There are often situations in life when you need to unscrew or tighten bolts and nuts. Most often, an ordinary wrench is used for this: from the simplest (with different horns on both sides) to more expensive models (allows you to choose the required size yourself). And if experienced specialists can determine the size of a nut by its appearance, then an ordinary person will most likely have to make do with brute force.
In this article we will tell you how to correctly determine the size of a nut or bolt, provide a table with standard sizes for convenience, and also share some tips.
How to Determine the Size of a Nut or Bolt
For reliable and high-quality fastening of 2 or more parts to each other, it is fundamentally important to select the correct dimensions of the fastening elements.
This question often causes difficulties, because even the sizes of wrenches are selected taking into account the sizes of the fasteners themselves. Therefore, we will consider all the nuances that are important to consider when choosing the necessary hardware. The main parameters by which bolts and nuts are selected are the diameter of the product, its thickness and length. But besides them, there is a number of important data, information about which is printed on the hardware. This:
The numbers next to the letter designation of the parameters are data indicated in millimeters. To find out the type, as well as correctly determine the size of, for example, a bolt, you must first find out what type of fastener is needed. Here it is permissible to use domestic GOST, European ISO quality standards or even DIN standards (Germany).
Bolt and nut sizes
All mechanisms in structural elements have certain types of bolted connections. Information on the connection is indicated by the manufacturer in the technical and also accompanying documentation. However, consumers may not always have access to such documentation, due to many factors. How then? In this case, you can quickly and accurately determine the dimensions of bolts and nuts:
Dealing with this issue most often does not arise, but if you have any doubts, then it would be right to seek help from a specialist who will help you deal with the fasteners.
TEST METHODS
4.1. Inspection and verification of the dimensions of bolts and nuts is carried out in accordance with GOST 1759-70, and washers - in accordance with GOST 6960-68.
4.2. The straightness of the bolt shaft is checked for inclusion in the control matrix with a hole, the diameter of which must correspond to the diameter of the through hole of the first row according to GOST 11284-65 with a hole length of 100 mm.
4.3. Tensile testing of bolts is carried out with nuts screwed onto them using a tensile testing machine. The rupture must occur in the rod, without tearing off the head, with a temporary tensile strength within the limits specified in the table. 5.
The tensile strength is calculated based on the cross-sectional area with a diameter equal to
where d 2 is the nominal average diameter of the thread, and where d 1 is the nominal internal diameter of the thread and
H
is the theoretical height of the profile.
Notes. 1. Bolts that are not long enough to be installed in the clamps of a tensile testing machine are allowed to be tested with a special technological nut screwed onto two bolts at once. The process nut thread is cut for each bolt to a length not exceeding the height of the nut according to this standard.
2. The calculated cross-sectional areas of bolts and loads corresponding to the standard values of tensile strength are given in Appendix 5.
4.4. The tensile test of bolts with an oblique washer is carried out in accordance with GOST 1759-70, the temporary resistance must be within the limits specified in the table. 5 of this standard.
4.5. The impact strength test of the bolt material is carried out in accordance with GOST 9454-60.
4.6. Test for relative elongation and relative contraction of bolt material. Performed according to GOST 1497-61 on “short” samples with a diameter of 10 mm.
4.7. Tests according to paragraphs 4.5 and 4.6 are carried out before the metal of this melt is put into production. For this purpose, the melt is divided into batches weighing no more than five tons. From each batch, two samples are tested for impact strength and two samples for relative elongation and relative contraction. In this case, sampling for testing is carried out in accordance with GOST 4543-61. The results of these sample tests apply to batches of bolts made from a given batch of steel using the same heat treatment regime.
4.8. The hardness test of bolts and nuts is carried out according to GOST 9012-59* washers - according to GOST 9012-59* or GOST 9013-59.
4.9. Nuts are tested for test load according to GOST 1759-70. The test load must correspond to the temporary resistance of the bolts 110 kgf/mm 2 and can be taken according to Appendix 5 of this standard.
