This is the first issue in a series of articles about DBMS, in which I will provide information in fairly simple words about what is currently on the database market and what to choose to solve your problems.
I noticed that when you ask someone, especially during an interview, what types of DBMS exist, the first thing that many people remember are relational databases and NoSQL, but they often forget about the varieties or cannot formulate their differences. Therefore, let's start with a simple listing of the most used ones.
- Relational
- Key-value
- Documentary
- Graph
- Speaker
Those who don’t want to read for a long time can go straight to the summary table.
It is necessary to make a remark that some large manufacturers have several types of DBMS in their arsenal, both in the form of separate products and in the form of internal implementation. For example, Oracle actually has everything, starting with a classic relational DBMS, continuing with a separate product Oracle NoSQL Database, which can be used as a document database, as a columnar database, and as a key-value database. A separate solution from the same Oracle, Autonomous Data Warehouse is a specialized solution for data warehouses. Another separate product from Oracle is Oracle Graph Server for working with graphs, and much more. This could be the subject of a separate series of articles.
Information about the manufacturer of the woodworking combined machine BDS-4
The manufacturer of the universal sharpening machine BDS-4 is the Vitebsk grinding machine plant Visas , founded in 1897.
Since 1940, the company has specialized in the production of sharpening equipment and today is the only manufacturer in the CIS of machines for the manufacture and sharpening of any cutting tool. The plant's products are used in more than sixty countries around the world.
It also produces woodworking equipment.
Machines produced by the Vitebsk sharpening machine plant, Visas
BDS-4 combined woodworking machine. Purpose, scope
The semi-industrial 3-operational combined woodworking machine BDS-4 is designed for complex processing of parts from various types of wood.
The BDS-4 machine has a simple design: an electric motor with a two-stage pulley and a planing shaft (spindle) with a take-up pulley are connected by a V-belt. The planing shaft (spindle) has two rotation speeds - 2400 and 4000 rpm when rearranging the V-belt.
A receiving pulley and a circular saw (disc cutter) are attached to the end of the planing shaft.
The machine performs the following operations:
- Planing (jointing) on a plane up to 200 mm in width and up to 3 mm in depth in one pass at a workpiece feed speed of up to 2 m/min. Knife shaft rotation speed - 4000 rpm;
- Planing along the ribs (edge) at an angle from 0 to 45°;
- Sawing along and across the fibers of boards up to 50 mm thick at a workpiece feed speed of up to 1.0 m/min. Circular saw rotation speed 2400 rpm;
- Milling with a disk cutter with a depth of up to 16 mm at a workpiece feed speed of up to 2 m/min;
- Sharpening the tool with a grinding wheel.
Recommendations for choosing woodworking equipment
Before you begin selecting equipment, you need to set performance goals. In other words, you need to determine why you are purchasing equipment: deep processing of round timber, lumber production, construction of a house or other objects. Band sawmill
The main advantage of band sawmills is the maximum output of finished products (the efficiency of lumber output is 60 - 70%), this is achieved due to the minimum cutting thickness of 1.8 - 2.2 mm. Band saw machines are well suited for small businesses, as machines on which you can obtain finished products: edged boards, timber, timber, sleepers, carriages, unedged boards. The band sawmill has low energy consumption up to 15 kW. Band sawmills are used as equipment of the first row, since the cutting of logs into a camber reaches 90 - 100 cm (Taiga T4, Atlant), for sawing into a carriage and its subsequent feeding to a multi-saw machine.
To increase the productivity of the sawmill you need to:
Convenient and efficient supply of logs (blanks) to the bed. To do this, it is possible to use a hoist, crane, winch or roller. Moving and turning the log during the sawing process (convenient clamps and stops for the log, use of a hook) Convenient and efficient collection of finished products for sorting and further processing. To speed up the process of setting the dimensions of the board and calculating the thickness of the board, an additional device is used - an electronic ruler (motion controller). It allows you to programmatically set the thickness of the board and makes it possible to more accurately position the saw blade when sawing logs. The motion controller also allows you to programmatically take into account the thickness of the cut to simplify mathematical problems for the framer. More precise positioning of the saw blade ensures better geometry of the finished product.
