When working with bolted fasteners, a wrench is most often used. Its main purpose is to use a lever to increase the torque for tightening or unscrewing a bolt or nut.
Currently, the industry offers a wide selection of keys that meet GOST standards. These tools help to work with fastening hardware of various types, even in cases where access to them is limited, which often happens in various equipment, structures and mechanisms. The most common wrenches are designed for DIN hex bolts.
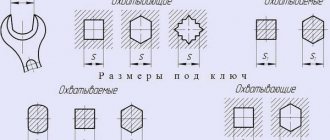
Dimensions
Let's say we have a double-sided open-end wrench in our hands with the designation 12/13 . This is the distance between the “horns” in mm. The numbers are printed on the side surface of the instrument. But there are no such markings on the nuts. How to choose a fastening element for 13 ?
Technical characteristics of nuts are established by GOST 5915-70 . It was developed back in 1970 . The size is indicated by an alphanumeric code. For example, for a 13 M8 is suitable . Other matching options are shown in the table:
| Thread diameter, M | Key size | ||
| Main S, mm | Reduced S, mm | Increased S, mm | |
| M1 | 3.2 | — | — |
| M1.2 | 3.2 | — | — |
| M1.4 | 3.2 | — | — |
| M1.6 | 3.2 | — | — |
| M2 | 4 | — | — |
| M2.5 | 5 | — | — |
| M3 | 5.5 | — | — |
| M4 | 7 | — | — |
| M5 | 8 | — | — |
| M6 | 10 | — | — |
| M7 | 11 | — | — |
| M8 | 13 | 12 | — |
| M10 | 17 (16) | 14 | — |
| M12 | 19 (18) | 17 | 21 (22) |
| M14 | 22 (21) | 19 | 24 |
| M16 | 24 | 22 | 27 |
| M18 | 27 | 24 | 30 |
| M20 | 30 | 27 | 32 (34) |
| M22 | 32 (34) | 30 | 36 |
| M24 | 36 | 32 | 41 |
| M27 | 41 | 36 | 46 |
| M30 | 46 | 41 | 50 |
| M33 | 50 | — | 55 |
| M36 | 55 | 50 | 60 |
| M39 | 60 | 55 | 65 |
| M42 | 65 | 60 | 70 |
| M48 | 75 | — | 75 |
| M52 | 80 | — | 80 |
| M56 | 85 | — | — |
| M60 | 90 | — | — |
| M64 | 95 | — | — |
| M68 | 100 | — | — |
| M72 | 105 | — | — |
| M76 | 110 | — | — |
| M80 | 115 | — | — |
| M85 | 120 | — | — |
| M90 | 130 | — | — |
| M95 | 135 | — | — |
| M100 | 145 | — | — |
| M105 | 150 | — | — |
| M110 | 155 | — | — |
Here S is the distance between the “horns” of the key. It’s better not to rely on the numbers in brackets. For household needs, the basic sizes in the second column are quite sufficient.
Inch keys
What if the instrument is not 12/13 , but 1/4 ? This means that we have a key “sharpened” for the English, inch system of measures. There, the labeling approach differs from the traditional one. The number does not at all indicate the distance between the “horns”. This is the thread diameter of the fastener.
You can’t just take a metric Russian wrench and tighten an inch nut with it. There is a difference of several millimeters. Therefore, you need to choose the tool and fasteners of one system. Let's list the values in the table:
| Thread diameter (key size), inch | Nut size, inch | Nut size, mm |
| 1/4 | 7/16 | 11.11 |
| 5/16 | 1/2 | 12.7 |
| 3/8 | 9/16 | 14.29 |
| 7/16 | 5/8 | 15.88 |
| 1/2 | 3/4 | 19.05 |
| 9/16 | 13/16 | 20.63 |
| 5/8 | 15/16 | 23.81 |
| 3/4 | 1 1/8 | 28.58 |
| 7/8 | 1 5/16 | 33.34 |
| 1 | 1 1/2 | 38.10 |
| 1 1/8 | 1 11/16 | 42.86 |
| 1 1/4 | 1 7/8 | 47.63 |
| 1 3/8 | 2 1/16 | 52.39 |
| 1 1/2 | 2 1/4 | 53.15 |
| 1 3/4 | 2 5/8 | 66.68 |
| 2 | 3 | 76.20 |
| 2 1/4 | 3 3/8 | 85.73 |
| 2 1/2 | 3 3/4 | 95.25 |
| 2 3/4 | 4 1/8 | 104.76 |
| 3 | 4 1/2 | 114.30 |
For reference: there are 2.54 1 inch .
