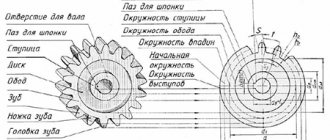
§ 8.15. Gear materials
§ 8.14.
Gear materials The choice of gear material depends on the purpose of the gear and its operating conditions. Steel, cast iron and plastic are used as wheel materials.
Become. The main materials for gears are heat-treatable steels. Depending on their hardness, steel gears are divided into two groups.
The first group is wheels with tooth surface hardness Η <350 HB. Used in light and medium-loaded gears. The materials for wheels of this group are carbon steels 35, 40, 45, 50, 50G, alloy steels 40Х, 45Х, 40ХН, etc. Heat treatment - improvement is carried out before cutting teeth. Wheels with tooth surface hardness <350 HB can be easily worn in and are not subject to brittle fracture.
For uniform wear of the teeth and better break-in, the hardness of the spur gear should be (25...50) HB greater than the hardness of the wheel.
For helical gears, the hardness HB of the working surfaces of the gear teeth is desirable to be as high as possible.
The second group is wheels with surface hardness H >350 HB [1]. High hardness of the working surfaces of the teeth is achieved by volumetric and surface hardening, carburization, nitriding, and cyanidation. These types of heat treatment make it possible to increase the load capacity of the transmission several times compared to improved steels.
Wheel teeth with surface hardness Η > 350 HB are not run-in. For non-running-in gears, it is not necessary to ensure a difference in the hardness of the gear teeth and the wheel.
Surface hardening of teeth with heating by high-frequency currents (HF) is advisable for gears with a module of mm, working with improved wheels, due to the good running-in of the teeth. With small modules, a small tooth is calcined through, which makes it brittle and accompanied by warping. For hardening of t.v.h. steels 45, 40Х, 40ХН, 35ХМ are used.
Cementation is used for wheels whose dimensions must be minimal (aviation, transport, etc.). For carburization, steels 20Х, 12ХНЗА, etc. are used.
Nitriding provides particularly high hardness of the surface layers of the teeth. For gears in which there is no abrasive wear of the teeth, nitriding can be used. It is accompanied by low warping and allows you to obtain teeth of the 7th degree of accuracy without finishing operations. To increase the strength of the tooth core, the wheel blank is subjected to improvement. For nitriding, steels 40ХНМА, 40Х2НМА, 38ХМУА, 38Х2У are used.
[1] At Η >350 HB, the hardness of the material is measured on the Rockwell scale, 10 HB" 1 HRC3.
Nickel-free, high-strength, deeply hardenable steel grade 38Х3М1Ф1А with increased nitriding capacity
Group of materials:
Steels for heavy-duty, large gears
Applications:
- Marine engineering;
- Power engineering;
- Petrochemical engineering.
Purpose:
Nickel-free, high-strength, deeply hardenable steel grade 38Х3М1Ф1А with increased nitriding is intended for the manufacture of large-sized gear parts for main ship gearboxes with increased requirements for strength and wear resistance.
Description:
Provides high strength properties (KP70 - KP100) in a cross section of up to 500 mm in combination with optimal parameters of the nitrided layer of large-module gear parts.
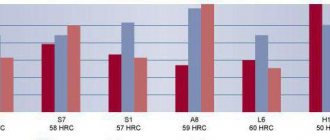
Mechanical properties of steel grade 38Х3М1Ф1А (not less)
| Strength category | σ 0.2, MPa | σ in, MPa | δ5% | ψ, % | KCV (20), J/cm2 |
| KP 70 | 690 | 780 | 10 | 35 | 45 |
| KP 80 | 780 | 880 | 9 | 30 | 40 |
| KP 90 | 880 | 980 | 11 | 40 | 45 |
| KP 100 | 980 | 1080 | 10 | 35 | 40 |
With a nitrided layer thickness of 0.45; 0.75 and 1 mm surface hardness is 750, 650, 550 HB, respectively.
Nitriding modes ensure high performance of heavily loaded gearboxes.
Product types:
Forgings are ring-shaped, solid, like shafts.
Comparison with analogues.
The developed steel is not inferior to the requirements of the best foreign standards and rules of classification societies of advanced countries in the field of shipbuilding.
There is a copyright certificate.
Legal protection
A patent was received for the developed steel. Technical and technological documentation for organizing the production of semi-finished products (propeller shaft blanks for nuclear icebreakers) from 38ХН3МФА steel is protected as a trade secret.
Cooperation proposals:
- Transfer on a contractual basis of technical and technological documentation for smelting, forging, heat treatment and nitriding of heavily loaded large gear parts, semi-finished products (ring forgings, solid forgings such as shafts, etc.) from steel grade 38Х3М1Ф1А.
- Materials science support for the manufacture of deformed, heavily loaded large-sized gear parts, semi-finished products (ring forgings, solid forgings such as shafts, etc.) from steel grade 38Х3М1Ф1А.
Structural steel grade 38HN3MFA
Group of materials:
Steels for heavy-duty, large gears
Applications:
- Marine engineering;
- Power engineering;
- Petrochemical engineering.
Purpose:
Structural steel grade 38KhN3MFA is intended for the manufacture of large-sized gear parts, forged blanks for long propeller shafts with and without a through axial hole for marine vessels of any purpose, as well as for high-strength fasteners.
