Home / Accessories and parts
Back
Reading time: 2 min
0
3317
Typically, low resistance is used in welding work, since this ensures that no current energy is lost. This is achieved by using low resistance materials as conductors.
The ballast is needed in order to create an artificially increased resistance, which may be necessary in some situations.
In this case, the current value is also higher than necessary and must be adjusted. The welding ballast helps to carry out welding faster and easier.
- STRUCTURE AND PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
- WHAT ARE THERE ARE BALLASTNIKS?
- WE MAKE THE BALASTNIK INDEPENDENTLY
- INSTEAD OF CONCLUSION
Ballast for testing a welding inverter with your own hands
interesting homemade radio circuits
- ELWO
- 2SHEMI
- BLOG
- DIFFERENT SCHEMES
- THEORY
- VIDEO
- LED
- MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
- MEASUREMENTS
- TECHNOLOGIES
- REFERENCE
- REPAIR
- PHONES
- PC
- FOR BEGINNERS
- Battery and charger
- SECURITY
- AUDIO
- AUTO
- BP
- RADIO
- MD
- TRANSMITTERS
- MICROCIRCUITS
- QUESTION ANSWER
There was a desire to make an active load for welding inverters to diagnose their output characteristics. I came across this article on the Internet. Since the load will be used exclusively on devices with a constant output voltage and with strict observance of polarity, therefore the circuit presented in this article has been slightly simplified:
Do you think this scheme will work correctly with the introduced simplifications? Is the transistor IRLS3036-7PPbF suitable? It seems to be suitable for current and voltage. Plus, the article says nothing about the power of resistors R1 and R2. What should it be like? or even a nichrome spiral should be used. And what are the requirements for the op-amp, in addition to a single-pole 12V power supply? ——————————————— In general, I figured out the resistors. These should be nichrome spirals, with the indicated resistances and powers - the first is 3.6 kW, the second is 4.5 kW. A maximum current of 300 A will flow through them. The only question left is whether the redesigned circuit will correctly stabilize the voltage at the junction of spirals R1 and R2 at 20 V.
Yes, I also wanted to do that at first. A current shunt, an ammeter and a voltmeter are available, everything has been purchased. I started looking on the Internet for what could be used as a ballast load, and came across this article.
Tell me, where can I get a spiral like the one in the photo and what resistance should it be?
For each electrode there is such a parameter as arc voltage. We divide it by the range of operating currents (welding - cutting) for a given electrode. we get the range of spiral resistance. We accept more. Then you can move the crocodile mass to a smaller one. Just don’t forget to calculate the power at the cutting current. that is, determine the cross-section of the spiral conductor so that it does not burn out during cutting. For nichrome, the current density is 10 A/mm2.
Yes, even from the TV. if it uses a powerful induction motor with a wound rotor and requires an accelerating station! They also come flat wound with a diameter of about 45 mm. So they don't burn out. Here is my long-used welding resistance!
Ballasts in welding: how, why and for what?
After all, what is a conductor? This is a material with minimal resistance so that electric current passes through them with the same minimal losses. This is common practice. The exception is cases with tasks “on the contrary”: when resistance needs to be increased.
This need arises when the current readings are too high and need to be regulated. It is for such purposes that a welding ballast exists. It makes welding easier and faster.
- How it works?
- How to make a ballast with your own hands?
- Ballast rheostat settings
- RB-302
- RB-302U2
- RB-306
- BBR
- Rules for working with ballast rheostats
How it works?
At its core, it is a ballast rheostat - a special device for generating increased resistance for welding electricity. This rheostat is distinguished by its simplicity. It is built into many advanced and expensive models of welding machines, and can also be purchased separately.
In addition, you can build a ballast yourself without any problems. It should be noted that every self-respecting welding master has such a device in his storage room.
According to the principle of its operation, the welding ballast is a point of obstacle in the path of the movement of electric current; it is a “point” of high resistance. From an external point of view, it looks like a complex thick spring.
Why do you need a ballast?
This spring is always equipped with a movable contact, which, when moving along the spring, changes the length of the path that the current passes through the ballast.
This device cannot boast of a particular variety of models.
There are some differences, they are determined by the following criteria:
- Dimensions of the spring: the longer it is, the longer the path of electrons through all turns of the rheostat, the greater the resistance reduces the current strength.
- The nature of the metal with certain resistance coefficients.
- The thickness of the spring is also directly proportional to the resistance force. The thickness is related to the length of the rheostat.
In fact, it turns out as follows: without a ballast rheostat, the current would have a force of 250 A. If you connect a ballast to this circuit, the electric flow will begin to lose strength and would have only 10 A at the output.
Of course, the regulator can change the length of the spiral path along which the flow passes. The losses in this case would be different.
What is the correct name for a grinder tool?
