Each bolt manufactured according to established standards is marked:
- Brand mark of the manufacturer.
- Product strength class.
- Left-hand thread sign (if necessary).
The strength class consists of two numbers separated by a dot:
- 1 - temporary resistance, measured in N/mm2.
- 2 is the ratio of the ultimate yield relative to its tensile strength, measured as a percentage. The yield strength is the ultimate load; after it is exceeded, irreversible deformation of the part will occur.
For example, marking 9.8 means:
- 9Х100=900 N/mm2 - temporary resistance.
- 9Х8х10=720 N/mm2 - yield strength.
All bolts with a strength of at least 800 N/mm2, according to the international classification, are usually classified as a high-strength group. This means that all products marked 8.8 and higher belong to the high-strength group.
Bolt strength classes and markings - table
The strength class of a bolt is a technical and operational characteristic that reflects the maximum load on a metal product when fastening parts, shows resistance to deformation, impact and rupture.
Strength classes reflect the maximum load when fastening parts.
According to GOST 1759.4-87 (ISO 898.1-78), hardware is divided into 11 groups: 3.6; 4.6; 4.8; 5.6; 5.8; 6.6; 6.8; 8.8; 9.8; 10.9; 12.9.
The higher the value, the greater the force the fastener can withstand, the stronger and more durable it is.
Categories from 3.6 to 6.8 include bolts intended for use in lightweight structures, 8.8-12.9 are highly reliable.
The mechanical properties of fasteners depending on the strength indicator are presented in the table below:
| Strength class | Nominal tensile strength, N/mm² | Vickers hardness (min/max), HV | Yield strength (min/max), MPa |
| 3.6 | 300 | 95/250 | 180/190 |
| 4.6 | 400 | 120/250 | 240 |
| 4.8 | 400 | 130/250 | 320/340 |
| 5.6 | 500 | 155/250 | 300 |
| 5.8 | 500 | 160/250 | 400/420 |
| 6.6 | 600 | 190/250 | 360/480 |
| 6.8 | 600 | 190/250 | 640 |
| 8.8 | 800 | 250/335 | 640/660 |
| 9.8 | 900 | 290/360 | 720 |
| 10.9 | 1000 | 320/380 | 900/940 |
| 12.9 | 1200 | 385/435 | 1080/1100 |
What is put on the bolt head?
There is a marking on a standard bolt made according to GOST 7798-70.
It includes:
- Strength class. Determines the degree of load and scope of application.
- Manufacturer's mark. Allows you to identify a company engaged in the production of hardware.
- Arrow. Indicates left-handed threads.
Standard location of markings on bolts
Designations are applied to the top of the head. They are convex and recessed. The geometry is determined by the manufacturer.
On bolts and screws with a diameter of more than 6 mm, marking is required. Smaller fasteners do not have a number.
A standard bolt is marked with a strength class.
On parts of small size or non-standard shape, symbols from the dial system are used.
Interpretation of signs on stainless metal bolts:
- Designation of austenitic steel grade:
- A2 – resistance to water;
- A4 – resistance to salts, alkalis, acids.
- The strength limit is 50, 60, 80, which corresponds to 500, 600, 800 MPa and classes 5.6(8), 6.6(8), 8.8.
Possibly a factory mark.
Products made from a martensitic alloy are marked similarly to carbon alloys, with the numbers at the bottom underlined. The standard allows not to put a period in the designation.
In BVP, signs are indicated in accordance with GOST 52644-2006.
As an example: D 11.14 8.8 S HL, where:
- D – manufacturer identifier;
- 11.14 – heat number;
- 8.8 – strength limit;
- S – bolt with a 6-sided enlarged head;
- “HL” – climatic version (cold region).
Products made of martensitic alloy have a factory mark.
Symbols are applied to studs if the thread diameter exceeds 12 mm.
Requirements according to GOST
Hardware must comply with the dimensions, mechanical properties, accuracy class, quality standards prescribed in GOST standards, and be free from major defects and traces of corrosion.
On drawings and specifications, engineers mark bolts strictly according to the standard.
What is yield strength and how to determine it
The yield strength σт is the critical load on a detachable connection, at which an irreversible process of destruction of the structure occurs without increasing the acting force.
The parameter is affected by temperature. As it increases, σt decreases.
There are 2 formulas to calculate the indicator:
- For temporary tensile strength: the 1st digit in the designation of the strength class is multiplied by 100, then multiplied by the 2nd digit, the result is divided by 10. So, for hardware of group 5.8 σt=400 MPa (5x100x8:10=400).
- By strength class: the 1st and 2nd digits are multiplied by each other, then by 10. For category 5.8: σt=400 MPa (5x8x10=400).
The yield strength is the critical load on a detachable joint.
The higher the yield strength, the longer the part is able to remain in a state of tension and resist dynamic and stationary forces. When selecting fasteners, a 2- or 3-fold safety factor is taken into account.
Strength class and steel grade
The quality of products is affected by the carbon content in the alloy. With a decrease in the amount of substance, the reliability, hardness and strength of the part increase.
Bolts are produced:
- low strength - from St. 10, 20;
- medium - from steel up to 0.4% carbon (U4);
- high - from structural low-, medium-carbon and alloy steels with strengthening additives.
The necessary properties are achieved as a result of heat treatment (hardening) in electric furnaces. The hardened alloy has high performance characteristics.
The most common grades for the manufacture of BVP are St30KhGSA; St35; St35X; St35HGSA; St38ХА; St40X; St40X "Select"; St20G2R.
High-strength fastener material
To ensure fasteners have high strength, only certain grades of steel are used in their production. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
High strength bolts
When choosing raw materials for the manufacture of such fasteners, manufacturers take into account, first of all, consumer requirements for the strength characteristics of the final product.