Description:
Structural steel grade 38KhN3MFA has high strength and visco-plastic properties (depending on the strength category) and a high endurance limit in air. Can be used for large gear parts and fasteners.
Mechanical properties of steel grade 38KhN3MFA (not less)
| Strength category | σ 0.2, MPa | σ in, MPa | δ 5, % | ψ, %, | KCV (20), J/cm2 |
| KT70 | 690 | 834 | 14 | 40 | 59 |
| KT80 | 780 | 883 | 12 | 50 | 78,5 |
| KT90 | 880 | 981 | 11 | 45 | 58,8 |
| KT100 | 980 | 1079 | 10 | 35 | 49 |
The supply of blanks for propeller shafts and blanks for fasteners is carried out in accordance with GOST.
Product types:
Large gear parts, large blanks for fasteners.
Propeller shafts.
Comparison with analogues
The requirements for the material are not inferior to the requirements of the best foreign standards and rules of classification societies of advanced countries in the field of shipbuilding.
Legal protection
A patent was received for the developed steel. Technical and technological documentation for organizing the production of semi-finished products (forged blanks for gear parts, forged blanks for long propeller shafts with and without a through axial hole, large blanks for fasteners) made of 38ХН3МФА steel is protected as a trade secret.
Cooperation proposals:
- Transfer on a contractual basis of technical and technological documentation for smelting, forging, heat treatment and nitriding of heavily loaded large gear parts, semi-finished products from steel grade 38Х3М1Ф1А.
- Transfer on a contractual basis of technical and technological documentation for semi-finished products (forged blanks for gear parts, forged blanks for long propeller shafts with and without a through axial hole, large blanks for fasteners) made of steel grade 38ХН3ММА.
- Materials science support for the production of deformed semi-finished products (ring forgings, solid forgings such as shafts, etc.) from steel grade 38ХН3МФА.
Welded spur gears
Compared to cast wheels, conventional welded wheels produce more noise. To reduce noise, it is advisable to equip the wheels with ribs. Gear wheels of small diameter are made with a hub welded to the end of the wheel or with a through bushing (Fig. 8, a). Large wheels can be welded from several parts - a hub, one or two disks with ribs and a crown, which can be a forging from the desired metal (Fig. 8, b).
A welded gear wheel of a conventional design has a hub diameter (Fig. 8, c) d1=(1.55...1.7)d mm; hub diameter with flange d1=d1+10 mm; crown thickness (da–D0)/2 mm; thickness of the crown with side (da–D0)/2+5 mm; diameter of holes in the disk D1=(D0–d1)/2 mm; diameter of holes in the disk d2 = (D0 – d1)/5 mm; disk thickness c ≈ 0.4d-2 mm; rib deepening s=0.8c mm; chamfer n=0.5m mm.
Rice. 8. Welded spur gears
Types of gears
Today there are quite a large number of different types of gears:
- straight teeth;
- helical;
- with internal gearing;
- screw;
- sectoral;
- with circular teeth;
- gear racks;
- "stars".
Spur gears are considered the most popular version of this mechanism. The manufacturing process of this type of gear involves the use of metal, plastic and composite materials. Spur gears are necessary to transmit translational torque only to shafts located in the same plane.
Helical gears are an improved version of their straight-cut counterparts. In this case, the teeth are located at different angles. This design feature helps reduce noise, increase transmission smoothness and increase the permissible transmitted power. The disadvantage of such gears is considered to be increased friction due to the increased tooth area.
Internal gears are distinguished by the presence of teeth on the inner surface. Due to this design feature, the drive and driven shafts rotate in the same direction. These gears are used to create small-sized mechanisms. They can also be used in pumps and planetary gears.
The helical gears are made in the form of a cylinder. In them, the teeth are located along a helical line. These mechanisms are designed for use in non-intersecting shafts located perpendicular to each other.
Sector gears are used when there is no need for a full rotation of the shafts. They can be found in stepper mechanisms and steering racks.
Gears with circular teeth are distinguished by their original design. The teeth in them have a slight bend along the radius. Such mechanisms are characterized by smooth operation and the ability to withstand high load levels. But it is worth considering that the method of manufacturing gears with circular teeth is much more complicated. At the same time, their efficiency is lower than that of conventional analogues.
Bevel gears transmit rotational motion in mechanisms in which rotating shafts intersect on a plane (at an angle of about 90 degrees). These mechanisms can be circular, curvilinear, tangential or straight. Most often, this type of gear is used in automobile differentials and gearboxes.
The star gear is equipped with an additional element - a chain. This mechanism transmits rotational and translational torque from one shaft to another. The advantage of chain transmission is that there is no slippage problem.
Manufacturing Features
The technological process of gear manufacturing involves the use of two methods - copying and running. Copying technology involves milling, during which a cut is formed between the cavities of the teeth. This result is achieved through the use of end, disk or modular cutters. After the cavities are formed, the workpiece is rotated by one tooth. The peculiarity of this technology is that the shape of the cutting tool used follows the shape of the cavity.
The break-in method is used much more often. It involves simulating the engagement of a gear pair, one of the elements of which is a hob cutter. High-strength metal is used to manufacture gears using this method.
Metalworking is the specialty of our company. If you want to get acquainted with the range of products and services in more detail, go to the appropriate section of the site.