Copper and bronze, also known as the “red metals,” may look similar at first glance, but they are actually completely different metals.
Copper and bronze are radically different in chemical composition, areas of use and properties. Copper is a pure chemical element and natural mineral that is found primarily in soil and, in smaller quantities, in water. In contrast, bronze is an alloy that contains copper as the main component, with tin and other metallic and non-metallic compounds. There are bronze alloys of various types, with different compositions; so different alloys have different properties and applications. Copper is an excellent electrical and thermal conductor. This metal is used in various fields. However, the key difference between copper and bronze is that copper is a pure chemical element and a natural mineral, while bronze is a metal alloy.
What is copper?
The word "Copper" comes from the Latin word "cuprum". It is a chemical element with atomic number 29 and the letter symbol "Cu". Copper is a ductile metal with very high electrical and thermal conductivity. Copper, due to its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance and good strength, is used to produce a wide range of industrial products. For example, copper is widely used as a conductor of electricity and heat, a building material, and in the production of various metal alloys. Pipes and fittings are primarily manufactured using copper due to its corrosion resistance.
There are many types of copper, which can vary in the amount of impurities they contain. Oxygen-free grades of copper are used in products that require ductility and conductivity.
One of the most important properties of copper is its ability to fight bacteria. After extensive antimicrobial testing by the Environmental Protection Agency, 355 copper alloys, including many brass alloys, were found to kill more than 99.9% of bacteria within two hours of contact. It is worth noting that the normal tarnishing of copper over time does not reduce its antimicrobial effectiveness.
Copper was one of the earliest metals discovered by man. The Greeks and Romans turned it into tools or jewelry, and there is even historical evidence that copper was used to sterilize wounds and purify drinking water. Today it is most often found in electrical products, such as wiring, due to its ability to efficiently conduct electricity.
How to sell scrap bronze profitably, price per 1 kg at collection points
Most people associate the word “bronze” with objects of art and interior design:
- monuments;
- busts;
- antique candelabra;
- antique figurines;
- bells.
But bronze alloy , which is based on copper, is used not only in the artistic industry, but also in industry.
Before you sell bronze scrap, you should familiarize yourself with the types of this alloy, find out where it is used and how it is assessed at collection points. With such information, it is possible to get the maximum benefit from the transaction.
Prices and conditions of admission
Bronze scrap is a low-melting material that does not require a complex technological process for processing. Scrap is accepted continuously; the cost depends on the type of bronze scrap and its chemical composition.
Tin bronze has the highest price, since tin is an expensive non-ferrous metal, the cost of copper is several times higher.
According to GOST, the category of bronze scrap includes 15 items . Each company defines its own criteria when evaluating metal waste, but they are all united by the desire to obtain this type of non-ferrous scrap metal by any means.
Main types when assessing bronze:
- lump scrap;
- scrap mix;
- shavings;
- bronze products (casting).
Since bronze is very similar to brass, the main component of which is also copper, the alloy is analyzed using a special spectrometer.
Also, the composition of the alloy is determined using chemical reagents .
Large volumes of waste are more expensive.
Art and interior items are priced individually.
If the weight of bronze is more than 100 kilograms, it is possible for a specialist to visit the waste storage site to conduct an assessment. For non-cash payments, 10% is added to the accrued amount.
Below is information about how much bronze costs; average prices for 1 kg of scrap are given in table form:
| Scrap | 0-50 kg | 50-100 kg | 100-500 kg | From 500 kg - 1t |
| Scrap bronze - piece | 115-204 rub. | 170-215 rub. | 175-215 rub. | 190-228 rub. |
| Scrap mix | 180-184 rub. | 180-215 rub. | 180-215 rub. | 210-215 rub. |
| Shavings | 65–100 rub. | 100-170 rub. | 100-170 rub. | 110-180 rub. |
| Art and interior items | Price is negotiable | Price is negotiable | Price is negotiable | Price is negotiable |
Lump scrap includes bronze items with permissible contamination of up to 3% , a piece weighing no more than 100 kg .
Usually this:
- industrial waste,
- parts of super-power cranes,
- turbines
The main requirement is a homogeneous alloy composition of the entire batch.
Scrap with contamination up to 10% belongs to grade 2 ; scrap fragments can be made of various alloys.
Wood chips , industrial waste, in which the contamination is no more than 2%, are rated no less highly.
They are excellent for recycling without prior fractionation.
