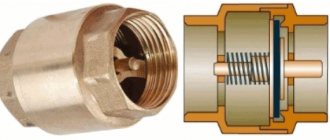
A pressure gauge is a technical device that measures pressure at any time in any enclosed space at the installation site. Without such devices, the operation of vessels operating under excess pressure is prohibited.
The principle of a pressure gauge is to equalize the measured pressure and the amount of deformation of the spring mechanism inside the device. The deflection of the spring is converted into rotational movement of the needle on the dial.
On our website you can find not only a valve for a pressure gauge, but also a wide range of shut-off valves.
What is this device?
A pressure gauge is a device for measuring excess, that is, artificially created, pressure of water, steam or other working medium.
In simple terms, it shows how much greater the water pressure in the pipe is than atmospheric pressure.
In everyday life, in the housing and communal services sector and in industrial enterprises, the most common devices are those with a spring in the form of an oval tube (named after Bourdon, the man who patented it). They are simple in design and inexpensive.
Externally, a water pressure gauge is a round object in a metal or plastic case. The dial with the scale is covered with plexiglass made of methacrylate or polycarbonate.
How to use a technical pressure gauge
Basic operations for using a pressure gauge include checking its condition, zeroing it, applying pressure, and taking readings. If the fluid in the pressure gauge is contaminated, it must be replaced, otherwise it will reduce the accuracy of the measurements taken.
You should also check that there is enough fluid in the pressure gauge to measure pressure. If there is not enough fluid, it should be topped up in accordance with the instructions of the device manufacturer.
All pressure gauges must be leveled before measurements are taken. Without this, measurements will be inaccurate. Most inclined pressure gauges have a special device for leveling the device. The device is rotated until the bubble in the level indicator reaches the correct position.
Inclined pressure gauge leveling device
To ensure accuracy, the gauge must be set to a reference zero before pressure is applied and readings are taken. The reference zero of the pressure gauge is made in the form of a handle, which makes it possible to set the zero mark on the scale in accordance with the liquid level.
These preparations will help ensure that the pressure gauge functions properly. Next, pressure is applied and the necessary readings are taken.
Why is it installed?
Measuring instruments are installed to monitor the state of the system . The pressure in the pipelines should not exceed a certain threshold value. At the same time, it must be sufficient to operate various devices.
To operate a shower with hydromassage, you need a pressure of 3-4 bar, a washing machine - about 0.5 bar, and a reverse osmosis filter - 2-6 bar.
Installation locations:
- pumping stations;
- boiler rooms;
- railway transport, automobiles, aircraft and water vessels;
- pressure pipelines;
- water heating devices;
- filtration systems.
Pressure gauges are purchased for personal use, in order, for example, to periodically monitor the pressure of the water entering the mixer.
They are permanently installed at pumping stations next to hydraulic accumulators and pressure switches to automatically turn the pump on and off. Often pressure gauges are part of automation units.
How does a pressure gauge work?
According to GOST R 8.905-2015, a vacuum gauge, pressure and vacuum gauge, pressure gauge, draft gauge, draft pressure gauge are all pressure gauges.
Liquid instruments are used for laboratory measurements.
The operating principle of this type of device is based on the property of communicating vessels. When pressure is applied to one end of the U-tube, the filler moves and a difference in fluid levels is observed. This difference, expressed in millimeters, gives the measured pressure.
The body of the spring device resembles a low metal cylinder of different diameters, most often 5 cm, with a glass lid. Under the glass there is a dial - this is a scale with divisions in bars or pascals.
The principle of operation of this type of pressure gauge is to balance the pressure of the liquid and the deformation force of the membrane or spring. As a result of this process, the elastic sensing element is displaced, which activates the indicating arrow of the device. The division price of the device depends on the upper limit of measurement.
Requirements for pressure gauges:
- Install the device so that its readings are clearly visible to operating personnel, that is, vertically or tilted forward up to 30°, at a height of 2 to 3 meters.
- The timing of checking pressure gauges and safety valves is at least once a year.
- The accuracy class of the pressure gauge must be at least 2.5.
Operating principle
In a deformation (spring) pressure gauge, water enters a curved tube made of copper alloy. The water pressure causes the tube connected to the mechanism to deform, which causes the needle to turn.
Pressure gauges with a single-turn spring are designed for pressures up to 100 atm. To measure higher pressures, springs with several turns twisted into a spiral or screw are used.
