tetrachromate electrolyte has a composition that is quite unusual for chrome plating electrolytes - along with chromic and sulfuric acids, it contains a fairly large amount of alkali, which partially neutralizes the acid. Despite this, during the electrodeposition of chromium from a tetrachromate electrolyte, all the process features characteristic of other chromium plating electrolytes are retained. The features of the tetrachromate electrolyte include the fact that it has a higher dissipative ability than all other chromium plating electrolytes. The advantage of this chromium plating electrolyte is that chromium is deposited from it at room temperature (18-25°C) with a high current efficiency. As the temperature increases, the tetrachromate decomposes and the electrolyte loses its specific properties. Therefore, during operation, it is very important to constantly monitor and maintain a low temperature, cooling the electrolyte solution if necessary.
Electrolytes of the tetrachromate type also include electrolytes in which calcium carbonate is used instead of alkali. In some cases, it is recommended to add 0.5-10 g/l tungstates or magnesium salts to the electrolyte, in the presence of which chrome coatings are deposited, which have better polishability.
Composition of tetrachromate chrome plating electrolyte, g/l:
Chromic anhydride (CrO3) -350-400
Caustic soda (NaOH) - 40-60
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) - 2.5-2.7
Trivalent chromium (on Cr2O3) - 10-15
Electrolyte temperature -18-250C. Current density -10-80 A/dm2
Tetrachromatic electrolyte is used exclusively for the production of protective and decorative coatings. Due to the fact that electrolysis is carried out at room temperature, the precipitates are gray. However, due to their low hardness and fairly high ductility, they can be polished to a mirror finish, characteristic of shiny decorative chrome coatings. The relatively high dissipative ability of the tetrachromate electrolyte allows it to be used for applying chromium coatings to molds used, for example, for the manufacture of plastic parts.
Chromium coatings obtained from tetrachromate electrolytes have significantly lower porosity compared to chromium from sulfate electrolytes, but tetrachromate electrolytes are not used to obtain wear-resistant coatings. Chromium coatings made of tetrachromate electrolyte with a thickness of 5-10 microns can be used for local protection of the surface of steel parts during gas carburization or nitrocarburization.
Electrolytes black chrome plating
Black chrome plating is used to coat optical systems and parts that must have good heat transfer into space. The thickness of the black chrome layer is 1.5-2.0 microns. Black chrome plating has good heat resistance and, unlike black nickel or black oxide coatings, is wear-resistant.
| Electrolyte composition and deposition mode | №1 | №2 | №3 | №4 | №5 | №6 | №7 | №8 |
| Chromic anhydride | 250 | 200 | 250-400 | 250 | 150-400 | 250 | 250 | 200 400 |
| Acetic acid | — | 6.5 | 5 | — | _ | 3 | . | |
| Ammonium vanadate | — | 20 | — | — | _ | _ | ||
| Ferrous oxalate | — | — | — | — | 15-75 | — | — | — |
| Urea | 2.5 | |||||||
| Chromium fluoride | ||||||||
| Boric acid | — | — | — | — | 15 | _ | ||
| Sodium nitrate | 3-5 | — | — | 5 | _ | |||
| Sodium hexafluoroaluminate | 0.2 | — | — | — | 0.1 | — | — | — |
| Hydrofluoric acid | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.21 | |
| Silicofluoric acid | — | — | — | 1.25 | — | — | — | |
| Chromin | 2-3 | — | — | 1.53 | — | — | — | |
| Temperature, °C | 18-25 | 10-30 | 10-30 | 18-25 | 18-25 | 15-25 | 60-70 | 18-40 |
| Current density, A/dm2 | 15-30 | 50-100 | 50-100 | 10-60 | 10-50 | 10-50 | 20-30 | 50-120 |
The duration of the black chrome plating process is 4-6 minutes.
Impurities in the chrome plating electrolyte.