Of particular importance in the assessment of mixed alloys is the purity of the metal being submitted .
This indicator for bronze is not specified in GOST; it is agreed upon between both parties: the receiver and the client.
Many people are interested in the question - what is more expensive: copper or bronze? Having analyzed the average prices for receiving non-ferrous metal, you can find out that individual components of the classic alloy are more expensive than bronze itself - copper from 260 to 300 rubles per kilogram, and tin is even more expensive. And the price for scrap bronze does not exceed 215 rubles per 1 kg.
You can hand over bronze scrap to any non-ferrous scrap metal collection point.
Due to the similarity of the metal to brass, inspectors who do not use spectral analysis may mislead you into thinking that the metal is brass. The cost of this metal is less. To prevent this from happening, it is important to know the characteristic differences between these alloys.
How to distinguish bronze from brass:
- The color of the bronze alloy is darker than that of brass and has a characteristic reddish tint.
- Scratches remain on brass products due to mechanical impact .
- The fracture of the products differs in structure and color. Brass has a light-colored and fine-grained fracture surface. Bronze has a dark-colored fracture with a coarse-grained texture.
- Brass is never used in shipbuilding, since sea water has an aggressive effect on it.
Brass and copper are even more similar. Read more about how to distinguish them in a separate article.
To make it more profitable to hand over bronze scrap, it is preferable to agree on the handing over of the alloy with an organization that collects metal waste legally.
The following companies have metal analyzers
- spectrometers;
- steeloscopes;
- laboratories for chemical analysis.
When an appraiser visits a client to inspect scrap, an express analysis of alloys is possible, which will affect the objective value of the metal.
If a sufficient amount of metal waste has accumulated, then a large company will undertake the delivery of scrap to one of its collection points.
for legal entities include:
- preparation of documents for disposal in compliance with all legal regulations;
- free dismantling of bulky structures;
- collection of recyclable materials using your own special transport.
But it is not always possible to find such a company everywhere and not always.
If you turn to private traders involved in collecting scrap metal, the price will be more modest, but there will be no transportation costs. Don't forget to ask them about their license.
In any case, the scrap metal will go to its intended destination, namely to a processing plant, where it will be used to create secondary metal for the needs of metallurgy and other industrial sectors.
Recycling scrap bronze is saving copper natural resources .
It is impossible to imagine the life of a modern person without the use of metals. Landfills of rusting metal trash not only pollute the environment, but also lead to the gradual depletion of natural resources.
This situation is especially true with copper-containing ores and minerals that are not replenished by nature.
Selling scrap bronze is beneficial for people and the planet .
If, after reading the article, you change your mind about handing over scrap bronze, then watch the video that will help you melt it down yourself:
What is bronze?
Bronze is a metal alloy that contains copper as the main component and about 12 percent tin. Some other metals and non-metals can also be included in its composition, depending on the requirements, to obtain the desired properties. The most commonly added metals are aluminum, manganese, zinc or nickel. Examples of other components are silicon, phosphorus or arsenic. The addition of various metallic and non-metallic compounds results in a wide range of bronze alloys with varying properties.
Composition of copper and bronze
Copper is naturally present in soil as a mineral at a concentration of 50 parts per million. The main source of copper is copper sulfide (CuFeS2), which is also known as chalcopyrite. But it exists in its pure form as a natural mineral, not combining with other elements; this is "native copper". There are 29 isotopes of copper, of which only two types (63Cu and 65Cu) are stable, while the other isotopes are radioactive.
Bronze is a metal alloy containing copper (Cu) as the main element, the second important element being tin (Sn). Their percentage varies depending on the properties required, but most often the alloy contains about 12% tin and 88% copper. Their percentage changes slightly with the addition of other metals and non-metallic compounds.
There are many many bronze alloys and they have different properties depending on their use.
Main types of alloys:
- Commercial bronze: copper (90%), zinc (10%);
- Architectural bronze: copper (57%), zinc (40%), lead (3%);
- Plastic bronze: contains significant amounts of lead (Pb) to improve ductility;
- Phosphor bronze (or tin bronze): copper, tin (0.5% to 1.0%), phosphorus (0.01% to 0.35%);
- Aluminum Bronze: copper, aluminum (6% - 12%), iron (6% -max), nickel (6% -max);
- Silicon bronze: copper, zinc (20%), silicon (6%).
