Humanity began to use the pipe a very long time ago - its prototype was reed and bamboo, from which the first water pipelines were built. Even in ancient Rome they learned to make pipes from bronze. The first methods of industrial production of such metal products arose in the early 19th century. Currently, millions and millions of tons of product are produced, without which a huge number of branches of human economic activity cannot do.
In the production of rigid metal structures from solid billets, pipe bending is increasingly being used as an alternative to welding and threading. This is due to a number of reasons:
- reduction in material consumption, since there are no welded pipes;
- reduction in labor intensity when creating structures compared to welded and threaded connections;
- better hydro-aerodynamic passage performance;
- no adverse effect on the metal structure compared to welding;
- advantage in sealing relative to threaded connections;
- better appearance of the final product.
Pipe bending is carried out using various methods. The use of a particular technology is determined by the following main factors:
- material of manufacture;
- Wall thickness;
- profile;
- section size (diameter or profile height);
- bend radius;
- required bending accuracy;
- permissible limits of deformation of a bent structure;
- quality indicators of strength and durability at the bending point.
Electromechanical pipe benders
Most often, they are used to bend pipes with different cross sections. The main difference between an electromechanical pipe bender and other machines of this type is the high accuracy of the bending radius and the complete absence of the need for human effort.
The cost of these devices is quite high, so they are mainly intended for professional use. Using electromechanical pipe benders, you can bend pipes of significant diameters: the limitation in this case is solely the dimensions of the machine itself
When bending steel pipes in this way, it is important to strictly adhere to the relevant standards. For this purpose, there are special interchangeable templates in a wide range of sizes.
Hydraulic pipe benders
Pipe bending
These devices are also used for bending small diameter pipes. Here the application of a small force is compensated by a special hydraulic cylinder. The use of this device is to determine the location of the bend and further carry out this procedure, having first inserted one edge into the device. Then, using the lever, you just need to perform translational movements. Here it is also necessary to take into account the minimum bending radius of the pipe.
Pipe bending methods and their advantages
Pipe bending is a technology where the desired rotation in the direction of the pipeline line is created by physical impact on the workpiece, the method has the following advantages:
- Reduced metal consumption; there are no adapter flanges, couplings or pipes in the line.
- Reduced labor costs when installing pipelines compared to welded joints.
- Low hydraulic losses due to unchanged profile section.
Rice. 3 Mandrels for pipe benders
- Unchangeable structure of the metal, its physical and chemical parameters compared to welding.
- High quality sealing, the line has a uniform structure without breaks or joints.
- Aesthetic appearance of the highway
There are two main bending technologies - hot and cold, devices and methods can be divided into the following categories:
- According to the type of physical impact, the pipe bending unit can be manual or electric with a mechanical or hydraulic drive.
- By bending technology - mandrel (bent using special internal protectors), mandrelless, and rolling installations with rollers.
- By profile - installations for metal profile rectangular or round products.
Rice. 4 Hot pipe bending methods
Hot bending
This technology, popular in everyday life, is used in cases where there is no pipe bending machine or it is not possible to carry out work using a cold method; the process consists of several operations:
- The workpiece is filled with fine-grained river sand without foreign inclusions in dry form. To do this, insert a plug at one end, fill it with sand and close the hole on the other side.
- The bending point is heated to a temperature of no more than 900 degrees to avoid burnout, and the part is gradually smoothly mechanically wound around a round template.
- At the end of the process, the plugs are removed and sand is poured out of the workpiece.
Cold bending methods for round pipes
Cold methods have undeniable advantages over hot technologies: they do not damage the structure of the metal, are more productive and require less costs. The following defects occur during cold bending:
- reducing the cross-section of the pipe on the outside of the profile;
- curvature in the bend in the form of a corrugation on the inside;
- changing the profile shape at pipe bending points from round to oval.
Rice. 5 Bending metal profile blanks at home
Most often, such defects occur when thin-walled pipes are deformed, so when operating with them, an internal protector is used - a mandrel inserted into the internal cavity.
The mandrel is a device consisting of a rigid rod with movable segments on the edge of a spherical or hemispherical shape. Before work, the device is placed in the internal cavity of the workpiece so that its moving elements are located at the bending point; at the end of the procedure, the mandrel is removed from the finished element and the process is repeated.
Plastic pipes
Bending plastic is a rather complicated procedure, since there is always a threat of damage to the material and a decrease in wall thickness. A more optimal solution is to purchase a special rotary adapter. If for some reason it is not possible to use a square, the procedure for bending a plastic pipe is carried out using a construction hair dryer.
The optimal temperature in this case is 140 degrees. Warming up the bending area should be done slowly to prevent overheating. The fact is that at a temperature of 175 degrees, plastic usually begins to melt.