The presence of foreign impurities in chrome plating electrolytes can lead to deterioration in the quality of the chrome plating. The reason for the appearance of impurities is often a violation of the chrome plating technology itself. It should be emphasized that the least accumulation of harmful impurities occurs in electrolytes used for shiny decorative chrome plating. This is explained by the fact that due to the short duration of the shiny chrome plating process, pendants with parts constantly carry electrolyte with impurities on their surface. And the need to regularly add either water or a fresh portion of electrolyte leads to dilution of the electrolyte solution and prevents the accumulation of impurities in it in dangerous concentrations.
Chromium deposition on aluminum and its alloy
Chromium is deposited on parts made of aluminum or its alloys mainly in cases where it is necessary to increase their wear resistance, heat resistance or improve anti-friction properties. Direct chromium plating of aluminum and its alloys is impossible, which is explained by the presence on the surface of aluminum of an inert oxide film firmly adhered to the base. This film increases the anti-corrosion properties of the aluminum surface, but at the same time prevents chrome and any other galvanic coatings from obtaining the necessary adhesion to it. If you remove this film and immerse aluminum in a solution of salt or any metal, then due to the high electronegative potential of aluminum, more electropositive metals contained in the solution, such as copper, nickel, chromium, tin, or cadmium, etc., will be contacted on its surface. .P. And as is known, contact deposition does not allow obtaining satisfactory adhesion of the coating to the base. Therefore, as in the case of titanium, special technologies are used for electrodeposition on aluminum.
There are two types of them used in industry:
— Activation
(removal of the oxide film with simultaneous light etching) of the aluminum surface and simultaneous deposition on its surface of a thin layer of metal firmly adhered to the base, serving as a sublayer for the subsequent application of a coating layer;
— Anodic
oxidation
of aluminum in order to form an oxide film of a certain structure and thickness on it, which ensures reliable adhesion of the subsequent coating to it.
"Zincate" alkaline treatment
consists of processing aluminum products in a zincate solution containing a solution of alkali and zinc oxide. The process is carried out by lowering the aluminum part for a few seconds into a zincate solution at a temperature of 18-25°C. In this case, the existing oxide film is etched from the surface of the aluminum and, at the same time, a thin layer of zinc is formed in its place. In principle, chrome coating can already be applied to this layer. However, to improve adhesion, it is recommended to remove the first layer of zinc by dissolving it in a solution of nitric acid (300-500 g/l). Then, after thorough washing, the parts are again immersed in the zincate solution for 10-15 seconds. This method is called "double zincate treatment" or "double zincate". To obtain denser, more compact films with better anti-corrosion properties, it is recommended to add ferric chloride and Rochelle salt to the zincate solution.
Useful tips
In order to get a high-quality result and maintain the effect for a long time, you need to take into account the following tips:
- if the procedure is being carried out for the first time, you can first practice on a prototype;
- if for some reason it is impossible to chrome plating at home, it is permissible to replace chrome with nickel;
- the chrome coating may fade over time; if this happens, the part must be rinsed well in warm water using household chemicals, then the product is dried and rubbed with a soft material;
- when exposed to low temperatures, chrome plating can quickly fade;
- At the final stage, do not neglect polishing the part.
Currently, you can purchase ready-made chrome-plated parts in the store. But in some cases you have to do this procedure yourself. You can coat both plastic and metal parts with the solution. The processing process is complex and requires preparation. However, if you know how to do chrome plating at home and take care of safety, you can get a perfect, shiny part without harming your own health.
Dimensions
The variety of sizes of mirror plastic is enormous, considering that these are different materials, which are also produced by numerous manufacturers around the globe. For example, polymethyl methacrylate can be found in the form of sheets of various sizes and shapes, but with dimensions no more than 305 by 205 cm. The thickness is relatively small - only 2-3 mm. The adhesive base may or may not be present.
Mirror polystyrene, despite its flexibility, is also sold not in roll form, but in sheets. At the same time, the fragments are slightly smaller - it is difficult to find a sheet larger than 300 by 122 cm on sale. The thickness of the product ranges from 1 to 3 mm, and here you still need to think about the choice: a sheet that is too large a priori cannot be thin, but increasing the thickness negatively affects flexibility and increases fragility.
