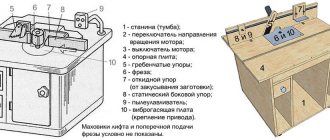
Wood is easy to process. Using simple tools, you can create things of amazing beauty and functionality.
Separately, it is worth noting products that have the shape of rotation figures: tool handles, staircase balusters, kitchen utensils. To make them, an ax or chisel is not enough; you need a lathe.
Buying such a device is not a problem, but a good machine is expensive. It’s not difficult to acquire such a useful tool and save money, because you can make a wood lathe with your own hands.
Why is it needed and how does it work?
A lathe is designed for the manufacture of wooden products that have a cylindrical or similar shape. This is an indispensable thing when renovating a country house with a wooden staircase, a carved porch, but not only.
If you have some experience, a turning tool will allow you not only to save on purchased decorative elements, but also to earn money, because handmade wooden products are highly valued.
Whether such a machine is needed in a home workshop is up to the master to decide.
Of course, if you need several handles for chisels, it is easier to buy them, but if you want to make an all-wood staircase, then a set of balusters will cost a very large sum. It is much cheaper to make them yourself. By the way, you don’t even have to spend money on buying equipment - a simple machine can be made in your own workshop using scrap materials.
The operating principle of a wood lathe is not particularly complicated. The cylindrical workpiece is fixed along the axis of rotation. Torque is transmitted to it. By bringing various cutters or grinding tools to the workpiece, it is given the desired shape.
Main parts of lathe:
- a frame on which all components are fixed;
- electric drive;
- headstock;
- tailstock;
- handyman
For ease of operation, schemes for changing the rotation speed are used. In professional equipment, this is a real gearbox, a system of gears that allows you to regulate speed within a very wide range. This is difficult; it is enough to equip a homemade wood lathe with a belt drive with several pulleys of different diameters.
Spindle rotation speed and feed speed of a CNC milling and engraving machine: how to choose it?
When drawing up a technological map for turning or milling, a specialist needs to find the optimal balance between machine performance and the requirements for surface cleanliness of the finished part. The main parameters that it can affect are the spindle speed and feed rate. The choice of processing modes is carried out by calculation or experiment.
The difficulty of working on portal milling and engraving machines lies in their multitasking. One control program can contain several types of processing: contour cutting, milling of grooves and through holes, engraving. At the same time, the materials - wood, plastic and composites - differ in cutting resistance and structure. Many novice operators are faced with such unpleasant moments as burns, insufficient machining cleanliness, and premature wear of the cutting edge. Below we will try to give general recommendations on setting the spindle speed and feed without complex calculations.
What is spindle speed and feed?
Rotation speed is one of the main spindle parameters. It is expressed in revolutions per minute (rpm) or hertz (Hz). CNC gantry machines do not use complex mechanical gearboxes and the speed is controlled by electronic components. With an increase in rotation speed, the productivity of the machine increases and the service life of the cutting tool decreases. The latter is associated with the release of excess heat, which does not have time to dissipate. As a result of overheating, the hardness of the cutting edges decreases and they lose their sharpness.
Manufacturing of the bed
The bed is a frame that combines all parts of the machine into a single whole. The strength of the structure as a whole depends on its reliability, therefore the best material for the frame is a steel angle. You can also use a rectangular profile pipe.
First of all, the dimensions of the future unit are outlined. This indicator largely depends on what specific products the machine is needed for. The average bed size of a home lathe is 80 cm. Using a grinder with a metal circle, cut two identical workpieces.
Laying wooden blocks, the angles with the shelves up and inward, are laid on a flat surface, their upper edges should create an ideal plane. The same distance is maintained between them, approximately 5 cm. To orient them correctly, use a strip of appropriate thickness.
The longitudinal parts of the base are fixed with clamps. Cross members are made from the same square. There are three of them. Two are attached to the edges of the structure, the third, which is a support for the headstock, is approximately twenty centimeters from the left edge. The exact dimensions depend on the type of motor used and the parameters of the pulley that could be found.
All that remains is to weld the frame into a single whole. The seam must be reliable and of high quality; it can be welded manually or using an automatic machine.
It is important to immediately decide how the machine will be used. Desktop installation or production of a stand-alone unit is possible. In the second option, it is necessary to provide legs. They can be made from the same square, or they can be cut from timber of suitable thickness. The use of wooden legs will allow you to save on material, in addition, the machine can be made collapsible.
Main details
Turning technology has been developing for a long time, acquiring new skills and increasing the level of skill. Thanks to this, today all wooden products are distinguished by a smooth surface, conciseness and completeness. And their appearance will not leave anyone indifferent.
All samples of wood turning work are divided into several parts:
- parallelepiped;
- cone;
- pyramid.
