Bronze products are widely used among amateur craftsmen who make various objects of art, weapons and accessories, jewelry, etc.
The lack of a production base is not an obstacle to the work; the main problem is the lack of information about the properties, melting point of bronze and processing modes of copper alloys. Most amateurs do not know that bronze casting is also done at home; the main thing is to follow the technology and provide the necessary conditions for the process to proceed.
Main characteristics of bronze alloys
Bronze is the collective name for copper alloys with various alloying additives. There are many such additives that can be used:
Classification of bronze alloys
- Tin.
- Aluminum.
- Lead.
- Beryllium.
- Silicon.
All types of bronze contain small amounts of zinc, lead or phosphorus. At the same time, alloys of copper with zinc (as a full-fledged component) do not belong to bronze and are classified as brass. A separate group are alloys of copper and nickel (constantan, cupronickel, copel, nickel silver).
Bronzes are divided into:
Copper alloys - characteristics
- tin. They are alloys of copper and tin in one ratio or another;
- tin-free. Instead of tin, other materials are present (beryllium, aluminum, etc.).
Tin types are the most common. Widely known bell bronze (80% copper and 20% tin). The disadvantage of tin bronze is its fragility.
Tin-free compounds have a lot of specific qualities that are successfully used to perform various tasks.
Common types of tin-free bronze are:
- Beryllium bronze. Has high strength, superior to high-quality steel.
- Silicon-zinc. It is resistant to friction and has high fluidity in the molten state, which is facilitated by the addition of silicon.
- Lead. Demonstrates high resistance to corrosion.
- Aluminum. It is resistant to corrosion and has high friction capabilities.
Alloying additives of alloys in bronze
She's so different
History has honored bronze, giving it an entire era in the development of mankind. The Bronze Age advanced humanity forward, contributed to the development of crafts, cities and... the redistribution of territorial property.
Bronze is a “versatile” alloy. It was used as a strategic metal (bronze weapons - knives, shields, swords, gun barrels) and as a material for works of art. Bronze statues were considered the pinnacle of ancient Greek art.
Bronze mirrors were known to the mysterious Etruscans as early as the 6th century BC, and were used in Japan in the 18th century AD.
Bronze spear tip (7th-4th century BC).
The production of bronze in ancient times was associated with magic and witchcraft rituals. Blacksmiths were akin to healers or priests, experts in herbs and minerals. In the Russian “Collection of ... craft techniques” you can read:
“... take green copper, add yellow arsenic (orpiment), you get white copper...”
Sugar bowl made of patinated bronze
Production technologies developed and the use of the alloy expanded.
It's not copper!
Our fusion in art has always resonated. And we want to tell you about the glorious “Bronze Horseman”. About what is happening in the second capital, St. Petersburg. The famous equestrian statue of Peter the Great, which stands on a pedestal, the Thunder Stone. The Frenchman Falconet was invited to sculpt the reformer king. Russian sculptor Fyodor Gordeev was entrusted with making a snake, and even then according to a Frenchman’s sketch.
Figurine cast in bronze
Sculpture is the calling card and guardian (as has long been believed) of the city. Only the rider and horse are not copper. They are bronze. He was nicknamed “Copper” by the light hand of our Alexander Sergeevich Pushkin. This is how poetry (the poem “The Bronze Horseman”) overcame the truth...
We recommend: LITHIUM - in space, on earth, under water
However, Pushkin’s example was quite worthy - even the old man Homer, without hesitation, called a bronze weapon copper.
Bigger does not mean better: a quarter of a century ago in China, a huge statue of Buddha made of metal, or rather a bronze alloy, was erected on a hill. The statue is considered the largest in the world.
Generally accepted marking of alloys
It is necessary to understand that the composition of any alloy contains several additives that give this brand of bronze certain specific qualities. For example, the BrO3Ts12S5 alloy contains tin, zinc and lead.
You can learn about the composition of this alloy from its markings. The letters present in it, except for the first Br (bronze), mean:
Bronze markings - explanation
- aluminum – A;
- iron – F;
- manganese – Mts;
- tin – O;
- antimony - Su;
- zinc – C;
- nickel – N;
- phosphorus - F;
- silicon – K;
- lead - C;
- beryllium - B.
Preparing for bronze casting at home
To melt bronze at home, you must have the appropriate equipment and devices. The process occurs at high temperatures, with the release of smoke and other combustion products, so it is best to work in a garage or workshop; it is not recommended to perform all actions in an apartment.
Melting furnace used at home - device
Melting bronze compositions requires a high temperature, in the range of 900–1200°, so it is impossible to do without a muffle furnace or forge. It will be necessary to equip high-quality exhaust ventilation; the floor covering must meet all fire safety requirements. It is necessary to prepare a container for melting (experts recommend making the melt in a cast iron container with an elongated spout for casting precision, which is called a crucible).
