A grinding machine is a device used to process workpieces made of various materials with an abrasive tool and can provide surface roughness from 0.02 to 1.25 microns. Grinding machines, which can have different designs, allow you to effectively solve problems associated with processing the surfaces of parts made of different materials.
One of the many types of grinding machines
Application of grinding machines
Using a grinding machine, you can carry out a number of technological operations:
- grinding of internal and external surfaces of parts having different shapes and purposes;
- sharpening of tools for various purposes;
- peeling, grinding, as well as cutting of metal castings and products with complex profiles;
- processing of gear parts and threaded parts;
- formation of keyed and spiral-type grooves on steel bars.
A grinding machine is practically indispensable when working with parts made of ceramic and magnetic materials that are difficult to process and highly fragile. In addition, grinding machines are capable of performing technological operations of grinding and roughening at high speed modes, which makes such equipment efficient and productive. On these machines, it is possible to remove a large amount of metal from the surface of the workpiece in a short period of time during processing.
The video below shows the operation of a CNC cylindrical grinding machine:
All grinding machines operate on the same principle: metal processing is carried out by simultaneous rotation of the abrasive wheel and movement or rotation of the workpiece. The working surface is the periphery or end of the abrasive wheel, and the workpiece moves relative to it along a straight or arc path. Any grinding machine contains in its design several kinematic chains that provide:
- movement of the work table in the longitudinal and transverse directions, which is possible thanks to a hydraulic drive;
- rotation of the working tool - the grinding wheel, carried out due to the individual drive of the working tool;
- feeding the workpiece or tool in the transverse direction due to a hydraulic or electromechanical drive;
- wheel dressing, which can be done manually using an electromechanical or hydraulic system;
- rotation of the workpiece or work table;
- supply of the working tool to depth, which can be performed using a hydraulic or mechanical drive.
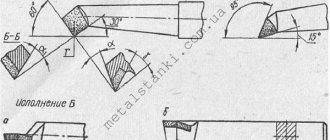
1.16.2. Features of the design and design of machines for high-speed and rough grinding
With the development of new designs of machines for abrasive processing, new abrasive materials and tools, new coolant fluids and methods for their supply, conditions appear for the widespread introduction into industry of various types of high-performance grinding - high-speed and grinding, a variety of which are high-speed grinding (HSG) and creep-feed grinding.
When designing machines operating using high-speed grinding technology (HSG), the use of:
- grinding wheels of standard types (made of corundum or silicon carbide on a ceramic or polymer bond); the peripheral speeds of the circle are 60 - 120 m/s;
- CBN grinding wheels on a super-hard bond; peripheral speeds are up to 150 m/s;
- steel circles coated with CBN on a galvanic bond; peripheral speeds are up to 250 m/s.
The effectiveness of high-speed and, especially, rough grinding (processes with very high thermal stress) largely depends on the removal of heat from the processing zone.
High cutting speeds, reaching 250 m/s, cause high dynamic loads on the elastic system of the machine. Therefore, the procedure for preparing and using abrasive tools is strictly regulated. Before installation on the machine, grinding wheels are tested for tensile strength. Large diameter circles are statically balanced.
Grinding machines are equipped with devices for dynamic balancing of wheels and ongoing monitoring of their vibration characteristics.
As grinding wheels wear out during operation, their peripheral speed and strength decrease. Therefore, wear of the circles is allowed no more than 20% of the diameter.
To maintain a constant cutting speed, machines are equipped with special static electricity converters with frequency control of current.
Due to the high probability of the wheels breaking during operation, the machines provide reliable protection of the processing area and blocking of the opening of the protective casing.
To ensure high processing accuracy, machines are equipped with active size control devices and adaptive control systems (in most cases, based on the power of the main drive).
When working with increased grinding conditions, for better removal of cuttings, it is necessary to supply an increased amount of coolant to the cutting zone under a pressure of 0.5 - 1 MPa.
The design of the machines should be cabinet type with a completely isolated cutting zone capable of accepting a large amount of coolant.
On high-speed and power machines, double cleaning of the coolant is used: preliminary with the help of hydrocyclones and final with conveyors with paper belts. To obtain high processing accuracy, the degree of coolant purification should be no more than 5 microns. On machines with a closed area, refrigeration units with freon or air coolers are used to remove heat.
