How much does metal weigh?
Specific gravity of metals in kilograms and tons.
| Metal | Weight of a cube (cubic meter), kg. | Weight of a cube (cubic meter), t. |
| Aluminum | 2689 | 2,689 |
| Tungsten | 19350 | 19,35 |
| Graphite | 1900-2300 | 1,9-2,3 |
| Iron | 7874 | 7,874 |
| Gold | 19320 | 19,32 |
| Potassium | 862 | 0,862 |
| Calcium | 1550 | 1,55 |
| Cobalt | 8900 | 8,90 |
| Lithium | 534 | 0,534 |
| Magnesium | 1738 | 1,738 |
| Copper | 8960 | 8,96 |
| Sodium | 971 | 0,971 |
| Nickel | 8910 | 8,91 |
| Tin (white) | 7290 | 7,29 |
| Platinum | 21450 | 21,45 |
| Plutonium | 19250 | 19,25 |
| Lead | 11336 | 11,336 |
| Silver | 10500 | 10,50 |
| Titanium | 4505 | 4,505 |
| Uranus | 19040 | 19,04 |
| Chromium | 7180 | 7,18 |
| Cesium | 1873 | 1,873 |
| Zirconium | 6450 | 6,45 |
Specific gravity of alloys in kilograms and tons.
Source
Basic properties
Smelting copper from ore
Copper, as a metal, is obtained by smelting ore; in nature it is difficult to find pure nuggets; mainly enrichment and extraction is carried out from:
- chalcocite ore, in which the copper content is about 80%, this type is often called copper luster;
- Bronite ore, here the metal content is up to 65%
- covellite ore - up to 64%.
In terms of its physical properties, copper is a red-colored metal; a pink tint may be present in the section; it is classified as a heavy metal because it has a high density.
A distinctive characteristic is electrical conductivity. Due to this, the metal is widely used in the manufacture of cables and electrical wires. In this indicator, copper is second only to silver; in addition, there are a number of other physical characteristics:
- hardness - on the Brindel scale equals 35 kgf/mm²;
- elasticity - 132000 MN/m²;
- linear thermal expansion - 0.00000017 units;
- relative elongation - 60%;
- melting point - 1083 ºС;
- boiling point - 2600 ºС;
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 335 kcal/m*h*deg.
The main properties of copper include the elastic modulus, which is calculated by various methods:
| Copper grade | Shear modulus | Young's modulus | Poisson's ratio |
| Cold drawn copper | 4900 kg/mm² | 13000 kg/mm² | — |
| Rolled copper | 4000 | 11000 kg/mm² | 0,31 — 0,34 |
| Cast copper | — | 8400 | — |
The shear modulus is useful to know in the production of materials for the construction industry - it is a value that characterizes the degree of resistance to shear and deformation under the influence of various loads. The modulus calculated using Young's method shows how the metal will behave under uniaxial tension. The shear modulus characterizes the response of a metal to shear load. Poisson's ratio shows how a material behaves under uniform compression.
Development of mines for the extraction of copper and other metals
The chemical properties of copper describe the combination with other substances into alloys and possible reactions to an acidic environment. The most significant characteristic is oxidation. This process actively manifests itself during heating; already at a temperature of 375 ºC, copper oxide begins to form, or scale as it is called, which can affect the conductive functions of the metal and reduce them.
When copper reacts with a solution of an iron salt, it turns into a liquid state. This method is used to remove copper coating on various products.
Long stay in water causes cuprite
When copper is exposed to a humid environment for a long time, cuprite, a greenish coating, forms on its surface. This property of copper is taken into account when using metal to cover roofs. It is noteworthy that cuprite performs a protective function; the metal underneath does not deteriorate at all, even for a hundred years. The only opponents of copper roofs are environmentalists. They explain their position by the fact that when copper cuprite is washed off by rainwater into the soil or water bodies, it pollutes it with its toxins, which especially has a detrimental effect on microorganisms living in rivers and lakes. But to solve this problem, builders use drainpipes made of a special metal, which absorbs copper particles and accumulates them, while the water flows free of toxins.
Copper sulfate is another result of chemical action on metal. This substance is actively used by agronomists to fertilize the soil and stimulate the growth of various crops. However, uncontrolled use of vitriol can also have a detrimental effect on the environment. Toxins penetrate deep into the layers of the earth and accumulate in groundwater.
How much does a cube of copper weigh?