There are devices in which a thin two-plate membrane is installed instead of a tube. They are suitable for viscous or contaminated solutions, withstand strong vibrations, but are sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
LLC "KomplektEngineering Technologies"
When designing and operating heating systems, the most important indicator and parameter is coolant pressure. At normal pressure, which is within the hydraulic graph, the work process proceeds without disruption, the coolant reaches the most remote points of the heating system. If the pressure exceeds the critical point, there is a danger of pipeline rupture. When the pressure drops below the permissible level, there is a threat of cavitation - the formation of air bubbles, leading to corrosion and destruction of pipelines. In order to keep pressure levels at the required level, you need to constantly monitor them. This is precisely what pressure gauges are used for - devices that measure this very pressure.
Pressure is the ratio of the force acting perpendicular to a surface to the area of that surface. Pressure largely determines the progress of the technological process, the state of technological devices and their operating modes.
TYPES OF PRESSURE:
- Atmospheric (barometric) pressure is the pressure created by the mass of the air column of the earth's atmosphere.
- Absolute pressure is the total pressure taking into account atmospheric pressure, measured from absolute zero.
- Excess pressure is the difference between absolute and barometric pressure.
- Vacuum (rarefaction) is the difference between barometric and absolute pressure.
- Differential pressure is the difference between two measured pressures, neither of which is ambient pressure.
Based on the type of pressure measured, pressure gauges are divided into:
- overpressure gauges,
- absolute pressure gauges,
- barometers,
- vacuum gauges,
- pressure and vacuum gauges – for measuring excess and vacuum pressure;
- pressure gauges – pressure gauges for low excess pressures (up to 40 kPa);
- draft gauges – vacuum gauges with an upper measurement limit of up to 40 kPa;
- differential pressure gauges – means of measuring pressure difference.
The general principle of operation of pressure gauges is based on balancing the measured pressure by some known force. According to the principle of operation, pressure gauges are divided into:
- liquid pressure gauges;
- spring pressure gauges;
- membrane pressure gauges;
- electrical contact pressure gauges (ECM);
- differential pressure gauges.
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION OF LIQUID MANOMETER
In liquid pressure gauges, the measured pressure or pressure difference is balanced by the hydrostatic pressure of the liquid column. The devices use the principle of communicating vessels, in which the levels of the working fluid coincide when the pressures above them are equal, and when the pressures above them are unequal, they occupy a position where the excess pressure in one of the vessels is balanced by the hydrostatic pressure of the excess liquid column in the other. Most liquid pressure gauges have a visible level of working fluid, the position of which determines the value of the measured pressure. These devices are used in laboratory practice and in some industries.
There is a group of liquid differential pressure gauges in which the level of the working fluid is not directly observed. Changing the latter causes the float to move or the characteristics of another device to change, providing either a direct indication of the measured value using a reading device, or conversion and transmission of its value over a distance.
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION OF A SPRING MANOMETER
Spring pressure gauges are the most widely used among instruments for measuring pressure. Their advantages are that they are simple in design, reliable and suitable for measuring medium pressure in a wide range from 0.01 to 400 MPa (0.1 to 4000 bar).
Elastic sensitive elements of deformation pressure gauges:
a - tubular springs;
b - bellows;
c, d - flat and corrugated membranes;
d - membrane boxes;
e - flaccid membranes with a hard center
The sensitive element of a spring pressure gauge is a hollow, curved tube of ellipsoidal or oval cross-section, which deforms under pressure. One end of the tube is sealed, and the other is connected to a fitting, through which it is connected to the medium in which the pressure is measured. The closed end of the tube is connected to a transmission mechanism mounted on a stand, which consists of a driver, a gear sector, a gear with an axis and a pressure gauge pointer. To eliminate backlash between the teeth of the sector and the gear, a spiral spring is used. The scale is graduated in pressure units (pascal or bar) and the arrow shows the direct value of the excess pressure of the measured medium. The pressure gauge mechanism is housed in the housing. The measured pressure enters the tube, which, under the influence of this pressure, tends to straighten, since the outer surface area is greater than the inner surface area. The movement of the free end of the tube is transmitted through a transmission mechanism to the arrow, which rotates at a certain angle. There is a linear relationship between the measured pressure and the deformation of the tube, and the arrow, deviating relative to the pressure gauge scale, shows the pressure value.
