Carbon tool steel U13A - characteristics, properties, analogues
This page shows the technical, mechanical and other properties, as well as the characteristics of steel grade U13A.
Classification of material and application of grade U13A
Brand: U13A Material classification: Carbon tool steel Application: tools with increased wear resistance, operating at moderate and significant pressures without heating the cutting edge
Chemical composition of U13A material in percentage terms
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Cu |
| 1.26 — 1.34 | 0.17 — 0.33 | 0.17 — 0.28 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.018 | up to 0.025 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.2 |
Mechanical properties of U13A at a temperature of 20oC
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| The tape is annealed. | 0.08 — 3 | 900 |
Explanation of symbols, abbreviations, parameters
| Mechanical properties : | |
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] |
| sT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, [%] |
| y | — Relative narrowing, [%] |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
| Physical properties: | |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o— T), [1/degree] |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o—T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
Other brands in this category:
Please note that this information about the U13A brand is provided for informational purposes. The parameters, properties and composition of the actual U13A brand material may differ from the values given on this page. More detailed information about the U13A grade can be found on the information resource Brand of steel and alloys. You can check with our managers for information about the availability, delivery times and cost of materials. If you find inaccuracies in the description of materials or errors found, please inform the site administrators using the feedback form. Thanks in advance for your cooperation!
c-met.ru
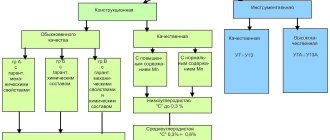
General principles for classifying steel grades
The main classification characteristics of steels: chemical composition, purpose, quality, degree of deoxidation, structure.
- Steels according to their chemical composition into carbon and alloy. Based on the mass fraction of carbon, both the first and second groups of steels are divided into: low-carbon (less than 0.3% C), medium-carbon (C concentration is in the range of 0.3-07%), high-carbon - with a carbon concentration of more than 0.7%.
Alloyed steels are those that contain, in addition to permanent impurities, additives introduced to increase the mechanical properties of this material.
Chromium, manganese, nickel, silicon, molybdenum, tungsten, titanium, vanadium and many others are used as alloying additives, as well as a combination of these elements in various percentages. Based on the number of additives, steels are divided into low-alloy (alloying elements less than 5%), medium-alloy (5-10%), and high-alloy (contain more than 10% additives).
- According to their purpose, steels are classified as structural, instrumental and special-purpose materials with special properties.
The most extensive class are structural steels , which are intended for the manufacture of building structures, parts of devices and machines. In turn, structural steels are divided into spring-type, improved, cemented and high-strength.
Tool steels are distinguished depending on the purpose of the tool produced from them: measuring, cutting, hot and cold deformation dies.
Special-purpose steels are divided into several groups: corrosion-resistant (or stainless), heat-resistant, heat-resistant, electrical.
- According to the quality of steel, there are ordinary quality, high-quality, high-quality and especially high-quality.
The quality of steel is understood as a combination of properties determined by the process of its manufacture. Such characteristics include: uniformity of structure, chemical composition, mechanical properties, manufacturability. The quality of steel depends on the content of gases in the material - oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, as well as harmful impurities - phosphorus and sulfur.
- According to the degree of deoxidation and the nature of the solidification process, steels are calm, semi-calm and boiling.
Deoxidation is the operation of removing oxygen from liquid steel, which provokes brittle fracture of the material during hot deformation. Mild steels are deoxidized with silicon, manganese and aluminum.
- According to their structure, steels are divided into annealed (equilibrium) and normalized states. Structural forms of steels are ferrite, pearlite, cementite, austenite, martensite, ledeburite and others.
Carbon tool steel U13A - characteristics, properties, analogues
This page shows the technical, mechanical and other properties, as well as the characteristics of steel grade U13A.
Classification of material and application of grade U13A
Brand: U13A Material classification: Carbon tool steel Application: tools with increased wear resistance, operating at moderate and significant pressures without heating the cutting edge
Chemical composition of U13A material in percentage terms
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Cu |
| 1.26 — 1.34 | 0.17 — 0.33 | 0.17 — 0.28 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.018 | up to 0.025 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.2 |
Mechanical properties of U13A at a temperature of 20oC
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| The tape is annealed. | 0.08 — 3 | 900 |
Explanation of symbols, abbreviations, parameters
| Mechanical properties : | |
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] |
| sT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, [%] |
| y | — Relative narrowing, [%] |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
| Physical properties: | |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o— T), [1/degree] |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o—T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
Other brands in this category:
Please note that this information about the U13A brand is provided for informational purposes. The parameters, properties and composition of the actual U13A brand material may differ from the values given on this page. More detailed information about the U13A grade can be found on the information resource Brand of steel and alloys. You can check with our managers for information about the availability, delivery times and cost of materials. If you find inaccuracies in the description of materials or errors found, please inform the site administrators using the feedback form. Thanks in advance for your cooperation!