Specific gravity of metals in kilograms and tons.
| Metal | Weight of a cube (cubic meter), kg. | Weight of a cube (cubic meter), t. |
| Aluminum | 2689 | 2,689 |
| Tungsten | 19350 | 19,35 |
| Graphite | 1900-2300 | 1,9-2,3 |
| Iron | 7874 | 7,874 |
| Gold | 19320 | 19,32 |
| Potassium | 862 | 0,862 |
| Calcium | 1550 | 1,55 |
| Cobalt | 8900 | 8,90 |
| Lithium | 534 | 0,534 |
| Magnesium | 1738 | 1,738 |
| Copper | 8960 | 8,96 |
| Sodium | 971 | 0,971 |
| Nickel | 8910 | 8,91 |
| Tin (white) | 7290 | 7,29 |
| Platinum | 21450 | 21,45 |
| Plutonium | 19250 | 19,25 |
| Lead | 11336 | 11,336 |
| Silver | 10500 | 10,50 |
| Titanium | 4505 | 4,505 |
| Uranus | 19040 | 19,04 |
| Chromium | 7180 | 7,18 |
| Cesium | 1873 | 1,873 |
| Zirconium | 6450 | 6,45 |
Specific gravity of alloys in kilograms and tons.
The density of copper (pure), the surface of which has a reddish tint and a pinkish tint at the fracture, is high. Accordingly, this metal also has a significant specific gravity. Due to its unique properties, primarily excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, copper is actively used for the production of elements of electronic and electrical systems, as well as products for other purposes. In addition to pure copper, its minerals are also of great importance for many industries. Despite the fact that there are more than 170 types of such minerals in nature, only 17 of them have found active use.
Copper is widely used in manufacturing
Where to look for copper for scrap?
Finding sources of copper is a complex issue. This is due to the fact that it is almost impossible to find it in large quantities. The problem is aggravated by the fact that such metal weighs less than others. To get a few kilograms of raw materials you will have to spend a lot of time and effort.
Where to look:
- At home. The sources are outdated televisions, radios, tape recorders, and refrigerators. By disassembling such equipment, a certain amount of metal is obtained. In addition to copper, the device may contain lead, another rare and valuable material.
- In landfills. Used equipment and cables can often be found in landfills. The search for raw materials is hampered by a large amount of waste. But with the right approach, it is possible to identify sources of copper, disassemble them and extract recyclable materials.
- Abandoned enterprises. In old plants, factories, and industrial workshops, different types of ferrous and non-ferrous metal are found. The difficulty lies in disassembling and transporting raw materials. Some abandoned businesses are guarded and attempts to enter are illegal.
Discarded cables can be found near power plants. Spent transformers containing copper are also found there. Other non-ferrous metals contained in electrical appliances can also be taken to the copper scrap collection point.
Where to look for copper for scrap is a difficult question, not because there are few sources of the material. The difficulty is that there are many people who want to make money selling recyclable materials. Therefore, all easily accessible sources of metal are quickly depleted.
Copper density value
The density of this metal, which can be viewed in a special table, has a value equal to 8.93 * 10 3 kg/m 3. Also in the table you can see another, no less important than density, characteristic of copper: its specific gravity, which is also 8.93, but measured in grams per cm 3. As you can see, for copper the value of this parameter coincides with the density value, but do not think that this is typical for all metals.
The density of this, and any other metal, measured in kg/m3, directly affects the mass of products made from this material. But to determine the mass of a future product made of copper or its alloys, for example, brass, it is more convenient to use the value of their specific gravity rather than density.
Basic information about copper
Copper is the most common non-ferrous metal. It received its name in Latin - Cuprum - in honor of the island of Cyprus. It was mined there by the ancient Greeks thousands of years ago. Historians even came up with the Copper Age , which lasted from the 4th to 5th centuries BC. e. At that time, people made from popular metal:
- weapon;
- dishes;
- decorations;
- coins.
In the table D.I. Mendeleev, it ranks 29th. This element has unique properties - physical, chemical and mechanical. In ancient times, copper could be found in the natural environment in the form of nuggets, sometimes of very large sizes. People heated the rock over an open fire and then cooled it sharply. As a result, it cracked, which made it possible to restore the metal. This simple technology made it possible to begin the development of a popular element.
Specific Gravity Calculation
Today, many methods and algorithms have been developed for measuring and calculating not only density, but also specific gravity, which make it possible to determine this important parameter even without the help of tables. Knowing the specific gravity, which differs between different alloys of copper and pure metal, as well as the density value, you can effectively select materials for the production of parts with given parameters. It is very important to carry out such measures at the design stage of devices in which it is planned to use parts made of copper and its alloys.