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION OF A DIAPHRAGM PRESSURE GAUGE
The operating principle of a membrane pressure gauge is based on pneumatic compensation, where the force developed by the measured pressure is balanced by the elastic force of the membrane box.
The sensitive element of the device consists of two membranes welded together, forming a membrane box 1. The measured pressure is supplied through a fitting to the internal cavity of the box. Under the influence of the difference between atmospheric and measured pressure, the box changes its volume, which causes the rigid center of the upper membrane to move, which moves the needle of the device 4 through the leash 2 and the lever 3.
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION OF AN ELECTRIC CONTACT PRESSURE GAUGE
Electrical contact pressure gauges (ECM) are used in automatic control, regulation and alarm systems. Two special arrows, set to the minimum and maximum pressure within the scale, have electrical circuit contacts built into them. When the moving arrow reaches one of the contacts, the circuit closes, which causes a signal to be sent or a corresponding action of the system to which the pressure gauge is connected.
1 — index arrow; 2 and 3 - electrical contact settings; 4 and 5 - zones of closed and open contacts, respectively; 6 and 7 - objects of influence.
Version 1 - single-contact for short circuit;
Version 2 - single-contact opening;
Version 3 - two-contact open-open;
Version 4 - two-contact for short-circuit;
Version 5 - two-contact open-short;
Version 6 - two-contact for short-circuiting.
Electric pressure gauges have a typical operating diagram, which can be illustrated in Fig. a). When the pressure increases and it reaches a certain value, index arrow 1 with an electrical contact enters zone 4 and closes the electrical circuit of the device using base contact 2. Closing the circuit, in turn, leads to the commissioning of impact object 6.
Types of ECM:
- Electrical contact pressure gauges on microswitches: vibration-resistant (liquid-filled), industrial, in a stainless steel case, corrosion-resistant with a flat membrane or tubular spring.
- Electrical contact pressure gauges with magnetomechanical contacts: corrosion-resistant with flat or tubular membrane, industrial.
- Explosion-proof electrical contact pressure gauges: with an explosion-proof shell made of stainless steel or aluminum alloy, and also used for low pressures.
- Differential diaphragm pressure gauges are used to measure pressure drop in gas filters or in flow meter restriction devices.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF A DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE GAUGE
In most pressure gauges, the technology for determining and calculating data is based on deformation processes in special measuring units, for example, in a bellows unit. This element acts as an indicator that senses pressure changes. The block also becomes a difference converter in pressure indicators - the user receives information in the form of moving the pointer arrow on the device. In addition, data can be presented in Pascals, covering the entire measurement spectrum. This method of displaying information, for example, is provided by the Testo 510 differential pressure gauge, which during the measurement process eliminates the need for the user to hold it in his hand, since there are special magnets on the back of the device.
Bellows differential pressure gauge type DS:
a - diagram of the bellows block; b - appearance; 1 - working bellows; 2 - silicon organic liquid; 3 - internal cavity of the bellows; 4 - rod; 5 — springs; 6 - fixed glass; 7 — lever; 8 - torenoy; 9 - axis; 10 — rubber rings; 11 - corrugations; 12, 13 - shut-off and equalization valves
In mechanical devices, the main indicator is the location of the arrow, controlled by a lever system. The pointer moves until the changes in the system cease to exert a certain force. A classic example of this system is the DM 3538M series differential pressure gauge, which provides proportional delta (pressure difference) conversion and provides the result to the operator in the form of a unified signal.
What types are there?
List of main types of water pressure gauges:
- The most common are general technical spring pressure gauges for water, with a measurement range from 0 to 10 or from 0 to 6 atmospheres. The case diameter can be from 40 to 160 mm, most often 100.
- Boiler units – with a body diameter of 250 mm. They are needed to take instrument readings from a distance.
- Vibration-resistant pressure gauges - filled inside with a viscous liquid, in particular a glycerin solution or silicone oil. Measure pressure under conditions of strong vibrations. They are used at pumping stations, cars, compressors, trains.
- Corrosion-resistant pressure gauges – for working with chemically aggressive media.
- High-precision ones are needed for testing and crimping.
- Digital electronic - mechanical force is converted into an electrical signal. Readings are taken from the display, can be programmed, and some devices can be connected to a computer.