First, let's figure out what a “grinder” is. The name “grinder” is very strongly attached to this instrument. In professional language, this tool is called an angle grinder (angle grinder). But historically, this tool was first assembled in Bulgaria, which is why the name “grinder” was attached to the angle grinder.
Why do you need a grinder?
A grinder or angle grinder performs a simple function - grinding. But many craftsmen use angle grinders not only for grinding, but also for working on concrete, metal and even wood. But this tool was originally created only for grinding, however, a modern grinder can easily cut, polish and clean materials.
At the same time, grinding and cleaning can be done with almost any material that comes to hand. To do this, use various nozzles, each suitable for its own type of material. Angle grinders can process: cement, concrete, slate, brick, glass, porcelain, wood and even plastic.
The main advantage of this tool is that it is almost universal; you only need to change the attachments.
The first criterion is the size of the disk used
The most important and first criterion that you need to decide on when buying an angle grinder is the size of the disc used. At the moment, the minimum size of a cutting disc is 0 115 mm, and the maximum possible size is 230 mm.
Just note that not the entire part has the ability to cut, but only the one protruding beyond the body of the angle grinder. This means that if the case is at least 55mm wide, then about half of a 115mm disc (even less) can cut something. Simply put, a 115 mm grinder can cut a board no thicker than 30 mm (and in practice, a maximum of 25 mm). At the same time, all disks tend to wear down, that is, in a minute of operation this figure can be halved. Based on this, you can already think about the size of the disk.
After all, for cutting metal pipes with a diameter of 20 millimeters or more, a 115 mm grinder will no longer be appropriate due to low wear resistance. And if you buy an angle grinder for cutting pipes, then at least 180 mm. And this is only for cutting, but what if you need a tool for grinding? There is no need to take more here; it will be enough to choose a tool for 125 mm, which is the norm for most grinding attachments.
As you noticed, choosing is not so easy; you first need to think about what the tool is needed for, and only then start selecting it.
Let us characterize the types of angle grinders based on size so that we can more easily understand what will suit us best.
Angle grinder 115 mm
This is the smallest saw blade size that can be purchased. It is suitable for the simplest work, and often, wheels of this diameter are used exclusively for grinding, since the smaller the size, the less the weight. This is the best option for small jobs.
Angle grinder 125 mm
This is the next largest type and at the moment it is the most popular among our population
Grinders of this size are not heavy, but very comfortable and have decent power characteristics, and, importantly, still have a low cost. This grinder can be used for both grinding and cutting. Of course, such an angle grinder will not be able to handle parts that are too thick, since the depth of penetration of the blade is much less than the radius, but for household work this grinder is just right
Of course, such an angle grinder will not be able to handle parts that are too thick, since the depth of penetration of the blade is much less than the radius, but for household work this grinder is just right.
Angle grinder 150 mm
This type of grinder is not very popular in everyday life, but is sometimes in demand. This grinder is somewhat more powerful than the previous ones and allows you to perform more voluminous work.
Angle grinder 230 mm
This is the maximum you can buy based on the diameter of the circle. The most important advantage of such an angle grinder, of course, is in a large circle. With this tool you can cut bricks, tiles, boards and even pipes without much effort, but it is better not to use such a grinder for grinding. Firstly, it has a very large weight, which is extremely inconvenient when grinding material, and secondly, a large circle will prevent you from getting to narrow grinding spots. You should buy such an angle grinder only if you are planning a major renovation or large-scale construction. This grinder is not suitable for small jobs
How to make a ballast with your own hands?
The first step is to find a suitable metal wire. It could be, for example, copper. Additionally, you will need a cylindrical shape, for example, a pipe and an ammeter. You need to think about what to make the moving contact from; it could be a wire.
The straight wire needs to be turned into a tight spring. To do this, it is wound onto a cylindrical shape, trying to place the turns as close to each other as possible. The end of the twisted wire must be connected to the wire for current. We also attach a moving contact.
The next step is very important: you need to check the operation of the new rheostat with help. Ammeter. The fact is that a homemade ballast for a welding machine is not as accurate as factory models.
The next caveat is that our rheostat is not equipped with a housing, so compliance with safety regulations becomes even more mandatory.
Ballast rheostat settings
The main thing in a high-quality welding process is stable performance of the electric arc, or rather, its current-voltage characteristics. Modern inverters cope well with this requirement.
Marking of ballast rheostat.
This is done by converting the current into two stages and switching the inverter itself. All other welding machines cannot boast of such characteristics. Therefore, a ballast rheostat must be present next to them.
It is designed for stepwise control of arc operation and compensation of the current component during recharge from the transformer. Nichrome wire in the parallel connection circuit is the main component element. It is important that each section of the rheostat is connected to the network independently, using a switch.
Such a rheostat has only two working functions:
- Current regulation in a discrete manner.
- Compensation of the direct current component formed during the feeding of the welding element using a transformer.
The performance and overall efficiency of a ballast rheostat directly depend on the number of turns or sections of the spiral. After all, each of them is an element of a chain that is broken using a switch.
