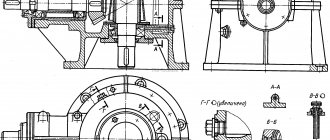
Design
The design of jaw clutches may vary depending on their type, but they all have the following main parts:
- drive coupling half, fixed on the drive shaft;
- ring gear (sprocket);
- the driven coupling half can move longitudinally along its shaft using a keyed or splined connection.
In the disconnected state, the coupling halves are spread apart, the shafts are able to rotate independently of each other. At their ends, cams in the shape of triangles or trapezoids are machined, which serve to engage with the teeth of the sprocket. cams
Between the coupling halves there is a ring gear, its teeth are made in the form of an involute.
When it is necessary to make a connection, the movable coupling half moves towards the fixed one. Their cams engage, the sprocket rotates at a small angle and takes up space between the cams, ensuring tight contact between them. The shafts are connected and ready to transmit torque.
The sprocket for the claw coupling is made of an elastic elastic material. It serves to dampen dynamic loads that occur when the clutch is engaged and during further rotation. The cams of the coupling halves and the sprocket teeth are designed to fill the entire volume of the engagement zone, turning the structure into an almost solid part. This is necessary to transmit high torques and high power without losing energy to impacts, friction and vibration.
The profile of the cams and teeth has the shape of an involute. This eliminates the edge pressure of the cams on each other when their angular position does not coincide and ensures smooth engagement
To minimize vibrations during operation, the surfaces of the coupling halves and sprockets must be made with high precision and carefully machined.
Connecting/disconnecting a jaw clutch at a high relative axial rotation speed (over 1 meter per second) results in severe shock and damage to the device. It is strictly unacceptable to disconnect the coupling while it is under operating load.
Calculation
The performance of cam clutches is determined by the wear of the cams, which depends on the bearing stresses on the contact surfaces. These stresses are calculated approximately based on the assumption that the load is distributed evenly between the cams:
σ CM = 2 KM z D 1 bh ≤ , {\displaystyle \sigma _{CM}={\frac {2KM}{zD_{1}bh}}\leq ,}
where: z
— number of cams of the coupling half; K
— dynamic load factor.
σcm = 90...120 MPa
- when turned on without relative rotation;
σcm = 50...70 MPa
- when switched on at low speeds;
σcm = 35...45 MPa
- when switched on at high speeds.
To reduce wear, the surface of the cams must have high hardness, which is achieved by surface heat treatment or carburizing. The use of the latter preserves the viscosity of the core, which increases the impact strength of the cams. Couplings with carburized jaws are made from steels 15Х, 20Х, and with surface hardening - from steels 40Х, 30ХН.
Classification of jaw couplings
According to the type of drive that moves the movable coupling half, elastic jaw couplings with an asterisk are divided into:
- Mechanical. They are connected manually through a lever system. The operator moves a lever or turns a handle with a worm or crank drive that converts rotary motion into linear motion. This drive is simple and reliable, but often requires great physical effort from the worker. It is also necessary to install a lock that does not allow the clutch to be manipulated while the machine or transmission is moving. Caring for such a coupling is simple and consists of periodic inspection and lubrication.
- Hydraulic. The coupling half moves using a hydraulic cylinder. It is characterized by high response speed and ease of control, but requires a hydraulic system on the machine. It is also necessary to organize a locking system. Hydraulic maintenance is much more complex and expensive than mechanical maintenance.
- Electromagnetic. The drive is carried out by an electromagnet solenoid. They are compact, precise in operation and easy to control. Easily integrated into automatic locking and control systems. Maintenance is simple and consists of periodic inspection and lubrication of moving parts.
Depending on the cam profile used, sprocket couplings are divided into:
- Rectangle. They have a maximum area of lateral contact and are capable of transmitting maximum power. They require very precise positioning of the driving and driven coupling halves to engage.
- Symmetrical trapezoid. Precise positioning is not necessary; compensation of lateral clearances occurs due to variable seating depth of the cams.
- Asymmetrical trapezoid. Allows you to transmit rotation in only one direction. The absence of reverse is achieved by tilting the back side of the profile. The angle is chosen so that when the coupling half begins to rotate in the opposite direction, the cams begin to slip and the engagement stops, and no torque is transmitted. The device is not designed for continuous operation in this mode.
