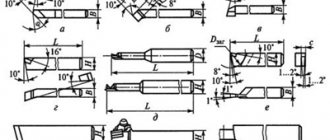
The most important operation when processing shafts is turning, which is carried out mainly in the centers.
The centers are the basis for a number of operations: finishing and rough turning, thread cutting, keyway milling, grinding, etc., as well as for straightening and checking.
During repair work, the preserved center holes are also used for turning worn or damaged journals, for straightening, polishing and other work.
Center holes in cutting tools such as taps, drills, countersinks, reamers, etc. are needed not only for processing, but also for checking, sharpening and regrinding during operation.
Due to the importance of the center holes, alignment must be done very carefully.
Center holes must be drilled correctly and the product must be maintained in good condition from the start of processing.
They must be of sufficient size, and their taper angle must exactly coincide with the taper angle of the machine centers.
Failure to comply with these rules leads to rapid development of the center holes and damage to the centers themselves.
When to use center mounting
installation of the workpiece using a mandrel: 1 - middle part of the mandrel; 2 - flat; 3 — center holes; 4 - blank
- This is how long parts are machined, the length of which is five times the diameter;
- if you need to create concentricity of surfaces during fixation;
- the further stage of turning takes place on grinding equipment;
- technology does not provide for other methods.
Processing Features
Rigidity of installation in the centers will be ensured if the ratio of length and diameter is maintained to 12-15. Longer parts are supported by rests.
Center holes on the workpiece are made during the preparatory operation using a center drill.
Turning involves an automatic cycle. The machine can be easily reconfigured to produce parts with different dimensional parameters by making changes to the control program. The time required for an operation can be reduced by 1.5-2 times compared to working on a universal machine.
The work is based on the use of a contour processing system with linear-circular interpolation. The system performs processing of a complex contour, divided into roughing and finishing passes. The final operation is carried out by traversing the contour of the part by the working element in one pass.
The tool path when producing parts in a series of roughing passes is parallel to the axis of rotation of the part, perpendicular or at an angle. During the first pass, a layer of scale is removed from the workpiece and existing shape defects are corrected. The remaining roughing passes have a constant depth of cut.
After completing the working pass, the tool is retracted and the idle transition is carried out parallel to the contour, perpendicular to it or along an inclined path.
When manufacturing shafts on multi-stage profile machines, the allowance is divided into sections perpendicular to the axis of the part. The sequence of the turning operation in elementary sections is set so that the processing element travels the shortest distance.
Fastening technology
rear center as support for long parts
The workpiece is fixed in the centers using special mandrels. To do this, the mandrel cone should not exceed 1:2000. At the preparatory stage, central recesses are made at the ends of the part into which the tops of both centers will be inserted. The mandrel is treated with lubricant and the blank is pulled tightly. For greater density, gently tap the end of the mandrel with a wooden block. Securing the part in this type of mandrel may vary depending on its diameter.
The movement of the blank is transmitted through a driving chuck, which is put on the spindle thread. The pin of the drive chuck forces the blank to rotate. This method is more dangerous for the machine operator, so it is preferable to use a drive-type faceplate with a protective cover. The bolt is secured with a clamp, which rests on the flat of the mandrel.
The installation of workpieces with holes (for example, gears or bushings) occurs using centering mandrels of various shapes. One type of mandrel has a cylinder-shaped neck; a workpiece is placed on it and secured with a washer and nut. The nut is pressed against the collar and secures the resulting structure. A clamp is attached to the left with a screw. The part is fixed in the turning machine by recesses at the end sections of the mandrel.
Description of equipment
Classification of CNC machines:
- According to the orientation of the main spindle axis: horizontal and vertical turning.
- According to the set of tools: single and multi-tool.
- According to the level of automation: semi-automatic with manual installation of workpieces and automatic with automation of all work operations.
- What is the location of the guides: in a vertical or horizontal plane, at an angle.
- According to the type of installed tool storage: with a turret head, one or a group of supports, combined.
- According to the nomenclature of operations: a machine of the cartridge type, centered or cartridge-centered.
Automated units are equipped with a tool magazine or a turret-type head for 4, 6 and 12 cavities. Each socket accommodates two tools for turning external and internal elements. On CNC lathes, the orientation of the turret axis relative to the main spindle axis is parallel, perpendicular and inclined.
Small-capacity magazines are installed in CNC lathes, because 10 tools are enough to produce one part.
A capacious storage of working elements is necessary on equipment where difficult-to-process materials are processed. In this case, the tools have a short service life and require frequent replacement.
CNC machines are used to produce parts from a wide range of materials:
- cast iron of various types;
- steel of ordinary quality, tool and special;
- stainless materials for the medical and food industries;
- non-ferrous metals and their alloys (copper, titanium, brass, bronze);
- composite materials;
- plastics;
- tree.
CNC centering machines (for example, 1725F3,1B732F3) process shafts of various configurations. Turning of cylindrical outer surfaces, conical transitions, shaped necks is carried out and various threads are cut.
