In what cases is it necessary?
During operation, chips rub against the working surface of the tool. Due to the increase in temperature during operation, the part wears out. If sharpening is not carried out, the full service life of the part and all equipment is significantly reduced.
The documentation indicates acceptable cutter wear parameters. If these parameters are exceeded, the tool cannot be used. It must be sharpened along the front and back surfaces.
The permissible amount of wear differs depending on operating conditions and ranges from 0.3-2 mm.
Performing finishing
After selecting a machine for sharpening metal cutters and carrying out the procedure itself, grinding in the working elements should be carried out. It is performed according to the same algorithm as processing. Finishing is needed to eliminate roughness and polish the base to a shine. The better the finishing you do, the less friction there will be and the more stable the tool will be.
Finishing is done using boron carbide abrasive paste on a rotating cast iron disc. You can also use GOI pastes or other products intended for polishing for these purposes. This product is applied to the disk and rotated, while the chisel should fit tightly to the circle. This is necessary so that the grains of the abrasive paste smooth out roughness. In this way, the geometry of the product, suitability for use and its original purity will be completely restored.
The procedure for processing chisels at home requires the master to have certain skills and knowledge of the necessary techniques. Carrying out the process is not difficult, but it will require a lot of effort from the person and strict adherence to the rules for performing the work. Otherwise, the geometry of the parts will not be completely restored, as a result of which the quality and service life will be reduced.
Tools and accessories
Depending on the alloy, hardness, sharpening angle and other technological details, it is necessary to select a tool for sharpening the cutters. Each device has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Musaty
An effective tool, which is a metal rod with a ridge. Processing is carried out using a handle.
Sharpening stones
Another option for manual processing. Sharpening cutters using sharpening stones requires skill, which can only be acquired with experience. The cutter must be applied to the part and passed over it at least 10 times.
Mechanical sharpeners
Automated sharpening method. First you need to set the input parameters and, depending on them, actively operate the tool.
Electric sharpeners or sharpening machine
This is the most universal and simple method. The sharpening machine is convenient to use; in appearance it resembles a metal bar with holes of different sizes.
Emery, diamond wheel
The diamond wheel is widely used because it ensures high cleanliness of cutting surfaces. Also, with the use of diamond wheels, the service life of sharpening cutters increases - the number of possible resharpenings increases by 20-30%.
Rules for sharpening metal cutters for a lathe
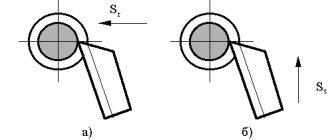
Sharpening turning tools is a responsible procedure. When carrying it out, you need to take into account the features of the equipment and material. Sharpening of a working tool is carried out in three stages:
- The rear part is cut at an angle that is identical to the rear angle of the holding element of the device.
- Next they work with the back of the working head.
- The final stage is adjusting the angle to the desired position.
You can sharpen in three ways:
- Using an abrasive wheel.
- By coating the surface to be sharpened with chemicals.
- Using specialized equipment.
In order not to spoil the cutting element of the device, to make it more durable, you need to take into account a number of rules:
- Do not attempt to sharpen the edge using a sharpening stone. It is extremely difficult to make the desired angle with hand tools. The heat that occurs during friction degrades the performance of the tool's working head.
- It is preferable to sharpen the cutting edge using a cooling system.
- Before you start sharpening with an abrasive wheel, you need to check it. It should be smooth, without chips or cracks. During torsion, the disk should not deviate to the sides. This can cause equipment breakdown and damage to the cutting edge.
- It is forbidden to hold the cutter suspended. To do this, you need to use a special emphasis. It is installed at a distance of 5 mm from the abrasive wheel.
- To avoid overheating of the material during rotation of the wheel, do not press the equipment against the abrasive. Effort should be minimal.
- When working, you need to wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from metal shavings.
- You cannot sharpen disposable models made in the form of plates.
- The best option when choosing the type of abrasive to coat the grinding wheel is carborundum. It is a green abrasive crumb. This material is suitable for sharpening carbide inserts. Carbon steels need to be sharpened with corundum wheels.
- Do not quickly cool the cutter after sharpening. This will lead to damage to the integrity of the metal.
- Change sharpening stones periodically.
We must not forget about fine-tuning the equipment. This technological operation allows you to get rid of chips, microcracks, and unevenness on the blade. To carry out finishing, special equipment is used on which diamond-coated wheels are fixed. The cutter is clamped in a vice, which is moved to the grinding wheel using a handle. Using a flywheel, bring the cutting edge to the finishing state.
Detailed diagrams and instructions on how to do it yourself
The master must know the complete technological process in order to properly sharpen the tool with his own hands.
Technological process
The technological process includes several main points:
- The rear surface is machined at an angle equal to the rear angle of the holder.