Strength class 12.9. In this case, the following grades of steel are usually used:
- chromium-nickel-molybdenum high-quality alloyed structural steel St.40ХНМА;
- chromium-silicon-manganese alloy structural St. 35HGCA;
- medium-alloyed structural high-quality St. 30XGSA.
Strength class 10.9. The following steels are suitable:
- Art.35ХGCA and Art.30ХGCA;
- alloyed structural St.40X and St.40X Select;
- cold-worked carbon structural steel St.40M2;
- high-quality carbon structural St.45G and St.45;
- high-quality alloy structural St. 38XA;
- low-alloy structural St.35X.
Strength class 9.8. The following steels are used in this case:
- boron manganese alloyed St.20G2R;
- Art.35ХGCA and Art.30ХGCA;
- Art.40X and Art.38XA;
- Art.45 and Art.35X;
- structural high-quality carbon St.35.
Strength class 8.8. The following steel grades are used: St.20G2P, St.40X, St.38XA, St.35X, St.35 St.45.
High strength nuts
For the manufacture of high-strength nuts, steel of almost all of the above grades is used.
- Strength class 12. Suitable steels are St.40ХНМА and St.30ХГСА.
- Strength class 10. Alloys of grades St.40ХНМА, St.30ХГСА, St.40X, St.45, St.38XА and St.35X are used.
- Strength class 9. The following grades of steel are used: St.40X, St.45, St.38XA and St.35X.
- Strength class 8. The production of nuts with strength characteristics corresponding to the standards of this class is carried out on the basis of steels St.40X, St.20G2P, St.45 and St.35.
Strength of highly specialized bolts
Separate standards and requirements are provided for BVP for narrow industry purposes. Fasteners are made enlarged.
The characteristic that determines the strength of a metal is the stress corresponding to the maximum force and preceding rupture.
The group of specialized BVPs includes bridge bolts, shoe bolts, anchor bolts, railway bolts, etc.
Some of them are designed for use in difficult and extreme conditions and are marked:
- “HL” – for harsh climates with temperatures down to -60°C;
- “U” – for areas with an average cold (moderate) regime down to -40°C.
Mechanical properties are specified in GOST 22353-77, R 52644-2006, 24379.1-80.
Screw classification
Let us now consider the screws available in the TsKI assortment. The largest group of them are general purpose screws. We meet them every day in everyday life and at work. They all have a fully threaded shaft (although there are exceptions) and different shaped heads. The heads have slots or recesses for different types of keys.
Another large group of screws are set screws. The name comes from their purpose. For the most part, they are designed for precise installation and fixation of parts in mechanisms. To do this, they have various protrusions or recesses at their ends.
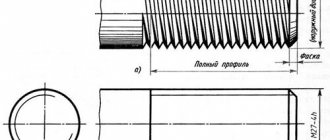
According to GOST 12414-94 (ISO 4753:1999): “Ends of bolts, screws and studs. Dimensions" the following setscrew ends are provided:
The torque is driven by the following elements:
The summary table shows the actual, most common combinations of setscrew heads and ends, indicating the DIN standard.
Types of bolt fastening
Threaded connections are structurally different from each other.
Bolted
A bolt is a part equipped with a head and threads at different ends. The thread is necessary to screw on the nut. The head is picked up from the outside with a wrench.
To install hardware, holes of larger diameter are drilled on the surfaces to be joined. The end side is chamfered.
The bolted fastening is easy to replace if broken.
The disadvantage of the connection is that it requires a lot of space, which leads to an increase in the size and weight of the structure.
Advantage: easy replacement if broken.
Screw
The screw is screwed into the housing using a special end tool. The head comes in different shapes, including 6-sided. The main difference is the small installation area.
Negative point: during installation, the thread is often damaged, and it is difficult to remove part of the fastener. Therefore, screw connections are not used for repeated installation/disassembly.
Using studs
A stud is a cylindrical fastener without a head, the ends of which have threads of the same diameter. There is a tight cut on one side. The other end is needed to install the nut.
Fastening with studs is required for frequent assembly of the structure.
The element is in demand for frequent assembly/disassembly of the structure and installation in hard-to-reach places. The stud may bend and lose strength. The thread often breaks due to heavy loads.
Production of high-strength fasteners
The technological process for manufacturing fasteners characterized by high strength includes the following steps:
- Preparing a metal alloy for upsetting.
- Stage of planting products. This operation can be performed using two methods - both hot and cold heading. The purpose of this is to reduce the length of the workpiece while simultaneously increasing its thickness.
- Thread rolling.
- Heat treatment. This is a mandatory step for high-strength fasteners. The main types of heat treatment are: surface or volumetric hardening, annealing (sometimes of the first and second kind), tempering. The type of heat treatment is selected by the manufacturer.
- Anti-corrosion protection. You should be aware that inorganic coatings made by chromating and phosphating are not suitable for high-strength fasteners.
- Acceptance of finished products.
- Package.
Connecting bolts using threads
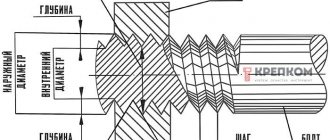
Thread classification:
- metric;
- inch;
- cylindrical pipe;
- conical;
- rectangular;
- trapezoidal;
- persistent;
- standardized round.
Metric thread is the main type of threaded connection. Its parameters are the nominal diameter and thread pitch in millimeters, established by GOST 8724-81.
Connecting bolts using threads is reliable and technologically advanced.
Advantages:
- reliability;
- multifunctionality;
- manufacturability;
- the ability to adjust the compression force;
- availability of a wide range of products.
Disadvantage: tendency to self-unscrew.