Profile pipes are widely used in private and industrial construction. They are used to create gazebos, greenhouses, garages, outbuildings, and billboards. Designs are not only classic rectangular, but can also have a wide variety of configurations. Therefore, it is very important to correctly calculate the maximum permissible bend of the pipe. This will ensure the structure’s strength, durability and allow it to maintain its original shape.
When making structures from a profile pipe, you cannot bend it “by eye” - the appropriate calculations must be made
Properties and features of profile pipe products
It is customary to call profile pipes whose cross-section differs from round. The most common options are square and rectangular products. What makes them especially popular is the fact that the final structure created on their basis is relatively lightweight. Moreover! Thanks to the specific shape, fastening pipe elements to various surfaces and to each other is greatly simplified.
These building products are made from a wide range of alloys and metals. However, profile pipes made of low-alloy and carbon steel are most often used. Each metal is characterized by such a natural quality as a point of resistance. It can be both maximum and minimum. The first, in particular, causes deformation of constructed structures and leads to kinks, which can result in fractures.
When bending, it is important to take into account such characteristics as the type of product and its density, cross-section, size, as well as the flexibility of the material and its rigidity. Knowing all these properties of the metal, the performer will be able to understand how the structure will behave during operation.
In addition, it should be remembered that when the product is bent, its internal parts are subject to compression, which leads to an increase in their density and a decrease in size. The length of the outer layer increases accordingly, it becomes more stretched, but less dense. Moreover, even after the process is completed, the original characteristics of the middle sections are preserved.
When bending a pipe, you need to take into account the properties of the material from which it is made, its dimensions and wall thickness
Important! Stress when bending a pipe profile will necessarily arise even on the segments of the product that are furthest from the neutral zone. Particularly high pressure will be experienced by layers located in close proximity to the above-mentioned neutral zone.
Additional recommendations
If you do not perform preliminary calculations of permissible radii, as well as the force and rate of deformation, then critical deformations will occur:
- the inner side of the profile pipe, when squeezed, will wrinkle into uneven folds;
- in the area with the maximum radius, wall ruptures will occur due to the radial force limit.
To perform cold forging, the best option is to use sheet or profile blanks with a thickness of up to 10 mm.
In practice, when the selected sheet material or profile pipes do not allow bending along a given radius, specialists decide to use another metal or use preheating technologies to high temperatures. Have questions? Request a call back!
How does the strength of the material affect the permissible bending radii?
The GOST standards in force in our country regulate in sufficient detail the characteristics and properties of the elements used in calculating the bending strength of a pipe. First of all, in this context, the minimum radius by which a profile pipe product can be bent is considered. It depends on the bending conditions. If this procedure is carried out with heating or filling the pipe cavity with sand, the value of the outer diameter starts at 3.5 DN (DN refers to the nominal bore).
In the case where the contractor has access to specialized equipment (for example, a pipe bending machine), which allows the sequence of necessary operations to be performed without heating or other additional measures, then the minimum diameter is 4 DN.
If it is necessary to make a fairly sharp bend, the diameter should be at least 10 DN, since this procedure will be carried out by other methods, mainly at high temperatures.
Of course, the values provided by state standards can be slightly reduced, but then it is necessary to calculate the profile pipe for bending very carefully. Deviations from GOST are possible if, with the bending method used, the wall thickness is guaranteed to change from the original by 15%. Only then can you be sure that bending by smaller amounts will not have a significant impact on the strength of the structure in the future.
It is possible to bend a pipe to its maximum permissible radius only using a special machine or device
Instructions for the calculator
Please note that in non-integer numbers it is necessary to put a period, not a comma, that is, for example, 5.7 m, not 5.7. Also, if something is not clear, ask your questions through the comment form located at the very bottom.
Initial data
Calculation scheme:
Span length (L) - the span through which a beam or console length is thrown.
Distances (A and B) - distances from supports to places where loads are applied. For scheme 3, A is equal to the length of the beam console resting on 2 supports.