The disadvantages of band sawing are the geometry of the lumber and the cleanliness of processing; lumber from the band is not listed for export due to the variation in thickness and the wave of the lumber. Boards from the band sawmill are well suited for the domestic market or further processing. Edge trimming machine
To improve the geometry of the board, you can use the Taiga K2 edge trimmer; it will provide more accurate sawing along the width of the board, but will not improve the quality of the lumber along the cutting plane. Edgers are equipment of the second row and reveal all the advantages when they work in conjunction with band and tire sawmills.
Disc sawmill
The horizontal sawing sawmill provides excellent surface quality and sawing geometry. The disadvantage of sawing is the cutting thickness is 4.5 - 6 mm, while the efficiency of the finished lumber output will be no more than 60%. The speed of circular sawing is higher than that of a band sawmill.
A circular sawmill can be a machine of the first or second row, depending on the purpose of the equipment.
The double-disc horizontal sawing sawmill has a high sawing speed and high production productivity, the diameter of the processed log is up to 60 cm (0.6 m), a double-disc sawmill.
The main advantage of radial sawmills (angular sawmill) is the large diameter of the processed log, up to 1.2 m. Export quality of lumber and high cleanliness of wood processing, which is ensured by processing with a circular saw.
Tire sawmill
The Murka tire sawmill M1 (petrol) and M5 (new petrol version) are characterized by mobility and practicality in operation. The self-powered sawmill allows you to cut a log into beams and boards or sleepers right in the forest. The STIHL MS660 chainsaw can be used separately from the sawmill, as a felling chainsaw; to do this, you only need to unscrew the 2 nuts securing the saw, and change the bar and rip sawing chain to a more suitable one. Gasoline consumption 0.8 l./40 min. Splint sawing gives precise cutting geometry and the absence of waves when sawing. The disadvantage of tire sawmills is their low productivity compared to band sawmills, so such sawmills are a solution for small and medium-sized businesses. For people who buy a sawmill for their farm, this is an ideal option, and Murka tire sawmills are in great demand among farmers and collective farmers.
Composition of the combined machine BDS-4
The machine consists of a frame on which the main shaft (spindle), which is a blade shaft, is mounted in rolling bearings.
A pulley is mounted in a cantilever on the shaft, to which rotation from the electric motor is transmitted through a V-belt drive. The electric motor pulley is a two-stage one, providing two rotation speeds of 2400 and 4000 rpm. The spindle rotation speed is selected by transferring the V-belt on the electric motor pulley. The speed of 2400 rpm is better for working with a circular saw, the speed of 4000 rpm is suitable for planing.
The frame is equipped with planing tables with a knife shaft guard and a saw table. The tables are height adjustable.
Graph DBMS
Graph DBMS is a specific type designed to work with graphs, with their nodes, properties, and arbitrary relationships between nodes.
A very simple example is the organization of connections in various types of social networks, where you need to store connections between users (nodes) according to different criteria (family ties, colleagues, common interests).
Well-known representatives of this type of database are Neo4j, Amazon Neptune, InfiniteGraph, InfoGrid.
When to choose graph DBMS
It is definitely worth paying attention to graph DBMS if you are building some kind of social network, or implementing a system of ratings and recommendations. Well, in all cases when you understand well what graphs are and why they are needed.
When not to choose graph DBMS
In almost all other cases, except those mentioned above, it is better to refrain from using graph DBMSs.
BDS-4 General view of the combined machine
Photo of the combined machine BDS-4
Photo of the combined machine BDS-4
Photo of the combined machine BDS-4
Photo of the combined machine BDS-4
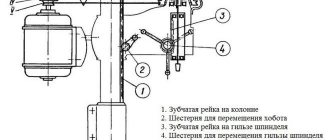
Location of components and controls of the BDS-4 machine
- Machine support legs
- bed
- Knife shaft bearing
- Planing reception table
- Thrust bar
- Electric motor
- Electrical cabinet
- Circular saw guard
- Knob for adjusting the height of the infeed planing table
- Handle for adjusting the height of the receiving planing table
- 220 V mains switch
- Start button
- Stop button
- Planer table position clamp screws
Preparatory operations
Sharpening angles for wood cutting tools
Adjusting knives in the planing drum of the BDS-4 machine
Bar for calibrating knives in the planing drum of the BDS-4 machine
The knives must be installed so that they protrude 1 mm beyond the dimensions of the knife shaft. When installing, control the uniform alignment of the knives along the entire length of the shaft.