www.c-met.ru
Steel structure
The internal structure is called structure. It can change due to heat treatment or mechanical loads. The grain sizes and their shape are determined by the composition and alloying additives, as well as manufacturing technology and changes in temperature indicators (phase). The phases are divided into temperature ranges, which can vary depending on the alloying components. There are several main phases in the structure of metal.
- Pearlite, consisting of ferrite and carbide in equal parts. It is formed during the process of slow cooling (to +7270) of austenite (nickel alloy).
- Austenite is a phase with a temperature range of up to +14000.
- Martensite. A phase with a supersaturated carbon solution, characteristic of hardened steels.
- Ferrite. The phase consists of solid solution carbon.
- Bainite is a phase formed during sharp cooling of austenite to +5000.
Phases indicate the structure of the metal, its physical qualities and on which the class of the steel alloy depends: foundry, tool, etc.
U13A
U13A Chelyabinsk
| Brand: | U13A |
| Classification: | Carbon tool steel |
| Application: | tools with increased wear resistance, operating at moderate and high pressures without heating the cutting edge |
| Foreign analogues: | Known |
Chemical composition in % of material U13A
GOST 1435-74, the latest version of GOST does not contain the material
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Cu |
| 1.26- 1.34 | 0.17- 0.33 | 0.17- 0.28 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.018 | up to 0.025 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.2 |
Temperature of critical points of the U13A material.
| Ac1 = 730, Ac3(Acm) = 830, Ar1 = 700, Mn = 190 |
Mechanical properties at T=20oC of the U13A material.
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| The tape is annealed. | 0.08-3 | 900 |
| Hardness U13A after annealing, | HB 10 -1 = 217 MPa |
Physical properties of the U13A material.
| T | E 10— 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| hail | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 7800 |
Foreign analogues of material U13A
Attention! Both exact and closest analogues are indicated.
| Japan | France | Italy | Bulgaria | Hungary | Poland | Czech |
| JIS | AFNOR | UNI | BDS | MSZ | PN | CSN |
Designations:
| Mechanical properties : | |
| sв | -Short-term strength limit, [MPa] |
| sT | - Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] |
| d5 | -Elongation at break, [%] |
| y | -Relative narrowing, [%] |
| KCU | -Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | -Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
| Physical properties: | |
| T | -Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] |
| E | -Elastic modulus of the first kind, [MPa] |
| a | -Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o-T), [1/degree] |
| l | -Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | -Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | -Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o-T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | -Specific electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
U13A-carbon tool steel U13A-chemical composition, mechanical, physical and technological properties, density, hardness, application
Affordable metal products
Material U13A Chelyabinsk
Not a single production can operate without steel, be it heavy engineering or the manufacture of household electrical appliances. There are many brands of this product, as well as a large number of dispensing forms. Our company sells U13A material in large quantities and with a minimal margin. To clarify the properties and characteristics of a particular brand, you can contact the company’s managers.
Like all products, U13A material is purchased from leading manufacturers. Therefore, we are ready to provide a quality guarantee with full responsibility. The minimum number of intermediaries determines the low cost. Coupled with fast delivery, this enables our business partners to conduct stable and mutually beneficial cooperation.
In addition to tempering, in the form of one or another part (blank), our company carries out metal processing. All events undergo strict control for compliance with GOST and rules. The specialists of our company carry out such work as galvanizing, creating parts according to customer drawings, producing castings, manufacturing various profiles and much more.
Having the latest equipment and vast experience in our arsenal, we can offer product testing for a number of parameters, such as strength characteristics, chemical composition, alloy purity, and so on.
Each buyer is offered a huge range of products in various formats, as well as current services and works. To quickly understand and choose a product that meets your needs, you need to contact the company manager and receive detailed information on all issues of interest.
Material U13A buy in Chelyabinsk
Individual cost is built through personal communication with each potential customer. Managers take into account the volume of the transaction, offer discounts to regular customers and maintain an open dialogue. As a result, even when controversial situations arise, we are able to find a compromise and come to a solution that satisfies both parties.