- Electrical contact (signaling) devices in which upper and lower pressure limits are set. If they are overcome, the electronic device is triggered and transmits a signal to the control device.
- Thermomanometers are devices that measure pressure and temperature in a heating or water supply system. On the front side there are two scales on which readings are taken.
Types of pressure measurement systems
There are many different pressure gauges for measuring low and high pressure. But their technical characteristics are different. The main distinguishing parameter is the accuracy class. The pressure gauge will show more accurately if the value is lower. The most accurate are digital devices.
According to their purpose, pressure gauges are of the following types:
Based on the principle of operation, the following types are distinguished:
Liquid measurement systems
The value in these pressure gauges is measured by balancing the weight of the liquid column. A measure of pressure is the level of fluid in communicating vessels. These devices can measure values in the range of 10−105 Pa.
They have found their application in laboratory conditions. Essentially, it is a U-shaped tube containing a liquid with a higher specific gravity compared to the liquid in which the hydrostatic pressure is directly measured. This liquid is most often mercury.
This category includes working and general technical devices such as TV-510, TM-510. This category is the most in demand. They are used to measure the pressure of non-aggressive and non-crystallizing gases and vapors. Accuracy class of these devices: 1, 1.5, 2.5. They have found their application in production processes, in the transport of liquids, in water supply systems and in boiler rooms.
Electrical contact devices
This category includes pressure and vacuum gauges and vacuum gauges. They are intended for measuring the volume of gases and liquids, which are neutral in relation to brass and steel. Their design is the same as that of spring ones. The only difference is in the large geometric dimensions. Due to the design of the contact groups, the body of the electrical contact device is large. This device can influence the pressure in a controlled environment by opening/closing contacts.
Thanks to the electrical contact mechanism used, this device can be used in an alarm system.
Reference meters
This device is intended for testing pressure gauges that measure values in laboratory conditions. Their main purpose is to check the serviceability of these working pressure gauges. A distinctive feature is a very high accuracy class. It is achieved thanks to design features and gearing in the transmission mechanism.
Special devices
These devices are used in various industrial sectors to measure the pressure of gases such as acetylene, oxygen, hydrogen, ammonia and others.
Basically, pressure can be measured with a special pressure gauge for only one type of gas. Each device indicates the gas for which it is intended. The device is also colored to match the gas for which it can be used. The initial letter of gas is also written. There are also vibration-resistant special pressure gauges that are capable of operating under strong vibrations and high pulsating environmental pressure. If you use a regular pressure gauge in such conditions, it will quickly break, since the transmission mechanism will fail. The main criterion for such devices is corrosion-resistant steel housing and tightness.
Recording devices
A distinctive feature of such devices is that they are able to record the measured pressure on a diagram, which will allow you to see changes at a certain time. They have found their application in industry with non-aggressive means and energy.
Ship and railway
Marine pressure gauges are designed to measure the vacuum pressure of liquids (water, diesel fuel, oil), steam and gas. Their distinctive features are high moisture protection, resistance to vibration and climatic influences. They are used in river and sea transport.
Railway gauges, unlike conventional pressure gauges, do not display pressure, but convert it into a signal of another type (pneumatic, digital, etc.). Various methods are used for these purposes.
Such converters are actively used in automation systems and process control. But despite their purpose, they are actively used in the nuclear energy, chemical and oil production industries.
How is it different from a sensor?
A pressure gauge is a device that makes it possible to determine pressure at any time. It can be equipped with a sensor, thermometer and other additional elements.
The sensor is part of the warning system . It only works at a certain pressure value. The sensor readings are converted into a signal that allows you to adjust the operation of the system in automatic or manual mode.
Types of pressure gauges
Today there are a large number of varieties of pressure gauges. They have different designs and are suitable for different purposes. To measure the pressure of the working medium in pipelines and various equipment, the following types of instruments are most often used:
- spring
— the amount of pressure is balanced due to the force generated when the spring deforms. The devices are characterized by a simple design, so if necessary, it is not difficult to disassemble the pressure gauge for repairs;
- membrane
— the main functional element is the membrane, which is deformed under the influence of the pressure of the working medium, due to which a balancing elastic force arises;
- piston
— to balance the pressure, a piston with a load of a certain size is used;
- electrical contact
— these devices are used in automatic control and alarm systems.