Difference between metal and alloy
There are several methods to distinguish non-ferrous metal from its alloys. This can be done both without the use of special means and with the help of chemical reactions and tools. The best experts in metals are the people who work with them, as well as those who are well aware of their properties. So, a person who knows the difference between copper and brass is a foundry worker, a chemistry teacher, a scrap metal acceptor with extensive experience, a pawn shop worker, or a jeweler. All of them, to one degree or another, work with metals and know a lot about them.
Definition of color and sound
The main difference between a metal and its alloys is color. To determine what a product is made of, you need to:
- Clean it from the layer of dirt and patina.
- Examine carefully under daylight or under a white fluorescent lamp. Under no circumstances should the product be examined under the light emanating from an incandescent lamp.
- The best option would be to compare a brass or bronze product with a copper one. A piece of wire, which is always made of non-ferrous metal, is suitable as such an example.
Copper always has a reddish tint, brass is yellow or golden , and the color of bronze can be from yellow-pink to brown.
The main thing in this method is to take your time and carefully examine the sample. But if brass contains more than 80% bronze, then the color of the alloy will not differ much from the color of the metal.
A characteristic feature that allows you to distinguish brass from bronze is the sound heard when a metal object hits the sample under study. The difference will be fairly easy to hear. A copper object has a muffled and low sound, while a brass object, on the contrary, has a ringing and high-pitched sound. This is a very effective method, but is only used when testing large samples.
We recommend: Bags for large volumes of construction waste
Application of chemical solutions
To check whether the person in front of you is copper or brass, you can use a small amount of hydrochloric acid solution. This chemical is dropped onto the test sample and the reaction is monitored. Nothing will happen to pure metal, but a white substance will be released on the surface of the brass - zinc oxide. But a salt solution helps to distinguish copper from bronze. It needs to be heated and poured over the sample being studied. The metal will darken when exposed to a hot saline solution, unlike bronze, which will not change at all.
Use of copper and bronze
Copper has a wide range of uses in many areas; mainly in electrical, roofing and plumbing applications due to its high electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance and durability. It is also used in architecture, in coinage, and in the manufacture of various alloys and machine parts. Small amounts of copper are used to produce food additives and fungicides.
Bronze is widely used in shipbuilding, in the manufacture of parts and mechanisms for boats. One of the advantages of bronze is its resistance to seawater corrosion. It is also used to produce medals and musical instruments.
Application area
Bronze alloys, due to the diversity of their properties, find a wide variety of applications.
- The most famous is the material for sculptures and many decorative items: figurines, ashtrays, lamps, grilles, railing decorations and more. Casting bronze allows you to obtain the most complex castings that literally depict the pores of the skin.
- In jewelry, the material is used much less frequently, although it used to be almost the basis of women's jewelry.
- Bronze fittings - overhead hinges, locks, handles, taps, mixers and even plumbing fixtures. The alloy provides not only exceptional durability and corrosion resistance of objects, but also allows you to turn them into an elegant decorative element.
- Many parts are made from cast bronze of different compositions - gears, bushings, seals, parts of equipment designed to work under water.
- Deformable bronzes are used in high-precision technology.
- Other types of alloys are used in areas where the usual tin bronze is not used. For example, beryllium bronze has much higher thermal and electrical conductivity, and therefore is actively used in electrical engineering.
The alloy performs excellently under conditions of variable dynamic loads. Therefore, parts of aircraft navigation instruments, car circuits, etc. are made from beryllium bronze.
- Another well-known application is fittings of various kinds. For more active use in water supply, bronze is too expensive a material, however, the most critical components, as well as numerous fasteners, are made from a copper alloy, since it is extremely resistant to corrosion and inhibits bacterial activity.
Bronze is the oldest and most famous alloy in human history. The diversity of its composition and properties ensures that it is widely used today.
This video will show you how to clean bronze items:
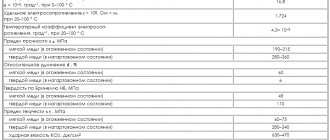
Melting temperature
Almost every type of metal has a different melting point. It is therefore not surprising that copper and bronze differ in melting point.
Pure copper melts at about 2000 F (1090 C).
Bronze has a lower melting point than pure copper because bronze is often made by combining copper with tin, which has a melting point of 450 F (230 C). Thus, the melting point of bronze will fluctuate between these two values, up or down, depending on the percentage of copper and tin.