Specific gravity, the value of which (as well as density) can be seen in the table, is the ratio of the weight of a product made either from metal or from any other homogeneous material to its volume. This relationship is expressed by the formula γ = P/V, where the letter γ denotes specific gravity.
Specific gravity and density, which are inherently different characteristics of a metal, should not be confused, although they have the same meaning for copper.
Knowing the specific gravity of copper and using the formula for calculating this value γ = P/V, you can determine the mass of a copper billet having a different cross-section. To do this, it is necessary to multiply the specific gravity value for copper and the volume of the workpiece in question, which is not particularly difficult to determine by calculation.
Technical indicators of metal alloys
The most common copper-based alloys are brass and bronze . Their composition is also formed from other elements:
- zinc;
- nickel;
- tin;
- bismuth.
All alloys differ in structure. The presence of tin in the composition allows the production of bronze alloys of excellent quality. Cheaper alloys include nickel or zinc. The produced materials based on Cuprum have the following characteristics:
- high ductility and wear resistance;
- electrical conductivity;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- low coefficient of friction.
Copper-based alloys are widely used in industrial production. They are used to produce dishes, jewelry, electrical wires and heating systems. Materials with Cuprum are often used to decorate the façade of houses and make compositions. High stability and ductility are the main qualities for the use of the material.
Units of specific gravity
Different units are used to express the specific gravity of copper in different measurement systems.
- In the GHS system, this parameter is measured in 1 dyne/cm3.
- The MKSS system uses a unit of measurement of 1 kg/m 3.
The SI system uses a unit of measurement of 1n/m3.
If you are faced with different units of measurement for this parameter of copper or its alloys, then it is not difficult to convert them into each other. To do this, you can use a simple conversion formula, which looks like this: 0.1 dyne/cm3 = 1 n/m3 = 0.102 kg/m3.
Copper ore before processing
Who is responsible for accepting copper recyclables?
What is a reception point?
As noted above, obtaining copper through secondary processing is very effective. For this purpose, in almost every city or town there are special collection points for scrap metal , including copper, from where it is then supplied to processing plants.
Thanks to recycling, it becomes possible to produce new technology, parts or equipment without using natural materials.
The acceptance of copper scrap is usually carried out by so-called individual entrepreneurs or LLCs, specializing in the processing of recyclable materials. These can be small private firms, large companies, as well as various environmental organizations that have the necessary equipment, professional knowledge and experience in receiving, storing and transporting scrap. Scrap metal is also accepted by individual resellers, however, this method of disposal is not considered successful, since they usually do not have the appropriate license permitting this type of activity.
Only official points with a license have the right to receive, store and transport scrap metal
How to choose a collection point
The choice of collection point for the delivery of copper scrap metal should be approached responsibly. First of all, you need to study the metal receptacles that are located in the city. You can do this using the search engine on our website:
To view collection points in your city, use the “Select recyclables and city” button located on the right. You will be able to familiarize yourself with prices, addresses and telephone numbers, and based on this, choose the acceptance that suits you best. It should be noted that preference should be given to those reception points that are closest to your place of residence.
Calculate weight using specific gravity value
To calculate the weight of the workpiece, you need to determine its cross-sectional area, and then multiply it by the length of the part and by the specific gravity.
Let's calculate the weight of a rod made of copper-nickel alloy MNZH5-1, the diameter of which is 30 millimeters and the length is 50 meters.
We calculate the cross-sectional area using the formula S = πR 2, therefore: S = 3.1415 15 2 = 706.84 mm 2 = 7.068 cm 2
Knowing the specific gravity of the copper-nickel alloy MNZH5-1, which is equal to 8.7 g/cm 3, we obtain: M = 7.068 8.7 5000 = 307458 grams = 307.458 kg
Let's calculate the weight of 28 sheets of copper alloy M2, the thickness of which is 6 mm and the dimensions are 1500x2000 mm.
The volume of one sheet will be: V = 6 1500 2000 = 18000000 mm 3 = 18000 cm 3
Now, knowing that the specific gravity of 1 cm 3 of M3 copper is 8.94 g/cm 3, we can find out the weight of one sheet: M = 8.94 18000 = 160920 g = 160.92 kg
The mass of all 28 rolled sheets will be: M = 160.92 · 28 = 4505.76 kg
Sheet copper. Weight of copper sheet.
I produce copper sheets in accordance with GOST 495-92. For their production, copper is used that meets the GOST 859-2001 standard. Copper grades M1, M1r, M2, M2r, M3, M3r correspond to this standard.
You might be interested in my other articles:
Copper pipe for water supply and heating. Specifications.