4.10. For testing to determine the torque coefficient, at least five parts are selected from each accepted batch of bolts, nuts and washers. The parts should not have dirt, rust or excess factory lubricant on the surface. Before testing, the nut is driven along the entire length of the bolt thread.
4.11. Determination of twist coefficient K
can be carried out using any device (equipment) that allows you to simultaneously record the specified bolt tension N and the applied torque
M
with an accuracy of ± 5%, the testing device (equipment) must have a form with annual inspection marks by the bodies of the Chamber of Weights and Measures.
4.12. Twist factor K
determined by the formula
where M
— torque applied to the nut to tension the bolt by force N, in kgm:
N—bolt tension force in t;
d
— nominal bolt diameter in mm.
The tension force N is taken for bolts with a diameter of 18 mm - 13 t, with a diameter of 22 mm - 20 t, with a diameter of 24 mm - 24 t and with a diameter of 27 mm - 30 t.
4.13. If during testing the twist coefficient turns out to be more than 0.20 or less than 0.14, then repeated tests are carried out on a double number of sets of parts. If the results of the repeated test are unsatisfactory, the tested batches of parts are considered not accepted.
Note: A twist factor of 0.13 is allowed for one of the sets of parts being tested.
4.14. Lots of parts that do not meet the specified value of the twist coefficient can be reassembled and presented for acceptance a second time in accordance with the requirements of this OST.
4.15. In case of unsatisfactory results of checking the twist coefficient of newly assembled lots, these lots are rejected.
How to choose a wrench for the nut size
Most nuts used in bolting today have metric threads. Therefore, in order to determine the size of the nuts relative to the diameter, it becomes necessary to perform a slightly larger number of actions. If possible, it is recommended to check not the size of the nut, but, for example, a screw or bolt.
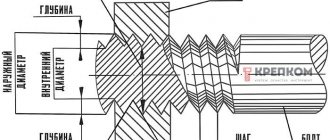
To determine the thread diameter of the hardware as accurately as possible, you will need to find out the correspondence of the internal diameter in relation to the outer diameter of the bolt that is used with a specific nut. The work is carried out using a special table.
It will not be difficult for a specialist to determine the size of the nut visually. But in any case, you need to measure the height of the nut, since this value can change, which affects the choice of bolt relative to the height. This is especially important if connection reliability is a priority.
When classifying nuts, you can use the method when choosing a size directly for the wrench. Accuracy is guaranteed, and tasks can be completed as quickly as possible.
You can determine the thread pitch of a nut using a method that is also used in the case of a bolt. To accurately determine the pitch, you will need to use a thread gauge; if such a device is not available, then you will need to count the number of turns at a specific interval
If you correctly select the bolt and nut relative to each other, then it will not be difficult to select the size of the keys that will provide sufficient tightening force for the bolts to securely fix the connection.
Source
Methods for determining key diameter
Universal tools are designed in such a way that there is no need to select the right wrench size. Their working units independently adjust to the diameter of the nut. But there are copies on sale, the range of settings of which is not suitable for working with the diameter of the existing fasteners. In this case, it is worth knowing how to determine and select the size. There are two effective methods.
Read also: Making a bright terry flower from leather
According to the thread diameter of the part
For a hex nut, a tool should be taken with a diameter that corresponds to the distance between the parallel edges of the nut itself. In order not to use a caliper or ruler in measurements, this value can be calculated from the diameter of the fastener thread. Such data is contained in the technical documentation, which is attached to the bolts and nuts by the manufacturer.
For standard thread diameters, two head sizes are given - reduced and normal. The first option is rare. The size chart for wrench tools is presented below:
- wrench 7 – bolt 4 mm;
- by 8 – 5 mm;
- turnkey bolt 10 has a thread diameter of 6 mm;
- 8 mm – tool No. 13;
- 10 mm – at 17;
- 12 mm – at 19;
- 14 mm - by 22.