Almost all of these figures can be obtained by turning. Before placing a piece of wood on a lathe, the bark is first removed from it and the cracks are cleaned out. In order for the processing to be carried out correctly, the prepared solid piece is securely fixed to the device with special devices. After all the work has been completed, the craftsmen do expressive painting on the products according to ancient traditions (its magnificence can be judged by the famous Khokhloma and Russian nesting dolls).
Electric motor for machine
The basis of the lathe drive is the engine. When choosing this unit, it is important to pay attention to its main characteristic – power. For a home machine, models with a power from 1200 to 2000 W are suitable. The type of connection is important; there are single-phase and three-phase motors.
In a low-power table lathe, you can use a motor from a washing machine. It is unlikely to cope with the processing of large workpieces, but it will help produce small decorative elements and kitchen utensils.
Direct drive or belt drive
There are several ways to transfer rotation to the workpiece. The simplest is direct drive. In this case, the workpiece is attached directly to the motor shaft. A distinctive feature of this design is its simplicity. With all this, direct drive has a number of significant disadvantages.
First of all, a direct drive machine does not allow you to adjust the rotation speed, which is critical when working with hard material. It is also worth considering the load on the electric motor, especially when working with large workpieces. No matter how well it is centered, it cannot do without vibration. Motor bearings are not designed to withstand longitudinal loads and will often fail.
To protect the engine from damage and provide the ability to adjust the speed of rotation of the workpiece, it is worth considering a belt drive. In this case, the engine is located away from the axis of rotation of the workpiece, and torque is transmitted through pulleys. Using pulley blocks of different diameters, it is easy to change the speed within a fairly wide range.
It is advisable to equip a machine for your home with pulleys with three or more grooves, which will allow you to process wood of any species with equal success, and, if necessary, work with soft alloys.
Cutting modes for turning
During turning, excess metal, called allowance, is removed from the workpiece in a certain number of passes. The result is a product of a given shape with the required dimensions and surface roughness class. In general, the operation of turning a part on a lathe looks like this: the cutter sequentially moves with a given feed deep into the metal of a rotating workpiece, while its cutting edge removes a given thickness of metal from the workpiece for each revolution.
Cutting modes during turning are determined based on a number of technical indicators, among which the most significant are the tool feed and the rotation speed of the part fixed in the machine spindle. The correct selection and application of processing modes guarantee not only geometric accuracy and cost-effectiveness of manufacturing, but also the safety of the part, tools and equipment, as well as the safety of the machine operator.
Main settings
One of the main tasks of technological preparation of production during turning operations is the determination of rational cutting conditions. When calculating them, the characteristics of the product being processed and the capabilities of the machine park, as well as the availability of appropriate tools, fixtures and equipment should be taken into account. The layout of the components and assemblies of a lathe allows for the implementation of two defining types of movement that form a given configuration of the surfaces of the part: rotation of the workpiece (main movement) and movement of the cutter deep into and along the surface of the part (feed). Therefore, the main technological parameters for turning equipment are:
- cutting depth;
- spindle feed and speed;
- cutting speed.
There is mutual influence of cutting modes and the main elements of the production economy. Among them, the most significant are:
- equipment performance;
- quality production indicators;
- cost of manufactured products;
- depreciation of equipment;
- tool durability;
- safety.
The concept of cutting modes
Turning at extreme conditions increases the productivity of turning equipment. However, such operation of machines is not always possible and advisable, because There are limitations in the form of the maximum power of the main drive, the rigidity and strength of the workpieces, as well as the technological parameters of the tool and equipment.
Another limitation is the characteristics of individual materials. For example, titanium and stainless steel for turning are among the most complex materials and require a special approach when determining the parameters of a technological operation.
If the technological parameters are incorrectly calculated or selected, working at high speeds can cause increased vibration and imbalance of individual mechanisms of the lathe. This leads to a decrease in the accuracy and repeatability of product dimensions. In addition, the risk of tool breakage and machine failure increases.
Depth
Allowance is the thickness of metal removed by a turning tool from the workpiece before it reaches the final size. When turning and boring, it is removed in stages over a given number of cuts. The thickness of the metal removed per single cutter pass is called the depth of cut in machining and is measured in millimeters. In technological calculations and tables, this parameter is denoted by the letter t.
During turning operations, it is equal to 1/2 the difference in diameters before and after turning the part and is calculated by the formula:
where t is the cutting depth; D—diameter of the workpiece; d – specified diameter of the part.
During trimming operations, this is the size of the metal layer removed from the end of the workpiece in a single pass of the cutter, and during grooving and cutting, this is the depth of the groove.
Ideally, one pass of the cutter is required to remove the stock. But in reality, the turning process, as a rule, includes a roughing and finishing stage of processing (and for surfaces with high precision - even semi-finishing). If the characteristics and shape of the workpiece are good, both of these operations are performed in two or three passes.
Headstock and tailstock
The workpiece being processed is clamped between two devices called the headstock and tailstock. Rotation from the engine is transmitted to the front one, which is why it is a more complex unit.
