Outdated
If you need to purchase a heat treatment furnace on favorable terms, you should familiarize yourself with the latest information on the portal mml-me.ru. Here you will find a wide variety of such stoves to choose from. There is also a special information block where you can study information on such important issues as types of furnaces and features of their operation. The information below describes this information more briefly.
Chamber furnaces
This type of unit is used in the firing of ceramics, porcelain, in the preparation (heating) of metal blanks before forging, rolling, and various types of heat treatment. In this case, the products being processed are motionless.
They vary in design and are divided into vertical, bell-type, pit, bogie, heating well, and so on. The temperature inside the unit can be constant or gradually change, ensuring uniform heating (cooling) of the products. Gas, liquid fuel, or electricity can be used as a heat source. Electric power supply provides more even heating. The most widespread are chamber furnaces with a fixed hearth. They are installed in forge shops.
Cooling steel during hardening
The basis of most coolants used in hardening steel products is water. It is important that such water does not contain impurities of salts and detergents, which can significantly affect the cooling rate. A container containing water for hardening metal products is not recommended for other purposes. It is also important to take into account that running water cannot be used to cool the metal during the hardening process. The optimal temperature for coolant is 30 degrees Celsius.
Hardening steel products using ordinary water to cool them has a number of significant disadvantages. The most important of them is cracking and warping of parts after they have cooled. As a rule, this cooling method is used when cementing metal, surface hardening of steel, or heat treatment of parts of a simple configuration that will later be subjected to finishing.
For products of complex shapes made from structural steels, another type of coolant is used - a 50% caustic soda solution heated to a temperature of 60 degrees Celsius. After cooling in such a solution, the hardened steel acquires a light shade.
It is very important to follow safety precautions when working with caustic soda; be sure to use a hood placed above the bathtub. When a hot part is lowered into a solution, vapors are formed that are very harmful to human health.
Hardening steel in a muffle furnace
The best coolant for thin-walled parts made of carbon steels and products made of alloys are mineral oils, which provide a constant (isothermal) cooling temperature, regardless of environmental conditions. The main thing to avoid when using such a technical fluid is getting water into it, which can lead to cracking of parts during their cooling. However, if water does get into such a coolant, it can be easily removed from it by heating the oil to a temperature above the boiling point of water.
Tempering steel using oil as a coolant has a number of significant disadvantages that you should definitely be aware of. When oil comes into contact with a hot part, vapors are released that are harmful to human health; in addition, the oil may catch fire at this moment. An oil bath also has the following property: after its use, a residue remains on the parts, and the coolant itself loses its effectiveness over time.
All these factors should be taken into account when hardening metals in an oil environment and the following safety measures should be taken:
- immerse parts in an oil bath using tongs with long handles;
- carry out all work wearing a special mask made of tempered glass and gloves made of thick fabric with fire-resistant properties or rough leather;
- reliably protect your shoulders, neck, chest with work clothes made of thick fire-resistant fabric.
Oil bath cooling
To harden certain grades of steel, cooling is carried out using an air flow created by a special compressor. It is very important that the cooling air is completely dry, as the moisture it contains can cause the metal surface to crack.
There are methods for hardening steel that use combined cooling. They are used to cool parts made of carbon steels that have a complex chemical composition. The essence of such hardening methods is that the heated part is first placed in water, where in a short time (a few seconds) its temperature drops to 200 degrees, further cooling of the part is carried out in an oil bath, where it should be moved very quickly.
Muffle furnaces
To prevent heated objects from coming into contact with fuel and combustion products, they are placed in a special compartment - a muffle. Such furnaces are called muffle furnaces. The muffle is made of fire-resistant materials; the air inside it is heated to a certain temperature, which is then maintained at a constant level.
Since their use does not require high temperatures, they usually operate from an electrical network. Such units have a wide range of uses: for firing ceramic products, in jewelry, chemical, medical production, and the food industry. They are equipped with replaceable muffle chambers for working with different materials.
Classification by type of working environment
Muffle furnaces can provide heating of workpieces in various environments:
- Air
- Inert gas
- Vacuum
The simplest type of muffle furnaces are heaters with a traditional air chamber . The heating chamber in such furnaces is simply a hollow space into which the workpiece is placed.
In many cases, the presence of air is not critical for heat treatment. But there are still some technological operations for which the presence of air in the heating chamber is either undesirable or unacceptable.
When hardening many grades of steel and various alloys, air reacts with the surface layer of metals, which worsens the performance characteristics of the workpieces. Furnaces with inert gases or carbon dioxide supplied to the heating chamber have been developed especially for such cases . Neutral gas displaces air, creating a reliable protective layer.