Compared to traditional grinding machines, VSS machines have a number of features. Thus, they have increased wheel rotation drive power, providing high metal removal rates; the cutting speed (feed to depth) has been increased to obtain higher metal removal rates; the rotational speed (or longitudinal movement for surface grinding machines) of the part is increased to ensure an optimal ratio of the wheel speed to the speed of the part (table) v/v = 60.
Classification of grinding equipment
Depending on the application, grinding machines are divided into a number of types.
Cylindrical grinders
This equipment is designed for grinding cylindrical (Ø 25–600 mm) and conical workpieces. Such machines have in their design a spindle that rotates in a horizontal plane, which can move on a special slide. The part to be machined may be clamped in the chuck or between the centers of the tailstock and headstock.
Cylindrical grinding machine
Universal cylindrical grinding
machines Such machines are used for grinding the outer and end surfaces of cylindrical workpieces (Ø 25–300 mm), as well as conical parts. To perform processing, workpieces can be fixed in centers or in a chuck.
Universal cylindrical grinding machine
Plunge cylindrical grinding
Grinding machines of this type are used for processing cylindrical (Ø 150–400 mm), conical and profile workpieces, which are fixed in the centers of the equipment. Processing is carried out due to the transverse movement (cutting) of the abrasive wheel.
Plunge cylindrical grinding machine
Centerless cylindrical grinding
Processing on such equipment can be performed according to two schemes: by pass (cylindrical surfaces (Ø 25–300 mm)) and by plunge method (cylindrical, conical and profile surfaces). A distinctive feature of grinding machines of this type is that their design does not provide centers for fixing workpieces.
Centerless cylindrical grinding machine
Roll grinding
This includes machines for grinding rolling rolls of cylindrical, conical and profile configurations. Fixation of workpieces on machines of this type is carried out using equipment centers.
Roll grinding machine
For grinding crankshaft journals
On such machines, working using the plunge method, simultaneous or sequential grinding of the crankpins of crankshafts is performed.
Machine for grinding crankshaft journals
Internal
These devices allow you to process cylindrical and conical holes in a wide range of sizes (with a diameter of 1–10 cm on a benchtop grinding machine and up to 100 cm on a production one).
Internal grinding machine
Surface grinding
Processing on such equipment is performed with the end or periphery of the abrasive wheel. Grinding machines of this type can be equipped with additional devices, which makes it possible to process metal workpieces of complex configurations. Depending on the location of the spindle, surface grinding machines can be horizontal or vertical. The design of such devices may also include one or two columns.
Surface grinding machine
Double-sided surface grinding
This equipment can simultaneously process two flat surfaces, which significantly increases its productivity. Such grinding machines, in which the workpieces are fixed on a special feeding device, can be of a vertical or horizontal type.
Double-sided surface grinder
For grinding guides
The maximum length of guides that can be processed using these grinding machines is 1000-5000 mm. Guides of these types are equipped with beds, work tables, slides and other equipment components for various purposes.
Universal sharpening
Such grinding machines are used for sharpening various tools with a maximum diameter of 100–300 mm (taps, reamers, countersinks, cutters, etc.). The technical capabilities of equipment of this type make it possible to equip it with additional devices for processing cylindrical workpieces, as well as for internal and end grinding.
Universal sharpening machine
Roughing and grinding
This grinding equipment is used for roughening and cleaning the surface of workpieces by grinding. These machines use abrasive wheels with a diameter of 100–800 mm.
Roughing and grinding machine
Flat-lapping
This grinding equipment is used to perform grinding of workpieces with flat and cylindrical surfaces. The diameter of the abrasive discs that are installed on such machines is 200–800 mm.
Flat lapping machine
Round lapping
On this equipment, lapping of calibration and measuring tools made of metal is performed. The maximum diameter of gauges and tools that can be processed on machines of this type is 50–200 mm.
Grinding and lapping
With the help of such equipment, holes are ground in, the maximum diameter of which is 100–300 mm.
Grinding and lapping machine
Grinding and finishing
These are machines designed to perform finishing (lapping) operations. Such devices process various metal products: crankshafts with a maximum diameter of 100–200 mm, equipment spindles, pistons, etc.
Polishing
Such machines are used to polish metal parts. This universal equipment can be used to polish flat, cylindrical, conical, internal surfaces, as well as workpieces of complex configurations. An endless belt with a width of 100–200 mm or a soft polishing wheel with a diameter of 100–200 mm can be used as a working tool on these machines.