After the product acquires the necessary plasticity, it is carefully bent. To ensure that the thickness of the outer walls does not change, it is covered with small pieces of plastic and also heated
In this way they are welded, and the area in the knee receives additional protection from breakthrough.
Results
Pipelines make people's lives much more comfortable and efficient, and this applies to both the domestic and industrial spheres. When arranging various communications, it is almost impossible to avoid turns and bends, for the organization of which various devices and methods are used
When bending pipes made of various materials, it is very important to avoid haste and strictly follow the rules for bending pipes.
How to bend a pipe yourself
If you need to bend a pipe with your own hands, you can use the universal formula (five pipe diameters) when calculating.
For example, let's calculate the bend for a pipe with a diameter of 1.6 mm:
- First you need to imagine exactly what kind of circle you want to get in the end (for an accurate fold, ¼ of a circle is required).
- Next you need to find out the radius. To do this, 16 is multiplied by 5 - the result is 80 mm.
- Now the starting points for the bend are calculated. In this case, you need to use the formula C=2π∙R:4. Here C is the section of pipe that will participate in the work. Two π and the value of the outer radius of the pipe are used.
- At the last stage, the values are replaced by known indicators: 2∙3.14∙80:4. The result is 125 mm, which is equal to the duration of the segment in which the minimum permissible bending radius will be 80 mm.
If you can’t get the calculations using the formulas above, you can do them using a calculator program, of which there are plenty on the Internet.
Having determined the load on the round pipe and carried out all the calculations, you can begin bending work, for which it is better to use a special manual pipe bender, which will greatly simplify installation. There are several varieties of such instruments. The segment device will allow you to carry out work based on special templates, the shape of which is selected for a specific cross-section and shape of pipes. The pipe can be bent up to 180˚.
A mandrel pipe bender has a moving element inside that prevents the formation of deformations.
Aluminum pipes
Aluminum pipes bend in much the same way as copper pipes, because the degree of flexibility of these metals is very similar. In general, bending aluminum pipes does not pose any particular difficulties. In addition to sand, in the case of aluminum, you can use water frozen inside the pipe. Naturally, this method can only be implemented in frosty weather.
To do this, you will need to plug one end of the pipe with a chopper in order to pour water inside it. After this, the product filled with water is exposed to the cold until the liquid freezes completely. The further procedure is carried out in exactly the same way as in the case of sand.
Example of pipe bending
Bending aluminum pipes is approximately the same as copper pipes. The reason for this is the malleability of these two metals. But in the case of aluminum, you can also use ice. To do this, simply pour water into the cavity, after placing the plug on one end. Bay, you need to put it outside (a prerequisite is frosty weather). After the water has completely frozen, you can gradually bend it. Ice works just as well here as sand.
Example of pipe bending
Copper pipes
If in the case of steel everything is simple, then copper tends to quickly burst and deteriorate when bending. In order to avoid undesirable consequences, you can use ordinary sand.
Before bending, pour sand into the cavity. Be sure to make sure it is dry. Next, heat the bending area with a torch. Plain paper will help check whether the heating is sufficient. It should light up when you bring it near the pipe. Next, gradually, without sudden movements, you need to determine the required bending radius of the pipes. The main thing is to be careful, as you can easily tear the material.
Metal-plastic pipes
As metal-plastic pipes spread, many began to use them in all possible communications. They are reliable, practical, inexpensive and easy to install. But how to bend metal-plastic pipes? To do this, either simple manual labor is used (if the metal in the pipe is soft), or the bending method using a spring (discussed above). It is mandatory to fulfill the condition that the metal-plastic pipe cannot be bent more than 15 degrees for every 2 centimeters. If this parameter is neglected, the pipe may simply become unusable due to a large number of damages.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q-yVb4YMkVE
As we found out, there are quite a few folk ways of bending pipes. With a little practice, you can achieve good results. However, it should be remembered that the quality of bending performed using professional equipment will always be higher.
The video in this article contains additional information on how to bend metal-plastic pipes. If you have any difficulties during this operation, ask questions in the comments, and I will definitely try to help you.
Bending in dies using pressing
Bending of blanks no longer than 70 centimeters can be done using stamping. In this case, hydraulic or mechanical presses are used. This method allows the production of structural elements with complex shapes.
Pressing blanks is the most expensive bending method. However, its productivity is the highest. This method allows us to produce a wide range of products.
Pipe bending machine equipment
Pipe bending on an industrial scale is carried out using machines.
Bending by rolling.
The most common machines are those that bend products using rolling. The most commonly used equipment is with three rolls, designed for bending long workpieces. It can be used to produce spiral pipes.
The product moves through rollers, the location of which determines its bending radius. At the same time, it is compressed on both sides by a deforming cylinder. It is located between the rollers, so that it is possible to bend the workpiece in weight. Rollers serve as a support during metal processing.