Standard and design loads are the loads for which a square pipe is designed. You can calculate them using the following materials:
- calculator for collecting loads on a floor beam;
- example of collecting loads on a floor beam;
- An example of collecting loads on rafters.
F max is the maximum permissible deflection, selected according to Table E.1 of SNiP “Loads and Impacts”, depending on the type of structure. Some values of this indicator are given in Table 1.
Table 1. Maximum deflection for some structures according to SNiP.
| Type of beam | Span length | Requirements | Fmax _ |
| Beams for floors, coverings, roofs | L ≤ 1 m | Aesthetic and psychological, that is, those in which the deflection of the beam will not be “conspicuous” | 1/120 (1/60) |
| L = 3 m | 1/150 (1/75) | ||
| L = 6 m | 1/200 (1/100) | ||
| L = 12 m | 1/250 (1/125) | ||
| Beams of coverings and floors if they contain elements susceptible to cracking (screeds, floors, partitions) | any | Constructive | 1/150 (1/75) |
| Jumpers | any | Constructive | 1/200 |
| Notes: 1. Without brackets, Fmax is indicated for the span, in brackets - for the cantilever. 2. In the case of intermediate values of the span length L, the maximum deflection Fmax is found by linear interpolation. | |||
Number of pipes - usually one beam is indicated, but if you want to strengthen it and put another similar beam next to it, then you should select “two” in the column.
Design resistance Ry - this parameter depends on the steel grade. The main values of this indicator are given in Table 2.
Table 2. Design resistance of steel according to GOST 27772-88.
| steel grade | Analogue | Rolled thickness | Design resistance, Ry |
| Unknown | — | any | 210 MPa |
| C235 | St3kp2 according to GOST 535-2005 | 2 - 20 mm | 230 MPa |
| 20.1 - 40 mm | 220 MPa | ||
| S245 | St3ps5, St3sp5 according to GOST 535-2005 | 2 - 20 mm | 240 MPa |
| 20.1 - 30 mm | 230 MPa | ||
| S255 | St3Gps, St3Gsp according to GOST 535-2005 | 4 - 10 mm | 250 MPa |
| 10.1 - 20 mm | 240 MPa | ||
| 20.1 - 44 mm | 230 MPa | ||
| S275 | St3ps according to GOST 535-2005 | 2 - 20 mm | 270 MPa |
| S285 | St3sp, St3Gps, St3Gsp according to GOST 535-2005 | 4 - 10 mm | 280 MPa |
| 10.1 - 20 mm | 270 MPa | ||
| S345 | 12G2S, 09G2S according to GOST 19281-2014 | 2 - 10 mm | 335 MPa |
| 10.1 - 20 mm | 315 MPa | ||
| 20.1 - 40 mm | 300 MPa | ||
| S345K | 10KhNDP according to GOST 19281-2014 | 4 -10 mm | 335 MPa |
Pipe size - here you need to select the pipe size that you want to test for the specified loads.
What formulas and tables are used
To correctly calculate the bending strength of a pipe, you need to know the length of the part. This is done according to the following formula:
D= 0.0175×P×Y+p1, where
D is the length of the workpiece; P – pipe bending radius (mm); Y is the required bending angle; р1 – distance for holding the workpiece, required when using special equipment.
Next, we estimate the size of the area expected to bend using the following formula:
D1= π×U/180(P+DN/2), where
D1 – length of the bending section; π is a known mathematical constant; Y – bending angle (degrees); DN – diameter along the outer surface of the pipe (mm).
GOSTs No. 617/90 and No. 494/90 contain the lowest values of the main characteristics, on the basis of which the bending strength of a profile pipe product is calculated.
Good to know! This approach - regulation of minimum values - ensures the convenience of the master, as well as the greatest safety when performing work and, of course, during the operation of structures, in particular, those built from brass and copper profiles.
The main characteristics used in the process of calculating the bending strength of a pipe are given in the table below.