PVC sheets of the standard type are characterized by a small thickness - often at the level of 1 mm. Their dimensions are the most modest - up to 100 by 260 cm.
Combined reflective glasses
Rice. 9. Reflective glass
This type of glass is able to absorb and reflect sunlight. Manufactured using standard technology, but with additional improvements. After heating and giving the required shape, 4 layers of metal oxide are applied. The surface is hardened with the help of air. Then, after partial cooling, another layer is applied - silver and the workpiece cools.
Solar radiation is reflected from the surface to a given extent. Harmful radiation is almost completely absorbed. One of the additional benefits is the significant degree of heat retention in the room. The creation of this type of glass is expensive, since it requires the application of a large number of layers. The process is labor-intensive, long, and the final cost of the material is high.
The thickness of the product can be 6, 8, 10 mm. The length varies according to customer preferences. For example, glass in large shopping centers is often made with dimensions of about 6x3 meters with a thickness of 6 mm.
Advantages of reflective glasses
Rice.
10. Breakage of coated glass Reflective glass of mirror glass units has the following advantages:
- high aesthetic qualities - the use of modern technologies allows you to give the material the necessary shade;
- the possibility of improving the microclimate of the room due to the property of partial transmission of light rays;
- high reflective properties do not allow you to see what is happening behind them. There is a choice of specularity: from minimal to full;
- thanks to processing and hardening they have high strength;
- it is possible to laminate and additionally harden;
- if it is necessary to improve the characteristics, it is possible to apply additional layers;
- the building acquires a presentable appearance thanks to panoramic glazing;
- Can be used in single glass, double glazing.
Current
Unfortunately, the beautiful, shiny chrome surface eventually develops small scratches that reveal the metal underneath the chrome.
Under the influence of oxygen, an oxidation reaction occurs, as a result of which rust appears on the surface. Important! To prevent any damage to the chrome surfaces of your car, you should first of all take care of them:
- When washing a car with chrome elements, it is advisable to use warm soapy water. It is necessary to wipe all chrome parts with a soft cloth or sponge immediately after washing.
- It is better to wipe the chrome-plated bumper with a cloth moistened with warm water to make it soft.
Topdetal.ru Blog How to restore gloss to chrome?
There are 12 ways to restore shine
A fine abrasive removes light deposits. — GOI paste is designed for glass and perfectly cleans metal. Has 3 grain sizes.—With experience, rust stains will go away and the surface will shine. Non-abrasive chemicals - cleaning solutions:—Silit spray for removing plaque and rust or a similar gel;—Ammonia (ammonia) is contained in washing liquids glass;—Vinegar—food grade or apple cider vinegar is suitable;—Citric acid is contained in lemon, sold dry in grocery stores;—Alcohol—ethanol, isopropanol, methyl;—Orthophosphoric acid (Coca-Cola, Fanta) is easily accessible for cleaning.—Wipe the part with a rag , soaked in the composition.
After 5 minutes, rinse with water. Specialized automotive chemicals for chrome Fine abrasive pastes and liquid polish cleaners are designed for cleaning, polishing and protecting chrome coatings.
Chrome painting
You can do chrome plating at home in several ways - by covering parts or body elements with film, or by doing catalytic, galvanic or chemical chrome plating yourself.
Covering a car with chrome film is an easy to implement and inexpensive solution. Its advantages are a wide range of film shades (from gold to pearlescent), and the ability to remove worn-out coatings. The film also performs a protective function, preventing scratches and abrasions from appearing on the surface of the body.
Also, do-it-yourself chrome plating at home is often done by painting with catalytic chrome paint. Such compositions are applied with a spray gun and dry at room temperature, but at the end you get only a decorative reflective effect (the reflectance coefficient for high-quality paints is up to 95%), and do-it-yourself catalytic chrome plating does not provide the protective properties characteristic of coatings obtained by galvanization.