Structurally, the headstock of a homemade lathe is a metal U-shaped structure, between the side faces of which a shaft and one or more pulleys are mounted on bearings. The body of this unit can be made of thick steel; bolts of sufficient length are suitable for assembling it into a single whole.
An important part of the headstock, as well as the machine as a whole, is the shaft, a spindle with three or four pins designed to fix the workpiece. This shaft is passed through the bearing of one of the cheeks of the U-shaped housing, then pulleys are mounted on it. To fasten them, a key or a means for fixing cylindrical parts is used, the second cheek is put on last, and the structure is securely tightened with bolts.
The tailstock's job is to support the long workpiece while allowing it to rotate freely. You can buy a ready-made part from a factory machine, or you can use a powerful electric drill chuck mounted on a square of suitable length. A shaft with a pointed end is clamped into the cartridge itself.
The headstock and tailstock are installed on the bed. It is important to understand that the axes of rotation of both shafts must completely coincide. Otherwise, breakage of the workpiece, failure of the machine, and possibly injury to the turner are likely.
Selecting a transfer method
In most homemade wood lathes, the working drive is provided by the two most popular methods - direct transmission or through belts. Both schemes are excellent for small-sized lathes with primitive devices for clamping a wooden workpiece in the form of a trident and a cone.
Direct transmission
In addition, direct transmission does not allow adjustment of the speed. If the engine produces 1425 rpm, then the workpiece will also rotate, alas, this is clearly not enough for turning hardwood.
Belting
The design of the headstock using a belt drive significantly expands the capabilities of the lathe. Even if a pulley of the same diameter is used, this makes it possible to increase the shaft rotation speed and protect the electric motor from heavy loads; in this case, it is definitely not in danger of jamming.
If a multi-lane pulley is mounted on the working shaft, and the engine is mounted on a movable slide, then it becomes possible to regulate the speed of rotation of the shaft by moving the belt from a smaller diameter to a larger one. This is the best option; it makes it possible to process wood of a wide variety of species.
Tool support: tool rest
A tool rest is a table on which the tool rests during operation. In principle, it can have any configuration, the master can choose, the main criterion is convenience. One of the best options for a tool rest is a trapezoidal turntable made of thick steel, mounted on a platform that allows you to move it in all directions. It will allow you to process any workpieces and produce products of various sizes and shapes.
The simplest tool for turning work is a square welded to the base. The height of its upper edge must correspond to the level of the axis of the headstocks.
Wood cutters
Cutters are used as cutting tools for a lathe. You can buy such a tool at almost any hardware store. Individual cutters and entire sets are available for sale.
If there is no store nearby, but you have the opportunity and desire, you can make the necessary tool yourself. To do this, you will need a metal-cutting machine, as well as a sheet of tool steel; it can be replaced with an old tool. A high-quality turning tool can be obtained, for example, from an old Soviet file.
Mini machine for small jobs
Often there is a need to turn several small wooden parts, in this case it is not at all necessary to make a full-fledged machine; you can get by with a mini-wood lathe. Its production does not require much labor and will not take much time.
The design of such a machine is extremely simple. A motor from an old tape recorder, powered from an external power supply, is ideal as an electrical component. The bed of the mini-machine will be a piece of board of the required length.
The engine must be secured. Of course, a belt drive is not suitable for a small machine; the workpiece will have to be mounted on the motor shaft. The best device for this is a faceplate. The drive housing is a U-shaped plate, in the center of which a hole is drilled for the shaft. The engine in the housing is mounted on the frame using self-tapping screws.
The main part of the machine is ready, all that remains is to make the tailstock. Its body is made of a block of suitable size. A hole for the shaft is drilled in it exactly at the height of the engine; a dowel-nail of suitable length is used as it. The headstock is attached with glue and several screws.
Using a power source with the ability to adjust the output voltage, you can create a machine with variable rotation speed. It is convenient to regulate the speed using the foot control pedal. The design of this device can be very diverse, it all depends on the available parts.
History of development
It is believed that the first lathes were used by the Egyptians as early as 1300 BC. e. In 650 BC. e. The Romans used them to produce bows and arrows, which were intended for warrior-defenders of the empire. This process required incredible titanic efforts.
In the 14th-15th centuries, wood turning was performed on machines with a foot drive, similar to the pedal on sewing machines of the 20th century. In addition, they were equipped with metal parts, which made it possible to process more complex materials. Turned wood products have had a great influence on the development of mankind: from the production of simple household utensils, agricultural implements, marine parts (for example, pulleys for blocks and tackle) to furniture, musical instruments, sports equipment, measuring instruments, etc.
In the 18th century, the Russian mechanical scientist A.K. Nartov developed the world's first screw-cutting unit with gear wheels and a mechanized caliper. This invention made it possible to create exquisite bas-reliefs.
Currently this production is fully automated. Modern technological devices make it possible to produce a wide variety of wood turning products.