It seems to me that every self-respecting CNC specialist already has his most favorite and necessary tools, which he will pass on to his son, and he to his son, etc. Therefore, most likely, this article will be more useful to beginners who are just learning this wonderful world of CNC technology. Today we will look at tools that will make your life easier both when working on CNC machines and in the warehouse/shop in general. Everyone has screwdrivers, hex wrenches and pliers, so we won't include them in our list today.
We will also not include safety glasses here, since every self-respecting operator should know safety precautions and constantly use them!
And so, ladies and gentlemen, DARXTON provides you with a list of the best things to work with in 2022. Here we will only list high-quality versions, and not all consumer goods from Ali. Why? Because you want to use these tools constantly throughout your career, and not throw them away after opening the package.
No. 1 Touch caliper with digital display
You will use this tool almost every day. Do you need to machine a part to fit the dimensions of an existing one? Buy a fastener or spare part with exact dimensions? Check the correctness of the workpiece parameters in production? You will always need a digital caliper with display
and a division price of 0.01-0.0005 mm. It is used for quickly determining external and internal dimensions, as well as for measuring protrusions.
We do not recommend saving on calipers since one of the main problems with using calipers is the backlash of the jaws and their poor fit to the part. Particularly difficult
in this case, measuring small details runs the risk of a large error
Equipment and devices: types and types
In the West, there is a saying among milling operators: “fixtures are where you make your money,” which translates roughly as: “Fixtures are what you make money from.” If you can make gadgets that save time, you will reap big profits.
T-slots
T-slots are the most common method of positioning and holding your work fixture. They are simple, reliable and work. To attach anything to a T-slot table, use T-slot nuts and matching studs or other fasteners that fit the nuts.
T-slot nuts
Although they are common, they have some disadvantages compared to other solutions. Aside from the fact that T-slots can collect chips and other debris, their biggest disadvantage is that it makes it difficult to return your vise or other table mount fixture to the exact same location and orientation. This can result in additional work each time the machine must be set up with new work attachments for a new job. Over time, the cost of such inefficiency can be quite high.
Just imagine what if, instead of a tool changer and tool table, you had to dial in each tool every time you used it? Wouldn't this be a huge barrier to improving the productivity of your processing workflow? Well, setup time can also be a big hindrance to productivity, and T-slots don't help here.
There are a few solutions that tried to make them a little better:
No. 2 Micrometer
When your caliper's graduations aren't accurate enough (i.e., you need to measure to a tolerance of less than 0.005 cm), it's micrometer time. The micrometer features a clamping screw and ratchet. The ratcheting thimble reduces the chance of errors due to inconsistent compression.
Micrometers come in digital, dial, and vernier styles, just like calipers. If you have never used a micrometer before, we recommend starting with a digital one.
Pallets
The next step is pallets. It's like automatic tool plates when everything else was manual. A typical pallet machine allows you to adjust one while the machine is working on another. Changing the pallet occurs by removing the old pallet outside the milling zone of the machine and installing a new one. This minimizes the amount of time the machine must be idle and allows adjustments to be made in parallel with processing.
Some machines have what are called "pallet pools", which allow you to set up multiple pallets in advance and schedule them to run. A pallet pool can allow a machine to run unattended for quite some time and can be a useful part for full automation.
Pallets are typically only seen on horizontal machining centers and some high-performance vertical machining centers. This is a full production feature that is quite expensive, so the cost needs to be justified.
No. 3 Mechanical edge finder
Edge finders (edge finders) are tools (probes) designed to determine the edge of a workpiece on milling and turning machines.
If you think this tool is extremely ancient, slow and difficult to use, then how about the Haimer 3D “Taster”:
They are far from cheap, but price = quality. Just remember one thing - be sure to buy a few extra tips. It's not a question of "If" but "When" the tip will break and you have to be prepared for it!