Do-it-yourself chrome plating of parts using the painting method consists of the following steps:
Chrome plating of parts is one of the budget tuning options
- The surface is matted with fine-grained sandpaper, dust is removed and the part is degreased with white spirit or solvent;
- The part is opened with 2-3 layers of base primer (black composition is used), after the primer has dried, one layer of ceramic varnish is applied. The varnish is dried within an hour at a temperature of 60 degrees;
- After the varnish has hardened, the part is kept for 3 days at 20 degrees and painted with chrome. The paint is applied with a spray gun with a 1.1-1.2 mm nozzle. in 4-5 thin layers, sprayed (from a distance of 30 cm at a supply pressure of 2.5-3 MPa);
- The surface dries for 24 hours at a temperature of 20 degrees (or 1 hour at 60 degrees), after which it is opened with a protective varnish in 2 layers. After drying, the varnish is polished with a microfiber cloth using polishing paste.
Painting compositions with a chrome effect, in addition to metal surfaces, allow you to chrome plating plastic parts at home; they are also suitable for processing glass, foam plastic, and wood.
Production and characteristics of acrylic mirrors
An acrylic mirror is a smooth transparent plastic surface coated with a layer of amalgam. The reflective layer is applied in the same way as on conventional glass mirrors. However, the resulting material has unique properties that allow the most daring design ideas to be realized.
Excellent reflectivity is the only thing that a plastic mirror has in common with the glass one we are used to. But unlike their prototype, acrylic mirrors have significantly greater lightness, increased strength and ease of processing.
Features of acrylic mirrors are:
- thickness 2 and 3 mm;
- maximum size 2000 x 3000 mm
- strength;
- versatility of use;
- ease of fastening;
- the edge is not processed;
- safety for children.
Procedure
The extent of damage is very difficult to assess if the chrome part is not cleaned of dirt.
This must be done very carefully, since the chrome film is very thin. When performing cleaning, the following rules must be observed:
- Work only in a warm room or outdoors at above-zero temperatures. Temperature changes during work are unacceptable.
- Do not use products containing salt for cleaning.
- It is forbidden to use rough rags and napkins with a corrugated surface.
First, rinse the part with warm water and then wipe with gasoline. You may need to repeat this procedure several times.
To prevent corrosion from harming neighboring areas of chromium, the source of damage must be localized. This can be done using regular wax or polish.
Unusual Effects
Thermochromic materials have earned the name “chameleon paints” due to their special qualities. Such coatings can change their appearance under the influence of temperature changes, for example:
- initially colored paint becomes invisible;
- when the temperature is heated or lowered, colorless paint takes on a certain shade;
- Due to changes in ambient temperature, the coating may change color completely.
There are compounds that can produce any of these effects every time the coating is exposed to heat or cooled, and some are designed for a single “reincarnation”. They are called, respectively, reversible and irreversible.
There are materials on sale that, when painted in chrome, give the coating a matte finish. When producing such paints, a special component is added to the composition to reduce the reflective potential of the coating. This paint is used to chrome plumbing fixtures, furniture fittings and much more. Matte chrome looks strict and elegant.
Two-component paints
Two-component chrome paint (mirror) for metal and plastic is a composition that is made of two components: a base and a hardener. They are combined before dyeing and kneaded thoroughly. The excellent performance characteristics of the coating make these varieties the most popular.
Their positive properties include:
- absolute resemblance to polished metal;
- increased wear resistance;
- heat resistance.
Carrying out self-staining with two-component compositions requires a lot of time and effort, but the result completely justifies these sacrifices.
Reflective glass
Rice. 6. Example of reflective glass
It has a number of properties, the ability to absorb light reaches 70%. The manufacturing technology involves applying a layer of metal oxide. The strength characteristics and impact resistance of the surface are increased.
There are several types of reflective glass, differing in features and manufacturing method. Types of materials:
- Absorbing. The main function is to absorb harmful solar radiation.
- Reflective. Protect from sunlight.
- Combined. They combine the positive features of each type of product.