Compression processing
Often in production, machines are used that bend workpieces with a small radius using a compression method. They process workpieces of small and large cross-sections. The process occurs with local heating of the products and simultaneous axial pressure on them.
The machine consists of:
- bed with a heater located on it;
- support roller;
- pairs of pincer clamps, the first of them is bending and rotary, the second is sedimentary.
The device is capable of bending elements at an angle of 180º. It clamps the workpieces with a constant force, regardless of their cross-section and the value of the axial force generated at the epicenter of deformation during bending of the product. The equipment can process square and rectangular profiles.
Rotary stretch bending
Rotary pipe drawing is carried out on machines with electric or hydraulic supports for moving pressure rollers. The latter serve to obtain the desired configuration and thickness of the produced element.
With rotary drawing, products are produced from hollow rotating rods, deformed by rollers along a moving mandrel. Nowadays, CNC rotary drawing machines are used in most cases. Their program takes into account the resistance of the material when it is deformed. When manufacturing products, the corresponding GOST is used.
Conclusion
Watch the video
In small volumes, pipe bending can be done using hand tools. On an industrial scale, this is done on special machines. Before work, it is necessary to calculate the minimum permissible bending radius.
Add to bookmarks
Home craftsmen today independently carry out almost all vital systems for their farms: plumbing, heating, sewerage; they build low-rise buildings, utility rooms, and greenhouses. They invent inexpensive devices for the manufacture and processing of building materials, bending all kinds of profiles, cutting and bending various pipes, and use welding and casting technologies.
Pipe bending is used to create metal fences; this allows you to eliminate the need for welding and achieve the desired result by simply bending a solid pipe at the required angle.
There are no recurring reasons for frequent bending of pipes in private households.
The task is to take and bend the required part.
Modern technologies for bending and measuring pipes
The interest of large industrial enterprises in pipe bending technologies is constantly growing. Specialists involved in the development of production in shipbuilding, power engineering, automotive, and aircraft manufacturing study types of bending and operating principles of equipment, and analyze technical and commercial proposals from various companies. And yet, most of them still have a lot of questions, the answers to which this article will try to give.
Requirements for curved pipelines
The automotive and aerospace industries place the highest demands on curved piping. For example, in 2010, Votkinsky Plant OJSC specified the following requirements at an auction for the supply of equipment: minimum axial bending radius (CLR) = 0.7 of the outer diameter of the pipe (D), cross-sectional ovality (deviation from roundness) - no more than 2.5 ..3% D, deviation of the theoretical pipe geometry is no more than 1 mm.
Rice. 1 Old pipe bending machine
In addition, pipelines that are bent in the automotive industry (for example, pipelines for the exhaust gas exhaust system) and in the aviation industry have extremely complex geometry, which uses many bending radii, often lacks straight sections between bends, and uses materials that are difficult to deform. such as corrosion-resistant steel, titanium alloys or heat-resistant steels. In this case, bending defects are not allowed: corrugation, marks on the surface of the pipe left by clamps, thinning of the wall. To solve these problems, very modern and technologically advanced equipment is required.
Operating principles of a pipe bending machine
A pipe bending machine is generally understood as a universal machine for mandrel cold bending of pipes, using the method of winding a pipe around a bending roller.
This method was invented more than half a century ago and was then used in a rather primitive manual pipe bender (Fig. 1).
Rice. 2 Bending scheme
Regardless of the complexity of the machine, bending is carried out according to the following scheme (Fig. 2, 3) with the participation of several moving parts of the machine:
Bending roller (1), front clamp (2), rear clamp (3), mandrel (4), crease smoother (5), mandrel rod.
A: the position for loading the pipe into the machine is shown: clamps 2 and 3 are retracted and do not interfere with loading the pipe.
B: The operator (or automatic loader) loads the pipe into the machine by sliding it onto the mandrel and clamping it into the collet.
C: Shows the movement of the front clamp: the pipe is now firmly clamped between the straight part of the bending roller (1) and the front clamp (2).
D: The back pressure is applied until it touches the pipe surface.
E: The bending roller (1) and the front clamp (2) rotate simultaneously, which winds the pipe onto the round part of the bending roller, while the rear clamp (3) moves forward at the speed of the axial movement of the pipe to compensate for the resulting radial forces, and also prevent damage to the pipe surface.
F: when a certain bending angle is reached, the mandrel (4) is pulled back to prevent it from creasing in the pipe.
G: Front and rear clamps move away from the pipe.
HJ: all elements are returned to their original position.
This is the operating principle of the simplest semi-automatic machine. It is called semi-automatic because the machine performs the sequence of movements from A to J automatically with one press of a pedal or button. The operator only sets the required bending angle and loads the pipe. However, such a machine allows you to bend the pipe only along one radius and only in one bending plane; in addition, the operator must manually move the pipe in order to make the next bend. Despite the fact that single-axis machines are still in demand, critical industries require more complex equipment.