Grinding and polishing machine
Honing
There are also honing machines that are used to perform fine grinding (0.04–0.08 mm per diameter).
Honing machine
Main components and mechanisms of grinding machines
Grinding machines for ordinary and special work, regardless of their design features, have the following common basic typical components and mechanisms:
- the frame, which serves as the basis for all components of the machine; it houses the drive for the reciprocating movement of the table and the machine controls;
- a table mounted on the machine bed, which can perform reciprocating or circular motion, which provides longitudinal or circular feed of the part. The table drive is usually hydraulic;
- a headstock located on the machine table and designed to install and transmit rotation of the part. The electric drive for rotating the workpiece is located in the headstock housing;
- a tailstock, also installed on the table and supporting the second end of the part when processing it in the centers;
- grinding head located on the bed. A grinding wheel is installed on the spindle of this headstock. The rotation of the grinding wheel is carried out by a special electric drive;
- electrical equipment;
- hydraulic equipment;
- control panel on which all machine control mechanisms are collected.
The listed components, except for the front and tailstocks, are available in grinding machines of all types. The front and tailstocks are used only on cylindrical grinding and slot grinding machines. On internal grinding machines there is only a headstock, while on surface grinding machines the front and tailstocks are replaced by a table.
Certain types of grinding machines have additional units unique to them. Thus, on centerless grinding machines, a support knife is used to install the part in the working position, and a drive wheel is used to rotate it.
Making a simple grinding machine with your own hands
Considering the fact that serial grinding equipment is not cheap, it makes sense to think about making such a machine yourself. Even the simplest homemade machine, which is not at all difficult to make, will allow you to grind workpieces of various configurations with high efficiency and quality.
The supporting element of a homemade machine for performing grinding work is a frame on which two drums and an electric motor are mounted. To make the frame, you can use a thick steel sheet, from which a platform of the required size is cut out.
With the engine, everything is much simpler: it can be removed from an old washing machine that has already served its useful life. The drums can be made in sets; for this it is convenient to use a chipboard, from which discs of the required diameter are cut.
A simple homemade machine made from improvised means
Drive shaft mounting
Driven drum
Engine mount
As an example, we will analyze the sequence of actions for the manufacture of a homemade grinding machine, the bed of which has dimensions of 50x18 cm. First of all, the bed itself is cut out of a steel sheet, as well as the work table on which the electric motor will be mounted. The dimensions of such a table will be approximately 18x16 cm.
It is important that the ends of the bed and work table, which will be connected, be cut as evenly as possible. The thick sheet of metal from which you will make the frame and work table is difficult to cut by hand, so it is better to perform this procedure on a milling machine. It is necessary to drill three holes in the frame and work table and securely connect them with bolts. Only after this is the motor installed and securely connected to the surface of the work table so that the base of the motor fits snugly to the surface of the platform.
Another homemade machine, assembled “on the knee”
When choosing an electric motor for your homemade grinding equipment, it is important to pay attention to the power: it should be at least 2.5 kW, and the rotation speed should be about 1500 rpm. If you use a drive with more modest characteristics, the machine will have low efficiency. You can avoid the need to use a gearbox if you correctly select the diameters of the drive and tension drums.
The diameters of the drums should be selected depending on the speed at which the abrasive belt will move. So, if the belt speed should be approximately 20 m/sec, then it is necessary to make drums with a diameter of 20 cm. To install the tension drum, a fixed axis is used, and the drive one is fixed directly on the electric motor shaft. To make rotation of the tension drum easier, a bearing assembly is used. It is best to make the platform on which the tension drum is installed with some bevel; this will ensure smooth contact of the abrasive belt with the workpiece being processed.
The homemade option is a little more complicated
It won’t be particularly difficult to make drums for a homemade grinding machine. To do this, you need to cut square blanks measuring 20 by 20 cm from chipboard, and drill a hole in the center of each of them. These blanks are then assembled into a 24 cm thick package, which is machined to form a cylindrical drum with a diameter of 20 cm.
To prevent the abrasive belt from slipping on the drums, you can stretch wide rubber rings onto their surface, which are usually cut from the inner tube of a bicycle or moped. The width of the abrasive tape, which you can make yourself, should be about 20 cm.