Hex keys
When repairing a car, you often have to deal with more than just nuts. Car manufacturers use socket head bolts a lot. They can only be unscrewed with a special hex key. In European countries, sizes are regulated by the DIN 912 , in Russia - GOST 11738-84 .
The main parameter here is the distance between the nearest parallel edges on the inner niche of the bolt. For clarity, let’s collect all the data in a table:
| Thread, M | Key size, mm |
| M4 | 3 |
| M5 | 4 |
| M6 | 5 |
| M10 | 8 |
| M12 | 10 |
| M14 | 12 |
| M16 | 14 |
| M18 | 14 |
| M20 | 17 |
| M22 | 17 |
| M24 | 19 |
| M27 | 19 |
| M30 | 22 |
| M33 | 24 |
| M36 | 27 |
Main types of keys
A wrench is a lever, at the ends of which there is a device, with the help of which the head of a bolt or the corresponding nut is securely grasped and turned. It is made of high-strength steel with special additives. This allows you to apply significant force to them without the risk of breaking the tool. Manufacturers offer models with double or single-sided grip. The single-sided grip allows for increased torque by extending the handle using a pipe or other removable handle. There are several types of wrenches available that can be used in different situations:
- Open-end wrench. This is the most popular instrument standard, usually of the double-sided type. It has an open mouth on one side, reminiscent of horns, which is where its name comes from, which meets the characteristics according to GOST 2839-90. The main parameter of such a wrench is the distance between the jaws, expressed in metric or inch measurement systems. For quick selection, the key number is marked on the handle on each side. In wrenches for metric threads, this number corresponds to the distance between the jaws in millimeters; inch wrenches are marked according to a different principle.
- Socket wrench. It has a closed working part with an internal hexagon, which fits onto the head of a bolt or nut. It does not need to be thrown over during operation, which speeds up the installation or dismantling of fasteners; in addition, it is characterized by increased strength. In this case, the tool does not break off like in an open-end wrench, but this type is not suitable if the space around the fastener requires periodic repositioning. Single- and double-sided options are available, as well as wrenches with removable heads into which the lever is inserted.
- Socket wrench. It is also called tubular, which is most often used by motorists when removing wheels or working with spark plugs. It is a tube in the form of a hexagon of a certain size. To tighten and unscrew, the key is placed on a nut or bolt and turned using a lever threaded through the hole in the pipe. Finished products with L-shaped handle are available.
- Adjustable wrench. It has universal characteristics, which is why it is the most popular tool among home craftsmen. It has one working part with jaws adjustable using a special screw and the shape of an open-end wrench. The same screw securely fixes the jaws of the key in the specified position. For ease of use, some models have special markings indicating the length of the jaws. To make use more comfortable, they offer three types of adjustable wrenches with a maximum size of 20, 30 and 46 mm.
- Pipe (gas) wrench. Another universal tool that allows you to work with any threaded connections, pipes, fittings, studs, etc. It has a wide range of adjustments and a long lever that allows you to develop high torque.
- Combination key. A double-sided tool that combines an open-end and a spanner wrench. Its peculiarity is that both working parts are the same size, which facilitates the practical use of the tool.
To provide maximum capabilities, manufacturers offer two types of keys - metric and inch sizes. The first is adopted in Russia and other countries with the metric system of lengths and is measured in millimeters. The second meets the standards adopted in the USA, Canada and Great Britain and uses inches and fractions of inches. If a conversion from one system to another is required, you can use the corresponding table or the ratio 1 inch = 25.4 mm. But in practice this is not required, since the tools of different systems are not suitable for working with different types of fasteners.
To work in explosive or flammable environments, special wrenches are used that, when dropped on concrete or metal, do not create sparks that could cause a fire. According to the requirements, they are marked in red, copper or yellow.
