Thread rolling rollers for metric threads
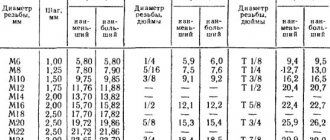
Machine thread rolling rollers GOST 9539
Thread rolling with rollers is the most versatile and accurate rolling method, characterized by the widest technological capabilities for the production of threads of various diameters, lengths and accuracy.
Depending on the nature of the tool feed, there are three varieties of this method: 1) with radial roller feed (Fig. 1) Standard: GOST 9539-72; 2) with tangential feed of the workpiece (Fig. 2); 3) with axial feed of the workpiece (Fig. 3).
1. The process of rolling a profile on the cylindrical surfaces of workpieces is carried out by rolling a profile applied on cylindrical rollers over the surface of the workpieces, with forced rotation of both rollers and radial movement of one roller under the action of the force developed by the hydraulic feed drive.
Cylindrical thread rolling rollers in accordance with GOST 9539-72 (Fig. 1) are used for rolling with radial feed of metric threads with a diameter of 3-68 mm with a pitch of 0.5-6.0 mm and are manufactured in two precisions: 1st increased and 2nd normal , with bore diameters of 45, 54, 63 or 80 mm.
The workpiece (rod), installed between the rollers on a knife support or in the centers of a special device, will rotate as a result of the friction forces that arise when the rollers come into contact with the workpiece and increase as the profile of the rollers is introduced into the workpiece and the formation of a profile on it that is negative to the profile on the rollers .
The thread profile of the rollers is usually ground, but in practice rollers with a knurled profile are used for threads with a tolerance range of 8g. The main dimensions of the rollers are determined by calculation, taking into account the diameter, pitch, length and degree of accuracy of the rolled thread, as well as the passport data of the rolling machine. One of the main conditions for proper operation is the correspondence of the helix angles on the rollers and on the thread. To ensure the same lifting angle, the threads on the rollers are made multi-start.
Thread rolling rollers of this type come in two types of thread execution: Execution No. 1 (rounding of the thread profile in the range from 0.144P to 0.12P) and Execution No. 2 with trapezoidal thread. Thread rolling rollers with radial feed are also marked:
- RH (standard) – rollers for rolling right-hand threads (the rollers themselves have left-hand threads);
- LH – rollers for rolling left-hand threads (the rollers themselves have right-hand threads);
2. Rolling with tangential feed of the workpiece is characterized by higher productivity than rolling with radial feed. During operation, the rollers maintain a constant center-to-center distance. The following schemes for rolling threads using rollers with tangential feed are distinguished: a) two backed rollers; b) two pairs of backed rollers; c) two backed rollers in the centers d) two cylindrical rollers with different peripheral speeds.
When rolling a thread with two backed rollers, for each revolution of the roller, one or more workpieces are rolled, depending on the number of notches on the backed tool. Backed rollers differ from cylindrical ones by the presence of intake, calibrating and ejection parts, as well as one or more recesses for loading and removing workpieces. Thread rolling with backed rollers can be done both on 2-roll semi-automatic thread rolling machines for thread rolling with radial feed, and on special installations that are simpler in design with a fixed position of the spindles.
Due to the complexity of the design, the cost of backed rollers is significantly higher than cylindrical ones. The use of two pairs of rollers makes it possible to roll threads on two workpieces or two ends of one workpiece.
Productive thread rolling with two round rollers with tangential feed of the workpiece can be carried out at different peripheral speeds according to two schemes. With the same diameters of the rollers, this is achieved by different frequencies of their rotation, and with the same frequency of rotation of the rollers, by their different diameters. The disadvantage of this method is the low quality of the rolled thread.
3. Rolling by the axial feed method is used when processing long threads (over 250 mm), which cannot be obtained by the longitudinal feed method. The rollers used in this method have a helix angle that differs (up or down) from the helix angle of the rolled thread. Therefore, the workpiece moves along its axis during the rolling process. The speed of the axial movement of the workpiece depends on the design of the rollers, their diameter, and the rotation speed of the rollers. Range of threads rolled by the axial feed method: diameter up to 200 mm, thread pitch up to 16 mm, thread length 2000 mm and above. The scope of application of rolling with axial feed is all parts with a thread length above 200 mm. Examples are threaded rods with metric and trapezoidal profiles, lead screws in metal-cutting machines, and lead screws for valves and valves in the valve industry.