Table 1
| Minimum bending radius | Minimum free length | External diameter |
| 90 | 60 | 30 |
| 72 | 55 | 24 |
| 36 | 50 | 18 |
| 30 | 45 | 15 |
| 24 | 35 | 12 |
| 20 | 30 | 10 |
| 16 | 25 | 8 |
| 12 | 18 | 6 |
| 8 | 12 | 4 |
| 6 | 10 | 3 |
The data in this table applies to brass and copper tubing. And the calculation of the bending load on a profile pipe made of steel is carried out in accordance with the data given below (GOST No. 3263/75).
table 2
| Pipe size | Free length (minimum) | Minimum bend radius | ||||
| Conditional pass | External diameter | Hot condition | Cold state | |||
| 100 | 114 | 230 | 340 | 680 | ||
| 80 | 88,5 | 170 | 265 | 530 | ||
| 65 | 75,5 | 150 | 225 | 450 | ||
| 50 | 60 | 120 | 180 | 360 | ||
| 40 | 48 | 100 | 150 | 290 | ||
| 32 | 42,3 | 85 | 130 | 250 | ||
| 25 | 33,5 | 70 | 100 | 200 | ||
| 20 | 26,8 | 55 | 80 | 160 | ||
| 15 | 21,3 | 50 | 65 | 130 | ||
| 10 | 17 | 45 | 50 | 100 | ||
| 8 | 13,5 | 40 | 40 | 80 | ||
The main parameters that must be taken into account when determining the bending load also include the wall thickness and diameter of the workpiece being processed. The correlation of these two indicators is presented in the next table. By the way, the information contained in it can also be used to calculate the load on a round pipe.
Table 3
| Diameter (mm) | Bend radius (minimum) for wall thickness | |
| Thickness more than 2 mm | Thickness less than 2mm | |
| 60/140 | 5D | 7D |
| 35/60 | 4D | 6D |
| 20/35 | 3D | 5D |
| 5/20 | 3D | 4D |
One more thing needs to be said. Various online calculators available on the Internet are intended to replace the manual calculation of the load of this type. They work in accordance with the formulas laid down in them, focused on various samples of pipe products. The range of applications of a modern online calculator is very wide: from the simplest calculation of a round pipe for deflection, and ending with calculating the load on a profile pipe when it is bent.
Deformation of pipes at the bend is sometimes inevitable, but it can degrade the performance of the finished structure
Calculation of pipe bending radius using a ruler
To carry out the calculations, you need to take two rigid rulers 30 and 50 cm long. Initially, the bending radius of the already bent pipe is measured, which must be repeated on the workpiece. The ruler must be applied to the original pipe and the distance between the ruler and the middle of the pipe must be measured (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1 Measure the width in the original pipe.
Rice. 2. Pipe bending radius.
Using the obtained ruler measurement data, it is necessary to select suitable parameters for the radius and diameter of the arc from tables 1 and 2.
- A – pipe interval (width), mm
- D – arc diameter, mm
- R—bending radius, mm
Table 1. Using a 30 cm ruler
| Interval | 5 | 7,5 | 10 | 12,5 | 15 | 17,5 | 20 | 25 |
| Diameter | 4505 | 3008 | 2260 | 1813 | 1515 | 1303 | 1145 | 925 |
| Radius | 2253 | 1504 | 1130 | 907 | 758 | 652 | 573 | 463 |
| Interval | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 90 | 100 |
| Diameter | 780 | 603 | 500 | 435 | 391 | 340 | 325 |
| Radius | 390 | 302 | 250 | 218 | 196 | 170 | 163 |
Table 2. Using a 50 cm ruler
| Interval | 5 | 7,5 | 10 | 12,5 | 15 | 17,5 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Diameter | 12500 | 8341 | 6260 | 5013 | 4182 | 3589 | 3145 | 2525 | 2113 | 1603 | 1300 |
| Radius | 6250 | 4172 | 3130 | 2507 | 2091 | 1795 | 1573 | 1263 | 1057 | 802 | 650 |
| Interval | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 130 | 160 | 200 |
| Diameter | 1102 | 963 | 861 | 785 | 725 | 678 | 611 | 550 | 513 |
| radius | 551 | 482 | 432 | 393 | 363 | 339 | 306 | 275 | 257 |
Bending process
Any deformation leads to a decrease in the load-bearing capacity of the profile pipe and is accompanied by the occurrence of long-term stresses on its walls. On the inner layer, due to compression of the metal, the density increases, and on the outer part, tension, on the contrary, reduces the value of this indicator. The shape of the section also changes as expected. The combination of these factors leads to the fact that the load-bearing capacity of the structure at the bending point is noticeably reduced. This is true for a round pipe, as well as for rectangular and square pipe products. Moreover, for the last two, this phenomenon is not as pronounced as for a pipe with a round cross-section.