And so on.
Determining the turnkey size by the diameter of the bolt head
The second method is no less informative, but you need to use additional tools. As already mentioned, the size of the wrench corresponds to the distance between the two parallel edges of the nut. If there is no information about this value, then you should take a millimeter ruler, or better yet a caliper, and measure this distance. When using a straight edge, remember that it must be applied exactly through the center point of the bolt head. It is not always possible to do this correctly, so the most reliable result will be given by a caliper. The turnkey bolt size will correspond to the tool number.
How to determine the nut size?
A nut is a type of fastener that is used for threaded connections. The key difference between a nut is the presence of a thread. It is used in conjunction with other parts to obtain a bolted connection. Hexagonal configurations are considered the most popular in construction and renovation work. They are designed to fit the shape of a wrench. There are also other options for nuts on sale - square hole, notched, round and others.
All nuts differ not only in wrench sizes, but also in strength. The easiest and most reliable way to find out technical information about a product is to check the nut markings. It may denote GOST or other international standards that are fundamental in the production of parts. The nuts differ in height: especially high, high and normal.
Marking
Let's say we saw this code:
Nut M10-6N.5 (S18) GOST 5915-70.
Here M10 is the thread diameter in mm, 6H is the tolerance range, 5 is the strength class, S18 is the spanner size, that is, the external distance between parallel edges.
We told you how to select a nut for metric, inch and hex keys. They gave advice on unscrewing the cut fasteners and provided a table with weights.
Source
How to measure a nut: advice from professionals
Since most nuts are designed to have metric threads, measuring them will require more time and manipulation. When measuring the size of a nut, experts advise taking into account the bolt or screw with which the nut will have a threaded connection. This option will help achieve maximum accuracy. This measurement will allow you to find out the internal diameter of the product.
When correctly determining the diameter of the nut, the permeability of the product is taken into account. That is, one part of the part should be in firm contact with the nut, but the second should not. To determine the nut standard according to the GOST table, it is important to determine the height of the nut. To measure the thread pitch, you need a thread gauge. With its help it will be possible to calculate the number of turns at the required interval.
The nut is cast.
A cast nut is a special nut that is used to fasten cast rims of automobile wheels. If the disk is not laid tightly, it will be subjected to cyclic impacts, and the nuts will unscrew. When tightening a cast nut, you need to pay attention to the final length of the nut in the hub. If the revolutions are less than 6 mm, then you need to change the studs or the discs themselves, for your own safety. Long nuts fit alloy wheels. Before installation, you need to check the threads and characteristics of the nut for compliance with the alloy wheel. Cast nuts come with a round clamping part and a cone-shaped clamping surface. There are budget models made of ordinary metal and more expensive ones made of steel.
Centering rings
Another wheel fastening element that can only be used for alloy wheels is the centering ring. Rings will be needed if the diameter of the central hole of the disk is larger than what the car manufacturer recommends. The rings form a tight connection between the wheel rim and the seat on the hub. They are also designed to center the wheel on the hub and evenly clamp it with fasteners.
Centering rings must be plastic, and you should buy them in stores. Metal homemade products turned on a lathe cannot be used, as they cause an imbalance and become tightly stuck.
Nut sizes.
The dimensions of the nuts are the distance between the parallel edges; the dimensions depend on the requirements for a particular type of detachable connection. Thread diameter and pitch are the main parameters of a nut . The thread diameter is designated by the letter d, the thread pitch by the letter P. The dimensions are regulated by GOST, and non-recommended sizes of nuts with a thread diameter of less than 2 mm are also provided. Can be long or short. The standard and most common nut is considered to be hexagonal, with a thread diameter from 1.6 to 48 mm. For fastening which requires a wrench.
When a consumer of this type of fastener needs to purchase nuts, then first of all it is necessary to get acquainted with the offers from reliable, well-known suppliers in the market.