Classification of pipe bending machines
Pipe bending machines can be classified according to various criteria, but in world practice there has been a fairly stable and universal classification based on the number of CNC axes. Manufacturers of pipe bending machines refer to any independently programmed and CNC-controlled movement of the machine as an axis. In Table 1 we list the basic 3 axes that are necessarily present in any CNC pipe bending machine:
Table 1. Scheme of the first three axes
Such a 3-axis machine allows for fully automatic bending of three-dimensional pipelines along one bend radius and with straight sections between bends of 2..3 D in length.
However, if there is more than one bend radius on the pipeline, additional axes of machine motion are used (horizontal movement of the bending arm - X, vertical movement of the bending arm Z).
These two movements make it possible to install equipment on the machine, consisting of several rollers of different diameters and corresponding clamps, and to position a roller of the required diameter in front of the pipe for each bend using the vertical movement of the bending head (Z axis). The horizontal movement of the bending arm (X axis) is necessary in order to install the desired roller and clamp in the correct position while the pipe axis remains unchanged.
Rice. 3 Equipment positioning diagram
Why are the other axes needed? After all, now you can find not only 5-axis machines, but also pipe benders with 9, 11, and even 21 axis (Fig. 4, 5). The fact is that many manufacturers for the automotive and aviation industries offer fully electric pipe bending machines without the use of hydraulic drives. In these machines, all movements are carried out using electric servo drives controlled by CNC. Therefore, a separate axis is used for the movement of each of the clamps, the movement of the mandrel, and sometimes even for closing the collet.
In addition, the number of axes in the machine increases even more if the pipeline configuration requires bending in two directions. Only a few companies in the world make such machines, and their products are in demand only in special cases (Fig. 6). There are several layouts of machines, but, as a rule, for the second direction of bending, a second bending console is provided with tooling that mirrors the equipment of the first. Different manufacturers place this console in different ways: some are located below the main one (in this case the width of the machine does not change, and some of the drives are shared between the upper and lower halves of the console), and some are parallel to it, thereby increasing the width of the machine and completely duplicating all drives, except for the Y (pipe feed) and B (pipe rotation in space) axes. It can be said quite conventionally that the first type of arrangement of bending consoles is typical for bending pipes of relatively small diameter (up to 3040 mm), while the second is more common for bending pipes of large diameters (from 50 to 100 mm).
Rice. 4 9-axis machine SILFAX
Rice. 5 13-axis CRIPPA machine with an additional bending console mounted below for left-hand bending
Rice. 6 ShwarzeRobitec pipe bending machine, bending consoles for right-hand and left-hand bending are independent of each other
Control methods
After the bending operation, control of the geometry of the bent pipe follows. At the same time, in serial and mass production, the control operation must be carried out as quickly and accurately as possible. Moreover, due to the elastic properties of the pipe material, even the most advanced and accurate pipe bending machine is not able to bend the pipe without deviations the first time if the properties of the material were not previously known. Spring return of fractions of a degree in each bend ultimately leads to significant deviations from the theoretical model. To calculate the necessary program adjustments for subsequent products, a control measuring machine (CMM) is required.
The following types of measuring machines are in industrial use:
Mobile or stationary systems (Fig. 7) in the form of a hand-held measuring system, designed for measuring pipe sections by an operator using a contact sensor or a non-contact measuring device (laser measurement).
Rice. 7 Manipulator with non-contact laser sensors
Stationary three-coordinate measuring machines with the movement of the working device along the upper traverse (portal type) or with a horizontal quill using contact sensors, a digital and analog sensor scanning system and laser scanning for objects of complex shape (Fig. 8).
Rice. 8 Coordinate measuring machine
Video/Photo is an optical spatial measurement based on shooting the product being measured in a special camera using several image capturing devices located in different positions. The measurement is performed automatically without additional operator participation (Fig. 9).
Rice. 9 Optical scanner for pipe measurement
Three-axis CMMs are used extremely rarely for pipe measurement. The most widely used are manipulators with non-contact laser sensors. Most manufacturers of pipe bending machines, back in the late 80s, equipped their machines with software modules for automatically receiving correction tables via an Ethernet network, which made it possible to move to significantly more rapid detection of pipelines with geometry beyond the tolerance limits, instantaneous input of corrections into the program and, ultimately , increase productivity and quality of finished products.
Problems in the transition of Russian aviation enterprises to digital pipeline production
Many enterprises are taking steps to build digital pipeline production. Indeed, in the 21st century, an enterprise must receive a digital 3D model of a pipeline from a design bureau, load the resulting file into the CNC of a pipe bending machine, in one day, using a special simulator, generate a bending program and debug it on a model of the machine, tool and pipe in virtual reality, without using real machine, operator, materials and then immediately move on to the production of a new pipeline.