Criterias of choice
Before buying a device, you need to understand exactly what it is needed for and where it will be installed.
Important selection criteria:
- Measuring range. Rule: the working pressure in the pipeline should be no more than 2/3 of the maximum of the measurement scale, but not less than 1/3. If the pressure in the pipe is 5 atm, then you need to buy a pressure gauge with a scale of 0...10 atm.
- The accuracy class varies from 0.15 to 3. The lower, the more accurate. For a cold or hot water supply system, an accuracy of 1.5% is sufficient.
- The location of the fitting can be radial or end when it is from below; and axial or frontal, when he is behind.
- Operating temperature range.
- Temperature operating conditions.
- Working medium (water, steam, oil and so on);
- Diameter. It should be such that the device fits in the chosen location and the dial is clearly visible.
It is also necessary to pay attention to the connecting thread of the fitting. It can be metric - its parameters are measured in mm, denoted by the letter M, for example M20/1.5, which means the outer diameter is 19.9 mm, the inner diameter is 18.7 mm, pitch 1.5. Domestic manufacturers use it by default.
Pipe thread is designated by the letter G. G1/2" means an outer diameter of 20.9 mm, an inner diameter of 18.6, a pitch of 1.8 mm or 14 threads per inch.
The technical passport of a new device must contain a factory verification mark . A verification period of less than a year confirms that the device gives correct readings.
Operating principle of a technical pressure gauge
The operating principle of a pressure gauge is based on the fact that a column of liquid of a certain height has a certain pressure. The change in the size of liquid columns when a pressure source is applied to the device is used as an indicator of the change in pressure.
The liquids used in pressure gauges are mostly mercury and water. However, it is possible to use other specially prepared liquids, for example, special oil. For ease of use, colorant is usually added to colorless liquids. The effect of the weight of the dye is negligible and is not taken into account.
Where and at what price are they sold?
The price of a pressure gauge depends on its design. The simplest analog device costs about 120 rubles. If it is equipped with a thermometer, then the price doubles. Digital devices are tens of times more expensive.
Famous brands in Russia:
- ROSMA;
- Phystech;
- Manotom;
- METER;
- YUMAS;
- Heat control.
This is not a complete list. Foreign analogues, except for price, are not fundamentally different. The only exceptions may be highly specialized devices.
You can buy pressure gauges in an online store, directly from the manufacturer or a company that sells control and measuring instruments. They are sold in stores selling heating and water supply equipment.
Scope of use
The devices are installed wherever it is necessary to control the pressure level in order to avoid emergency situations and disruptions of technological processes:
The devices are used in all cases where it is necessary to know, control and regulate the pressure of water, other liquids, gases, and steam. It is difficult to name an industry that can do without this. Most often, pressure gauges are used in heat power engineering, chemical and petrochemical plants, and in the food industry.
The purpose of a liquid pressure gauge depends on the device, but they are used less and less often, since there is a possibility of it spilling and splashing out during a sharp surge in pressure.
Connection to the water supply system
To measure the pressure in the water supply system, you need to connect a pressure gauge to it.
Possible places to connect to the water supply in the apartment:
- shower hose;
- liner to the toilet cistern;
- hose for washing machine or dishwasher;
- connection to the faucet in the kitchen or bathroom;
- main filter.
In some cases, you will need to screw on an adapter to connect the pressure gauge. If there is no suitable adapter, then use a rubber hose, which is clamped with clamps.
Before depressurizing the system (opening the taps), you must turn off the water. If the pressure gauge is installed for continuous operation, then it must be protected from water hammer, fluid pulsations, and temperature changes.
To do this, install in front of it:
damper blocks - valves, three-way taps, needle valves that allow you to shut off water and relieve excess pressure;- siphon tube is used if the temperature of the working environment is more than 80℃;
- membrane separators protect against abrasive substances and aggressive media from entering the pressure gauge.
When installing a pressure gauge, you need to make sure that the dial is positioned vertically and the readings are clearly readable. It is forbidden to apply force to the housing when twisting it.
Metal pressure gauge
You have already seen the appearance of a metal pressure gauge in Figure 1. Let us now consider its internal structure, which comes in two main types. The first is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Design of metal pressure gauge No. 1.
A curved hollow tube 1, sealed at one end, is connected on the other side to a tap 4, which communicates with the vessel in which the pressure needs to be measured.