When assembling mechanisms that require high precision connections, for example, internal combustion engines, it is recommended to use torque wrenches. This is due to the fact that insufficient tightening force will lead to oil leakage or failure of components, and overtightening will weaken the bolts or studs, which will lead to their destruction and failure of the mechanism. Such keys have a mechanical or electronic device on which the required torque is indicated, upon reaching which the limiting mechanism is activated. The tightening torque for each specific connection is indicated in the technical documentation.
Fastener weight
It's good if you need to tighten a couple of nuts. But what if you have to work on an industrial scale and the number of fasteners runs into hundreds and thousands. Then a weight table will come in handy. The main indicator here is the nominal thread diameter. of GOST 5915-70 start from it .
| Nominal thread diameter, mm | Theoretical weight 1000 pcs. nuts, kg |
| 1,6 | 0,074 |
| 2 | 0,141 |
| 2,5 | 0,272 |
| 3 | 0,377 |
| 3,5 | 0,497 |
| 4 | 0,800 |
| 5 | 1,440 |
| 6 | 2,573 |
| 8 | 5,548 |
| 10 | 10,220 |
| 12 | 15,670 |
| 14 | 25,330 |
| 16 | 37,610 |
| 18 | 53,270 |
| 20 | 71,440 |
| 22 | 103,150 |
| 24 | 122,870 |
| 27 | 175,280 |
| 30 | 242,540 |
| 36 | 416,780 |
| 42 | 623,880 |
| 48 | 956,200 |
GOST 13682-80 Places for wrenches. Dimensions, GOST dated August 6, 1980 No. 13682-80
GOST 13682-80
Group G02
Date of introduction 1981-07-01
By Decree of the USSR State Committee for Standards dated August 6, 1980 N 4069, the introduction period was set from 07/01/81 IN REPLACEMENT OF GOST 13682-68 REISSITION. July 1994
1. This standard establishes the smallest dimensions for the heads of open-end wrenches in accordance with GOST 2839-80, GOST 2841-80, GOST 3108-71, double-sided ring wrenches in accordance with GOST 2906-80 and socket wrenches with replaceable heads in accordance with GOST 25605-83.
2. The minimum dimensions of spaces for wrenches must correspond to those indicated in Figures 1-8 and in the table.
Drawings 1-5. Dimensions for open-end wrench spaces
Dimensions for open-end wrench spaces
Damn.1
Damn.2
Damn.3
Damn.4
Damn.5
Damn.6. Size of spaces for ring double-sided crank wrenches
Size of spaces for ring double-sided crank wrenches
Damn.6
Drawings 7-8. Dimensions of spaces for socket wrenches with replaceable heads
Dimensions of spaces for socket wrenches with replaceable heads
Damn.7
Damn.8
| mm | ||||||||||
| Key mouth | ||||||||||
| 3,2 | 8 | — | — | 4 | — | 5 | 14 | 10 | 9 | 11 |
| 4,0 | 9 | 16 | 12 | 12 | ||||||
| 5,0 | 11 | 5 | 7 | 18 | 14 | 10 | 14 | |||
| 5,5 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 20 | 16 | |||||
| 7,0 | 14 | 12 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 26 | 20 | 13 | 16 | |
| 8,0 | 17 | 16 | 14 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 30 | 24 | 15 | 20 |
| 10 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 36 | 28 | 18 | 22 |
| 12 | 24 | 20 | 18 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 45 | 34 | 22 | 26 |
| 13 | 26 | — | 20 | 10 | 13 | 14 | 45 | 23 | ||
| 14 | 28 | 22 | 22 | 11 | 15 | 15 | 48 | 36 | 24 | |
| 17 | 34 | 26 | 28 | 13 | 16 | 17 | 52 | 38 | 26 | 30 |
| 19 | 36 | 30 | 30 | 14 | 17 | 19 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 32 |
| 22 | 42 | 32 | 34 | 15 | 19 | 24 | 72 | 55 | 36 | 36 |
| 24 | 48 | 36 | 36 | 16 | 21 | 25 | 78 | 60 | 38 | 40 |
| 27 | 52 | 40 | 40 | 19 | 24 | 28 | 85 | 65 | 42 | 45 |