Start tightening the bolts holding the knives from the middle of the wedge, and align the knives along the gauge bar. Before starting work, be sure to check that the knives are securely fastened. After turning on the jointer, make sure it is operating normally. It is necessary to monitor the operation of the knife shaft bearings. If the temperature rises, the bearings must be replaced.
Thicknesser attachment TD-2500
Description.
The thicknesser attachment is an indispensable tool for planing and makes it possible to obtain a workpiece of excellent quality. Using the attachment, you can carry out precise processing of lumber up to 103 mm thick.
The attachment is equipped with an adjustment of the thickness of the planing of the block in one pass (maximum removal of 3 mm), a casing with a pipe for removing chips, as well as a device to prevent the workpiece from being thrown away, which ensures easier manual feeding and clean wood processing. Designed for installation on the BELMASH SDM-2500 machine.
Specifications.
| Name | Options |
| Workpiece width, mm | 15÷250 |
| Planing depth range per pass, mm | 0÷3 |
| Thickness of the workpiece, mm | 5÷103 |
| Knife shaft rotation speed, min-1 | 7700 |
| Overall dimensions of the device, L×W×H, mm | 390×386×280 |
| Weight of one device (net/gross), kg | 15/16,5 |
| Overall package size, L×W×H, mm | 405×395×265 |
Pressing device BELMASH UP-2500
4,100 rub. 3,000 rub. to order
xn--21-6kclgd0ditp8a.xn--p1ai
Subd 4 machine
Before being allowed to work independently, a woodworking machine operator (hereinafter referred to as a machine operator) must undergo an internship for 2 to 14 shifts (depending on the nature of the work and the qualifications of the employee) under the supervision of a specially appointed person. violations by the machine operator of regulatory and legal acts (documents) on labor protection that could or have led to injury, accident or poisoning; during breaks in work for more than six months; receipt of information materials about accidents and incidents that occurred in similar industries - unscheduled. 5. The machine operator must have a clear understanding of the dangerous and harmful production factors associated with the performance of work, and know the basic methods of protection against their effects.
use, when performing work, personal protective equipment issued in accordance with industry standard standards for issuing personal protective equipment to workers and employees of enterprises”:
key-value DBMS
Probably one of the simplest types of DBMS. In a simplified form, this is a kind of table with a unique key and a value actually associated with it, which can contain anything. Most often, such DBMSs are used for caching, because they work very quickly, and this is not difficult when there is a unique key and the query returns only one value. Some DBMS data representatives have the ability to work entirely in memory, and it is also possible to set the lifetime of a record, after which the records will be automatically deleted.
The most well-known DBMS of this type are Redis and Memcached.
When to choose a key-value DBMS
If the DBMS will be used for data caching or for message brokers, then this is a very suitable type. Also, such a DBMS is well suited for databases where you need to store fairly simple structures and have very fast access to them.
When not to choose a key-value DBMS
If you expect to store many entities (tables) in the database, and the entities will have complex structures with different data types. Also, if you plan to make complex queries from this table that return multiple rows.
Universal household woodworking machine, DBMS-4B
Designed for woodworking in domestic conditions. It is a reliable assistant for performing various carpentry and joinery work during the construction of cottages, garden houses and farmsteads.
The greatest width of jointing and thicknessing in one pass, mm - 250 The greatest height of cut, mm - 55 The greatest thickness of the cut layer in one pass when planing, mm - 3 The greatest thickness of the cut layer in one pass when thicknessing, mm - 1 The greatest depth of drilling and milling (grooving), mm - 85 Electric motor power, kW - 1.5 Overall dimensions, mm - 750x555x370 Supply voltage, V - 220 Weight of the machine with all accessories, kg - 90 Saw rotation speed, rpm - 2810 Knife shaft rotation speed, rpm - 4500 Number of installed knives, pcs - 2
This concept implies connecting various industrial facilities to the Internet - machines, sensors, automated process control systems (APCS), capable of interacting with each other without human intervention.