Thread rolling with thread rolling rollers with axial feed of the workpiece is recommended for the manufacture of parts with long threads through the thread. When rolling with rollers with screw threads and intersecting axes, the axial feed is carried out due to the axial component of the rolling force that occurs when the axes of the rollers are intersecting. The axial feed speed reaches 9000 mm/min. This method is characterized by the accumulation of pitch errors of the order of 10 µm per 100 mm of length.
In Fig. a) a rolling scheme is presented, in which the movement of the axial feed of workpieces is carried out due to the axial component of the force that arises when working with rollers with parallel axes, in which the helix is inclined at an angle greater than the angle of inclination of the rolled thread. The disadvantage of this scheme is the slippage of the roller turns and the workpiece, leading to a decrease in tool life.
The rolling diagram with rollers with annular threads and axes intersecting at an angle corresponding to the helix angle of the rolled thread is shown in Fig. b). With one set of rollers, it is possible to roll both right-hand and left-hand threads of various diameters by changing the angle and direction of inclination of the rotary spindles of the rollers.
The design of rollers for thread rolling with axial feed differs from the design of conventional round rollers in the presence of a calibrating and taking parts. The diameter of the rollers does not have a significant effect on rolling and is selected in the same way as the diameter of conventional cylindrical rollers. Rollers can be ring or screw threaded depending on the rolling pattern.
Thread-rolling profile rolling rollers are made of cold-formed steels Kh6VF, Kh12M, Kh12F1, 6Kh6V3MFS, K110.
Thread rolling with rollers is carried out on 2- or 3-roll semi-automatic thread rolling machines. Semi-automatic profile rolling machines are universal machines and are designed for cold rolling of precise metric, trapezoidal and other types of threads, worms, profiles on lead screws, corrugations, fine-module helical wheels, as well as for straightening and calibrating cylindrical and spherical bodies.
The recommended speeds for thread rolling with two rollers are:
- for workpieces made of material with a tensile strength of less than 500 mPa 60-90 m/min;
- for workpieces made of material with a tensile strength of 500-700 mPa 30-50 m/min;
- for workpieces made of material with a tensile strength of more than 700 mPa 15-25 m/min.
Round Threaded Knurling Rollers
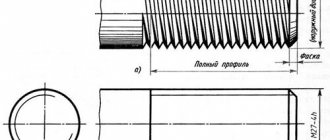
Round thread knurling rollers vary greatly in design, thread profile location, and operating pattern. The roller (Fig. 24) is a cylindrical body with a screw or ring thread on the surface of the cylinder. One to three or more rollers can be used simultaneously.
Rice. 24. Round threaded knurling roller
The process of forming threads on a workpiece can be carried out using radial, tangential, axial or combined feeds of the knurling roller. Schemes for rolling threads with rollers using various methods are shown in Fig. 25.
Rice. 25. Schemes for rolling threads with rollers: a - with radial feed: b, c, d - with tangential feed
Thread rolling with screw-threaded rollers with radial feed (Fig. 25, a) can be done with one, two, three or more rollers. Accordingly, the rollers in the knurling head are installed with an axial offset of 1/2, 1/3 steps, etc. The direction of the turns on the roller is opposite to the direction of the thread on the workpiece. The thread profile when rolling with rollers is formed gradually, by pressing the roller bits to the full depth over several revolutions of the workpiece. The number of these revolutions is determined by the depth of the rolled thread and the amount of radial feed, which in turn is assigned depending on the material of the workpiece being processed and its shape. In this way, it is possible to roll threads even on thin-walled workpieces, since it is possible by changing the feed to influence the forces that arise during thread rolling. The width of the roller covers the length of the rolled thread. The workpiece does not move in the axial direction. The axes of the workpiece and the rollers are parallel, and since the diameter of the roller is greater than the diameter of the rolled thread, in order for the helix angle of the rolled thread and the thread on the roller to be the same, the roller must have a multi-start thread. The number of starts i of the roller thread is determined from the relation de Dcp. roll—average roller diameter, mm; dcp - average diameter of rolled thread, mm.