A special design stands out, designed to connect shafts whose axes are parallel, but do not coincide. The dog-disc clutch was developed by John Oldham in the early 19th century. The mechanism operates three discs. Two of them are located on the drive and driven shafts, and the third is placed between them, connecting to each through a splined protrusion on the surface. The protrusions and grooves on different sides of the middle disk are placed perpendicular to each other. The middle disk, sliding in the grooves, moves around its own center of rotation, located in the middle between the axes of the drive and driven shafts. It makes one revolution per revolution of the drive shaft. The angular speeds and the number of rotations of the shafts coincide.
Such devices are much more compact than cardan drives.
Single drum models
A single drum compressor clutch may have one or more discs. Many models work by rotating the fingers. In this case, the plates can be installed behind the adapter. If we consider a standard water pipe coupling, it has three discs. In this case, the support plate is used with a large thickness. The devices can withstand pressure of 5 bar.
Many modifications can boast a durable body. The couplers in the devices are installed through the racks. The driven plates are usually located at the rear of the housing. It is also worth noting that there are couplings on one-way adapters. They allow water to flow in only one direction.
Delivery contents
Typically, a basic mechanical drive industrial dog clutch package includes two coupling halves, a ring gear assembly, packaging and documentation.
Often in shipping documents, coupling halves are called hubs.
A set screw is available as an additional option to facilitate installation of the device on equipment. If the dog clutch is equipped with an electromagnetic or hydraulic drive, a wiring diagram is added to connect to the hydraulics or electrical circuit of the unit.
At the manufacturer's factory, the coupling is assembled and tested on a test bench, and a note is made about the results in the product's shipping passport.
Installation of friction clutches on the low-speed shaft of the output gearbox
Often the product is installed on a gearbox to connect it to an electric motor. This can be attributed to the fact that the gearbox may jam, which leads to overheating of the engine. A friction clutch eliminates the possibility of such a problem. Among the installation features we note:
- Do not apply impact loads as they may damage the product itself.
- To simplify the entry of the cage, lubricant can be used.
- Violation of installation rules may cause damage to the main part.
Self-installation should be carried out exclusively taking into account the recommendations, since even a minor defect causes a reduction in service life.
There are simply a huge number of different parts on sale, due to which there are no significant problems when choosing. The main criteria include the type of material used in manufacturing, as well as the diametrical size
When choosing, attention is paid to how the displacement of the connected elements can occur
Selection of cam-disc clutch
The selection of a model for a specific drive is carried out based on its main parameters:
- shaft diameter;
- type of connection (key or spline);
- drive type (mechanical, hydraulic, electromagnetic)
- rotational speed;
- torque;
- maximum rotation acceleration;
- purchase price;
- cost of ownership during operation (including maintenance and repairs).
If the shafts are parallel, but not coaxial, the choice is made in favor of a claw-disc clutch.
A mechanical engineer analyzes these parameters as a whole and selects the most suitable one for the application conditions from the variety of models on the market.
The reputation of the manufacturer must be taken into account. Purchasing inexpensive devices from nameless manufacturers can lead to breakdown of not only the coupling, but also the entire unit, scattering of fragments, damage to equipment and injury to personnel.
Advantages
The main advantage of cam designs over friction ones is their ability to transmit large torques.
An important advantage is also recognized as the absence of slippage when the speed increases.
The elastic material of the sprocket dampens dynamic loads and torsional vibrations, increasing the stability of the entire unit.
Simplicity of design and maintenance also serves as an important operational advantage.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=NY9Bq-fTgLY
The disadvantage of the device is the need to stop rotation or reduce the speed to a minimum for connection. Another disadvantage is that the shafts must be absolutely aligned.
Transportation and storage conditions
Typically, couplings are stored and transported disassembled and packaged. If, according to the terms of delivery, delivery of the device in assembled form is required, measures should be taken to protect it from environmental influences, both mechanical and chemical.
Recommended storage conditions are room temperature and relative humidity up to 60%.
They should be placed on racks in one row, avoiding exposure of the elastic elements to heating devices, sunlight and aggressive environments.