- At the second stage, the cutting surface itself is processed.
- The sharpening angle should be a couple of degrees greater than the back cutting angle by a couple of degrees.
- Already at the third stage, the rear angle is formed.
After finishing, grinding follows as the final stage of sharpening.
Conducting fine-tuning
Finishing should be carried out according to the chosen method. Basic moments:
- cutters are not immersed in water, as they may break;
- When finishing, be sure to supply water for cooling;
- First, the back face is processed, then the main and auxiliary faces.
Grinding
Grinding is carried out using an emery wheel. The best option is a fine-grained model.
Sharpening angles
The following is a list of sharpening angles for all common materials. The first fraction indicates the relief angle during roughing, the second - the relief angle during finishing. The third fraction shows the size of the front angle. The numerator indicates the angles for cutters that sharpen and bore parts, and the denominator indicates the angles for tools that plane workpieces.
- Steel (hardness less than eight hundred Megapascals) – 8/6, 12/8, 15/12.
- Steel (hardness more than eight hundred Megapascals) – 8/6, 12/8, 10/10.
- Steel (hardness more than a thousand Megapascals) – 8/6, 12/10, 10/8.
- Gray cast iron (Brinnel hardness less than two hundred and twenty) – 6/6, 10/10, 12/8.
- Gray cast iron (Brinnell hardness more than two hundred and twenty) – 6/6, 10/10, 8/5.
- Malleable cast iron – 8/8, 10/10, 8/8.
The main plan angle should be 30 - 45 degrees. The width of the chamfer depends on the cross-section of the cutting rods.
What abrasive wheels are used for sharpening turning tools? Sharpening of a tool through the holder and at an angle of 5 degrees is carried out with a wheel made of electrocorundum, having a grain size of forty - fifty, hardness CM1/2. The peripheral speed of the circle is 25 m/s.
Preparatory sharpening is carried out with products made of black silicon carbide, having a grain size of twenty-five to forty, hardness M3-SM1. The final sharpening of the cutting tool is carried out with wheels made of green silicon carbide, having a grain size of sixteen - twenty-five, hardness M3-SM1.
The parameters of grinding wheels for steel and carbide cutters are specified in the table of sharpening modes. There you can also see the circumferential torsion speeds.
Currently, final sharpening is recommended to be done using a diamond wheel. This is especially true for inserts made of hard alloys. The peripheral speed of the circle during preparatory/final sharpening should not exceed twelve to fifteen meters per second.
Safety precautions
Every master who works on a lathe must be able to sharpen cutters with his own hands. It is only important to follow the safety rules. To do this, it is necessary to use protective equipment for the face. Touching the machine or the cutter is allowed only after it has completely cooled down.
Sharpening cutters for a machine tool is one of the most important technological processes that any qualified turner should be able to perform. The details of the process depend on the type of cutter, the work performed and the degree of wear.
Purpose of the cutter, design, types
To obtain parts from a metal ingot when turning on lathe equipment, a special tool is used. They are made of steel, and the hardness of the material is higher than that of the workpiece being processed. The holder rod and the working head, the main structural elements of a metal cutter, are used to secure the tool on the lathe.
The function of the second component is to cut off a layer of the metal surface during processing. The holder rod or the body of the cutter has a square or rectangular cross-section. The main cutting edge of the working head is shaped (wedge) or straight in cross-section. Metal cutting parts require regular sharpening during operation. In modern conditions there is a sufficient choice of incisors.
Turning tools for metal processing with replaceable inserts
When choosing gear, you should take into account such an indicator as angles. The classification of species is as follows:
- checkpoints;
- cutting;
- pruning;
- boring;
- shaped;
- grooved:
- chamfered;
- persistent;
Pass-through, this type of device processes cylindrical blanks. A cutting tool is used for cutting rods. Trimming is performed at a given angle. A cutting-type device is also used to cut grooves for various purposes in them. Scoring, this type of device is used for trimming blanks and reducing ledges. Boring, this tool is used to machine holes of the required diameter in workpieces or parts on a lathe.
Grooving - the purpose of such a device is to form internal and external grooves on a cylindrical surface, maintaining the required angles. Sometimes a cutting-type function is required when it is necessary to remove part of the metal from the workpiece. Thread-cutting machines use this device to cut threads on lathes. Shaped - the purpose of this cutter is to form protrusions and grooves on the blank being processed, thereby obtaining angles with the required parameters.
Read also: Soldering iron for SMD LEDs
Chamfering - with this device, after sharpening, internal and external chamfers are made on the product. The persistent one is used for turning metal parts with small ledges. To reduce vibration when working on a lathe, you need to check its position. Thrust is used for non-rigid parts.
Types of cutters are also divided according to the direction of processing of turning equipment into left and right, according to the material from which they are made, according to the method of attaching the cutting part to the holder and other parameters.