Tangential feed when rolling threads with rollers is obtained in various ways. For this purpose, for example, the difference in peripheral speeds on the outer surface of the rollers is used. Two rollers (Fig. 25, b) of the same diameter are given different rotation speeds n1 and n2, or two rollers of different diameters (Fig. 25, c) are given the same rotation speed n. The rollers rotate in one direction, the workpiece is captured by the rollers, set into rotation and gradually moves downwards on its own. The thread profile is formed gradually. The distance between the axes of the rollers remains constant during thread rolling. The rollers have a multi-start screw thread; the number of starts must be a multiple of the diameter of the rolled thread and is determined by the previously given formula.
Tangential feed when rolling threads can also be achieved due to the special design of the rollers. These rollers (Fig. 25, d) have recesses for placing and subsequent removal of the workpiece, and on the remaining screw threaded section there is an intake, calibrating and discharging part. The calibrating and discharging parts have a full thread profile, and the intake part is cut along an Archimedean spiral and in its profile resembles the thread on the intake part of a flat die shown in Fig. 22, c. Rollers of the same diameter rotate in the same direction, the workpiece enters the recess, is captured by the rollers, set into rotation, and the thread is gradually extruded on it. The processing cycle is completed in one revolution of the rollers. The rollers have multi-start threads, the number of starts is a multiple of the diameter of the rolled thread.
To roll long threads, the workpiece or rollers must be moved along the axis of the workpiece. The rollers can be with a ring or screw thread. Axial movement of the workpiece relative to the rollers is ensured by appropriate installation of the knurling rollers to the workpiece axis. So, for example, when rolling a thread with two rollers with annular threading, their axes must be turned to the angle of elevation of the rolled thread, as shown in Fig. 25, a. When using rollers with screw threads, the elevation angle of which λroll differs from the elevation angle of the rolled thread λ (λroll can be greater or less than λ), the angle of rotation of the rollers relative to the workpiece axis will be equal to the difference λroll - λ. The axial feed speed σоc is determined by the formula , where σокр is the peripheral speed of the roller.
Rice. 26. Scheme of rolling long threads with rollers: a - with ring cutting; b - with screw thread
The rollers have a intake cone and a calibrating part. The intake cone allows you to distribute the load when rolling threads over several turns of the roller, as a result of which thread profiling is carried out gradually, which helps to improve the quality of the rolled thread.
Thread rolling, thread cutting head VNGN VNGT
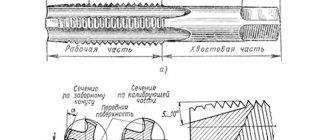
Products / Metal cutting tools / Thread rolling, thread cutting head VNGN VNGTThread-cutting (thread-rolling) head – devices for cutting various threads, both internal and external. Threading heads, their main difference from other threading tools is the high productivity and accuracy of the resulting thread. Unlike dies and taps, the resulting thread is of high quality in one pass.
Threading heads are a modern and most optimal way of cutting threads in industrial conditions. This method of obtaining threads has the greatest efficiency compared to others. Thread-cutting (thread-rolling) head, the algorithm of its operation consists in the screw movement of the tool relative to the workpiece being cut. Due to these movements, the thread profile is formed.
The cutting (shaping) tools in the heads are combs, which directly come into contact with the workpiece. The use of combs ensures simplicity and ease of use of the heads.
Threading heads are divided into rotating ones, which are used on automatic lathes and drilling machines. And non-rotating ones, working on turret machines. In addition, the heads differ in the location and design of the thread rolling dies. For example, round dies are usually used to produce external threads. Flat radial dies are used for internal threads. The die head is adjustable so different thread diameters can be produced.