The circuit is serial, and the connection of sections is parallel. This combination gives an excellent result: periodically connecting each of the elements to the work in order to regulate the voltage in the welding machine.
The connection of the rheostat to the welding circuit must be in series with the power source.
Control buttons are always located on the outer wall of the protective metal case. The most advanced rheostatic models have internal fans that cool the device’s elements while operating at high current levels.
Primary requirements
Grounding is done with a copper cable with a cross-section of at least 6 mm or metal fittings with a cross-section of at least 12 mm.
The copper cable is secured to the housing through a special bolt on the installation, marked “Earth” (another designation is possible). In addition to the main electric welding equipment, in arc welding machines it is also necessary to ground the terminal of the secondary winding to which the conductor going to the part being welded is connected. If the cable supplying current is two-core, then the “zero” and “phase” wires cannot be used to ground the welding transformer.
Basic requirements for ensuring electrical safety:
- all non-current-carrying elements of welding installations must be connected to the grounding circuit;
- welding machines, for connection to the grounding circuit, are equipped with a special bolt with the corresponding designation, to which the grounding wire is attached;
- a separate grounding point must be provided for each electrical installation;
- It is prohibited to ground welding machines in series;
- If there is no way to ground the equipment, a residual current device must be used.
For effective protection against electric shock, according to electrical safety standards, the resistance of the ground loop should not exceed 5 Ohms. In order to achieve the specified parameters, it is necessary to ensure the largest possible contact area of the ground electrode with the ground, as well as good current conductivity.
To connect the grounding electrode to the grounding conductor, a welding method is used or clamps are used. Regardless of the connection method, the joint must be protected from possible corrosion; for this, resin is most often used.
The presence of a short circuit between the transformer winding elements is checked, as well as the serviceability of the protection systems.
In electric welding machines in which an arc is created between the electrode and a part that conducts electricity, it is necessary, in addition to the housing elements, to ground the terminal of the secondary winding of the voltage source, which is connected by a return cable to the part.
Rules for working with ballast rheostats
Despite the simplicity of design and use, ballast rheostats require certain operating rules to be followed:
- Study, remember and work only if you comply with the conditions set out in the technical data sheet of the device. Don't forget to take into account climatic conditions.
- Do not work with RB in conditions of dense dust or near places where there is a lot of gas or steam, which very quickly destroys the electrical insulation in the device.
- Constantly check the device in the laboratory in accordance with GOST RD 03-614-03.
Ballast drawing and voltage graph.
If the rheostats overheat, you need to connect several rheostats to the arc - in sequential order. Well, if the welding current is less, then the resistance should be increased.
When working with aluminum, for example, the alternating current needs to be adjusted within very small limits, only up to 20%. In this case, incomplete compensation of the direct current component occurs.
If we are talking about full compensation, then you need to use devices of the UKDN or UDGU brands, which are equipped with capacitor banks.
Do-it-yourself ballast for a welding machine
For stable arc burning, a welding current of a certain value is required. It is easier to maintain current-voltage characteristics with a ballast rheostat. These devices are built into inverters and other unified welding machines. When using simple transformers and rectifiers, you can create increased electric current resistance using a factory or self-made ballast. Adjustable resistance provides the amperage required for welding workpieces. Used in welding machines where there are no appropriate settings.
Pros and cons of equipment
The advantages of rectifiers include:
- high power with compact dimensions;
- ability to generate current with constant parameters;
- supply of a unipolar charge to the electrode, facilitating the rapid appearance of an arc;
- economical consumption of electrical energy;
- reduced risk of accidental fire;
- the ability to control the quality of the seam at the stage of its formation;
- expanding the functionality of the equipment;
- reduced consumption of filler wire (savings become noticeable when using a rectifier in an industrial environment).
Along with the positive qualities of the device, there are also negative aspects, which include:
- loss of power;
- deterioration in the quality of operation of the device when the network voltage decreases;
- instability to moisture;
- sensitivity to short circuits in the power supply network.
Seam quality.
Purpose and principle of operation
High-quality welding work using the simplest welders is possible only by adjusting the operating parameters of the output current. The resistance must change in the required range; this effect is achieved using a regulator. The power of the ampere ballast directly depends on the number of turns (sections) along which the slider moves, changing the length of the electrical circuit. The switch breaks it if necessary.
A ballast rheostat for a welding machine has two main functions:
- discretion of electrical resistance for welding current values;
- compensation of current-voltage surges during arc ignition and metal transfer.
A set of constantan resistances does not heat up critically when voltage is applied. According to the principle of operation, the rheostat device is parallel-connected plates or a metal spring. The chain length is adjusted in steps. The rheostat's operation is based on Ohm's physical law. The high voltage electrical pulse is “extinguished” when it hits a ballast obstacle, the amperage decreases due to an increase in the “R” parameter. Resistance ballast allows you to work on high-frequency currents, weld thin parts, and connect workpieces made of aluminum and stainless alloys.