To remove the hot crucible from the furnace and grab the hot castings, you will need pliers (tongs) and a hook. Be sure to take care of protection from sparks or splashes of molten metal and prepare an apron and mittens from dense and durable material (ideally, you can use a welder’s suit).
You will need to make a casting mold, and you will need charcoal for the forge.
Casting technology
In order to make a complex structure or a high-quality part, you can use another method, which involves using a model made of fusible materials. In such a situation, you can use paraffin or wax to make a casting mold. This model is simply melted and placed in boiling water.
To ensure the accuracy of the geometric characteristics and shapes of the model, you can use the finished product. Using it, a plaster mold is obtained, which will be used to cast an exact copy.
Features of the casting process
The bronze melting process occurs in the following sequence:
- Bronze scrap is crushed and placed in a crucible.
- The crucible is placed in a muffle furnace, which is recommended to be heated in advance.
- The molten metal must be overheated, for which it is kept in the oven for 5 minutes longer than necessary. This makes the melt more fluid.
- Using a hook and tongs, the crucible is removed from the oven and immediately poured into the prepared mold.
The mold should be prepared by thoroughly calcining it in the oven. If this is not done, the metal will immediately cool down and become hard when casting begins, without filling the entire mold.
Centrifugal casting
The form is prepared in the following order:
- The oven heats up to 600°.
- The mold is placed in the oven and heated to the desired temperature.
- The heating of the oven is increased to 900° and the mold is maintained in such conditions for about 3–4 hours.
It should be taken into account that the melting temperature of bronze of a given grade should be lower than the heating value of the furnace. The melt must be heated to a higher temperature to obtain maximum fluidity (bronze has a high viscosity in the liquid state), as well as to obtain a certain temperature reserve for high-quality production of the casting.
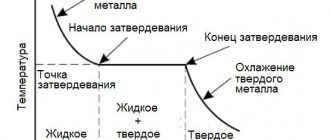
Processing temperature and technical properties of tin bronzes
Advantages and disadvantages
Bronze has many positive qualities. Among them:
- variety of properties and, consequently, areas of application;
- the ability to create options for various processing methods (casting or deformation) depending on needs;
- slight shrinkage (0.5 - 1.5%);
- the possibility of repeated processing without loss of properties, that is, bronze can be processed;
- high resistance to chemical influences of the environment (water, air, acids);
- greater elasticity of many options.
The main disadvantage is the high cost of some brands, for example, tin bronze. Types of other composition, such as aluminum alloy, are much cheaper. Thus, the cost of the materials under consideration is largely determined by the alloying elements included in their composition.
How to make a casting mold
The mold is made using molding sand and a mold. The mixture consists of sand (75%), clay (20%) and coal dust (5%). The components are thoroughly mixed until smooth.
The flask consists of two shallow boxes stacked on top of each other. One, the bottom one, has a bottom and is filled with molding sand to the very top. The second box does not have a bottom, but is equipped with two crossbars.
Mold making process:
Casting mold and its elements
- the model, previously coated with a thin layer of talc or graphite powder, is pressed halfway into the molding sand of the lower drawer;
- then the top box is installed and filled with the mixture, compacted so that the model is completely and tightly covered with it;
- for pouring, one or more holes are made - sprues;
- the form is cut along the junction line of the boxes and divided in half;
- the model is removed, and the boxes are connected again, the voids from the model are connected and form a cavity that has the required shape.
At the end of the process, the form must be dried a little and can be used for its intended purpose.
Pouring bronze into a mold
Pouring bronze melt into a casting mold
Pouring the melt in itself is not difficult - the metal is poured in a thin, even stream until the mold is completely filled.
Difficulties may arise if there are no air channels into which air can escape. If the outlets are clogged, air pockets will not allow the melt to completely occupy the entire mold, and the casting will be damaged. The problem can be solved by using a centrifuge, which distributes the metal inside the mold and helps it overcome the resistance of air pockets.
Collect Several Sertling Cores
Sertlings are (almost) cute fire creatures that live in the Swamps, Ashlands, and around fire geysers. After defeating them, Surtling Cores may drop, which will open up crafting options for Charcoal Kiln and Smelter.
If you don't like fighting waves of Surtlings, perhaps because you're playing alone, then you can try finding some burial chambers in the Black Forest biome. Inside these creepy looking tombs will be Surtling cores on sticks, like delicious (very hot) cotton candy. However, beware of skeletons.
You'll also need some stone and wood for the next steps, so be sure to stock up when collecting cores.
How to make high-quality castings
To obtain high-quality bronze casting, subsequent machining of the casting will be required. It is necessary to sequentially perform the operations of separating the sprues, removing flash, mechanical grinding and polishing of the product. It is impossible to immediately obtain a high-quality finished casting at home, so you need to prepare for finishing procedures.
Art bronze casting technology in pictures