Mail.Ru Group sees the industrial Internet as a huge market and a growth point.
“Our expertise and technology can be very useful to us in this.
These days, the whole world is becoming more and more digital, and industry is a huge part of the economy, where new technologies can provide a big leap,” said Denis Anikin.
IIoT is expected to help businesses improve productivity and reduce costs. According to him, the company intends to grow this business into a “separate serious direction” and enter the foreign market with it.
Columnar DBMS
Columnar DBMSs are very similar to relational ones. They also consist of rows that have attributes, and the rows are grouped in tables. The differences in logical models are insignificant, but at the level of physical data storage the differences are significant.
In relational DBMSs, data is stored “line by line”, which means that to read the value of a certain column, you will have to read almost the entire line, at least from the first to the desired column. In a columnar DBMS, data is stored “column-by-column”, i.e. a column is like a separate table. Accordingly, reading will occur from a specific column immediately. In practice, this actually works very quickly (I tested it on several implemented data warehouses).
The main advantages of columnar DBMSs are the efficient execution of complex analytical queries on large volumes, and easy, almost instantaneous changes in the structure of tables with data, plus significant compression and compaction, which can significantly save space.
Prominent representatives of columnar DBMSs are Sybase IQ (now SAP IQ), Vertica, ClickHouse, Google BigTable, InfoBright, Cassandra.
When to choose columnar DBMS
One of the compelling arguments for using a columnar DBMS is if you want to build a data warehouse and plan to make selections with complex analytical calculations. An indirect sign that can also signal that it makes sense to at least look towards columnar DBMSs is if the number of rows from which samples are made exceeds hundreds of millions.
When not to choose columnar DBMS
Considering the specifics of columnar DBMSs, it will not be effective to use it if the samples are quite simple, the sampling parameters are static, and if samples based on key values predominate. Also, if the number of rows in the table from which the sample is made is less than hundreds of millions of rows, then most likely there will not be much advantage compared to a relational DBMS.
You should also keep in mind that columnar DBMSs may have other restrictions. For example, there may be no support for transactions, and the query language may differ from classic SQL, and so on.
Choosing a woodworking machine for your home workshop
In addition, the advantage of using a universal machine is that it can be used to make truly unique things from wooden material that are quite difficult to find on store shelves. Using universal machines is quite easy.
On the domestic market, one can single out Russian products that are not inferior in quality to analogues from abroad, but at the same time their cost is much lower. After purchasing, it is recommended to immediately choose a place for comfortable work with the woodworking machine.
This could be a space in a garage or shed that can easily be converted into a workshop.
Often people worry that they don't actually know how to use such devices. The fact is that working on universal or special machines for wood processing is quite simple.
Relational DBMS
Let's start in order, classic relational DBMSs are most often used to build OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) solutions. In such solutions, the DBMS works with small-sized transactions, but with a large flow, and at the same time the system is required to have minimal response time, as well as the ability, under certain conditions, to cancel any changes made within the transaction. If you are building a system within which you need to store a significant number of entities (tables), with different types of relationships between them (one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many), then this is most likely a relational DBMS .
The most well-known DBMS of this type are Oracle, Microsoft SQL, PostgreSQL, MySQL.
When to choose a relational DBMS
One of the main signs that indicates that you need to choose a relational DBMS is high data normalization. Additional signs will be the need to process a large number of short transactions, with a larger share of insertion operations
When not to choose a relational DBMS
If you intend to store unstructured data, or, on the contrary, very simple key-value structures, then it is better to look towards document DBMSs and specialized key-value DBMSs, respectively.
Also, one of the signs that it makes sense to think about something other than relational DBMS is such a fact as the need to frequently update values in the same rows. This is usually "expensive" in relational DBMSs, and you need to use "advanced magic" to do it correctly.
Of course, there are a lot of “buts”, or “what if you really want to”, and other situations when these recommendations can be ignored. This is normal, especially when an expert who knows how to do it takes on the matter.