To transport electrical energy over a considerable distance and reduce technical losses, high-voltage power transformers (PTs) are used. They work on the principle of transformation, converting the electrical energy of 1 parameter into another dimension through electromagnetic induction. For this purpose, the electrical energy received from the brush device of the generators through the buses is supplied to transformers for upgrading and further transmission.
Power transformer 500 MVA
Design
Power transformers are made oil-dry. A high-voltage apparatus is complex engineering equipment.
The device includes:
- Installation stand.
- Rectangular oil tank.
- Thermosyphon filter.
- Magnetic cores.
- Low potential windings (2-layer cylindrical).
- High amplitude windings.
- Input bushings of 2 amplitude classes.
- Expansion tank.
- Gas relay.
- On-load tap-changer.
- Motor drive.
- Radiators with fans, coolers.
- Switching device drive.
- Shut-off valves for oil, water, gas.
Depending on the number of phases, transformers are produced: single-phase, three-phase.
Scheme
The power transformer circuit includes several basic elements. These include:
- Core (magnetic drive).
- Frame with beams (lower and upper).
- Low-voltage and high-voltage windings.
- Bends.
- Regulating branches.
- Bottom of inputs.
All components are fixed to the base with beams. A magnetic drive is necessary to reduce losses when the magnetic flux passes through the circuits. It is made of electrical steel.
In the magnetic drive core, sheets of metal are assembled according to a certain pattern. The rods with windings should be close in shape to a circle. This configuration makes it easier to wind the conductors. The joints between the individual core plates are covered with solid sheets.
The winding is made of round or rectangular wires. Gaps are left between the layers and the windings themselves for the circulation of the cooling component.
Principle of operation
The work of the ST is carried out according to the laws of electrical engineering. CT is no different from an ordinary transformer. The current passing in the primary winding changes in the time range by harmonics. It creates a powerful flow of magnetic fields in magnetic circuits. Induction penetrates the turns of the secondary winding, creating an electromotive force.
Transformer operating principle
The loads are removed from the bushings of the secondary winding on the roof of the transformer. The current parameters of the secondary winding are kept no higher than the calculated value. In this state, power plants operate for months, for a long time. 1 amplitude potential of low potential (6 - 10 kV) electricity is converted into a high amplitude class (35, 110, 220, 500, 1100 kV).
In operating mode, the ST is connected by switchgear buses and a power transmission line to the load of energy consumers. Without power take-off, the frequency of the electric current increases. STs working in a group are unloaded, close to idling operating modes. When power is taken from consumers, the frequency of the electric current decreases, the transformer is loaded at 100–140% power. When the frequency stabilizes at 50 + (0.5-1%), the power plants are transferred to a stable nominal operating mode. During the testing period, it is switched on briefly for short circuit modes. 99.99% of the electrical characteristics of the unit are checked, and its operating modes are adjusted.
Also read: Instrument current transformer
Short circuit mode
Transformers can be step-up and step-down, to determine this you need to find out the transformation ratio , with its help you can find out which transformer. If the coefficient is less than 1, then the transformer is step-up (this can also be determined by the values; if there is more in the secondary winding than in the primary, then it is step-up), and vice versa, if K>1, then it is step-down (if there are fewer turns in the primary winding than in the secondary).
Formula for calculating the transformation ratio
Where:
- U1 and U2 – HV and LV voltage,
- N1 and N2 – number of turns in the primary and secondary windings,
- I1 and I2 – current in the primary and secondary windings.
Heat removal system
During the conversion of electricity, part of the losses is released in the form of heat, so a heat removal system is invariably present in any PT. Powerful devices are equipped for this purpose with a special dual-circuit system, in which the oil is cooled in the following ways:
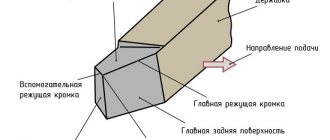
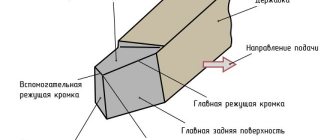
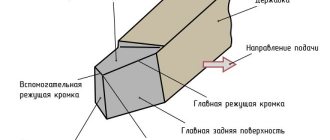
- By means of radiators (see E in Fig. 4), which provide heat removal to the secondary or external environment.
- Tank housing with a corrugated surface (used in low-power devices).
- Installation of ventilation equipment. This solution allows you to increase productivity by a quarter.