Chuck-center CNC machining centers (for example, 16B16F3, 1740RF3,16K50F3) have the ability to install a workpiece in the chuck and centers, perform turning and boring operations, threading, drilling, reaming and countersinking.
Center designs
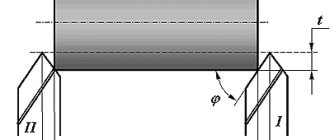
Turning centers can have different designs. The most common one is a cone, a workpiece is put on it, as well as a conical shank. The shank must match the holes of the quill and spindle of the machine.
To secure workpieces with external cones, reverse centers are used. The tapered end should coincide with the middle of the shank. To check the coincidence, the center is inserted into the spindle and started at low speeds. The serviceability of the part is indicated by the absence of runout.
The rear center is most often stationary, the front center rotates with the workpiece and spindle. As a result of friction, both surfaces fail, so it is necessary to apply lubricant:
- chalk - 25%;
- grease - 65%;
- graphite - 5%;
- sulfur - 5%.
Before mixing, it is necessary to grind the sulfur and chalk into powder without lumps. If lubricant is not used, the surfaces of the centers will collapse and their configuration will change.
When turning workpieces at high speeds, the centers wear out faster, and the hole in the end of the part itself increases. To reduce the destruction of the rear cone, a wear-resistant layer is fused onto it.
The standard center is used at speeds up to 120 rpm. When working with bulky and heavy workpieces at high speeds, when removing large chips, the structure has little rigidity: the part begins to vibrate and can be pressed out.
rotating center
Therefore, they use rotating centers mounted in the rear rack. It contains a spindle that rotates in an angular contact bearing. For high loads, a roller bearing is preferable; for medium loads, a ball bearing is preferable.
What is a data center for and who uses it?
Data processing centers, or data centers (from the English data center), are responsible for the uninterrupted operation of all equipment installed inside and the corresponding infrastructure. The data center must perform the following functions:
- Providing equipment with electricity.
- Removal of excess heat, which negatively affects the performance of systems and devices.
- Protection of equipment from negative environmental influences.
- Providing access to equipment to data center employees and restricting access to the same equipment to outsiders.
- Protecting computing and related equipment from incidents such as fires.
Data centers are used by business, government and research organizations for a variety of needs. They have one thing in common: the need to process and store huge amounts of information.
Redundancy of data center engineering systems
In order for the data center to operate without interruptions, critical systems can be duplicated many times thanks to various redundancy schemes. They are designated by the Latin letter N. The main redundancy schemes are listed below.
N+0. This is a basic level, non-redundant system. If something breaks or the power goes out, the entire data center stops working. Note that in data centers where uninterrupted operation of equipment is required, multiple redundancies are necessary, so the N+0 scheme is not suitable here.
N+1. The system is backed up once. The reserve element is activated after the main one fails, so that the entire complex continues to operate.
2N. Each main system or element has two reserves that operate in parallel so that the load is evenly distributed among all components. If one element fails, it is automatically replaced by a second one.
2N+1. The same circuit as above, but one more additional component is used.
2(N+1). Even additional elements are duplicated in this scheme. One of the most reliable schemes at the moment, which works flawlessly.
Diesel generators DC "Berzarina" Selectel
The Citadel Campus
Area: 720 thousand m2
Location: Nevada, USA
Citadel Campus is built and owned by Las Vegas-based Switch Corporation, which develops and operates large data centers. The data center is designed to exceed the Tier IV standard. Its fiber optic network offers latency as low as 9 ms to San Diego and Los Angeles, and connections to the TAHOE RENO 1 data center are as fast as 7 ms.
Switch holds 260 patents and is one of the most innovative data center service providers. In addition, Switch is the only company with a 100% clean energy index.
China Mobile
Area: 720 thousand m2
Location: Hohhot, China
China Mobile's data center is located in the Inner Mongolia Information Park in Hohhot. It has more than 40,000 racks spread across 720,000 square meters of buildings, and the entire complex covers 106 hectares, making it one of the largest data centers in the world. The initial investment in the facility amounted to $1.92 billion, which, in addition to providing corporate services, is focused on researching new technologies in the field of cloud computing and 5G.
Yotta NM1
Area: 76 thousand m2
Location: Mumbai, India
Yotta NM1 is the first of five buildings being built at the Integrated Yotta Data Center Park, located near Mumbai. The building has 7,200 telecommunications racks that consume 50 MW of electricity. Once completed, the facility will have a total capacity of 30,000 racks and capacity will increase to 250 MW. The data center has 4 redundant fiber optic paths connecting it to national highways.
Intergate Seattle
Area: 84 thousand m2
Location: Washington State, USA
Intergate Seattle is Sabey's flagship data center facility, with access to more than 70 MW of power, but for most of the year it uses clean and relatively cheap hydropower (3.1 cents per kWh) combined with free cooling. The data center has redundant air conditioning, ventilation and heating systems, as well as 2.75 MW generators with a guaranteed battery life of 72 hours at peak load.