Table of sizes and weights of hex nuts GOST 5927-70 from M1 to M10
1) Bolt, nut, washer according to actual dimensions
According to the option, a bolt with an M18 thread with a large thread pitch is specified (this is 2.5 mm for a diameter of 18 mm, the pitch is not indicated on the designation, only a fine pitch is indicated) bolt length 80 mm , version 2 according to GOST 7796-70 , we find this GOST in a search engine and open it.
GOST 7796-70 “Bolts with hexagonal reduced head, accuracy class B”
In it we will find all the necessary dimensions, and we will use them to draw the bolt in two projections.
Above the bolt we write the symbol Bolt 2 M18-6 g x 80.58 , which means bolt version 2 with metric thread M18 with a large pitch, length 80 mm, with a tolerance range of 6g and strength class 5.8 without coating.
The tolerance field, which establishes the size of the gaps between the threads on the rod (bolt, screw, stud) and in the hole (nut), is selected according to GOST 16093-81 . The following tolerance fields are established:
for threads on the rod - 4h, 6h, 6g, 6e, 6d, 8h, 8g;
for threads in a hole - 4Н5Н, 5Н6Н, 6Н, 6G and 7Н, 7G
From a tolerance field of 4h to a field of 8g for rods and from a tolerance field of 4H to 7G for holes, the gaps increase, i.e., the threads are manufactured with less and less accuracy. Students can limit themselves to this information without referring to the specified standard.
The strength class for bolts, screws, studs is selected from the series 3.6; 4.6; 4.8; 5.6; 5.8; 6.6; 6.8; 6.9; 8.8 according to GOST 1759-86,
and for nuts - from the row 4, 5, 6, 8 , etc.
When indicating the strength class in the designation of a threaded product, do not put dots between the numbers, i.e. write 36 instead of 3.6; 46 instead of 4.6 , etc.
It is advisable that the student understand the physical essence of these numbers by reading the specified standard, but the main thing to remember is that the larger the number, the stronger the material.
In educational drawings carried out in an engineering graphics course, it is allowed to conditionally assume that bolts, screws, studs are made of carbon steel of strength class 5.8 (58 is written in the designation), and nuts are made of the same steel of strength class 5 , that the threads are made with a field tolerance 6g (former accuracy class 2) for bolts, screws and studs and 6H for nuts and that they have not been subjected to protective (anti-corrosion) or decorative coatings.
GOST 15521-70 “Hex nuts with reduced turnkey size.” accuracy class B."
Open GOST and look at the required dimensions, draw out a nut with an M18 thread, version 2.
The nut of execution 2 differs from the nut of execution 1 in that it is chamfered not on both sides, but on one side.
Symbol for nut version 2 with thread diameter d=18 mm , with large thread pitch with tolerance range 6H , strength class 5 , without coating:
Nut 2 M18 -6N.5 GOST 15521-70
GOST 6402-70 “Spring washers. Technical conditions.”
We draw a washer - Washer 18.65G GOST 6402-70 ,
where 65G is spring manganese steel;
Nuts.
A nut is a fastening element that is made with a specific internal thread. A part that you cannot do without when assembling mechanical engineering components, when installing metal structures, during repair and service work. Enterprises that produce nuts of various sizes with inch threads, various quality and strength classes. The most common hexagon shape allows you to fix it with a wrench. The nut is used in any industry, there are several types, they differ from each other: thread size, shape and purpose. When using a nut, do not forget about the washer, which is placed under the head of the nut.
Thanks to the washer, the compression force on the surface around the fixed nut is distributed evenly.
Varieties of this part:
Each of them has its own abilities and areas of application. There are many more types of nuts not included in this list, which are also widespread.
Screw. How to determine size?
A nut is a fastener for a screw drive or threaded connection. They differ from other parts by having a threaded hole. Together with the bolt (screw), it forms a screw pair. The nuts that thread onto a stud or bolt make up a bolted joint. Most often, hexagonal nuts are produced in factories. They are specially made for a wrench. Also on sale you can also find nuts with wings, square shapes, round ones with a notch and other shapes. They are made from automatic steel. For this purpose, special automatic machines are used.
