Since melting iron at home requires a heat source with a high temperature, the design of a homemade furnace is chosen based on this condition. It must meet environmental safety requirements and not take up much space in the workshop or garage. These requirements are fully met by installations in which even refractory metal is melted by electric current.
Melting furnaces - transistorized
The transistor induction melting furnace is designed for the charge of ferrous and non-ferrous metals. It is produced on the basis of a mid-frequency induction heater, which is assembled using MOSFET transistors and IGBT modules, which allows saving on electricity up to 35%, having a high efficiency of 95%. More details
Transistor-based induction melting furnaces are suitable for small industrial foundries that need to melt small amounts of metal. The advantages of melting furnaces include their mobility and ease of maintenance, since they use a graphite crucible, which saves time on making the lining and drying it.
Device
An arc furnace with a bottom electrode or another design has a single design principle for such units:
- graphite electrodes for electric arc furnaces – 3 pcs. they are installed in special holders to which cables supplying electricity are connected;
- The furnace body is cylindrical in shape. The lower part is made in the form of a sphere; the charge is placed into it. In the space between the electrodes, after applying a load, an arc occurs, and the melting material is gradually melted and brought to a liquid state. The interior of the hearth is lined with refractory material that can withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures;
- the outer part is closed using a steel case, in the planes of which an automatic control system with many sensors and thermocouples is fixed. Furnace models can be additionally equipped with a water cooling system;
- a special chute is made to drain the melt;
- on the front side there are several cavities with doors for monitoring the progress of melting and taking samples for chemical analysis of the readiness and quality of steel;
- Several cavities are made in the body to remove slag and add alloying additives and adjust the composition of the steel.
For normal operation, it will be necessary to equip the structure with a high-voltage step-down transformer connected to the power line, buckets for draining finished steel and taps for loading charge and other additives. To ensure the operation of the units, safety valves and an emergency power shutdown system are installed, as well as an automatic control unit for the operation of the furnace.
An arc melting furnace has such a general device. But the design may change with different furnace options.
The figure shows the general diagram of an electric arc furnace.
The size of the electric arc furnace may affect the choice of transformer power, electrode dimensions and wall thickness, but the general design principle remains the same.
The dimensions of the electrodes are selected according to the data in the installation documents.
What steels can be produced in arc furnaces?
When asked what kind of steel can be produced in arc furnaces, an experienced metallurgist will answer without hesitation - all kinds and even cast iron. Even in the online games “space engineers” and “immersive engineering” you will find ways to build such furnaces and produce various alloys and steels. Electric arc structures are used for production on an industrial, laboratory or home scale:
- structural or alloy steel with varying levels of carbon and alloying additives;
- refractory alloys;
- melt gold, silver and other metals in small quantities for a jewelry or home workshop;
- production of all grades of cast iron and for its remelting into alloy steel;
- high-temperature steels are used for growing single crystals and melting optical glass and fibers.
Melting furnaces - thyristor - LEGNUM (Taiwan)
The Rosinductor company offers to buy LEGNUM induction melting furnaces (Taiwan); these furnaces are the most popular among Russian buyers. Thyristor induction melting furnaces Legnum are supplied in two modifications: hydraulics and gearbox, the main buyers are medium and large smelting plants with a capacity of 2000 tons/year. More details
The induction melting furnace is supplied with two melting units; they are installed on a pre-prepared foundation. The main advantages are efficiency, on average 20-30% more economical than any other analogues presented on the Russian market, reliability, modern design and affordable price. Rosinductor supplies induction melting furnaces not only to all regions of RUSSIA, but also to the countries of the former CIS. By contacting our company, be sure that the induction melting furnace you buy is guaranteed to have the best price, quality, reliability and delivery conditions. More details
Marking
The marking principle is as follows:
- They write the letters Br (meaning “bronze”).