Thread rolling heads and thread rolling rollers are classified as thread rolling tools. When using a thread rolling tool, the resulting thread quality and strength are higher than when cutting threads, this also applies to its accuracy.
In our company you can purchase and order for production: thread-rolling heads VNGT, VNGN, thread-rollers for VNGN, thread-rolling dies NPT. All of these thread-cutting tools are of high quality and are manufactured in accordance with technical requirements and GOSTs.
More details
The VNGN thread rolling head is used to produce right and left metric threads using the rolling method with a thread profile in accordance with GOST 9150-81. The tolerance field of the resulting thread is 6g with a pitch of 0.7 to 5 mm and diameters from 4 to 52 mm. The hardness of materials (metals) is no more than 200HB. The heads operate on the principle of self-tightening in rotating and non-rotating modes, both in lathes and drilling machines, and in automatic machines. Adjusting the knurling rollers and opening the head at the end of the working cycle is convenient to use and does not require special skills. Material of forming rollers – steel X12, X6VF X12MF according to GOST 5950-73, Hardness 58..62 HRC.
Thread rolling head VNGT according to specifications, designed for rolling external cylindrical threads G 1/2 - G2 on water and gas pipes GOST 3262-75, straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes in accordance with GOST 10704-76 without preliminary grooving of pipes. Providing simultaneous removal of burrs along the inner diameter of the pipe remaining after cutting the pipe.
The heads are capable of operating in both rotating and non-rotating modes on lathes, drilling and turret machines. The design provides for adjustment of thread rolling rollers to the diameter of the rolled thread plus automatic opening of the head after rolling the thread. The heads implement the principle of self-tightening, ensuring the production of cylindrical pipe threads of accuracy class B. The material of the knurling rollers is steel grades X12M, X6VF, X12F1, X12MF in accordance with GOST 5950-73. The hardness of the rollers is 58…61.
Threading heads RNGV are used to produce internal threads, namely metric right-hand threads with a diameter of 36 to 165 mm, cylindrical pipe G1 1/8...G4, including threads on casing non-nipple pipes with a diameter of 44 to 89 mm and on casing and core pipes with a nipple connection diameter from 44 to 146mm.
Heads are manufactured in 2 types: type No. 1 RNGV - MK for short threads, type No. 2 RNGV-MD - for long threads.
can work in rotating and non-rotating mode on various machines and automatic machines for carbon and alloy steel, cast iron, and non-ferrous metals. The design of the heads provides for adjustment of the thread-cutting dies to the diameter of the thread being cut and automatic opening of the head after cutting the thread. The result is a metric thread of the 6th degree of accuracy and a cylindrical pipe thread of accuracy class B.
threading dies 4-14A for
pipe thread 3/4″ at a price of 11,500 . excluding VAT for 1 set
Name
| price, rub. without VAT | Name | price, rub. without VAT | |