Scope of application and features
Nuts are used in many branches of modern production. First of all, we are talking about work related to the assembly of various structures, for example, in the automotive industry. And in order for the connection to be durable and reliable, during the production process the surface of this type of fastener is covered with a protective layer that has anti-corrosion properties.
There is another type of part used to fasten various objects, and also has a hole. This is a puck. The differences are as follows:
- there are threaded threads on the inner surface of the nut, while the washer is smooth;
- the nut is used as a direct fixation of the element to be fastened, while the washer plays the role of a gasket, and in some cases, insulation.
Even the round nut, or rather, its side surface, has notches that make tightening easy. And the puck is absolutely even.
How to measure a nut
Most nuts have metric threads. Measuring the thread diameter will require a little more steps than in other cases. If possible, it is recommended to check the size of the bolt or screw used for it rather than the nut itself. This way you can achieve a more accurate result.
The value obtained after measuring the internal thread is an indicator of the internal diameter din.
In order to accurately determine the diameter of the metric thread of the hardware, you will need to find out the correspondence between din and the outer diameter of the bolt used. This is done using a special table.
Accuracy is controlled through the use of certain pass-fail gauges. One part should connect well with the nut, the second part, on the contrary, should not.
The nuts differ in appearance, and it is easy to determine upon detailed inspection. To find out the standard of the fastener, you may need to measure the height of the hardware, since there are high, low, extra high and other options.
Turnkey dimensions are also used to classify hex nuts. This is explained by the fact that hardware also differs in its types.
To accurately measure the thread pitch, it is possible to use the method considered in the case of a bolt. You will need a thread gauge or you will have to count the number of turns at the required interval.
Determining the dimensions of inch nuts
To check the thread dimensions of an inch nut, you need to examine the threads of the bolt or other hardware used with it. If you don’t have a suitable one at hand, but have information about the presence of an inch thread, then use the appropriate thread gauge. Do not forget to divide the resulting value by 25.4 mm.
Determining washer dimensions
For washers, a short designation in the form D is used, which stands for the diameter of the metric thread of the hardware used for the fastener.
How to choose wheel nuts and bolts. Types of wheel fasteners.
When purchasing new rims, each owner is faced with the selection of the correct and reliable fasteners for their wheels. At first glance, the task seems quite difficult, but we will try to explain in an accessible and short way what you should pay attention to.
Types and differences of wheel fasteners
When selecting, you should pay attention to the following important parameters. The main differences are:
Pressing surface
The pressing surface of a bolt or nut serves to tightly press the disc to the hub or brake disc of the car, preventing the wheel disc from moving. Bolts and nuts have several types of such surface. The most common is a cone at an angle of 60° in front of the head; it may or may not have a 1.3mm headrest There are also nuts with a spout at the end. Less common are nuts with a 30° cone. Some people are accustomed to thinking that flare nuts are universal because... capable of pressing almost any disc. But due to an incorrectly selected pressing surface, the destruction of cast disks is possible. Or at best an imbalance .
There are also nuts with an enlarged cone, with press washers, eccentrics and others.
There are bolts with an eccentric tolerance of 2.4mm. Such bolts make it possible to install disks from other cars, for example, on Japanese ones from German ones and vice versa. But the parameters of the disks and hubs should not exceed 2.4mm. For example, 5x114.3 - 5x112, 5x110 - 5x108, 5x115 - 5x114.3, 4x98 - 4x100. A cone moving relative to the threaded well of the disk will allow the disks to be attached without distortion.
Head size
When choosing a nut. If the nut is a closed type, you should pay attention to the length of the head so that the pin does not rest against the head inside the nut. Which will lead to under-tightening of the wheel. It is also worth paying attention to what wrench your nut is used for. A size that is too large may leave no room for the socket head of a wrench or impact wrench. On some models of alloy wheels with narrow wells, it is possible to install nuts only with an internal key, such as a hex or sprocket. For open nuts, only the wrench size is important.