Vices and fixtures with key
If your T-slots are correct, you can install wrenches on the bottom of the vise or mounting plates that line up with the T-slots. You can also install the wrenches in T-slots that line up with the edge of the vise plate or base. This can save you quite a bit of time pulling out vices and such, and it's not difficult, so it's definitely worth thinking about.
The problem is that these solutions will help with one dimension (usually the short table dimension is the Y axis and is perpendicular to the slots), but we still have the problem of positioning along the T-slot axis. .
Luckily, there is a better way - auxiliary mounting plates (also called mounting plates).
Mounting plates, tooling plates and modular fastening
Accessory fixture plates (also called fixture plates or tool plates) are plates that fit on top of a T-slot table to provide a new way to position and secure fixtures. A typical tool plate looks like this:
Typical mounting plate
Tooling plates typically use a pattern of holes that alternate between holes for precision locating pins and threaded holes for fasteners. If this mesh is positioned accurately (or even if it is not and the positions are precisely known), you have a very repeatable way to install the tooling on the plate. The locating pins ensure precise positioning to within 0.01. Imagine being able to install a vise on a separate mounting plate with mounting pins and mounting holes, the repeatability of this operation will be about 0.01. If all your fixtures can fit on the tooling plate, you can actually switch the machine to a new fixture configuration very quickly. Saving time allows you to quickly recoup the cost of such a system.
The vise can be installed on one of these plates within one or two minutes. A CNC machine can be reconfigured in 5 or 10 minutes for a completely different job. In addition, the skill required of machine operators, as well as the likelihood of errors, are greatly reduced if fixtures do not have to be carefully adjusted each time. There are also advantages to creating modular G-code because it can rely on a positioning grid.
If accuracy greater than 0.01 is required, it is often better to use probing along with the selected g-code parameterization to correct the remaining error. You can try to fine-tune the parameters manually, but the probing solution may rely on everything being nearly correct to determine the last little bit of error correction that needs to be applied in the g-code itself. For example, you can very accurately apply rotation to g-code based on sensor output (aligning objects to axis motion).
Tool plates are usually made of cast iron or aluminum, although steel plates are also available. They can be purchased or made from scratch. For a complete guide, be sure to visit our page on mounting plates.
No. 4 Hour indicator
Interapid hourly indicators are some of the best
Any operator will need (DTI) for many setup tasks, such as pulling the clamps of your cutter to make sure they are perpendicular to the travel of one of your CNC's axes. We tried various indicators from Starrett, Interapid and others, and we can say that Interapid are the most reliable, Swiss-made after all. If you want something simpler and cheaper, we recommend taking a closer look at Guanglu
Design
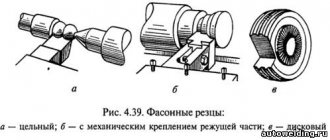
The equipment is secured to the machine thanks to a unified tail section. The fastening is reinforced by elements for connecting to the cutting mechanism. Fastening is carried out manually. The shank of the device has a cylindrical shape and a grooved flat. This design provides a higher level of fastening reliability.
Tooling systems vary depending on what tasks the machine is used for. A quick system change is required when drilling and milling work is carried out. The machine is readjusted by replacing the program carrier. The higher the rigidity of the additional mechanism, the more intense its work will be. The intensity of the work determines how quickly it will be completed.
Rigidity is ensured by durable fastening. To achieve high fastening strength, parts made of hard alloys are used. It is recommended to configure the additional mechanism before installing it on the machine. This will help reduce operating time. Multi-spindle heads simplify the installation of technology on a CNC machine. Such equipment is especially effective for small-scale tasks.
No. 6 Probes
When mass producing parts, manually checking each part for defects takes a long time and is ineffective, but what can be done to avoid this defect? Manually adjusting the desired position of turning and milling heads has always been an extremely difficult and painstaking task. To make this process easier, you can use feeler gauges.