Copper sheets are made in two ways: hot-rolled and cold-rolled; you can see more details about the methods in another article about steel sheets . Depending on the production method, the range of sheet thickness depends. For example, sheets whose thickness dimensions are made by cold rolling will range from 0.4 to 12 mm, and those made by hot rolling will be from 3 to 25 mm. According to the state of the metal, they are divided into soft, semi-hard and hard. They are designated by the letters “M” - soft, “P” - semi-hard and, accordingly, “T” - hard.
Chemical composition of copper.
Hard grades of copper are formed by adding antimony, nickel, zinc, tin and iron. These chemical elements reduce the thermal and electrical conductivity of the material.
If you need better electrical conductivity, then you need to choose copper sheets of grades M0 and M1. In these sheets the percentage of copper is 99.90% and only 0.1% impurities, we can see these values in table 1 below. Impurities include chemical elements such as sulfur, arsenic, antimony. With the addition of antimony to the copper composition, hot forming becomes more difficult. Bismuth and lead also affect pressure processing. These chemical elements are practically insoluble in copper and do not affect electrical conductivity in any way.
Oxygen mixed with copper negatively affects it. The mixture becomes brittle and, accordingly, less plastic, its strength decreases, and its electrical conductivity, weldability and soldering properties decrease. In M0b copper sheets, oxygen is completely absent. Sheet grades M1, M2 and M3 contain about 0.05 – 0.08% oxygen, and grades M1p, M2p and M3p about 0.01%.
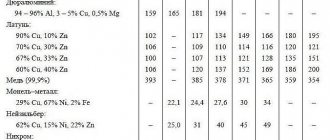
Table 1.
| Copper grade | M00 | M0 | M0b | M1 | M1r | M2 | M2r | M3 | M3r | M4 |
| Copper content,% | 99,99 | 99,95 | 99,97 | 99,90 | 99,90 | 99,70 | 99,70 | 99,50 | 99,50 | 99,00 |
Notation.
The most popular brands of copper sheets are: M1 and M2. The number to the right of the letter indicates the percentage of copper and impurities. In this case, “M1” means that there is 99.90% copper and 0.01% impurities, and in the “M2” grade the percentage of copper is 99.70%, and the impurities will be 0.03%. The lower the number, the lower the impurity content.
Application.
Due to their qualities, copper sheets are used in construction work: in the water supply system, roofing work, in the design of buildings and structures (decorative elements). Various equipment in the climatic and food spheres are made from copper sheets; special conditions are imposed on it in terms of corrosion resistance, fire resistance, in general, such conditions, the operation of which is difficult due to the aggressive environment. Musical instruments, electrical devices, and pipes .
Determination of the mass of 1 pm of rolled metal
For stainless steel pipe: m = ?*(d – s)*s*?/1000
For the “black” pipe: m = (d – s)*s/40.55
where: m – theoretical. weight of one linear meter of pipe in kg, ? = 3.14 (constant value), d – outer diameter in mm, s – wall thickness in mm, ? – density in g/cub. cm.
where: m – theoretical. mass of 1 p/m of circle in kg, ? = 3.14 (constant value), d – outer diameter in mm, ? – steel density in g/cubic meter. cm.
| Determination of the theoretical mass of one sheet |
where: m – theoretical. weight of 1 p/m sheet in kg, V – sheet volume = Thickness x Width x Length, mm, ? – steel density in g/cubic meter. cm, 1E6 – the number 10 to the 6th power.
| Determining the approximate number of sheets in one ton |
Where: ? – steel density in g/cubic meter. cm V – sheet volume = Thickness x Width x Length, mm,
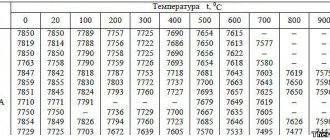
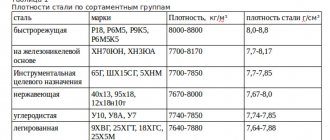
Density of different steel grades (according to GOST 9941-81)
| steel grade | Density, ?, g/cm3 | steel grade | Density, ?, g/cm3 |
| 04Х18Н10 | 7,90 | 08Х18Н10 | 7,90 |
| 08Х20Н14С2 | 7,70 | 08Х17Т | 7,70 |
| 10Х17Н13М2Т | 8,00 | 08Х13 | 7,70 |
| 08Х18Н12Б | 7,90 | 12Х13 | 7,70 |
| 10Х23Н18 | 7,95 | 12Х17 | 7,70 |
| 08Х18Н10Т | 7,90 | 15Х25Т | 7,60 |
| 08Х18Н12Т | 7,95 | 12Х18Н9 | 7,90 |