Delivery
Logistics work is included in the package of our professional services. We constantly improve our knowledge, acquire the latest equipment, so that the cargo is delivered anywhere in Russia.
The presence of our own railway sidings significantly increases the speed of shipment and subsequent delivery. Having such resources, we guarantee delivery of cargo of any volume and dimensions. This professional approach makes us leaders in the metal products market.
metcontinent.ru
Steel 15ХН3 Moscow and Moscow region
Steel has a wide range of applications in mechanical engineering, manufacturing, construction, shipbuilding, aircraft manufacturing and many other industries. There are many grades of steel, most of them are made to order, there are grades that are constantly in stock due to regular demand. The Resurs company sells 15ХН3 steel directly from the manufacturer. With constant demand, we are ready to offer mutually beneficial terms for the supply of many grades of steel. Including 15ХН3.
The favorable price for the 15ХН3 brand is determined by the minimum markup and the absence of intermediaries. We take full responsibility for the supplied material and guarantee the quality of delivery. The cost of products is determined by warehouse and logistics costs; we have the ability to supply steel directly from the manufacturer’s plant, this allows our clients to run their business stably.
Carbon tool steel U13 - characteristics, properties, analogues
This page shows the technical, mechanical and other properties, as well as the characteristics of steel grade U13.
Classification of material and application of grade U13
Brand: U13 Material classification: Carbon tool steel Application: tools with increased wear resistance, operating at moderate and significant pressures without heating the cutting edge
Chemical composition of U13 material in percentage terms
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Cu |
| 1.26 — 1.34 | 0.17 — 0.33 | 0.17 — 0.33 | up to 0.25 | up to 0.028 | up to 0.03 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.25 |
Mechanical properties of U13 at a temperature of 20oC
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| The tape is annealed. | 0.08 — 3 | 900 |
Explanation of symbols, abbreviations, parameters
| Mechanical properties : | |
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] |
| sT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, [%] |
| y | — Relative narrowing, [%] |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
| Physical properties: | |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o— T), [1/degree] |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o—T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
Other brands in this category:
Please note that this information about the U13 brand is provided for informational purposes. The parameters, properties and composition of the actual U13 grade material may differ from the values given on this page. More detailed information about the U13 grade can be found on the information resource Brand of steel and alloys. You can check with our managers for information about the availability, delivery times and cost of materials. If you find inaccuracies in the description of materials or errors found, please inform the site administrators using the feedback form. Thanks in advance for your cooperation!
www.c-met.ru
About color coding
The color designation is used only for rolled steel. This allows you to avoid errors during transportation and storage. For this, dots or stripes are used. The purpose of the steel alloy is marked with its “own” color, but the group and deoxidation are not taken into account.
Yellow color is used for structural steels: general purpose, automatic, cemented, improved.
A red circle or stripe indicates that this type belongs to a high-strength steel alloy: alloyed, tool, high-speed, hardened.
Blue color indicates rolled stainless steel: with sulfur, austenitic, martensitic.
The green designation marks steel for universal use: high-strength cast iron, general purpose, automatic, cemented, nitrided, improved carbon.
Steel grades and their purpose
- According to the marking, structural carbon steel 08 kp and 10 is used for the manufacture of stamped parts (cold stamping and heading), gaskets, tubes, hardware, caps, as well as for parts that do not require high strength: bushings, stops, rollers, copiers, clutches , wheels with teeth.
- 15, 20 for parts with low load, thin elements that are subject to abrasion, hooks, levers, cross-beams, bolts, liners.
- 30, 35 – for parts under low voltage: spindles, rods, axles, sprockets, disks, levers.
- 40, 45 – for elements of increased strength: crankshafts, camshafts, ring gears, wheels, plungers, clutches, axles.
- 50, 55 – used for the manufacture of rolling rolls, rods, gears, eccentrics, springs. Before parts are manufactured, the steel is hardened.
- 60 – for the production of strong and elastic parts: clutch discs, spring rings, rolling shafts.
- Thin-sheet, low-alloy, universal steel is marked: 09G2, 09G2S, 10 HSND, 15 HSND, 15 GF. Areas of application: mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, chemical engineering, carriage building. These are welded structures, steam boilers, car parts, complex and shaped profiles.
- Structural alloy steel is marked: 15 Х, 15 ХФ, 18 ХГТ, 20 Х, 20 ХГР, 20 ХНЗА, 35 ХМ, 38 ХА, 40 Х, 40 ХС and others are used for products that operate at high speeds, for parts of components and mechanisms operating under high loads.