However, in any case, a careful approach is required to assess the degree of applied load when bending the workpiece. Then unnecessary breaks and distortions will not appear on it. From the point of view of functional purpose, this concerns, first of all, round pipes from which outlets for water supply systems are made.
Good to know! The folds formed lead to blockages, increase the resistance of the transported liquid and reduce the permeability of the working environment.
Therefore, the degree of oval deformation for a part with a diameter of up to 20 mm should not exceed 15 percent. As the diameter increases, the value of this indicator decreases to 12.5 percent. The same figures are also used when determining the optimal deflection load for a pipe with a profile cross-section, and the above diameter values refer to a circle inscribed/circumscribed in/around a rectangle(s) or square(s).
Methods for bending pipes along a radius
The process of bending steel pipes along a radius allows them to be given a partial or complete curved-smooth configuration, which does not depend on the shape of the profile section. So, when bending a hollow profile on a steel workpiece, a force simultaneously acts, compressing it along the inner wall and a force, stretching it along the outer radius. The specificity of this process is that:
- the profile at the moment of giving it a bend shape may become distorted, in which the pipe will lose alignment;
- when the outer wall of the pipe is stretched in the area of maximum radius, the wall may rupture due to the influence of radial force;
- the compressed inner part of the pipe, with uneven contraction, will be crushed by folds in the form of corrugations from the application of tangential forces.
Therefore, there are two main ways to bend a pipe along a radius, namely:
- directly on the cold pipe,
- when heating the bend area.
The cold method is used mainly for pipes with a small diameter, but in this case it is necessary to clearly know the minimum bending radius of the pipe along the center line.
When the bending site is heated, more favorable conditions are created for the process of a given deformation, since the metal acquires sufficient ductility, reducing the likelihood of the formation of various defects. Hot methods of bending a pipe along a radius are used mainly for large-diameter workpieces, since this technique is more expensive and requires more time to perform a single bend.
When using both methods, it is necessary to know the technological process that will ensure a uniform cross-section of the metal pipe throughout the entire radius of curvature and the complete absence of cracks and folds on the walls.
What load acts on the corrugated pipe?
An important criterion that is taken into account when calculating is the exposure time and type of load. These indicators are regulated by SP 20.13330.2011 “Loads and impacts”. There are different pressure forces:
- Constant, when the mass and the acting force do not change over a long period of time. Impacts are created by building elements (load-bearing and enclosing structures), soils, and hydrostatic pressure.
- Long lasting. Temporary gypsum plasterboard partitions, stationary equipment, stored materials, and also as a result of changes in humidity or shrinkage.
- Short-term. Equipment, weight of people and vehicles, climatic conditions created by snow, wind, temperature changes, icing.
- Special. Seismic and explosive impacts leading to changes in soil structure, the result of vehicle collisions and caused by fire.
The Code of Rules provides calculation formulas, tables and diagrams for each type of load. A realistic combination of all types of pressure is also taken into account.