The largest data centers in the Russian Federation
As an introduction, we will present the three largest data centers in the Russian Federation, each of which is focused on providing a specific type of service. You can easily find the official web resource of such companies in a search engine to get acquainted with the technologies used, a description of the center itself and reviews of partners.
DataLine
The main service that can be purchased from this company is space in the data center. To do this, you need to contact the official website with a request for a calculation. Experts will tell you what capacity should be allocated and how much maintenance will cost.
Additionally, DataLine provides a huge number of other information technology-related services. They use VDI to transfer employees to remote work, provide workplace infrastructure, backup, cloud services and information security.
KROK
CROC is a cloud services company that works with offices, providing data storage, backup, security and general infrastructure management.
CROC supports several dozen different projects, which can be found on the official website. All platforms are equipped with the latest technologies, and their list is indicated on the same web resource.
I-Teco
I-Teco is positioned as a leading Russian system integrator. They are introducing various data center-related technologies into offices. These can be print control systems, video surveillance, mini-CHP, software and hardware solutions, data storage systems and much more.
In addition, the company is engaged in telecommunications, information security and outsourcing. On the page with a list of services for each of them there is a detailed description of how integration occurs and what advantages this provides when organizing business processes.
You have just learned basic information about data centers, figured out their organization, levels and popular Russian representatives. There are also a huge number of technical and economic nuances that cannot be discussed in a general article. This includes geo-distribution to ensure data security, infrastructure configuration, and much more.
Data center reliability levels
The more important the task a data center performs, the more reliable it must be. A few minutes of data center downtime can cost a business several million dollars. To assess the reliability level of data centers, Uptime Institute has developed a special certification system - Tier. Certification levels:
- Tier I. This is a basic data center that uses an N+0 redundancy system (more on this below). In most cases, such objects do not have redundant systems. The maximum level of data center availability (fault tolerance) is 99.671%.
- Tier II. A more reliable object that uses an N+1 redundancy scheme. The systems are backed up, but if repairs are required, the data center must be shut down. Tier 2 data centers must have a raised floor. Data center fault tolerance - 99.75%.
- Tier III. If any of the data center systems breaks down, the operation continues and repairs can be carried out without stopping the entire facility. Data center fault tolerance - 99.98%.
- Tier IV. This is currently the highest level of certification. Any engineering system has a reserve of both the main and additional nodes (2N+1 redundancy scheme). Fault tolerance is 99.99%, downtime is kept to a minimum. There is practically no danger of stopping such a data center.
Lakeside Technology Center
Area: 102 thousand m2
Location: Chicago, USA
Digital Reality is an investment fund that manages 280 data centers with a total area of more than 3 million square meters worldwide. The most impressive facility is located in Chicago. In 2005, Digital Realty bought the building for $140 million, which now houses data centers focused primarily on the financial market. The data center has 4 main communication channels and 3 power supplies with a capacity of 100 megawatts.
One of the unique features of this building is the cooling system, using a 3 million liter coolant tank, which reduces air conditioning costs during off-peak hours.
Basic data center services
The main task of the data center is to ensure uninterrupted operation of the equipment. But the possibility of placing such equipment by clients of a company that owns a data center is already a service. Main data center services:
- Rent a rack, cabinet or entire data center.
- Physical placement of servers in a data center (Colocation).
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) - providing the entire IT infrastructure to the client.
- Data backup.
- Server administration.
All Selectel data centers comply with Uptime Institute Tier III standards.
There are six of them in total: “Berzarina” (Moscow), “Tsvetochnaya 1”, “Tsvetochnaya 2”, “Dubrovka 1”, “Dubrovka 2”, “Dubrovka 3” (St. Petersburg and Leningrad region).
- DC "Berzarina" is equipped with uninterruptible power supplies, N+1 diesel generators, as well as a free cooling system with adiabatic aftercooling.
- The Tsvetochnaya 1 DC is equipped with precision air conditioners, uninterruptible power supplies, and diesel generators.
- The Tsvetochnaya 2 DC is equipped with uninterruptible power supplies, diesel generators with N+1 redundancy, chillers, and an automatic fire extinguishing system.
- 4 Gesan diesel generator sets are installed in the Dubrovka 1 DC. They are connected according to a 3+1 scheme, which allows you to reserve the full capacity of the data center.
- The Dubrovka 2 DC is equipped with uninterruptible power supplies, N+1 diesel generators, an automatic gas fire extinguishing system and precision air conditioners.
- DC “Dubrovka 3” uses the same things, but instead of air conditioning, free cooling with after-cooling is used.
Apple's Mesa Data Center
Area: 120 thousand m2
Location: Arizona, USA
The Mesa Datacenter was originally designed by solar panel company First Solar Inc., but Apple said in 2022 that it would spend $2 billion over the next decade to further improve the facility. However, the company, known for its secrecy, has not shared details about what happens inside the data center, citing security, although it is known to employ 150 people. Apple calls the facility its global data operations center.
In order to provide its data centers with clean energy, Apple built a 120-hectare solar power plant in Arizona. It has a capacity of 50 MW, enough to power 12,500 homes. This doesn't make the data center 100% green, but it does offset Mesa's energy consumption.