| 30 | 58 | 45 | 45 | 20 | 26 | 30 | 98 | 75 | 48 | 48 |
| 32 | 62 | 48 | 48 | 22 | 28 | 32 | 100 | 80 | 50 | 52 |
| 36 | 68 | 52 | 52 | 24 | 31 | 36 | 110 | 85 | 55 | 60 |
| 41 | 80 | 60 | 60 | 26 | 36 | 40 | 120 | 90 | 60 | 63 |
| 46 | 90 | 65 | 68 | 30 | 40 | 45 | 140 | 105 | 68 | 70 |
| 50 | 95 | 70 | 75 | 32 | 44 | 48 | 150 | 110 | 72 | 75 |
| 55 | 105 | 78 | 80 | 36 | 45 | 52 | 160 | 120 | 80 | 85 |
| 60 | 110 | — | — | 38 | — | 55 | 170 | 130 | 85 | 95 |
| 65 | 120 | 42 | 60 | 185 | 145 | 92 | 98 | |||
| 70 | 130 | 45 | 65 | 200 | 160 | 98 | 105 | |||
| 75 | 140 | 48 | 70 | 210 | 170 | 105 | 110 | |||
| 80 | 150 | 48 | 75 | 230 | 190 | 115 | — | |||
| 85 | 160 | 52 | 82 | 250 | 195 | 125 | ||||
| 90 | 170 | 58 | 88 | 260 | 200 | 130 | ||||
| 95 | 175 | 92 | 280 | 210 | 135 | |||||
| 100 | 190 | 65 | 98 | 300 | 230 | 145 | ||||
| 105 | 200 | 68 | 102 | 310 | 240 | 150 | ||||
| 110 | 205 | 70 | 105 | 320 | 250 | 155 | ||||
| 115 | 215 | 72 | 110 | 340 | 270 | 160 | ||||
| 130 | 245 | 80 | 120 | 380 | 290 | 190 | ||||
| 145 | 275 | 95 | 140 | 430 | 320 | 210 | ||||
| 155 | 295 | 100 | 150 | 450 | 350 | 225 | ||||
| 175 | 330 | 110 | 165 | 510 | 390 | 255 | ||||
| 180 | 335 | 115 | 170 | 530 | 410 | 265 | ||||
| 185 | 345 | 175 | 540 | 420 | 270 | |||||
| 200 | 370 | 120 | 180 | 580 | 450 | 290 | ||||
| 210 | 395 | 130 | 205 | 610 | 470 | 305 | ||||
| 225 | 420 | 140 | 220 | 650 | 500 | 325 | ||||
Note. The size is recommended to be equal to size.
The text of the document is verified according to: official publication M.: Standards Publishing House, 1994
docs.cntd.ru
Unscrew the cut nut
It is not always possible to choose the right tool. Especially when you need to turn in the dark, with insufficient lighting. Or the second case. The nut was pinched. As a result, the sharp edges of the edges were cut off and became “bald.” What is the way out of the situation?
Tool manufacturers have developed helical sockets that are designed to remove problem fasteners. Due to its “corkscrew” shape, the key catches and securely fixes the nut. This is how you can emerge from the most hopeless situation as a winner.
Advantages and disadvantages
A well-thought-out, high-quality tool is always used with pleasure by both professionals and amateurs. In this sense, the design of the gas key has a number of advantages:
- the ability to fix the pipe and clamp the thread without cutting special edges;
- ability to work in hard-to-reach places;
- simple design, maintainability;
- high-quality materials used in the manufacture of tools ensure reliability and long service life (naturally, if the tool is branded);
- Great physical force is not required to clamp the pipes, you just need to choose the right size;
- special teeth on the jaws cling to a smooth surface and make it easier to fix the part.
The main disadvantage is the possibility of crushing and even breaking the pipe. However, it should be mentioned that this only happens when the tool size is incorrectly selected and the adjusting nut is overtightened, as a result of which the compressive force exceeds the strength of the part (coupling or pipe).
Marking
Let's say we saw this code:
Nut M10-6N.5 (S18) GOST 5915-70.
Here M10 is the thread diameter in mm, 6H is the tolerance range, 5 is the strength class, S18 is the spanner size, that is, the external distance between parallel edges.
We told you how to select a nut for metric, inch and hex keys. They gave advice on unscrewing the cut fasteners and provided a table with weights.