Sharpening angles
The following is a list of sharpening angles for all common materials. The first fraction indicates the relief angle during roughing, the second - the relief angle during finishing. The third fraction shows the size of the front angle. The numerator indicates the angles for cutters that sharpen and bore parts, and the denominator indicates the angles for tools that plane workpieces.
- Steel (hardness less than eight hundred Megapascals) – 8/6, 12/8, 15/12.
- Steel (hardness more than eight hundred Megapascals) – 8/6, 12/8, 10/10.
- Steel (hardness more than a thousand Megapascals) – 8/6, 12/10, 10/8.
- Gray cast iron (Brinnel hardness less than two hundred and twenty) – 6/6, 10/10, 12/8.
- Gray cast iron (Brinnell hardness more than two hundred and twenty) – 6/6, 10/10, 8/5.
- Malleable cast iron – 8/8, 10/10, 8/8.
The main plan angle should be 30 - 45 degrees. The width of the chamfer depends on the cross-section of the cutting rods.
What abrasive wheels are used for sharpening turning tools? Sharpening of a tool through the holder and at an angle of 5 degrees is carried out with a wheel made of electrocorundum, having a grain size of forty - fifty, hardness CM1/2. The peripheral speed of the circle is 25 m/s.
Preparatory sharpening is carried out with products made of black silicon carbide, having a grain size of twenty-five to forty, hardness M3-SM1. The final sharpening of the cutting tool is carried out with wheels made of green silicon carbide, having a grain size of sixteen - twenty-five, hardness M3-SM1.
The parameters of grinding wheels for steel and carbide cutters are specified in the table of sharpening modes. There you can also see the circumferential torsion speeds.
Currently, final sharpening is recommended to be done using a diamond wheel. This is especially true for inserts made of hard alloys. The peripheral speed of the circle during preparatory/final sharpening should not exceed twelve to fifteen meters per second.
How to make wood turning tools yourself
Many people who like to work with wood themselves prefer to make homemade cutters for a wood lathe in their workshop. Having certain metalworking skills, making a turning chisel or rake according to your own drawings is not difficult. To do this you need:
- select a workpiece from a suitable metal;
- carry out pre-processing to give it the required geometric shape;
- sharpen the cutting part in compliance with all sharpening angles and directions;
- make a handle;
- assemble the entire structure.
The blank for a wood turning tool is selected from various grades of steel. The main requirement for them is the required level of rigidity and strength. The most commonly used are blanks made of carbon tool steel. Its carbon content does not exceed 0.7%. These include: U8, U10 and U12. In terms of their physical and mechanical characteristics, they fully satisfy the requirements.
In addition to pre-prepared blanks, improvised material is used, which can be found quite easily. These products include used steel tools. For example, sheets of automobile springs, files that have lost their characteristics, trimmed sheet metal. Some products have increased strength and are quite difficult to process (especially those that have undergone thermal hardening during manufacturing, especially in large-scale production conditions). To reduce labor costs, it is advisable to choose a workpiece whose geometric shape is closest to the configuration of the future product. This will eliminate the need to use complex technologies.
To work with workpieces, turning tools, made of steel grades with increased strength, it is necessary to preheat. Using the properties of the metal, give the future product the required shape. Then the cutting edge is processed to a given level. After all operations are completed, the finished cutter is hardened. The hardening procedure involves heating the cutting edge of a turning tool, followed by rapid cooling. Such heating can be done in a home workshop using a gas burner or blowtorch. Rapid cooling is carried out in a container with liquid: for example, water or machine oil. It turns out to be a kind of home heat treatment workshop.
Cooling of turning tool blanks made of high-alloy and high-carbon steels should not be done in water. This causes increased internal stress at various levels of the metal. Ultimately leads to the appearance of serious defects. After making a turning tool, I first test its capabilities on wooden blanks of simple shape, preferably made of soft wood. This will help to identify all the shortcomings and shortcomings that arose during the production process and avoid damage to the main products.
What is needed to make cutters?
Manufacturing turning tools of this class is not particularly difficult if you have three components: suitable material, sharpening equipment and certain metalworking skills.
To give the product a given shape and create a high-quality cutting edge, a sharpening machine or grinding machine is needed. In both cases, it is necessary to have several abrasive wheels of different grain sizes. The final finishing is done manually, fixing the cutter in a vice using files or needle files. At the initial stage, a stone with the largest grain is used, which makes it possible to outline the main contours of the future cutting edge. Next they move on to the stone with the finest grain. All tools must be checked and stones carefully secured.
Most often, professionals use sharpening in several stages. At the initial stage, the manufacture of the cutter is carried out on a grinding wheel. Then they gradually move on to more precise processing. To prevent overheating during processing, the metal part is poured with machine oil.