Calculation of the load on a profile pipe calculator
When using a profile pipe to create load-bearing structures, bending calculations must be performed. This type of rolled pipe is used in industrial, commercial and private construction. Canopies, all kinds of frame and stair structures, trusses, shelving, canopies, greenhouse structures, roofing system elements, and gazebos are made from it. Therefore, it is impossible to do without correct and careful calculations. Exceeding the permissible pressure will lead to deformation or rupture of the product at the bending point of the corrugated pipe.
Using methods for calculating loads on a profile pipe, you can:
- maintain the original shape of the products;
- give the structure increased strength;
- increase the period of operation;
- minimize material costs;
- avoid negative destructive consequences.
Indicators of mass and bending load
When calculating a profile pipe: mass and bending are the main indicators. It is necessary to know the weight of a linear meter of rolled steel so as not to make a mistake in the strength values of the structure being created. The determination method is aimed at selecting the optimal cross-section of rolled pipe at different lengths. A clear example of the relationship between these two indicators is presented in the tables below.
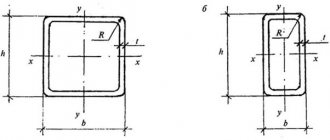
Table No. 1. Values for square products:
Table No. 2. Values for rectangular products:
Pipe bending methods
The need to bend pipes may arise in a number of cases, for example, during the installation of a pipeline, if it is necessary to “bypass” any obstacle. It is also often necessary to resort to this operation in the process of manufacturing various metal structures, such as canopies, greenhouses, gazebos, etc.
It should be noted that when it comes to pipe bending, we mean the following types:
Types of pipes suitable for bending
Next, I will tell you how to bend all of the above types of pipes at home.
Round metal
The process of bending metal blanks with a round cross-section is quite complex, since they are easily deformed and sometimes even torn. Therefore, when bending is carried out in industrial conditions, especially if a small radius is required, before carrying out this operation, the pipe is calculated for bending.
Bending a metal part at home
At home, of course, you won’t need the exact formula for calculating pipe bending. The only thing you need to determine is the minimum allowable radius. Its meaning largely depends on the way in which this operation is performed:
- when heating a part filled with sand – R= 3.5xDH;
- using a pipe bending machine (cold bending) – R=4xDH;
- bending to obtain corrugated folds (hot bending) - R= 2.5xDH.
A minimum radius equal to two diameters can be obtained by hot broaching or stamping. However, it is impossible to carry out such a bend at home.
These formulas use the following values:
| Letter designation | Meaning |
| R | Minimum bend radius |
| D.H. | Workpiece radius |
It must be said that there is a more universal calculation - the radius should be at least five pipe diameters.
So, we have sorted out the theory a little, now let's move on to practice. As mentioned above, there are several ways to solve this problem. The simplest of them is the use of a special machine - a pipe bender.
Hydraulic pipe bender
True, the price of such a tool is quite high - the cost of a hydraulic machine, which allows you to bend workpieces with a diameter of up to four inches, starts at 15,000-16,000 rubles. The cost of a manual pipe bender, which allows you to work with parts with a diameter of up to one inch, is 4,700-5,000 rubles.
If you often have to do this kind of operation, but don’t want to pay a lot of money for a pipe bender, you can do it yourself. On our portal you can find detailed information on how to make a machine for bending profile pipes with your own hands.
Scheme of bending a profile or round pipe around the pins
However, a pipe bender is not always available at hand, and, moreover, if you need to perform this operation one-time, then purchasing a tool for this, of course, does not make sense. In this case, you can bend it using pegs.
This is done as follows:
- first of all, you need to draw a bend radius on a suitable site;
- then metal rods are dug in along the contour. It is advisable to place them as close to each other as possible. For reliability, the rods can be concreted.
Next to the outer rod, you need to insert another one so that the part to be bent can fit between them. This is necessary to fix it;
- Next, you need to pour salt or sand into the bent pipe. In this case, wooden plugs should be driven into the holes on both sides;
- after this, the part is fixed between the first two rods and then bent around the remaining rods, as shown in the diagram above.