- Steels and alloys that are resistant to corrosion in their markings have the letters X, N, S, AG, TGR, MT, AM, DI, Yu, T. Scope of application: chemical engineering, gas processing, petrochemical industry, food production, light industry, mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, as well as in other areas where the operation of parts and mechanisms is associated with aggressive working environments.
- Non-alloy tool steel of various grades, marked: U, A, G, and is used in the woodworking industry, the manufacture of hand tools, for knives, forge dies, needle wire, cores, as well as tools with low wear resistance: surgical instruments, razors, for engraving .
- Spring steel is used for the production of springs, springs subjected to heavy loads and critical elements in springs.
- Bearing steel is in demand for the manufacture of bearings and their elements for the operation of machine tools, railway transport, aircraft engines, in precision instrument making, and in rolling mills.
material characteristics / Carbon tool steel / Steel brand – Metallinvest
Characteristics of material U13A
| Brand: | U13A |
| Classification: | Carbon tool steel |
| Application: | tools with increased wear resistance, operating at moderate and high pressures without heating the cutting edge |
Chemical composition in % of the U13A material.
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Cu |
| 1.26-1.34 | 0.17-0.33 | 0.17-0.28 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.018 | up to 0.025 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.2 |
Temperature of critical points of the U13A material.
| Ac1=730, Ac3(Acm)=830, Ar1=700, Mn=190 |
Mechanical properties at T=20oC of the U13A material.
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| The tape is annealed. | 0.08-3 | 900 |
| Hardness of U13A material after annealing | HB=217 |
Designations:
| Mechanical properties: | ||
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] | |
| sT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] | |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, [%] | |
| y | — Relative narrowing, [%] | |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] | |
| HB | — Brinell hardness | |
chel.m-invest.ru
Characteristics of steel grade 15ХН3
15ХН3 - high-quality structural chromium-nickel steel, case-hardened. Weldability is satisfactory. Welding methods: RDS, ARDS submerged arc and gas shield. Preheating is recommended when welding rigid structures.
It has found its application for the manufacture of gears, shafts, worms, claw couplings, piston pins and other cemented parts, which are subject to the requirements of high strength, ductility and toughness of the core and high surface hardness, operating under shock loads and at low temperatures.
U13A :: Metal materials: classification and properties
Steel U13A GOST 1435-99
| Mass fraction, % | ||||
| carbon | silicon | manganese | sulfur | phosphorus |
| no more | ||||
| 1,25 – 1,35 | 0,17 – 0,33 | 0,17 — 0,28 | 0,018 | 0,025 |
| Hardness of Heat Treated Steel | Hardness of samples after hardening in water | Tensile strength σВ, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), no more | |
| HB, no less | Temperature, OS | HRCе (HRC), No less | |
| 217 | 760 — 790 | 64 (63) | 750 (76) |
| Group become | Purpose of steel | Mass fraction, % | ||
| chromium | nickel | copper | ||
| no more | ||||
| 2 | For all types of products (except patented wire and tape) | No more 0,20 | 0,20 | 0,20 |
| 4 | For patented wire and tape | No more 0,12 | 0,12 | 0,20 |
| 5 | For hot-rolled and cold-rolled sheets and strips, including heat-treated ones (except for patented strips), as well as for hot-rolled and forged steel and steel with special surface finishing. | 0,20 – 0,35 | 0,20 | 0,20 |
Application: for tools with reduced wear resistance at moderate and significant specific pressures (without heating the cutting edge): files, razor blades and knives, sharp surgical instruments, scrapers, engraving tools.
Assortment:
forged round and square sections - GOST 1133-71;
hot-rolled round section - GOST 2590-88;
hot-rolled square section – GOST 2591-88, OST 14 – 2 – 205 – 87;
hot-rolled hexagonal – GOST 2879-88;
hot-rolled strip – GOST 4405-75 and GOST 103-76;
forged - GOST 4405-75;
calibrated - GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75 and GOST 8560-78;
steel with special surface finishing - GOST 14955-77.
markmet.ru
An example of decoding steel grade 12Х18Н10Т
12Х18Н10Т is a popular austenitic steel, which is used in welding machines operating in dilute acid solutions, in solutions of alkalis and salts, as well as in parts operating under high pressure and in a wide temperature range. So, what do these mysterious symbols in the name mean, and how to combine them correctly?