Fans of the forced cooling system ST - Additional water cooling systems. This is one of the simplest and most effective ways to remove heat.
- The use of special pumps that circulate oil in the heat removal system.
Operating voltage control devices
In some cases, it becomes necessary to increase or decrease the CT load voltage; for this purpose, most designs provide a special switch. Essentially, it changes the transformation ratio by switching to more or less turns in the coils.
As a rule, such manipulations are performed when the load is removed, but there are devices that allow you to change the CT without disconnecting consumers.
Types of additional equipment
To ensure stable operation and maintenance of CTs, their design may include the following devices, called attachments or additional equipment:
- The gas pressure switch is a protective system. If the CT goes into abnormal operation mode, then as a result of large heat release, oil decomposition occurs. This process is accompanied by the release of gas. When it forms quickly, a protection is triggered, disconnecting the device from power and load. If the gas formation process is slow, an alert is activated.
- Thermal indicators show the heating of the oil in various components of the heat removal system.
Oil temperature indicator - Desiccants. They are used in non-sealed oil heat removal systems and prevent the formation of water condensation.
- Oil regeneration systems.
- Pressure sensors, if it exceeds a certain threshold, the reset device is automatically turned on to normalize.
- Oil fill level sensor in the heat removal system.
Main purpose
Industrial ST is produced at large electrical plants in the country. The industry produces installations with a capacity of over 1 million kVA. The amplitude of industrial voltage classes reaches 1.15 - 1.5 megavolts. ST from TPP generators removes current with an amplitude of up to 24 kV from brush devices. A further increase in amplitude occurs in ST up to classes: 110 – 1150 kV. Throughout Russia, power lines operate with an amplitude of 10 – 1050 kV. The current is supplied to consumers via overhead lines by step-down devices with an amplitude of: 0.4 -10 kV for industrial purposes, 220 - 380 V in the housing and communal services sector, to the population of apartment buildings, private sectors.
Electricity transmission scheme
In substation networks, multiple cycles of electricity transformation occur. It is changed regularly with powerful ST. Their potential, amplitude is 30 times higher, taken from the brush apparatus of generators of thermal power plants, hydroelectric power stations, nuclear power plants, and wind farms. Industrial CT maintains a constant current frequency of 50 (+/- 1%) Hz. The deviation limit according to the PUE is kept at 1% due to the failure of all consumer installations. CT for industrial use is made in 3-phase version. For a 1-phase network, 1-phase devices are produced.
Classification
TMF transformers can be classified according to the following parameters:
- number of windings – two or more;
- climatic version - external and internal installation;
- transformer power – from 250 kV×A and above;
- rated voltage class of the primary winding of HV – from 6 to 10 kV;
- purpose – installed at step-down or step-up substations;
- Possibility of adjusting the output voltage - adjustable and unregulated.
Explanation of markings
Explanation of the markings, to enlarge the diagram, click on it
To enlarge the table, click on it
According to the number and connection diagram of the winding
STs consist of 2 or several windings. They are inductively coupled inside the apparatus. The power windings transmitting electrical power to consumers are called secondary windings. A multiphase type power plant is connected by windings into a star with many rays. 3-phase transformers are connected using a 3-beam star-delta circuit.
How to choose
Indicators characteristic of ST for the construction and installation of thermal power plants, hydroelectric power plants, nuclear power plants, diesel power plants are: power, reliability of electrical supply. For certain categories of electricity consumers, an important factor is the reliability of power supply. When selecting devices, attention is paid to power line protection. High degree of financial efficiency of ST – design of an optimal network of distribution devices: outdoor switchgear, indoor switchgear, ASU for electricity transmission.
The costs of purchasing and servicing transformers include electricity conversion devices. The company is developing for the future and reconstructing production. The requirements for the technical equipment of electrical networks and the characteristics of power transformers are changing.
Ensuring uninterrupted power supply to the enterprise is done by installing a second power supply. The first one is constantly at work. The 2nd is considered reserve. Periodically, 1 out of 2 devices is taken out for major, medium, current repairs, adjustments, and testing of networks and equipment. The enterprise installs 2 units with the condition that each unit operates with a power load factor of 0.7 of the nominal parameter. If 1 working device out of 2 fails, one device is constantly switched to standby mode. During operation, the following arise: malfunctions, problems with protection, disruptions in the operation of switchgear equipment and substation. 2, the operating unit becomes subject to a power overload of 1.4 times, i.e. the second transformer can only be overloaded by 40%.