Homemade pipe bender made from hooks
An alternative to this option is to use hooks that are attached to a piece of plywood and form the required radius, as in the photo above. If you need to get a smaller diameter, you should use a wide disk or roller as a template.
It must be said that both methods are suitable for parts with a diameter of no more than 16-20 mm. If you want to bend a workpiece of a larger diameter, the bending area should be well heated.
If you need to shape workpieces made of non-ferrous metals, the bending strength of which is significantly lower than that of their steel counterparts, you can use a spring. The latter must strictly correspond to the internal diameter, as it is inserted inside the tube. Of course, you can put the spring on the outside, but in this case it is inconvenient to bend it.
Having protected the tube with a spring, it bends with your own hands. The work should be done carefully to achieve the desired radius without damaging the part.
Profile pipes
Profile
Profile pipes are much more difficult to bend, since due to their shape they have increased strength. Small cross-section products can be bent using the methods described above.
There is also another method of bending a profile pipe, which allows you to work with workpieces of a fairly large cross-section. Its principle is as follows:
- you need to pour sand or salt into the workpiece, and then securely plug the ends with plugs;
- Next, the part must be securely clamped in a vice;
- then the bend area should be heated red-hot;
- After this, the workpiece must be adjusted with a mallet until the desired radius is obtained.
Cuts in a profile pipe
If you have a welding machine and a grinder, then you can bend workpieces of even the largest diameter without much effort. This is done as follows:
- first of all, the bending radius is marked on the workpiece;
- Then along the entire radius you need to mark strips on three sides of the profile blank. The smaller the radius, the smaller the step between the strips should be;
- then, using a grinder, cuts are made on three sides of the part according to the markings made;
- now the workpiece bends without any problems;
- after obtaining the desired angle, the cuts should be welded;
- To complete the work, you need to clean the seams and sand them.
In this way, it is possible to produce parts of even complex shapes, and the bending accuracy is very high. However, experience with an angle grinder and a welding machine is required.
Bending a metal-plastic blank by hand
Metal-plastic
Metal-plastic pipes, on the one hand, bend very easily, but on the other hand, they break easily. Therefore, the work must be done very carefully. It should be remembered that the minimum bending radius of a metal-plastic pipe is similar to the radius of metal blanks, i.e. must be at least five diameters.
If the diameter of the pipe is 16 mm, then it can be bent without any special devices. This is done as follows:
- Grasp the part with both hands from above. In this case, place your thumbs under the pipe, parallel to it, and close them together, as shown in the photo above;
- then bend the pipe with both hands and be sure to provide support with your thumbs;
- Having bent the pipe to the required radius, move it in your palms to the left or right, and then repeat the procedure;
- In this way, bend the workpiece and move it until you get the desired angle.
To get better at it, practice performing this procedure on pipe scraps, since it is likely that your pieces will break at first.
The photo shows bending of a metal-plastic blank using a spring conductor
It is much more difficult to bend a pipe with a diameter of 20 mm around your fingers. Therefore, any other suitable surface can be used as a stop. However, it is most convenient to carry out this work using a spring conductor, which can be either external or internal, i.e. which is inserted inside the workpiece.
To make a bend with an internal jig in the middle of a long piece, tie it to the rope and then push it to the desired depth. After making the bend, extend the spring by pulling on the rope.
Here, in fact, are all the folk methods of bending pipes that I wanted to share with you.
Load on round pipes
Application
Round pipes can be found anywhere. Supports, racks, columns, containers - this is not a complete list of the uses of shells (the shell is a cylindrical metal sheet without ends).
The ring pipe profile can be found when laying water, oil, and gas pipelines both at home and on an industrial scale. They are an excellent material for fence posts, gates, and gates.
Due to the presence of a closed contour, a round pipe has a significant advantage in comparison with channels and angles with similar linear parameters.