Pros and cons of closed and open nuts.
- — Rusting of threads and studs, ingress of reagents.
- + Low price.
When choosing bolts. As a rule, the head or head of the bolts has standard sizes for keys 17, 19 and 21. With the exception of “secrets”.
Thread sizes
Thread sizes for a nut imply the diameter of the threaded connection and the thread pitch . For bolts, the length of the threaded part is taken into account. It is important that a bolt that is too small will not be able to provide a reliable connection to the hub. And if it is too long, it can damage the parking brake elements when driving. An ideal bolted connection is considered when the protrusion of the bolt is no more than 1-2 turns.
You can see the exact information in the instructions for your car or consult with specialists.
How to determine thread sizes yourself
For nuts, the marking is formed MDxP .
For bolts and studs marking MDxPxL .
- M - metric thread icon;
- D —thread diameter in millimeters;
- P - thread pitch in millimeters;
- L - length in millimeters.
To determine the marking of the nut, you should measure the parameters of the stud. To measure you will need a caliper. For bolts and studs, dimension D is measured by the outer diameter of the thread.
The pitch P can be measured with a caliper or a simple ruler. Count a certain number of turns, measure the distances between these turns and divide by the number of turns. This way you can roughly determine the thread pitch. Then compare with the table of metric threads and the closest size and the correct pitch will be.
Length L is measured from the beginning of the bolt to the head or washer.
IMPORTANT! For imperial and metric thread sizes, the measurements are slightly different.
Measuring Thread Diameter (D)
Thread Pitch Measurements (P)
Bolt length measurements (L)
Material of manufacture
Nuts are made from steel, aluminum or titanium. Bolts are made of steel only. The material of manufacture does not play a big role; both of them are able to provide reliable clamping of the wheel. It is only worth noting the different service life for different use. Titanium ones are highly durable and reliable, but the downside is the high price. Aluminum is more affordable, sometimes silicon and magnesium are added to add strength. The best price-quality option is steel. But sometimes bolts and nuts are made from ordinary metal; such products are softer and rust quickly.
Coating
The nut can be coated with or without chrome plating. Chrome significantly prevents rusting of products, but steel nuts can also maintain their shine. In any case, when choosing, you should not be guided by aesthetic properties.
Tightening bolts and nuts on discs
To ensure reliable wheel clamping, the clamping surfaces of the disk wells and nuts can be lubricated with graphite lubricant to reduce the friction force. When using a torque wrench, the permissible tightening is 105 - 120 Nm. But it is better to use the recommendations for your car model.
Without torque wrench. After installing the wheel in a crosswise sequence (for 5 studs, one at a time), tighten the wheel until it stops. Then lower the car onto the wheel (remove the jack) and tighten the wheel in the same order, adding force on each lap, walk about 3 laps.
Secrets
To protect your expensive wheels, there are bolts and nuts with special keys, but often the owners themselves fall into their own trap when replacing seasonal tires or worn out pads. Always keep your safety head in the car so that in case of a tire puncture you can put on a spare tire. And under no circumstances lose it.
But you can also get into an awkward situation because of low-quality, cheap secrets. Which simply wear out quickly and do not provide enough grip. The nuts simply cannot be unscrewed. In this case, it is better to contact specialists in advance to remove the secretion. You should not try to unscrew such a nut yourself using a hammer and chisel. Most likely, you won’t achieve anything other than disk damage. A proven and working 100% effective method (for steel nuts) to carefully weld a nut with a head under a normal key.
Wheel nut.