- Write letters denoting alloying elements:
- Write numbers indicating the percentage of each element. For wrought bronzes, the numbers are written at the end of the markings in the same order as the letters. For foundries, a number is written after each alloying component. For example:
BrOF10-1 – deformable bronze. Tin is approximately 10%, phosphorus is 1%, the rest is copper. Or:
BrA10Zh3 – cast bronze, where aluminum is 10%, iron is 3%, the rest is copper.
There may be other impurities, but their number is insignificant.
Melting furnaces - main characteristics
During metal melting, the furnace is controlled mechanically or remotely. In both cases, the process must be managed by trained personnel with appropriate permits and approvals. The Rosinductor company performs work on setting up converters, troubleshooting and maintaining smelting equipment in working order.
When choosing a melting furnace, you need to think about the choice of crucible. This determines what metal will melt and how many melts it can withstand. On average, the crucible can withstand from 20 to 60 heats. For a long service life of the crucible, you must use high-quality and reliable materials. The melting time of metal takes no more than 50 minutes in a heated melting furnace, so a furnace of small volume and power can have high productivity.
The delivery set of melting furnaces includes the main elements: thyristor or transistor frequency converter, melting units, capacitor banks, templates, water-cooled cables, control panels, cooling systems.
How to make high-quality castings
To obtain high-quality bronze casting, subsequent machining of the casting will be required. It is necessary to sequentially perform the operations of separating the sprues, removing flash, mechanical grinding and polishing of the product. It is impossible to immediately obtain a high-quality finished casting at home, so you need to prepare for finishing procedures.
Art bronze casting technology in pictures
Melting furnaces for aluminum
Melting furnaces for aluminum have their own characteristics, because the melting point of aluminum is 660 °C (390 kJ/kg). When choosing a furnace for aluminum, you should know that the thyristor converter should not be powerful, and the melting unit itself differs in size from the unit for steel or copper by 2-3 times. Accordingly, it is not recommended to melt other metals in it.
Aluminum alloys can be melted in furnaces with oil, gas and electric heating, in flame reverberatory furnaces, but the highest quality metal and high speed are obtained when melting in induction melting furnaces, due to the homogeneous composition of the charge, which is perfectly mixed in the induction field.
Who invented it?
An electric arc furnace, namely the effect of melting metal using an electric arc, was first shown by the domestic scientist Popov at the beginning of the 19th century. Such experiments have shown that using an electric arc installation it is possible not only to melt metal and steel, but also to restore new materials from oxides when heated together with carbonaceous reducing agents. These experiments became the ancestor of electric arc welding.
But in parallel with Popov, research was also carried out by foreign scientists. Already in 1810, Davy Humphrey showed the first experimental installation of arc combustion, and in 1853 an attempt was made to build the first smelting furnace by Pichon. 1878 is the year when Wilhelm Siemens received a patent for the invention of the first electric arc furnace. But the world's first arc steel-smelting plant appeared only in 1899. Therefore, disputes about who invented this device continue to this day.
Widespread use of such devices in the steelmaking industry began after the end of World War 2.
Several photos of electric arc furnaces:
Melting furnaces for steel
Melting furnaces are heated to their maximum temperature when melting steel, 1500 - 1600 ° C and are accompanied by complex physical and chemical processes. When remelting steel, it is necessary to reduce the content of oxygen, sulfur and phosphorus, which form oxide and sulfide elements, which reduce the quality of steel.
A feature of steel melting in melting furnaces is the use of lining mixtures, in contrast to copper melting, where a graphite crucible is used. Melting furnaces mix the metal well due to the induction field, which evens out the chemical composition of the steel.
The above advantages are excellent for smelting alloy steels, with minimal losses of alloying elements: tungsten - about 2%, manganese, chromium and vanadium - 5 - 10%, silicon - 10 - 15%, taking into account the scarcity and high cost of alloying elements.