Furnaces that are adapted for melting metals are often equipped with a heating chamber with a vacuum sealer. Metal melted under vacuum conditions acquires a particularly high-quality structure. Aluminum is often melted in a vacuum.
Additionally, muffle furnaces with different types of heating chambers are often equipped with an exhaust hood . Ventilation removes combustion products, moisture and other vapors from the heating chamber, the presence of which is undesirable during heat treatment.
How to choose a muffle furnace based on heating temperature.
Muffle furnace SNOL
SNOL muffle furnaces are widely used for heat treatment (heating, hardening, calcination) of various materials and samples in research and industrial laboratories. Their volume can be different, depending on the purpose, starting from 1 liter, and the operating temperature can be in one of the ranges:
- moderate – 100-500°C;
- average – 400-900°C;
- high – 400-1400°C;
- ultra-high 400-2000°C.
They differ in the material from which their heating elements are made, it can be a high-quality alloy, silicon carbide heater or lanthanum chromium. The element may be partially or completely pressed. To make a muffle - working chamber, use:
- ceramics;
- fibrous material KTM;
- mullite-silica;
- corundum.
SNOL ovens are equipped with a digital microprocessor thermostat, which is used to regulate and control the temperature, which ensures the accuracy of the technological process. In this case, it is possible to set the duration of heating and holding time. Some models have additional features that allow for more complex programming.
What is the hardening of metal?
The ancient blacksmiths knew that the effect of high temperature on metal can change its structure and properties and actively used this in practice. Subsequently, it was scientifically established that hardening of products made of steel, which involves heating and subsequent cooling of the metal, can significantly improve the mechanical characteristics of finished products, significantly increase their service life and even ultimately reduce their weight by increasing the strength of the part. What’s noteworthy is that hardening parts made from inexpensive steel makes it possible to give them the required characteristics and successfully use them instead of more expensive alloys.
The meaning of the process, which is called hardening of steel alloy products, is to heat the metal to a critical temperature and then cool it. The main goal pursued by this heat treatment technology is to increase the hardness and strength of the metal while simultaneously reducing its ductility.
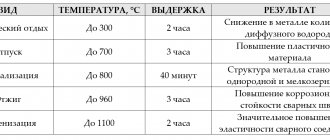
There are various types of hardening and subsequent tempering, differing in modes of implementation, which determine the final result. Hardening modes include the heating temperature, the time and speed of its implementation, the time the part is kept in a state heated to a given temperature, and the speed at which cooling is carried out.
The most important parameter when hardening metals is the heating temperature, upon reaching which the atomic lattice is rearranged. Naturally, for different grades of steel, the critical temperature value is different, which depends, first of all, on the level of carbon content and various impurities in their composition.
After hardening, both the hardness and brittleness of the steel increases, and a layer of scale appears on its surface, which has lost a significant amount of carbon. The thickness of this layer must be taken into account when calculating the allowance for further processing of the part.
Iron-carbon phase diagram
When hardening products made of steel alloys, it is very important to ensure a given cooling rate of the part, otherwise the already rearranged atomic structure of the metal may go into an intermediate state. Meanwhile, too rapid cooling is also undesirable, as it can lead to the appearance of cracks on the part or to its deformation. In order to avoid the formation of such defects, the cooling rate after the temperature of the heated metal drops to 200 degrees Celsius is somewhat slowed down.
To heat parts made of carbon steel, chamber furnaces are used, which can heat up to 800 degrees Celsius. For hardening certain grades of steel, the critical temperature can be 1250–1300 degrees Celsius, so parts made from them are heated in a different type of furnace. The convenience of hardening steel of these grades lies in the fact that products made from them are not subject to cracking when cooled, which eliminates the need for preheating.
You should take a very responsible approach to hardening parts of complex configurations that have thin edges and sharp transitions. To prevent cracking and warping of such parts during the heating process, it should be carried out in two stages. At the first stage, such a part is preheated to 500 degrees Celsius and only then the temperature is brought to a critical value.
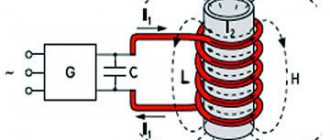
Heating of steel during hardening with high frequency currents
For high-quality hardening of steels, it is important to ensure not only the level of heating, but also its uniformity. If the part is massive or has a complex configuration, it is possible to ensure uniform heating only in several approaches. In such cases, heating is carried out with two delays, which are necessary so that the achieved temperature is evenly distributed throughout the entire volume of the part. The total heating time also increases if several parts are placed in the oven at the same time.