The two numbers at the very beginning of the alloy steel grade are the average carbon content in hundredths of a percent. In our case, the carbon content is 0.12%. Sometimes, instead of two numbers, there is only one: it shows how much carbon (C) is contained in tenths of a percent. If there are no numbers at the beginning of the steel grade, this means that there is a fairly decent amount of carbon in it - from 1% and above.
The letter X and the number 18 following it indicate that this brand contains 18% chromium. Please note: the ratio of an element in fractions of a percent expresses only the first number at the beginning of the mark, and this only applies to carbon! All other numbers present in the name express the number of specific elements as a percentage.
Combination H10 follows. As you may have guessed, this is 10% nickel.
At the very end there is the letter T without any numbers. This means that the content of the element is too small to pay attention to. As a rule, about 1% (sometimes up to 1.5%). It turns out that in this grade of alloy steel the amount of titanium does not exceed 1.5%. If suddenly at the very end of the brand you find a modestly standing letter A, remember that it plays a very important role: this means high-quality steel, the content of phosphorus and sulfur in which is kept to a minimum. Two letters A at the very end (AA) indicate that this grade of steel is especially pure, i.e. there is practically no sulfur and phosphorus here.
In the course of a simple analysis of combinations of letters and numbers, we found out that the steel grade 12Х18Н10Т (structural cryogenic, austenitic class) reports the following information about itself: 0.12% carbon, 18% chromium (X), 10% nickel (N) and a small content titanium (T), not exceeding 1.5%.
U13A in St. Petersburg ✅ — “StalExpress”
This page shows the technical, mechanical and other properties, as well as the characteristics of steel grade U13A.
Classification of material and application of grade U13A
Brand:
U13A
Material classification:
Carbon tool steel
Application:
tools with increased wear resistance, operating at moderate and significant pressures without heating the cutting edge
Chemical composition of U13A material in percentage terms
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Cu |
| 1.26 — 1.34 | 0.17 — 0.33 | 0.17 — 0.28 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.018 | up to 0.025 | up to 0.2 | up to 0.2 |
Mechanical properties of U13A at a temperature of 20oC
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| The tape is annealed. | 0.08 — 3 | 900 |
Foreign analogs of U13A
The table shows exact and similar analogues.
| Japan | France | Italy | Bulgaria | Hungary | Poland | Czech |
| JIS | AFNOR | UNI | BDS | MSZ | PN | CSN |
Explanation of symbols, abbreviations, parameters
| Mechanical properties : | |
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] |
| sT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, [%] |
| y | — Relative narrowing, [%] |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
| Physical properties: | |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o— T), [1/degree] |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o—T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
Other brands in this category:
metalloconstruction.ru
International analogues of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant steels
Corrosion-resistant steels
| Europe (EN) | Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) | Japan (JIS) | CIS (GOST) |
| 1.4000 | X6Cr13 | 410S | SUS 410 S | 08Х13 |
| 1.4006 | X12CrN13 | 410 | SUS 410 | 12Х13 |
| 1.4021 | X20Cr13 | (420) | SUS 420 J1 | 20Х13 |
| 1.4028 | X30Cr13 | (420) | SUS 420 J2 | 30Х13 |
| 1.4031 | X39Cr13 | SUS 420 J2 | 40Х13 | |
| 1.4034 | X46Cr13 | (420) | 40Х13 | |
| 1.4016 | X6Cr17 | 430 | SUS 430 | 12Х17 |
| 1.4510 | X3CrTi17 | 439 | SUS 430 LX | 08Х17Т |
| 1.4301 | X5CrNI18-10 | 304 | SUS 304 | 08Х18Н10 |
| 1.4303 | X4CrNi18-12 | (305) | SUS 305 | 12Х18Н12 |
| 1.4306 | X2CrNi19-11 | 304 L | SUS 304 L | 03Х18Н11 |
| 1.4541 | X6CrNiTi18-10 | 321 | SUS 321 | 08Х18Н10Т |
| 1.4571 | X6CrNiMoTi17-12-2 | 316 Ti | SUS 316 Ti | 10Х17Н13М2Т |
Heat-resistant steel grades
| Europe (EN) | Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) | Japan (JIS) | CIS (GOST) |
| 1.4878 | X12CrNiTi18-9 | 321H | 12Х18Н10Т | |
| 1.4845 | X12CrNi25-21 | 310 S | 20Х23Н18 |
High speed steel grades
| steel grade | Analogues in US standards | ||
| CIS countries GOST | Euronorms | ||
| R0 M2 SF10-MP | — | — | A11 |
| R2 M9-MP | S2-9-2 | 1.3348 | M7 |
| R2 M10 K8-MP | S2-10-1-8 | 1.3247 | M42 |
| R6 M5-MP | S6-5-2 | 1.3343 | M2 |
| R6 M5 K5-MP | S6-5-2-5 | 1.3243 | — |
| R6 M5 F3-MP | S6-5-3 | 1.3344 | M3 |
| R6 M5 F4-MP | — | — | M4 |
| R6 M5 F3 K8-MP | — | — | M36 |
| R10 M4 F3 K10-MP | S10-4-3-10 | 1.3207 | — |
| R6 M5 F3 K9-MP | — | — | M48 |
| R12 M6 F5-MP | — | — | M61 |
| R12 F4 K5-MP | S12-1-4-5 | 1.3202 | — |
| R12 F5 K5-MP | — | — | T15 |
| R18-MP | — | — | T1 |
Alloying - the mechanism of action of alloying elements
It is difficult to decipher steels. Materials science studies this subject comprehensively.