Steel melting has the following features and advantages:
- The most important castings are melted using the oxidation method, because during the boiling of the metal, all non-metallic inclusions are removed and the phosphorus content is reduced. The composition of the charge is taken from scrap carbon steel or cast iron to obtain an average carbon content of 0.5%;
- If you are going to melt steel with a high content of manganese, aluminum, chromium, you need to choose an acid lining, because the durability of the crucible will be twice as high;
- Before starting melting, the crucible is filled with metal, but the top should not be filled tightly, this can lead to the formation of arches and, accordingly, waste of metal, since the charge will settle during melting of the lower pieces;
- The steel melting time ranges from 50-70 minutes, depending on the heating of the melting unit;
- Melting furnaces for steel have high productivity in the production of castings of small mass and size.
Production of high quality castings
It is possible to obtain products of higher quality than by casting into the ground. For this purpose, lost wax casting is used.
The equipment is made of gypsum. It is disposable and destructible. To make a mold, you need a model of the product made of wax, paraffin or other fusible material. This material should be lighter than water. The following will explain why this is important.
A wax model is also made by casting into plaster casting. Models of complex configuration are made from several parts. And plaster equipment for the model is made according to the original product or its model, similar to equipment made from sand. The result is a chain: original product - plaster mold for wax model - model - plaster mold for metal - finished product.
When the tooling for the product is ready, a wax model is melted from it by immersing the mold in hot water or simply heating it. The melted wax flows out of the cavity through the same hole into which the metal will then be poured. That is why the material of the model must be lighter than water - so that when smelted in water it rises to the surface.
You can familiarize yourself with the process by following the instructions in the video provided.
Copper Melting Furnaces
Copper, copper alloys, bronze, brass can be melted in all melting furnaces, where the temperature is maintained at 1000 - 1300 ° C. However, it is preferable to use induction melting furnaces, since one melt in them will not exceed 40 minutes. The copper used in Russia today is not particularly pure. Typically it contains the following impurities: iron, nickel, antimony, arsenic. Copper with an impurity content of 1% is considered pure metal.
The main important quality of the metal is its high electrical and thermal conductivity. This determines the low temperature for melting. Copper smelting temperature is 1084°C. Copper is a fairly flexible metal that is widely used in various technical industries; here are some of its features:
- Copper can be melted in an open environment, in a vacuum and in a protective gas environment;
- Copper is melted in a vacuum to obtain oxygen-free copper, with the ability to reduce O (Oxygenium) oxygen to almost zero 0.001%;
- The main charge when producing oxygen-free copper is 99.95% cathode sheets; before loading the sheets into the furnace, they must be cut, washed and dried from the electrolyte;
- The lining of the melting furnace above the metal level is made of magnesite;
- To avoid oxidation, smelting is carried out using charcoal, fluxes, glass and other components.
Pouring bronze into a mold
Pouring bronze melt into a casting mold
Pouring the melt in itself is not difficult - the metal is poured in a thin, even stream until the mold is completely filled.
Difficulties may arise if there are no air channels into which air can escape. If the outlets are clogged, air pockets will not allow the melt to completely occupy the entire mold, and the casting will be damaged. The problem can be solved by using a centrifuge, which distributes the metal inside the mold and helps it overcome the resistance of air pockets.
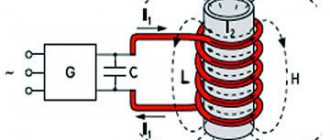
Induction furnace for metal melting
An induction furnace for metal melting heats the metal charge with high frequency currents (HFC) in an induced electromagnetic field under the influence of eddy electric currents. Melting furnaces consume a large amount of electricity, so we offer furnaces not only with a thyristor converter, but also with an economical transistor converter. The furnace uses a lining or a graphite crucible, in both cases they are only enough for 20-40 melts. High melting point allows one metal melt to be performed in 50 minutes.
ZAVODRR – furnaces for melting metals from Russian, Asian and European manufacturers with a crucible capacity from 1 to 10,000 kg. Supply, installation, commissioning and inexpensive maintenance of furnaces.