Features of installation and operation
If the claw coupling is correctly calculated and selected, there will be no problems with its installation.
To simplify the fitting of the hubs on the shafts, it is recommended to subject them to limited heating in a muffle or induction furnace. It is important to make sure that the elastic element does not participate in heating, and install it in the hubs only after making sure that they have cooled down. Axial fastening is performed with a mounting screw and washer.
The operating rules are set out in the product passport. The main ones are the following:
- Operating temperature range - from -30 to +100 °C. Prolonged operation at elevated temperatures will damage and destroy the elastic sprocket.
- Ensuring absolute alignment of the driven and drive shafts. Failure to comply with this requirement will result in runout and premature wear.
- The connection should be made when stopping or at the lowest speeds of rotation of the shafts - up to 100 rpm.
Cams worn down or knocked down during operation are subjected to surfacing followed by grinding in the expectation that their geometry will be completely restored and they will come into full contact.
If it is necessary to limit the maximum transmitted power, a claw overload clutch is used. If the permissible level is exceeded, the pressure on the cams overcomes the clamping force of the springs, and the clutch disengages. If you hear characteristic clicks, the rotation must be stopped immediately. Prolonged operation in this mode will lead to damage to the elements of the device or to its complete failure.
Devices with sprockets
Sprocket clutches are capable of maintaining high speeds. Their permissible pressure indicator starts from 3 bar. In this case, the housings are made with casings. Many models have a drum with threaded lugs. The pads are installed only on the front rings. At the back of the structures, as a rule, there are adapters.
The couplings are also equipped with special necks for filling oil. If we talk about the parameters, the diameter of the case is on average 5.5 cm. The springs are designed for a load of 6 N. The driven plates are installed at an angle of no more than 30 degrees. Some modifications are made to forks. Their outlets are located at the bottom of the structure
It is also important to mention that there are couplings on duct adapters. Rings for such devices are suitable only with double adjustments
Most models are made with small casting plates.
Scope of application of jaw couplings
Critical and highly loaded devices are used wherever it is necessary to transmit high torques or high angular velocities along a shaft. Couplings allow you to quickly connect and disconnect the driven shaft from the drive shaft.
They are in demand in areas such as:
- machine tool industry;
- technological equipment for the forestry, paper-making, chemical and food industries;
- metallurgy;
- transport;
- agricultural and road construction equipment
- mining industry;
- precision instrumentation;
- weapons production;
- energy and large infrastructure facilities.
In many cases where it is necessary to limit the maximum power, overload clutches are used. They are also used where it is necessary to prevent the transfer of torque in the opposite direction.
Mechanically driven jaw clutches are mostly used in small benchtop machines. More complex and large-scale units are equipped with a hydraulic or electromagnetic drive and controlled from a centralized automation system.
Rigid jaw clutches are used in the case of low speeds and high transmitted powers. At medium and high speeds, devices with an elastic damping element are used.
Rigid shaft connection
A fairly large number of different methods of connecting shafts are used, all of them are characterized by certain qualities. The rigid connection method is used when the connection is made taking into account the absence of the likelihood of the nodes moving relative to each other at the time of operation. The classic connection method is characterized by the following features:
- In most cases, the connection is made using flanges, which are part of various mechanisms. Installation of rigid couplings is also carried out; their installation is carried out using the pressing method.
- The single-support version of the shaft has become quite widespread. In this case, the connection itself is used as a second support.
- Bolts can also be used for fixation. At the same time, they must fit tightly into the hole, otherwise serious problems may arise.
- In this case, a gear or transversely folded coupling is often used.
The transversely folded version is used for connecting various parts that are installed in electrical machines and other various units. This design consists of the following elements:
- Two coupling halves. They are mounted on the ends of shafts, which are connected into one system.
- Both parts of the structure under consideration have centering protrusions and a special recess; the connection is ensured by strong bolts.
- Safety couplings cannot be turned due to a special key hole.
- Axial displacement is eliminated due to locking screws that are screwed in at the ends.
A more complex version can be called a gear coupling, which also consists of two separate parts. The outer surface consists of teeth that mesh to ensure a reliable connection. Axial displacement is eliminated through the use of bolts.