A wheel nut is an indispensable part that is used to secure wheels. They may have different shapes, colors, sizes; in addition, nuts from different manufacturers may differ in threads and the composition of the metal from which they are made. They are manufactured according to the same standards and have their own analogues. Typically, nuts are made of metal, less commonly titanium and aluminum. As for color, most often chrome-plated or nickel-plated nuts are popular, both of which do not differ in corrosion resistance. When choosing wheel nuts, everything is individual, color, appearance, everyone chooses for themselves. Regarding the color of the nut , you need to pay attention to the fact that there is no blue on it - this indicates that the part is overheated. The wheel nut must be made of quality materials and properly hardened. A poor quality nut can add unnecessary problems.
Bolt sizing
If the bolts have metric threads on the shank, the supplied documentation uses the MDxPxL format. The designation is deciphered as follows:
All listed parameters are indicated in millimeters.
In order to find out the type and dimensions of a bolt, you will need to determine its type. It is recommended to follow domestic GOST standards or European ISO standards. The use of German DIN is also allowed. Once the type is known, the dimensions can be determined.
The diameter of the fastener is determined using various tools - a caliper, a template ruler, and a micrometer. In this case, the accuracy of measurements is controlled by gauges of the “PR-NOT” type. The name of the device stands for “pass-no-pass”. The first part does not require any effort when screwed onto the bolt; the second part cannot be screwed in at all.
A ruler or caliper is also used to measure the length indicator. If you need to find out the thread pitch, then a special pedometer tool is used for the fastener. If the necessary device is not available, it is possible to measure the distance between a pair of turns using a caliper.
The tool will only work and provide accurate readings if you are measuring a large thread diameter. More correct parameters are obtained by testing several turns instead of two. The result obtained must be divided by the number of turns used for measurement.
If the number obtained as a result of the check coincides with any value of the thread series, then this is a reference value and the required pitch is present. If the measurement did not bring the required result, then you probably have an inch type of thread. In this case, additional clarification will be required to accurately determine the step.
Bolts have certain varieties, which are determined by the geometric shape of the hardware. Therefore, the measurement methods for each group are different. There are 2 options:
To determine the length of projecting head fasteners, you do not need to use the head itself.
If you have a bolt with a countersunk head, you will need to measure the length taking into account its dimensions:
To determine the type of bolt and the corresponding standard, the head size is used. For example, “turnkey” for heads with six sides, if the bolt is equipped with a cylindrical head, then the diameter is used.
How to correctly determine the size of an inch bolt
If we look at various documentation for inch bolts, we will see an abbreviation for the design in the form D”-NQQQxL. It is deciphered as follows:
If you need to find out the thread diameter for an inch bolt, then you need to divide the obtained values by 25.4 mm. The resulting value corresponds to inch. The numbers are then matched to the appropriate ones in the UNC table.
Source
How to determine the turnkey size of a bolt and nut?
Any person, even not associated with mechanics, has to unscrew and tighten bolts and nuts in everyday life. To do this, we most often use a wrench, of which there are about fifteen varieties today. The classic and most common tool is the double-sided open-end wrench, which can be found in every man’s toolbox. The dimensions of its working profiles are marked on its handle, for example: 7x8 or 17x19, etc. These numbers indicate the distance from one sponge to another in millimeters.
Key size 24
In technical reference books for fasteners, the turnkey size is designated by the letter “S”. But we won’t see it on the fasteners themselves. Experienced mechanics can visually determine by the size of the fastener head “how much wrench” should be taken for an M10, M12 or M16 bolt? And inexperienced craftsmen can easily make a mistake in their choice. And when the connection is in a hard-to-reach place, you will have to select a tool by trial. If a small key simply does not fit, then a large one, if it does not fit tightly, can “lick” the edges of the part and then further unscrewing can be problematic.
Hex key markings
Sizes by numbers
- KR-19 . The marking means that the lower jaw can only be opened by 19 mm, this will be the maximum size of the bolt to be unscrewed. This key is small in size and very convenient to use.
- KR-30 . Medium size adjustable wrench. The adjustment range of the lower jaw is from 0 to 30 mm. It is the golden mean, copes with most household duties, and is often used in plumbing work.