It would seem that back in the early 90s. last century, an optimal technological cycle was established in Western countries, and domestic enterprises could simply buy the same equipment and software and reproduce it at their own facilities.
However, everything turned out to be not so simple. The fact is that Western technology is “tailored” for pipelines, the design of which included the principles of machine bending manufacturability during the design, and production receives working documentation for pipelines in digital models.
At Russian aviation enterprises the situation is fundamentally different. There are thousands of 7080s piping standards that are not configured to be mastered on a pipe bender.
Moreover, the standards exist “in hardware”, and in order to enter a bending program into the CNC of a pipe bending machine, they must be somehow measured and parameterized.
Why is the master configuration not very suitable for machine bending?
If we return to the bending diagram, we can see that in position C the machine requires a straight section to clamp the pipe between the front clamp and the straight part of the bending roller. Can the machine bend a pipe with bends that have no straight sections between them? A modern machine equipped with Z and X axes certainly can. But then, for each such transition from radius to radius, you will need your own clamp and roller with curved streams that follow the contour of the already curved section of the pipe that needs to be clamped. The number of such streams is limited by the movement of the machine along the Z axis; in addition, the higher the level of equipment, the less rigid the machine tool system becomes, the greater the geometry deviations we will ultimately get. Therefore, the production of equipment with more than 34 bend-to-bend transitions without straight sections is expensive, complex, and low-tech.
In some standards there are 8...10, and sometimes even more, such transitions. It is almost impossible to manufacture them on a pipe bending machine without geometry optimization (Fig. 10).
Rice. 10 Multi-level equipment with profiled grooves for bending pipelines without straight sections
The second problem is programming the machine. At the same time, the question also requires solution: how to obtain a bending program for each standard? After all, most standards are extremely difficult to measure, even if the company has purchased a special CMM. When measuring, difficulties arise due to the fact that the standards do not have a clearly defined structure of straight sections and bends; often there are additional bends between the bends (due to manual production of the standard); not a single radius is clearly defined and varies from bend to bend.
For CMMs of the first two types (coordinate machines and manipulators with non-contact sensors), accurate and mass conversion of standards into 3D models is practically impossible.
Optical measuring systems provide great opportunities. In 2008, the National Institute of Aviation Technology carried out work to convert a number of pipelines of one of the MIG fighters into mathematical models. To do this, NIAT specialists used the ATOS2 measuring head, which removed a cloud of points from the measured product, and then manually approximated the obtained data into a polygonal model. The disadvantage of the resulting models was the impossibility of parameterizing the pipeline in LRA coordinates (polar coordinates that actually describe the pipeline in the three main axes of the CNC pipe bending machine).
The next step in the development of this technology is currently being taken by the Voronezh Aircraft Manufacturing Society as part of the Ministry of Education project to develop high-tech modern production technologies. The company purchased the latest Tubeinspect optical scanner, designed specifically for measuring pipe geometry, which it plans to adapt for mass digitization of AN148 aircraft standards and automatically obtaining already parameterized pipeline models.
After this, a lot of work will be done to analyze the geometry of each pipeline and optimize it for transfer to bending on CNC pipe bending machines. This optimization is needed primarily in order to reduce the range of equipment required for bending and minimize the need to use very expensive and difficult to produce rollers with profiled bending grooves. New Line Engineering LLC, as a consultant to VASO on modern production technologies, participates in this project as one of the developers of the concept of digital production of pipelines, as well as as a developer of methodologies, software and documentation necessary to launch the project.
Use of robots in pipe bending
In the last decade, robots have been increasingly used in pipe processing operations, primarily to automate the operations of loading workpieces into equipment and unloading finished products (Fig. 11). In this case, the robot can also transfer the workpiece to the next operation. For example, by loading a pipe into a pipe bending machine, after performing bending operations, the robot is able to grab the curved pipeline and place it in an optical measuring chamber to control the geometry, and then load the ends of the pipe sequentially into the forming machine and form the necessary folds.
Fig.11 Robotic cell
Increasingly, there are examples of using robots directly for bending pipes, when all movements of the pipe are carried out using a robot manipulator, which feeds the product into the bending head, replacing a number of standard movements of a CNC machine (Fig. 12).
Rice. 12 Using a robot in conjunction with a simplified bending head: the robot replaces several axes of a pipe bending machine at once.
Rice. 13 Robot with bending head
Integrated robotic bending rivals CNC machining, allowing a 6-axis robot to load tubes into the bending head, feed (Y-axis), turn tubes (B-axis), and unload after bending. The result is a flexible system that does not require any additional devices for operation.