The content of alloying additives in steel can vary within wide limits, depending on what properties need to be imparted to the metal. Thus, nickel and chromium can be present in steel in amounts up to 1%, in some cases more. Molybdenum, vanadium, titanium and niobium - 0.1-0.5%, manganese and silicon - from 1% or more.
The impact of alloying additives in any case is associated with distortion of the iron crystal lattice and the introduction of foreign atoms of a different size into it.
How is it easier to decipher steels (materials science)? The table provides useful information.
| Element | Designation | Chem. sign | Influence of an element on the properties of metals and alloys |
| Nickel | N | Ni | Nickel imparts corrosion resistance to alloys through strengthening the bonds between the nodes of the crystal lattice. The enhanced hardenability of such alloys determines the stability of properties over a long period of time. |
| Chromium | X | Cr | Improvement in mechanical properties - increased strength and yield - is due to an increase in the density of the crystal lattice |
| Aluminum | YU | Al | It is fed into the metal stream during casting for deoxidation, most of it remains in the slag, but some of the atoms pass into the metal and distort the crystal lattice so much that this leads to a multiple increase in strength characteristics. |
| Titanium | T | Ti | It is used to increase the heat resistance and acid resistance of alloys. |
Structural steel
| steel grade | Analogues in US standards | ||
| CIS countries GOST | Euronorms | ||
| 10 | C10E | 1.1121 | 1010 |
| 10XGN1 | 10 HGN1 | 1.5805 | — |
| 14 ХН3 М | 14 NiCrMo1-3-4 | 1.6657 | 9310 |
| 15 | C15 E | 1.1141 | 1015 |
| 15 G | C16 E | 1.1148 | 1016 |
| 16 HG | 16 MnCr5 | 1.7131 | 5115 |
| 16XGR | 16Mn CrB5 | 1.7160 | — |
| 16 CGN | 16NiCr4 | 1.5714 | — |
| 17 G1 S | S235J2G4 | 1.0117 | — |
| 17 ХН3 | 15NiCr13 | 1.5752 | E3310 |
| 18 HGM | 18CrMo4 | 1.7243 | 4120 |
| 18 X2 N2 M | 18CrNiMo7-6 | 1.6587 | — |
| 20 | C22E | 1.1151 | 1020 |
| 20 XM | 20MoCr3 | 1.7320 | 4118 |
| 20 HGNM | 20MoCr2-2 | 1.6523 | 8617 |
| 25 | C25E | 1.1158 | 1025 |
| 25 XM | 25CrMo4 | 1.7218 | 4130 |
| 28 G | 28Mn6 | 1.1170 | 1330 |
| 30 | C30E | 1.1178 | 1030 |
| 34 X | 34Cr4 | 1.7033 | 5130 |
| 34 X2 N2 M | 34CrNiMo6 | 1.6582 | 4340 |
| 35 | C35E | 1.1181 | 1035 |
| 36 HNM | 36CrNiMo4 | 1.6511 | 9840 |
| 36 X2 N4 MA | 36NiCrMo16 | 1.6773 | — |
| 40 | C40E | 1.1186 | 1040 |
| 42 XM | 42CrMo4 | 1.7225 | 4140 |
| 45 | C45E | 1.1191 | 1045 |
| 46 X | 46Cr2 | 1.7006 | 5045 |
| 50 | C50E | 1.1206 | 1050 |
| 50 HGF | 50CrV4 | 1.8159 | 6150 |