General information about the device and its purpose
The welder knows what a welding rectifier is: the device looks like a converter unit with voltage and current regulation. At the output of the rectifier there are 2 wires with negative and positive terminals.
When one of them is connected to the electrode, and the other to the workpiece, a powerful electric arc is excited, melting the metal.
Equipment is classified according to the complexity of its design and the presence of additional functions.
However, the assembly principle of all devices is the same: a transformer that produces the required voltage is included in the circuit along with semiconductors that pass the positive component of the current sinusoid.
What types of welding is it used for?
The rectifier for the welding machine is used in the following technological processes:
- Electric arc method using electrodes treated with various compositions. Through the use of such rods, a stable arc is maintained. This helps to obtain a uniform, strong seam.
- Welding large metal parts. Adjusting the current parameters allows you to work with workpieces up to 5 cm thick. At the same time, the device is also used for joining thin-walled parts. The installation of a rectifier explains the expansion of the scope of application of welding units.
- Melting of the edges of the workpieces or the core of the electrode used.
- Welding using filler wire. Rectifiers are indispensable when working with infusible tungsten-coated electrodes.
- Connecting parts made of stainless, low-carbon steel, cast iron, and difficult-to-weld alloys.
- Cutting metal blanks. To do this, the current strength is increased, due to which the arc begins to burn through the material.
Device
The basis of any ballast for welding machines is metal, which performs the function of electric ballast. The load value is changed by the regulator. This is essentially a movable contact element fixed to the linear surface of an electrical device. Since it delimits part of the electrical circuit, one of the poles must have a terminal to connect to the electrode or ground. The device is quite simple, understandable to schoolchildren studying the “electricity” section.
Sectional type devices are equipped with additional switches that include sections in a common chain. When the sections are closed, they are not activated and no voltage is supplied to them. When installing ballast rheostats, much attention is paid to the housing. It must withstand the thermal load created during operation. On factory versions, all controls, including toggle switches, are usually located on a common panel. Typically, cooler cooling systems and fans are provided. They increase the work cycle; the equipment does not need to be turned off regularly or several similar devices need to be connected to the welding machine at the same time to one welding machine.
Design and circuit diagram of the rectifier
The electrical circuit of the device includes the following components:
- Power transformer. According to the principle of operation, it is similar to a converter operating with variable parameters.
- Rectifier unit with semiconductors. To convert alternating current into direct current, silicon diodes (uncontrolled switches) and thyristors (controlled valves) are included in the circuit.
- Starting block. The device automatically turns off the welding unit when the rectifier fails.
- Control Panel. Includes means for adjusting parameters and measuring instruments.
- Overcurrent protection unit. Prevents device failure due to overheating. Such situations often arise due to non-compliance by the welder with the work technology.
- Cooling system. The circuit of this block contains a fan and several radiators. To maintain normal temperature in the rectifier housing after turning on the unit, the cooling system is periodically started for a while.
It is recommended to include a three-phase rectifier equipped with an appropriate transformer in the electrical circuit. In this case, voltage surges will be less pronounced, this will increase the efficiency of the welding equipment and improve the quality of the seam.
SV device.
Features and Specifications
The technical documentation of ballasts for welding indicates several important parameters:
- rated operating amperage with a conditional “dip” of voltage at the terminals;
- adjustment ranges;
- minimum difference between electric currents and currents of adjacent sections;
- duration of work under load (cycle time interval).
There is a classification of ballast rheostats; they are distinguished by several main characteristics:
- along the length of the circuit, it is possible to achieve fine adjustment of current parameters with high accuracy;
- the type of materials used, each alloy has an individual resistance (for high-power welders, a metal with a high electrical loss coefficient is chosen, for compact ones - with a low resistance);
- the thickness of the metal elements, the resistance per unit length and the size of the device depend on this.
When choosing welding equipment, it is advisable to take these features into account.
Purpose of ballast resistors
Currently, asynchronous electric motors with a wound rotor are widely used as electric drives for lifting devices and cranes. To regulate the speed and torque of an electric drive of this type, a circuit is used to connect special ballast resistors to the rotor supply circuit. This makes it possible to obtain a reduced rotation speed of the electric motor, which is a basic requirement when lifting and lowering loads.
Starting resistors create active resistance in the power supply circuit of electric motor windings. When choosing these resistors for a crane electric drive, it is necessary to take into account the mechanical characteristics of the drive and the power dissipation of heat losses. In each individual case, the connection diagram of the crane electric drive corresponds to a certain value of mechanical parameters. They display the dependence of the torque on the motor shaft on the rotor speed of the electric motor. In most cases, these characteristics are expressed in terms of relative units. For this reason, the resistance of ballast resistors is indicated in terms of these relative units, and the calculated current of the long-term permissible operating mode is indicated as a percentage of the rated value for the electric motor.