As the pressure increases, tube 1 begins to unbend, and with the help of lever mechanism 5 and gears 3 transmits movement to pointer 2, which moves along the scale of the device.
Tube 1 is elastic, and when the pressure decreases, it returns to its original position, and the pointer returns to the zero scale division.
Figure 6 shows a slightly different type of metal pressure gauge.
Figure 6. Design of metal pressure gauge No. 2.
The difference in structure is only that the tube is sealed on both sides, but has an outlet for connection to the vessel in which the pressure needs to be measured. There are also two rods (levers) 2.
Note that, despite slight differences in the device (Figures 4 and 6), the principle of operation of metal pressure gauges remains the same.
The actual appearance of the metal pressure gauge is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7. Realistic image of a metal pressure gauge.
Operating conditions and reading indicators
The dial of a water pressure gauge indicates pressure. It can be measured in bars, Pascals or atmospheres .
The relationship between the units of measurement is approximately the following: 1 atm = 100 kPa = 0.1 MPa = 1 bar = 1 kgf/cm2 = 750 mm Hg. Art. This is an approximate ratio. If you need to carry out measurements with high accuracy, then take into account that 1 atm = 101.325 kPa = 1.01325 bar.
The pressure gauge can only be used under the conditions specified in the technical data sheet. Pressure must be applied smoothly to the device.
Operation is prohibited if:
- when pressure is applied, the arrow does not move;
- the instrument glass is broken or cracked;
- the needle jumps and does not return to the zero position after the pressure is released.
To be sure of the correct pressure gauge readings, it is necessary to carry out verification. New devices are verified by the manufacturer. Next, the time between verifications is controlled.
The permissible period is indicated in the passport and is 1 or 2 years. Verification is carried out at the Center for Standardization and Metrology or at an organization that has a license.
Pressure gauge selection
When choosing a measuring device, a variety of parameters are taken into account. It is worth considering that a gas pressure gauge is selected primarily with safety in mind.
Other common criteria include:
- Accuracy class of the pressure gauge device. It is indicated by the manufacturer in the technical documentation or on the case. High-precision measuring instruments are expensive, but the error can be several fractions of a percent.
- Case diameter. Compact devices are easier to hide in a sealed, protected container. When choosing, attention is paid to the type of material used in the manufacture of the protective case. For example, metal is characterized by high mechanical protection, while plastic ones are lighter and much cheaper.
- Limit of measured values. It can vary over a fairly large range. The manufacturer indicates this parameter because it is selected depending on the medium being measured.
- The diameter of the threaded fitting and its location.
In addition, attention is paid to the popularity of the brand. Well-known manufacturers produce high-quality products that can last for a long period.
Possible breakdowns and ways to solve them
The cause of device failure is poor-quality manufacturing material or violation of operating rules , for example, exceeding operating pressure or use at a temperature for which it is not designed.
If there is a seal on the pressure gauge after verification, then it cannot be opened. In this case, you need to replace the device or send it for repair to the same company that carries out the verification.
But it is not always profitable. It is often cheaper to install a new pressure gauge.
Breakdowns that can be fixed:
- microcracks in the tube are sealed;
- bent and broken hands are replaced;
- a faulty spring that ensures the rotation of the arrow must also be replaced.
If the teeth of the transmission mechanism are worn out or the spring tube is bent, then such a pressure gauge cannot be repaired.
Device structure
Pressure gauges are produced by a variety of companies. The classic design is represented by a combination of the following elements:
- The housing is designed to protect the internal mechanism from environmental influences. Most often, a metal with high corrosion resistance is used in its manufacture.
- The arrow of the device acts as an indicator. It can make one revolution around its axis.
- The gears are designed to directly transmit rotation to the arrow. They are located inside the structure.
- The pressure gauge device for measuring pressure has a driver and a gear sector.
The design of the device has a special spring between the teeth and gears, which eliminates the possibility of backlash.
Pressure gauge device
The measuring scale is analog and is selected depending on the pressure of the medium being measured.
The pressure gauge device operates according to the following operating principle:
- The pressure of the measured medium enters the internal part of the structure.
- The free end of the tube moves in an attempt to align, thereby transmitting rotation to the arrow.
The deformation of the tube is directly proportional to the value the device displays. Due to its simple design, it is reliable and widely used in a wide variety of industries.