| Threading heads | Cams to heads | ||
| 1K-1KA-25 | 20500 | 1K - 1KA (A-Z) | 7000 |
| 2K-2KA-30 | 22500 | 2K - 2KA (A-Z) | 8800 |
| 3K-3KA-30 | 24300 | 3K - 3KA (B-Y) | 9000 |
| 4K-4KA-45 | 29800 | 4K - 4KA (A-Z) | 9730 |
| 4K-4KA-70 | 29900 | 5K - 5KA (A-Z) | 11900 |
| 5K-5KA 45 | 34800 | Combs to heads | |
| 5K-5KA-70 | 34900 | 1K-1KA | 6400 |
| RNGV thread-cutting heads for internal threads | 2K-2KA | 8500 | |
| 2MK,2MD | 30900 | 3K-3KA | 8800 |
| 3MK,3MD | 40900 | 4K-4KA | 9100 |
| 4MK,4MD | 57900 | 5K-5KA | 9730 |
| 5MK,5MD | 60600 | Dies for round, tapered and pipe threads | |
| Thread rolling heads | 2K 1/8″ | 6500 | |
| VNGN 2M (d 4..7 mm) | 47500 | 2K 1/4″ | 6500 |
| VNGN 3M (d 8..16 mm) | 52000 | ZK 1/4″ | 7500 |
| VNGN 4M (d 16..27 mm) | 89000 | 3K 1/2″ | 7500 |
| VNGN-5AM,5BM (d 30..52 mm) | 116000 | 3K 3/8″ | 7700 |
| VNGN 1M ladder | 91500 | 4K 1″ | 8000 |
| VNGN 2M, 3M tr | 116000 | 4K 1 1/4″ | 8200 |
| VNGN-4M ladder | 116000 | 5K 1 1/2″ | 8300 |
| Rollers for rolling heads | 5K 2″ | 8500 | |
| VNGN 2M (step 0.7..1 mm) | 3500 | Devices for measuring combs | |
| VNGN 3M (step 0.75..2 mm) | 7500 | 1K-2K | 16750 |
| VNGN 4M (step 1..3 mm) | 8900 | 3K-3KA | 17570 |
| VNGN-5AM,5BM (1.5..3 mm) | 10300 | 4K-4KA | 17900 |
| VNGN 1-3M ladder | 9700 | 5K-5KA | 22350 |
| VNGN 4M ladder | 9400 | Tools for sharpening combs | |
| VNGT pipe heads | 1K-4KA | 16300 | |
| 1/2″ — 3/4″ | 83700 | 5K-5KA | 20100 |
| 1″ | 84950 | Screws | |
| 1 1/4″-1 1/2″ | 89650 | 1K-3KA | 350 |
| 2″ | 92700 | 4K-4KA | 350 |
| Rollers for VNGT heads | 5K-5KA | 500 | |
| 1/2″ | 9500* | Asterisks | |
| 3/4″ | 9500* | 1K-2KA | 1300 |
| 1″ | 9200* | 3K | 1100 |
| 1 1/2″,1 1/4″ | 11820* | 4K | 1100 |
| 2″ | 12660* | 5K | 1200 |
* When ordering 2 sets or more, get a 10% discount
The durability (resource) of thread-acting rollers is 1200-1500 meters of thread
The service life of the threaded heads is 5 years of operation with the possibility of replacing the power part.
Set of rollers for VNGT 3/4 head
| Name | price, rub. without VAT |
| NPT dies | |
| 1/2-3/4 | 18760 |
| 1″ | 19100 |
| 1 1/4-1 1/2 | 20000 |
| 2″ | 21100 |
| Rollers for NPT dies | |
| 1/2″ -3/4″ | 7500 |
| 1″ | 8200 |
| 1 1/4″ — 1 1/2″ | 8400 |
| 2″ | 9100 |
| NP dies | |
| NP-1 | 16750 |
| NP-2 | 17100 |
| NP-3 | 17500 |
| NP-4 | 18800 |
| Rollers for NP dies | |
| NP 1 | 3000 |
| NP 2 | 4300 |
| NP 3 | 5400 |
| NP 4 | 6000 |
| Dies for RNGV-M heads | |
| 56*1,5 | 8500 |
| 60*2,0 | 8500 |
| 76*1,5 | 8500 |
Description of rollers for VNGT heads
The rollers are made with annular threading of turns. Roller material - steel Kh6VF and Kh12M according to GOST 5950-73, Hardness 58..61 HRC.
| Thread | Thread pitch, mm | D/d/H | Col. rollers included, pcs. |
| G ½” | 1.81 | 40/22/16 | 4 |
| G ¾” | 1.81 | 36/22/16 | 4 |
| G 1" | 2.31 | 29/16/16 | 6 |
| G 1 ¼” | 2.31 | 37,5/22/16 | 6 |
| G1 ½” | 2.31 | 32/22/16 | 6 |
| G 2" | 2.31 | 34/22/16 | 8 |
We offer spare parts for VNGN thread rolling heads
Eccentric axle VNGN-3M - 10,800 rubles without VAT
Eccentric axis VNGN-4M -
12,950 rubles without VAT
Production time 10 working hours. days.
Thread-cutting head VNGN on a lathe, see video for an example of operation