Robotic bending also offers a number of functionality advantages that cannot be fully achieved using a CNC machine. This is bending of composite pipes with additional attached elements, bending clockwise and counterclockwise of the same product, automatic loading and unloading of both short and long pipes on the same bending cell. The disadvantage of this system is the absence of a mandrel in the pipe, and, as a result, the bending quality is not very high.
For small diameter pipes (up to 20 mm), there are also special bending heads that can be installed on the robot. In this case, the robot moves the bending head mounted on it along a stationary fixed pipe, independently positions it along all axes and performs bending extremely quickly (Fig. 13). Such systems will certainly find their application in the production of air conditioning pipes, fuel and brake systems of automobiles, and the production of compact heat exchangers.
Pipe bending radius for devices used in everyday life and industry
On the construction market you can find a large number of devices for individual use for bending pipes, from simple springs to complex electromechanical machines with hydraulic feed.
Manual pipe benders
Pipe benders of this class are low cost, have a simple design, low weight and dimensions; the process of bending the workpiece occurs due to the physical effort of the worker. Based on the principle of operation, manual units produced by industry can be divided into the following categories.
Lever. Bending is achieved through a large lever, which reduces the applied muscle force. In such devices, a workpiece is inserted into a mandrel of a given shape and size (punch) and, using a lever, the product bends around a template surface - the result is an element of a given profile. Lever devices allow a 180-degree radius of curvature and are suitable for small diameter soft metal pipes (up to 1 inch). To obtain curves of various sizes, replaceable punches are used; to facilitate work, many models are equipped with a hydraulic drive.
Rice. 7 Hand-held crossbow devices
Crossbow. During operation, the workpiece is placed on two rollers or stops, and bending occurs by applying pressure to its surface between the stops of a punch of a given shape and cross-section. The units have replaceable punch attachments and movable stops that allow you to set the bending radius of a steel pipe or non-ferrous metal workpieces.
The bending shoe is mounted on a rod, which can be moved by a helical gear, hydraulic fluid pressure when manually pumping, or by electrically driven hydraulics. Such devices allow bending of pipes made of soft materials with a diameter of up to 100 mm.
Three-roller units (pipe bending rollers). They are the most common type of pipe bending units in everyday life and industry; they operate on the principle of cold rolling. Structurally, they are made in the form of two rollers, in the grooves of which the workpiece is installed, the third roller is gradually brought to the surface, simultaneously rolling the product in different directions. As a result, the workpiece is deformed without folding into a larger cross-section than in other manual pipe benders.
A distinctive feature of the unit is the impossibility of obtaining a small radius of curvature (the usual value is 3 - 4 times the internal diameter).
All of the listed devices are mandrelless units, therefore they are ineffective when bending thin-walled products; it is also undesirable to use them when working with workpieces with a welded joint of the walls - with plastic deformation, individual sections of the seam may open.
Rice. 8 Pipe bending rollers
Electromechanical pipe benders
Electromechanical units are mainly used in industry and provide the following technological processes.
Coreless bending. The machines are used when working with workpieces, for bending radii of 3 - 4 D., they are capable of bending thick-walled pipes for the furniture and construction industries, and main pipelines. The machines have the simplest design and control compared to other types, and are characterized by small overall dimensions and weight.
Booster treatment. Units that operate using a special technology for advancing the carriage with the part using an additional unit are designed to produce complex bends without thinning the walls. They are used for the manufacture of coils of various shapes in the thermal energy, boiler and water heating industries.
Mandrel bending. Units of this type allow high-quality bending of thin-walled elements with an outer diameter of up to 120 mm. Industrial machines can be automatic or semi-automatic with numerical control.
Three-roll bending. The design is widely used for bending any metals and alloys; it is versatile: it copes well with round or rectangular profiles, corners and flat plates. The versatility of the unit is achieved by changing rolls with different types of working surfaces and sizes.
Using this unit, it is convenient to bend elements of long length with the same large radius of curvature throughout.
Rice. 9 Industrial pipe benders
Sheet metal bending technology: features and classification
Bending technology, depending on the required modification of sheet metal, includes the following types:
- Single-angle (V-shaped) - considered the simplest. Under the influence of the bending force, the upper surface of the workpiece is compressed, and the lower surface is adjacent to the walls of the mechanism and stretched. This way the desired radius is achieved.
- Double-angled (U-shaped) - performed in a similar way except for the number of processing steps.
- Multi-angle bending.
- Radial bending of sheet metal (rolling) – allows you to obtain a smooth bend. Used to create hinges, clamps, etc.
This technology for processing workpieces does not require enormous effort, so preheating the material is not required.
Hot bending along a radius is used only for thick sheet blanks (12–16 mm), as well as low-plasticity metals. The latter include duralumin, high-carbon steels and their alloys.