4th axis, journals and tool columns
Sometimes it is useful to be able to apply another dimension to our thinking - in this case, the 4th Axis. In CNC, the 4th axis is usually the rotary axis. It is aligned to rotate along an axis parallel to one of the other three axes of the machine. On vertical machines, the 4th axis is often parallel to X or Y and routed downwards. On horizontal ones, the 4th axis is also parallel to X or Y, but it is vertical.
From a workplace perspective, the 4th axis can be used to introduce new orientations for two purposes:
1. It allows access to more sides of the part so processing can continue without the need to turn parts over by hand.
2. This allows access to more parts that can be positioned around the 4th axis.
To learn more about these applications, check out our excellent 4th Axis Basics series.
No. 10 Automatic Punch (colloquially Kern)
Here is the last interesting tool on our list. Basically, you push, it jams and fires, punch style, to make a mark on the workpiece. It saves you the hassle of trying to make an accurate mark with a regular nail and hammer.
This concludes our list of Useful Tools. You can also always choose high-quality tools at reasonable prices in the darxton.ru catalog
Ball locks and other solutions for quick tool insert changes
By now I hope you can see how much setup time you can save by using tooling plates. What could be better? There are at least two different ways to make setting up fixtures and accessories even easier: quick-change tool plates and trays.
With the Quick Change system, the time required to handle locating pins and fasteners is reduced with some kind of integrated solution that allows for precise positioning and very fast locking. One of them is the ball lock system:
Ball lock system
Ball locks are a system for quickly removing and installing tool plates. This system provides precise positioning and secure retention with 4 ball locks. Simply align the plate with the accessory plate (which has receiver bushings and is mounted on the table), drop the retainer ball shanks into the hole, tighten the bolt on top of the retainer ball shank, and you're done. It's really quick and easy to install four bolts without fiddling with locating pins or additional fasteners. We are talking about a 30-second changeover time, which is really very fast.
The most popular machines with auxiliary tools
The auxiliary tool can be used with any model of modern machine tools equipped with CNC. Their popularity depends on demand. The most commonly used types of devices are:
- turning-turret;
- vertical drilling;
- vertical milling.
The device is assembled in accordance with GOST 23597-79. It involves optimal settings for equipment to ensure production accuracy. The accuracy rate is partially adjustable. The level of distortion may vary depending on how professionally the program was installed. The program must take into account the functions provided by additional equipment. Together they can:
- prevent the indicator of distortion of the movement trajectory of the device;
- reduce the feed when using the device;
- adjust the size of the working device.
The design of the auxiliary tool may vary depending on the type of machine it is used for. But the main task remains the same - securing the working elements of the device. Without such equipment, the productivity and period of uninterrupted operation of the device will be significantly lower. The cutting devices will be less secure, which will reduce the quality of manufactured products and the variety of possible shapes.
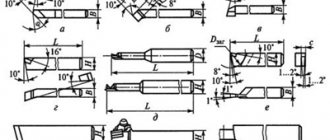
Types of cartridges
These fasteners provide greater processing precision. It is installed in a milling machine to clamp small cutters and drills. There are two varieties of this part:
- Cartridges with mechanical fasteners. It holds drills and cutters with a conical shank, such as Morse taper, Weldon, Whistle Notch, and so on.
- Cartridges with a rigid, non-deformable clamp. These include collet, hydroplastic, hydromechanical and other tools.
Working with the control system
The machines are equipped with controllers that are pre-programmed. These devices are responsible for control on various types of equipment. The preparatory stage of working with CNC and the software module provides certain methods:
- use of computer technology,
- manual programming outside the system,
- other methods of autoprogramming.
Most systems use auxiliary model installations. They include the following elements:
- power unit,
- CPU,
- memory with programmable characteristics,
- input and output modules.
The software and hardware complex is designed for creating and configuring professional programs. The equipment reads input commands from the input module and analyzes the data. The output module receives the final analysis results and ready-made solutions based on logical problems and numerical calculations. This way the machine continues to function and work stably.