Transformer protection
The standard type of protection according to the PUE is installed:
- Zero sequence current protection against external ground faults, clause 3.2.63.
- Protection against currents caused by external short circuits, clause 3.2.64.
- Operational acceleration of protection against currents caused by external short circuits with a time delay of 0.5 seconds, clause 3.2.65 (AT substations, ST block generator).
- Gas protection of the additional transformer clause 3.2.71.
- Protection of the on-load tap-changer contact device with a pressure relay, a separate gas relay, clause 3.2.71.
- Differential current protection of low voltage side circuits (AT) clauses 3.2.70 – 3.2.71.
- Differential phase overload protection.
- From internal damage: level + oil pressure, winding temperature, steel core, presence of gases.
CT protection panel:
terms of Use
CT requires a high degree of reliability with high voltage and power values. This affects the quality of operation and prevention. Routine work is carried out for proper, complete maintenance, repair, testing, and adjustment. Transformers and equipment are located in the place where personnel are constantly on duty. Daily inspection schedules, control and measurement devices check the operating condition of the electrical network and transformers.
Monitor the readings of instrument sensors, measure:
- Temperature.
- Pressure.
- Oil level.
- Degree of desiccant depletion.
- Condition of oil regenerators.
Also read: Measuring current transformer - TSP
Checks for oil leaks in the transformer cage, outdoor switchgear, closed switchgear, mechanical damage in the housing, flange joints (oil, coolant), radiators, fans, pipe sections. The number of operating fans and the oil level in the gas analyzer are monitored at a certain transformer load. For each mode, its own number of operating equipment, parameters of the cooling medium, gas, water, oil are given. In devices with permanent staff duty, inspections are done less frequently: once every 30 days. At least once every ½ year, an inspection of outdoor switchgear, indoor switchgear, indoor switchgear, and transformer points is carried out.
According to the maintenance schedule, during maintenance, oil is added and unsuitable transformer oil is replaced with a new composition. The quality of the oil is determined by chemical laboratory analysis. The PUE, instructions for transformers and equipment provide criteria for oil requirements, visual inspection, and color. In emergency situations or sudden changes in outside air temperature, unscheduled inspections are carried out.
Protection is subject to verification. Once every 365 days for major repairs, the oil is taken for laboratory analysis. The frequency of maintenance of voltage regulation devices of power transformers is associated with checking the contacts of copper and brass for oxidability. They perform preventive maintenance, cleaning, lubrication, reassembly, and tightening with a torque wrench to reduce the transition resistance in the contact assembly.
In order to change the oxide film, 2 times every 365 days the transformers are disconnected from the electricity, their load is removed to 0, the switches are placed in various adjustable positions several times. Methods of changing positions are done during the transitional autumn-winter period until the maximum load is gained.
Requirements for switchgears: outdoor switchgear, indoor switchgear, indoor switchgear
The power line is connected from the input of a remote substation. Switchgears: outdoor switchgear, indoor switchgear, indoor switchgear are designed for the length of the line section. ST, VL in switchgear protect against overvoltage and short circuit currents. Voltage reduction systems are installed between the electricity generation switchgear and the consumer. Powerful installations are installed at 2 nodes: switchgear and electrical substation. They are engaged in the transformation of high-power electricity.
Industrial installations include powerful installations:
- Power transformers.
- Autotransformers.
Transporting electrical energy over long distances requires reducing losses in switchgear, equipment, and the main network. The electricity transformation method is used. Electric current is supplied from the generators to the station. The voltage increases to the amplitude of the power line.
You can also read the information in the book, from pages 55 to 76: Open the book for reading
Operating principle
The operation of a device that converts current is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. An alternating current is supplied to the winding, creating an alternating magnetic field. The latter contributes to the further formation of electric current.
Oil, which has high dielectric properties, is poured into a tank equipped with valves and a screw-in cap. A shut-off valve located at the bottom allows oil samples to be taken for analysis. To increase the surface of the tank, metal plates can be used to speed up the heat exchange procedure between the oil and the outer air layer.
Once in the tank, the oil begins to move in the inner and outer circles. The function of the first circle is performed by two collectors forming a radiator.
The radiator temperature can be reduced naturally or using a specially designed ventilation system. Such a system, on the one hand, effectively cools the equipment, and on the other, reduces its load indicators by an average of 25%.