READ How to connect PlayStation 4 to the Internet via a laptop
How to make it yourself
It is easier to make your own ballast rheostat in the form of a spiral. Use soft (annealed) wire. You will need a cylindrical object for winding. You can use a piece of metal or plastic pipe. For a mobile contact, a wire from a welding holder is suitable.
It’s not enough to make a ballast yourself; you need to test it. You need to connect the contacts to an ammeter. All that remains is to wind the wire piece around the form and secure it to an electrically insulating stand. The end of the twisted wire is connected to a power source. The holder is attached to the moving current-carrying element.
After measuring the current strength with an ammeter in different positions of the holder, you can put a scale with current parameters on the supply. A homemade ballast rheostat is inferior in accuracy to a factory one. The open model cools naturally. The device must be used with caution.
A homemade ballast rheostat is inferior to a factory one in terms of accuracy and workmanship, so you need to use the device carefully, observing safety measures.
Popular models
The line of ballasts marked “RB” are 5- and 6-position options with value increments from 5 to 10 amperes. The numerical designation corresponds to the range from the minimum to maximum value of the welding current.
RB-302
For semi-automatic and manual welding in modes from 30 A to 70 A, it is recommended to connect this model of welding rheostat to transformers, rectifiers, and generators. The duration of activation is at least 10 minutes, this time is enough for welding in the garage or at home.
Rheostat with a 6-position switch, works with equipment connected to a single-phase 220 V and three-phase 380 V network. The housing and internal elements are made of modern materials, metal elements are fechral, support plates are ceramic.
RB-306
This is a resistor model with an improved cooling system. The resistances are modular, made of 3 mm fechral wire, they are easier to change. The first branch is a tubular heater. The current adjustment is quite accurate. The rheostat is combined with cutters and high-power cooking equipment. On the basis of RB-306, modifications of the BBR for multi-station welding are assembled.
Ballast rheostats and regulators
Ballast rheostats
The operation of devices consisting of several posts is unthinkable without a ballast rheostat. This device creates the necessary current-voltage parameters and is responsible for controlling the current strength in the electrical circuit during electric arc welding and deposition of a metal layer with a melting electrode. In addition, rheostats are also used in research laboratories and automated control schemes.
Species and types
Based on the type of resistor material, rheostats are made into metal, liquid and ceramic. Based on the cooling method, rheostats are divided into two types: liquid (oil, water) and air-cooled.
Metal air-cooled rheostat
Air-cooled metal rheostats are in greatest demand due to their compactness and efficiency. Such a rheostat is easiest to adapt to the characteristics of the task being performed, both in terms of electrical and thermal characteristics.
A typical example of a metal rheostat is RB-302 U2. It regulates the current strength during manual arc welding and electrode application of metal, from welding rectifiers to many posts and DC generators with a voltage not exceeding 70V. In comparison with analogues, the RB-302 U2 rheostat is lightweight - only 15 kg and has high efficiency.
Design and principle of operation
Rheostat RB - 302 U2 is a resistance having 7 stages, which are controlled by contact knives and toggle switches located on the front part of the device.
Current steps from 6 to 10A are controlled by adjusting toggle switches, and from 20 to 80A by contact knives. Controllable current range from 6 to 315A. The difference between the currents does not exceed 6A. The maximum resistance does not exceed 5 Ohms, and the minimum is not less than 0.095 Ohms. The load duration (LOD) of the rheostat is 60%, and the cycle duration is 5 minutes. The front panel of the rheostat shows the current at each of the 7 stages when the voltage on the rheostat is reduced to 30V. The 6A current stage resistance element is made of an electric heater, tubular in shape. Other resistance parts are made of heat-resistant fechral wire from 2.2 to 3.0 mm.
Rheostat RB - 302 U2 is used for welding both in confined spaces and under a roof canopy that protects it from rain or snow.
The ballast rheostat is connected to the welding circuit in series, the first contact goes to the output, and the remaining contact goes to the output of the regulator. When using RB-302 U2, you need to control that the voltage does not drop below 30V, otherwise the elements may overheat and the rheostat may fail. Repair and maintenance of the ballast rheostat RB - 302 U2 is facilitated by convenient access to the device elements due to the removable front panel and walls. For comfortable movement, the rheostat is equipped with two handles.
Safety
When using a rheostat, you should not forget that during operation its walls heat up to 100 degrees Celsius. It is prohibited not only to make repairs, but also to move the rheostat while the power source is connected. It is also unsafe to adjust contact knives and rheostat toggle switches in a loaded state.
Block of ballast rheostats
This device is used in electric arc welding, as well as for the assembly of automatic devices powered by a VDM and the assembly of welding stations when cutting metal with an electrode with its further separation using a jet of compressed air (gouging).
The block of ballast rheostats BBR - 4x315 (based on RB-302) is used to control the current of multi-station class welding rectifiers (VDM-6303, VDM-1202S) and to supply the required (current increase over time) current slope and voltage to welding machines of any design .