This method of processing sheet material is often used in combination with other operations, for example, cutting, cutting or punching. The result is complex three-dimensional metal products. To make them, they resort to stamps that can be used in several transitions.
From the point of view of spatial positioning, there are two ways to bend along a radius:
- Longitudinal - in this case, cold work technology is used, which does not allow processing thick sheet blanks.
- Transverse - includes several stages: first of all, the edges of the metal part are bent, then it is heated. Afterwards, the actual production operations begin: bending, upsetting and drawing.
For radius bending of sheet metal, a specialized manual or industrial machine is required. Its design is modified depending on the required shape of the product.
Working in cold technology requires maintaining an optimal ratio of bending radius, metal thickness and the size of the sheet itself. Deviation from the limit value is fraught with loss of strength characteristics of the workpiece and the possibility of damage.
Giving a radius shape to a workpiece under the influence of high temperatures can change the structure of the material. Thus, during cooling after heating, the bonds between the molecules in a sheet of metal become closer and more ordered, which helps to increase its hardness, strength and elasticity. In addition, the elongation at break decreases at this point. The plasticity of the material changes little.
Pipe bending methods without factory equipment
In domestic conditions, there is often a need to bend pipe blanks when carrying out construction work or installing gas pipelines. At the same time, it is not economically feasible to spend financial resources on purchasing factory pipe benders for one-time operations; many use simple homemade devices for these purposes.
Steel pipes
Steel is a fairly rigid and durable material that is very difficult to deform; the main method of changing its configuration is bending in a heated state with a filler under simultaneous physical impact. For thin-walled stainless steel pipes, the following technology is used to obtain a long section with a small bend radius:
- Place the workpiece vertically, close it at one end with a stopper and pour very fine dry sand inside; after it is completely filled, insert the stopper on the other side.
- Find a pipe or low vertical pole of the required diameter and firmly fix the pipe end to its surface.
- Wrap the part around the pipe axis, turning the template or walking around it.
- After winding, the end is released and the curved part is removed from the template, the plugs are removed and sand is poured out.
Rice. 11 How to obtain the required bending radius of a copper pipe
Copper pipes
Copper is a softer material than steel; it is also convenient to bend when heated or with the help of sand poured inside. You can also use a household mandrel substitute for bending - a steel spring with dense thick coils and a cross-section slightly smaller than the workpiece. When carrying out work, the element is inserted inside and located at the point where deformation occurs, and after the necessary operations it is easily removed out. But it is much easier to bend copper pipes with a special spring pipe bender (these products can be purchased at the retail chain), which are effective on short routes and work due to the uniform distribution of the applied force on the surface. The spring device works as follows:
- The spring is placed over the pipe in the desired place, after which it is manually bent along with the pipe.
- With further bending, the spring is moved and bent at another point.
- Upon completion of the operation, the spring segment is easily removed without the use of auxiliary means.
Another popular material is aluminum, which is easier to bend when heated with a torch.
Rice. 12 How to bend pipes without an aluminum machine
Metal-plastic pipes
When bending metal-plastic pipes in households, an internal or external spring (conductor) is used. The technology for carrying out the work is similar to operations with a copper pipe; when bending, the permissible radius restrictions must be observed to avoid damage to the product.
Plastic pipes
The main element for changing the configuration of plastic pipes is a construction or household hair dryer; sand can be used to facilitate the work. Products of complex shape are bent as follows:
- Self-tapping screws are screwed onto a wooden plate using a screwdriver according to the desired configuration of the workpiece.
- The pipe end is inserted between two screws and the pipe wall is heated with a hairdryer, ensuring the direction of the product with turns and flexibility along a given route.
- At the end of the work, unscrew the screws and remove the workpiece.
Rice. 13 Methods for bending metal-plastic pipes using external and internal conductors
You can use another simple technology:
- Pour sand into a plastic pipe and tightly close its ends.
- Place the product in boiling water for a while and then remove it to the surface.
- Give the workpiece the desired shape, fixing it in the desired position and waiting for cooling.
Rice. 14 How plastic elements are bent
Existing industrial and household methods for obtaining the required bending radius make it possible to carry out these operations with any materials of various diameters. To carry out the work, special devices of a manual or electromechanical operating principle are used, which often use hydraulic units. In households, effective bending methods are the use of special springs and heating of products with gas burners or a household hair dryer (when bending plastic).
Standards and adaptations
Naturally, each pipe uses its own standard angles. This indicator, as already mentioned, depends on the material and diameter. Most often, products with turns and flexibility are found in the construction of houses. For this purpose, special devices are used - pipe benders. Let's look at the most frequently used ones. So, there are pipe benders:
Pipe bending radius
- manual;
- hydraulic;
- electromechanical;
- plane-parallel plates;
- steel spring.