Many people think that in order to determine the strength of a riser along the axis under a compressive load, you need to have data on the magnitude of the load and cross-sectional area.
As a result of dividing the first parameter by the second, the required strength was obtained. After comparing the obtained parameter with the permissible value taken from the table, a conclusion is made as to whether such a load can be applied to a particular riser or not.
If the number is less than allowed, then everything is fine. But there is one thing: the calculations are valid for stretching, not compression
.
Using a calculator
For the option with compression of a round post, you can carry out the necessary calculations using an online calculator.
First you need to familiarize yourself with additional concepts. These include:
- Loss of overall stability. Checking the loss is necessary to avoid huge losses of other types.
- Loss of local stability. We are talking about an earlier “finishing” of the rigidity of the riser walls under the action of a load on the shell. In other words, the pipe begins to bend inward, and the round section turns into a profile of an irregular curvilinear shape, which leads to loss of stability.
Using Excel
There is a special Excel program for comprehensive verification of the calculation of risers regarding stability and strength. The basis of this program is the data of GOST 14249 89. With its help, you can calculate the maximum load on a round pipe, as well as the general forces on the shell of a circular cross-section.
On the Internet you can often find the following questions: “What load can a round pipe 3, 4, 6 meters long withstand? How to calculate this using an online calculator? Can I do this myself?
We will try to give a detailed answer to these and other questions. The best explanation would be a practical calculation of the magnitude of the vertical load on a round pipe. For example, let’s take a vertical round riser with a diameter of 57 mm and a length of 3 meters (most often used for arranging sheds, garages, and other structures) and calculate how much load the pipe can withstand.
What data is needed
The algorithm for working with the program is as follows:
- First you need to open GOST 14249 89, from which you need to write down the first 5 initial values. To quickly find parameters, use the notes for each cell.
- Fill in cells D8, D9, D10, entering the linear parameters of the risers into them.
- Enter possible loads in cells D11 to D15.
What happened as a result
You must not only be able to use the program, but also be able to explain the results obtained.
It is necessary to compare the ratio of the effective load to the permissible one: if you receive a number greater than one, the pipe is overloaded. Otherwise, the riser will withstand the given weight, provided that the load on the round pipe is calculated correctly.
Devices for bending profile pipes
The range of equipment designed for bending profile pipes includes devices of varying degrees of design complexity, productivity, and accuracy of the result.
Horizontal bending plate with holes
This simple device is used for bending a profile pipe of a small cross-section; it allows you to bend it without a pipe bender. It is a horizontally located steel sheet of considerable thickness, into the holes of which metal stop pins are rigidly installed. When bending, the product is placed between stops, which are positioned in accordance with the required bending radius. A nozzle is placed on one of the stop pins, which makes it possible to adjust the bending radius. The process starts from the center of the workpiece. This method requires the application of significant physical force. The shape accuracy of the resulting part is low.
Mandrel bending
To work with profiles with a wall height of up to 25 mm, a mandrel is made. A workbench with a large horizontal surface is used as the base of the device. The template is made from plywood sheet or MDF. The template and profile are attached to the workbench with clamps. The pipe is bent smoothly. If it is necessary to bend parts along different radii, several templates are made.
PG family of manual profile benders
Roll benders PG-1 and PG-3 are popular rolling devices, manually operated. They are used in individual farms and small repair and production workshops. The standard machine is designed to work with rectangular and square pipes, channels, strips of steel, as well as aluminum, copper and their alloys. To process round pipes, the purchase of an additional set of rollers is required. The rollers are installed between two supporting walls of the housing. In the PG-2 profile bender, the rollers are located outside the housing.
The PG-6 machine is the most powerful and productive in this family. Effective for serial bending of similar products. Moreover, you can simultaneously bend 3 profiles, the height of which does not exceed 40 mm. The maximum cross-sectional size that PG-6 can work with is 80 mm, wall thickness is 3 mm.