Constructions
BBR - 4x315 (based on RB-302) is a structure made in the form of a frame, into which four rheostats RB - 302 U2 are mounted, fixed in a stationary position using brackets. On the bottom tier there is a duplicated fixation block for connecting welding cables for each of the posts, and a block of clamps for connecting the network wire from the VDM. For maximum convenience, the clamp blocks with the output terminals of each ballast rheostat RB-302 are united by special buses.
Thanks to their potential, ballast rheostats not only enhance the efficiency of welding teams at a factory or construction site, but also facilitate the convenience of adjusting the current-voltage characteristic when using old welding machines equipped with a twist-type handle.
Operating and connection rules
According to GOST RD 03-614-03, it is necessary to regularly check devices in accredited laboratories or service workshops. When connecting a ballast in series to a welding machine, it is important to follow several rules:
- operating conditions must correspond to those stated in the technical documentation, usually indicating a temperature range from -40 to +45ºС and a relative air humidity of no more than 80%;
- there are restrictions on dust and gas contamination, they are associated with the design features of ballast rheostats; the housing has ventilation slots into which electrically conductive dust and vapors can get;
- it is necessary to monitor the heating of the body; when welding aluminum, some types of stainless steel, it is better to connect several rheostats at once or use one in 20% of the range to provide partial compensation instead of full.
The rules apply to self-made ballasts. Electrical safety requirements are becoming more stringent.
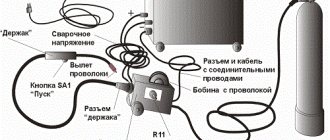
Ballast for testing a welding inverter with your own hands
Who has assembled devices and who is confident in their capabilities. I can recommend such a small test method and only then talk about currents!
I make a 0.5 ohm shunt. To check and remove oscillations, it is sufficient at a certain current and output voltage. And to fully load and calibrate the devices at the maximum current, I go down to 0.1-0.13-0.2 Ohm. We re-attach the welding clothespin specifically to the ballast, but at a minimum current so as not to pull the arc. Then we load it into a bucket of water, obviously metal, until it smells like fried network wiring and watch how the current on the device grows to 250-300 Amps, and the light in the room slowly goes out if the machine at the input does not work or your device fires. Let's see how the temperature on the radiators increases with a remote thermocouple and how various protective features work. We determine the true PV, and not who and how the four cut the channels and rails. In parallel, we connect a voltmeter to the terminals for connecting the welding ends. It is necessary to pick up the welding ends, for obvious reasons.
1. On a ballast of 0.17 Ohm for 2 minutes at a current of 190-200 A, it became more and more scary for the ballast. The voltage was assessed using a pointer voltmeter - approx. 22 V. Heating could only be assessed by the hand. The inductor and output diodes were heating up. 2. I didn’t talk about a bad network. Very good 227 V, good 219-220 V. 3. Measurements were carried out with a 300 A 75 mV shunt, converted from 500 A 75 mV, calibrated using a 150 A 75 mV shunt at currents of 75-100 A. 4. American input bridge, type I don’t remember exactly either E485 or AE485, 60 A, 400 V something like this 5. At the output, 150 ebu04 per piece in the shoulder. 6. Trans 18/3+3, section as per Negulyaev’s book, both primary and secondary. 7. A voltage multiplier is of course present. At XX about 110 V.
You intrigue me, I want to try cooking with five this weekend. Will it work out - no, I don’t know.
_________________ We need to eat more sweets. Then it will stick together. pa, and the hands will finally begin to grow from the right place!
JLCPCB, only $2 per PCB prototype! Any colour!
Register and receive two coupons for $5 each: https://jlcpcb.com/cwc
1. On a ballast of 0.17 Ohm for 2 minutes at a current of 190-200 A, it became more and more scary for the ballast. The voltage was assessed using a pointer voltmeter - approx. 22 V. Heating could only be assessed by the hand. The inductor and output diodes were heating up. 2. I didn’t talk about a bad network. Very good 227 V, good 219-220 V. 3. Measurements were carried out with a 300 A 75 mV shunt, converted from 500 A 75 mV, calibrated using a 150 A 75 mV shunt at currents of 75-100 A. 4. American input bridge, type I don’t remember exactly either E485 or AE485, 60 A, 400 V something like this 5. At the output, 150 ebu04 per piece in the shoulder. 6. Trans 18/3+3, section as per Negulyaev’s book, both primary and secondary. 7. A voltage multiplier is of course present. At XX about 110 V.
You intrigue me, I want to try cooking with five this weekend. Will it work out - no, I don’t know.
PCB Assembly from $30 + FREE Shipping Worldwide + Stencil
_________________ We need to eat more sweets. Then it will stick together. pa, and the hands will finally begin to grow from the right place!