Volume of water in the pipeline
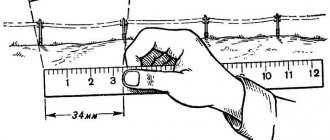
Knowing the volume of water that can be in a pipe is useful in many situations. This calculation can be useful when working on the heating system, water supply, and sewerage. The formula for an ordinary round pipe is not complicated. To carry out the calculation, you need to arm yourself with a caliper and a tape measure. To make the calculations easier, a calculator would be helpful.
First, measure the diameter of the pipe along the inner edges with a caliper. Divide the resulting value in half to find the inner radius. Based on the radius, we find the cross-sectional area of the pipe.
Next, you need to measure the length of the pipe with a tape measure. We multiply the resulting parameter by the previously calculated cross-sectional area. Ready! We found the volume of water that can be in the pipe. The volume can be expressed either in cube. m, or in l. These units correspond like this: 1 cubic meter. m = 1000 cubic meters dm = 1,000 l. However, this formula is only suitable if the pipe is completely filled with water.
For incomplete filling of pipes with water, much more complex geometric constructions and formulas are used to calculate the volume of liquid. We offer a drawing for your reference that shows how to make such calculations:
The throughput capacity of various pipes is determined using special tables. So, a pipe with a cross-section of 25 mm per minute passes up to 30 liters in 1 minute. If the pipe has a diameter of 32 mm, it is already capable of flowing up to 50 l/min. However, most faucets are capable of passing through no more than 5 liters of water in 1 minute.
It is also worth making allowances for the material from which the pipe is made. The fact is that polypropylene pipes have significantly smoother walls than metal pipes. This means that their ability to pass water with the same diameter will be higher. Limescale deposits that accumulate in metal pipes can have an even greater impact on throughput. Therefore, any table shows throughput only approximately.
Determination of the conductor cross-section at the input
You can check the nominal values in the Energosbyt company or in the documentation for the product.
For example, the rating of the machine at the input is 25 A, the power consumption is 5 kW, the network is single-phase, 220 V. The cross-section is selected so that the permissible current of the cores over a long period is greater than the rating of the machine. For example, a three-core copper conductor VVGng, laid in an open manner, was installed in a house. The optimal cross-section is 4 mm2, so you will need VVGng 3x4 material.
After this, the indicator of the conditional shutdown current for a machine with a nominal value of 25 A is calculated: 1.45x25 = 36.25 A. For a cable with a cross-sectional area of 4 mm2, the parameters of the continuous permissible current are 35 A, conditional - 36.25 A. In this case, it is better to take the input copper conductor with a cross-section of 6 mm2 and a permissible maximum current of 42 A.
Copper pipes
If there are usually no problems when bending steel products, then copper pipes can burst or be damaged during the bending process (read: “How to bend a copper tube - proven and reliable methods”). One of the easiest ways to protect yourself from such phenomena is to use simple sand. It is poured into the pipe before the procedure begins.
The sand must be dry. Next, using a burner, the bend area is heated. To check for the optimal heating temperature, just bring a piece of paper to the pipe: if it lights up, the burner can be turned off. The required bending radius of the copper pipe is determined gradually - sudden movements in this case will be unnecessary. It is accuracy that will allow you to avoid unwanted tears in the material.
Minimum bending radii of steel pipe
The minimum bending radii of a steel water pipe made in accordance with GOST 3262-75 are presented in the table.
Using a steel spring, pipe blanks made of soft, ductile metal are bent. Working with such products may damage the pipes or reduce the internal diameter.
Such defects significantly reduce the throughput of pipes. The procedure itself is quite simple and consists of immersing a spring inside the tube. In this way, the maximum and minimum bending radius of pipes made of copper, brass and metal-plastic is achieved.
Steel is a very strong material, so bending it can cause damage to the material. To prevent this from happening, it is better to heat the metal with a torch until it turns scarlet.
In this case, its bending occurs very easily. To obtain a small bending radius of a steel pipe, sometimes a strong blow with a sledgehammer to the bent area is sufficient. The strength of the material allows it to withstand such impacts without pain.
A steel spring is used when bending pipeline elements that are made of soft and very malleable metals. When bent, they can burst or create a transition in the internal diameter to a smaller value, which significantly reduces throughput.
The principle of operation is very simple: a spring is inserted inside and it bends. This method achieves the maximum and minimum bending radius of metal-plastic pipes, copper and brass products.
Steel is quite strong and can be damaged during the bending process. To avoid this consequence, you need to heat the metal to a scarlet color using a torch. Then simply bend it until the desired rotation occurs.
If you need to create a very small turn, you can simply hit the bend with a sledgehammer. Due to the strength of the material, the pipe will not be damaged, and you will get the desired bending radius.