Let's look at the features of furnaces for melting ferrous, non-ferrous and precious metals:
- Aluminum smelting furnace (aluminum smelting in furnaces is carried out at a temperature of 660 °C, boiling point 2400 °C, density 2698 kg/cm³);
- Furnace for smelting cast iron (cast iron smelting 1450 - 1520 °C, density 7900 kg/m³);
- Copper smelting furnace (copper smelting 1083°C, boiling point 2580°C, density 8920 kg/cm³);
- Furnace for gold smelting (gold smelting 1063°C, boiling point 2660°C, density 19320 kg/cm³);
- Silver smelting furnaces (silver smelting 960°C, boiling point 2180°C, density 10500 kg/cm³);
- Furnace for steel melting (steel melting in furnaces 1450 - 1520 °C, density 7900 kg/m³);
- Iron smelting furnace (iron smelting 1539°C, boiling point 2900°C, density 7850 kg/m3);
- Furnaces for melting titanium alloys (titanium melting 1680°C, boiling point 3300°C, density 4505 kg/m³);
- Furnace for lead smelting (lead smelting in furnaces 327°C, boiling point 1750°C, density 1134 kg/cm³);
- Brass smelting furnace (brass smelting in furnaces 880–950 °C. density 8500 kg/m³);
- Bronze smelting furnaces (bronze smelting in furnaces, 930–1140 °C 8700 kg/m³).
Electric furnaces for melting ferrous and non-ferrous metals are selected based on your technical requirements. The first deliveries of furnaces began in 2008; today furnaces for melting metals have been successfully operated by more than 50 foundries for 8 years.
How to make a casting mold
The mold is made using molding sand and a mold. The mixture consists of sand (75%), clay (20%) and coal dust (5%). The components are thoroughly mixed until smooth.
The flask consists of two shallow boxes stacked on top of each other. One, the bottom one, has a bottom and is filled with molding sand to the very top. The second box does not have a bottom, but is equipped with two crossbars.
Mold making process:
Casting mold and its elements
- the model, previously coated with a thin layer of talc or graphite powder, is pressed halfway into the molding sand of the lower drawer;
- then the top box is installed and filled with the mixture, compacted so that the model is completely and tightly covered with it;
- for pouring, one or more holes are made - sprues;
- the form is cut along the junction line of the boxes and divided in half;
- the model is removed, and the boxes are connected again, the voids from the model are connected and form a cavity that has the required shape.
At the end of the process, the form must be dried a little and can be used for its intended purpose.
Casting at home
Experienced metallurgy masters practice bronze casting at home. To carry out this process you need to purchase:
- bugle;
- forceps;
- charcoal or coal;
- crucible in which metal will be melted.
A gas burner is often used as a heating element for melting a bronze alloy. This is due to the fact that bronze can be melted at a low temperature. This way you can save on the purchase of an induction furnace.
Casting at home
Creating a casting mold
Casting bronze at home requires the correct production of casting molds. The molding mixture should consist of a mixture of sandstone, coal dust, and clay. Stages of mold making:
- The molding mixture is poured into a wooden box called a flask. It is compacted from above with weak blows.
- Next, a model of the future workpiece is immersed in the molding mixture.
- On top there is another box (flask). The molding mixture is poured into it. It's being compacted.
- Next, the master divides the form into lower and upper halves.
How to properly pour molten bronze into a casting mold
Bronze casting at home requires special preparation of casting molds. It is necessary to remove air from them in order to obtain durable castings without defects. The molds must be spun in an electrically driven centrifuge. After this, the molten metal can be poured.
How to get better quality castings
The casting quality can be improved. You need to use another modified technology. In this case, wax is used. It is used to make molds into which the castings will be poured. You can use paraffin. To make such a model, you need to use a ready-made mold that is heated in boiling water. Bronze casting has been known for many hundreds of years. Using this technological process, decorative elements, fences, lamps and sculptures are made. The composition of bronze includes various components that affect the characteristics of the alloy. There are different types of making bronze castings, which involve different technological processes.