When replacing electromechanical relays in a modern car with PROFET intelligent power switches produced by Infineon, it is necessary to take into account the features of their switching compared to “dry contacts” of the relay, as well as the features of controlling various types of loads with their help.
The webinar focuses on the design and integration of Quectel built-in and external antennas for 2.4 GHz cellular modems, navigation and data devices. At the webinar you will get acquainted with the product line and ways to solve design problems. In the program: selection of antenna type; key issues affecting antenna performance; OTA certification requirements; practical measurement of antenna parameters.
_________________ We need to eat more sweets. Then it will stick together. pa, and the hands will finally begin to grow from the right place!
Of course, I understand that books on welding are now freely available, and there are tons of specialist advisers! And cutting metal (especially fours) is done freely at 200A - this is the limit for a single-phase network. And as far as I remember, you were talking about 220A Four should cut like butter!
I’m not talking about a fence, but about testing the device! It’s good that you don’t have the desire to check what he’s actually capable of! And SSNI are capricious when it comes to consistency (they want a good one) - that’s why I advised you to try them! I advised thin electrodes - since not everyone has a well-tuned resonator - which does not allow using this range of currents
I am sincerely glad that your desires and desires are modest (though it’s not clear - why then make two of them?) Usually, whoever launches one, then a second or third follows, and so on ad infinitum (like creativity)
How to adjust the current when welding?
This is a fairly common question that has several solutions. There is one of the most popular ways to solve the problem; adjustment occurs through an active ballast connection at the output of the winding (secondary).
On the territory of the Russian Federation, welding for alternating current consists of a frequency of 50 Hz. A 220V network is used as a power source. And all transformers for welding have a primary and secondary winding.
Regulator for welding current
In units used in an industrial area, current regulation is carried out differently. For example, using the moving functions of the windings, as well as magnetic shunting, inductive shunting of various types.
Ballast resistance stores (active) and a rheostat are also used.
This choice of welding current cannot be called a convenient method, due to the complex design, overheating and discomfort when switching.
A more convenient way to regulate the welding current is to wind the secondary (secondary winding) by making taps, which will allow you to change the voltage when switching the number of turns.
But in this case, it will not be possible to control the voltage over a wide range. They also note certain disadvantages when adjusting from the secondary circuit.
Thus, the welding current regulator, at the initial speed, passes through itself a high-frequency current (HFC), which entails a cumbersome design. And standard secondary circuit switches do not require a load of 200 A. But in the primary winding circuit, the indicators are 5 times less.
As a result, an optimal and convenient tool was found in which adjusting the welding current does not seem so confusing - this is a thyristor.
Experts always note its simplicity, ease of use and high reliability.
The strength of the welding current depends on turning off the primary winding for specific periods of time, at each half-cycle of the voltage. At the same time, the average voltage readings will decrease.
The principle of operation of a thyristor
The regulator parts are connected both in parallel and counter to each other. They are gradually opened by current pulses, which are formed by transistors vt2 and vt1. When the device starts, both thyristors are closed, C1 and C2 are capacitors, they will be charged through resistor r7.
At the moment when the voltage of any of the capacitors reaches the avalanche breakdown voltage of the transistor, it opens, and the discharge current of the joint capacitor flows through it.
After the transistor opens, the corresponding thyristor opens and connects the load to the network.
Then the opposite half-cycle of the alternating voltage begins, which implies the closing of the thyristor, then a new cycle of recharging the capacitor follows, this time in the opposite polarity. Then the next transistor opens, but again connects the load to the network.
Welding with direct and alternating current
In the modern world, DC welding is used to a greater extent. This is due to the possibility of reducing the amount of filler material of the electrodes in the weld. But when welding with alternating voltage, you can achieve very high-quality welding results. Welding power sources operating with alternating voltage can be divided into several types:
- Instruments for argon arc welding. Special electrodes are used here that do not melt, making argon welding as comfortable as possible;
- Apparatus for the production of RDS by alternating electric current;
- Equipment for semi-automatic welding.
Alternating welding methods are divided into two types:
- use of non-consumable electrodes;
- piece electrodes.
There are two types of DC welding, reverse and direct polarity. In the second option, the welding current moves from negative to positive, and the heat is concentrated on the workpiece.
And the reverse concentrates attention on the end of the electrode.
A DC welding generator consists of a motor and a current generator itself.
They are used for manual welding during installation work and in the field.
Manufacturing of the regulator
To make a control device for welding current, you will need the following components:
- Resistors;
- Wire (nichrome);
- Coil;
- design or diagram of the device;
- Switch;
- Spring made of steel;
- Cable.
Operation of the ballast connection
The ballast resistance of the control apparatus is at the level of 0.001 Ohm. It is selected through experiment. Directly to obtain resistance, resistance wires of high power are mainly used; they are used in trolleybuses or on lifts.
Such resistance is turned on permanently or in another way, so that in the future it will be possible to easily adjust the indicators.