- KR-46 . The working range of the tool is from 0 to 46 mm. A key with this number belongs to a special type and, most likely, you will not see it in a home craftsman’s kit. It is mainly used in production for servicing machines and mechanisms.
When working, you need to take into account that adjustable wrenches have an allowance of 2-3 mm, and the jaws of the adjustable wrench can grab another couple of millimeters. For example, with a KR-30 key, you can freely unscrew the thirty-second bolt.
Determining the key number by the diameter of the fastener thread
The “wrench” size of a hex bolt or nut is the distance between two parallel faces. You can quickly and accurately find out it, without resorting to a ruler or caliper, by the diameter of the threaded part, which is indicated in the technical information for the fastener. The fact is that each standard thread diameter corresponds to a certain size of the working profile of the fastener - main (normal), reduced and enlarged. Bolts with reduced and increased head sizes are much less common.
Unscrew the cut nut
It is not always possible to choose the right tool. Especially when you need to turn in the dark, with insufficient lighting. Or the second case. The nut was pinched. As a result, the sharp edges of the edges were cut off and became “bald.” What is the way out of the situation?
Tool manufacturers have developed helical sockets that are designed to remove problem fasteners. Due to its “corkscrew” shape, the key catches and securely fixes the nut. This is how you can emerge from the most hopeless situation as a winner.
Selection of inch wrenches
The size of an inch wrench is expressed in inches and does not indicate the width of the wrench, but the diameter of the thread of the inch fastener it is designed to work with. The hexagonal working profile of inch bolts and nuts differs in size from the metric standard profile by fractions of millimeters. Therefore, metric wrenches will either not fit tightly onto the edges of inch fasteners, or will not fit at all. To work with it you need inch keys and socket heads.
Table 2. UNC/UNF Threads and Wrench Nut Sizes.
| Thread diameter (key size), inch | Wrench nut size, inch | Wrench nut size, mm |
| 1/4 | 7/16 | 11.11 |
| 5/16 | 1/2 | 12.7 |
| 3/8 | 9/16 | 14.29 |
| 7/16 | 5/8 | 15.88 |
| 1/2 | 3/4 | 19.05 |
| 9/16 | 13/16 | 20.63 |
| 5/8 | 15/16 | 23.81 |
| 3/4 | 1 1/8 | 28.58 |
| 7/8 | 1 5/16 | 33.34 |
| 1 | 1 1/2 | 38.10 |
| 1 1/8 | 1 11/16 | 42.86 |
| 1 1/4 | 1 7/8 | 47.63 |
| 1 3/8 | 2 1/16 | 52.39 |
| 1 1/2 | 2 1/4 | 53.15 |
| 1 3/4 | 2 5/8 | 66.68 |
| 2 | 3 | 76.20 |
| 2 1/4 | 3 3/8 | 85.73 |
| 2 1/2 | 3 3/4 | 95.25 |
| 2 3/4 | 4 1/8 | 104.76 |
| 3 | 4 1/2 | 114.30 |
Allen keys
Such bolts are often used in instrumentation and mechanical engineering. They have a cylindrical head, and to screw them in or remove them you will need another special key - an angled hexagon.
The size of the hex tool is determined by a similar method, only the distance is measured between the opposite sides of the internal hexagon. Such fasteners are produced according to state standards, which regulate the compliance of the thread diameter with a specific turnkey size. For easy selection, you can also use the table.
| Thread, M | M4 | M5 | M6 | M8 | M10 | M12 | M14 | M16 | M18 | M20 | M22 | M24 | M27 | M30 | M33 | M36 |
| Key size, mm | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 17 | 17 | 19 | 19 | 22 | 24 | 27 |
Using such tables is convenient especially for inexperienced craftsmen who cannot yet determine by eye the size of a key for an internal hexagon. By selecting a tool with the right parameters, you can maintain the integrity of the nut or bolt head without “licking” its edges with the wrong tool.