One edge of this resistance is connected to the output of the transformer structure, the other is provided with a special clamping tool that can be thrown along the entire length of the spiral, which will allow you to select the desired voltage force.
The main part of resistors using high-power wire is produced in the form of an open spiral. It is mounted on a structure half a meter long. Thus, the spiral is also made from heating element wire.
When resistors made of a magnetic alloy are combined with a spiral or any part made of steel, in the process of passing high current, it will begin to tremble noticeably. The spiral has such dependence only until the moment it stretches.
How to make a throttle yourself?
It is quite possible to make your own throttle at home. This occurs when there is a straight coil with a sufficient number of turns of the desired cord. Inside the coil are straight metal plates from the transformer. By choosing the thickness of these plates, it is possible to select the starting reactance.
Let's look at a specific example. A choke with a coil with 400 turns and a cord with a diameter of 1.5 mm is filled with plates with a cross-section of 4.5 square centimeters. The length of the coil and wire should be the same. As a result, the 120 A transformer current will be reduced by half.
Such a choke is made with a resistance that can be changed. To carry out such an operation, it is necessary to measure the deepening of the passage of the core rod into the coil.
Without this tool, the coil will have little resistance, but if the rod is inserted into it, the resistance will increase to its maximum.
A choke that is wound with the correct cord will not overheat, but the core may experience strong vibration. This is taken into account when screeding and fastening iron plates.
How to make a ballast for a welding machine with your own hands
The parameter of least resistance is extremely important, since the current passes almost unimpeded and does not lose energy. For this reason, almost all conductors are made from materials with the lowest resistance. But sometimes it is necessary to artificially simulate a situation of increased resistance, when the current indicator is too high and requires adjustment. For these purposes, there is a ballast for the welding machine. With it you can carry out welding work easier and faster.
A ballast rheostat for welding or simply a ballast is a structural element or a separate device that creates increased resistance to current and thereby regulates its strength. This device is simple and reliable. A ballast is found in many expensive welding machines, but it can also be purchased separately, which is not cheap. We suggest you make a ballast with your own hands. The design of the ballast is simple and clear, so every welder can make it himself.
Operating principle and design
So how does a ballast work? In simple terms, the current that flows unhindered through the circuit encounters high resistance at a certain point, due to which it loses its magnitude. The “culprit” of high resistance is precisely the ballast connected to the circuit. Visually, the ballast for a welding machine is a large spring with many thick turns. This spring creates ballast resistance. A regulator is connected to the spring, with which you can change the resistance value to more or less, and therefore change the current strength. The regulator is a movable contact that is moved along and thereby reduces or increases the length of current flow through the ballast. Ballasts are an integral part of any experienced welder's arsenal.
Classification
Ballasts are almost the same in their operating principle or design, but may have a number of features. The range of values that we can choose to set the desired resistance will depend on them. So, ballasts differ in the following parameters:
- Spring length. Everything is simple here - the longer the spring, the longer it takes for the current to pass through all the turns.
- Metal. Ballasts are made of various metals, each of which has its own resistance coefficient. The more powerful and serious the welding machine, the more carefully the ballast material is selected.
- Thickness. Both individual turns and the entire spring as a whole. This determines how strong the resistance indicator will be. The thickness indicator is closely related to the length indicator.
DIY ballast
To make a ballast we need thick metal wire. We used copper wire in our work. You also need a cylindrical shape (it can be pre-welded from any thick metal or take a small-diameter pipe), materials for the movable contact (we used a wire from the welding machine holder) and an ammeter.
We wind the wire around a pre-made cylindrical shape, placing the turns at a distance of no more than a centimeter from each other. We connect one end of such a spring to the current-carrying part. To this design we attach our wire from the holder, which will be used as a mobile contact. Ready! Now take measurements using an ammeter to understand how exactly your ballast works.
Before you make a ballast rheostat for welding with your own hands, please note that a home-made device may work less accurately than a factory-made device. Also follow safety precautions, because homemade ballasts are not hidden in a metal case and may not be fastened securely enough, which can lead to dire consequences.
WE MAKE THE BALASTNIK INDEPENDENTLY
The most important element that is needed for this is wire, in our example we took copper, but other metals are also suitable.
You will also need a cylindrical shape (you can use a ready-made small pipe or simply weld a new shape from thick metal), a removable contact (a wire from a welding holder is suitable for this) and an ammeter to measure the current.
The wire must be wound onto a cylindrical shape, placing a turn every centimeter. We connect the wire from the holder to the end of the springs where the current-carrying element will be located.
Then all that remains is to measure the current strength to understand exactly how the rheostat changes it.
Although it is easy to make a ballast rheostat with your own hands, you need to remember that a self-made device may be inferior in accuracy to a factory one. To avoid accidents, you need to work strictly according to safety precautions.
Do-it-yourself devices are not covered by a housing, which is why their fastening may not be very reliable.