GOSTs and specifications for steel
GOST 1133-71 “Forged steel round and square. Assortment"; GOST 12766.4-77 “Rolled long products from precision alloys with high electrical resistance. Technical conditions.”; GOST 18143-72 “Wire made of high-alloy corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant steel. Technical conditions.”; GOST 18907-73 “Work-worked, heat-treated, ground rods made of high-alloy and corrosion-resistant steel. Technical conditions.”; GOST 25054-81 “Forgings made of corrosion-resistant steels and alloys. General technical conditions.”; GOST 4986-79 “Cold-rolled strip made of corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant steel. Technical conditions"; GOST 5582-75 “Corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant thin-sheet rolled products. Technical conditions"; GOST 5632-72 “High-alloy steels and corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant alloys. Marks"; GOST 5949-75 “Sorted and calibrated steel, corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant. Technical conditions"; GOST 7350-77 “Corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant thick sheet steel. Technical conditions"; GOST 9940-81 “Hot-deformed seamless pipes made of corrosion-resistant steel. Technical conditions"; GOST 9941-81 “Cold- and heat-deformed seamless pipes made of corrosion-resistant steel. Technical conditions"; TU 14-1-2186-77; TU 14-1-1024-81; TU 14-1-1081-74; TU 14-1-1141-74; TU 14-1-1154-74; TU 14-1-1160-74; TU 14-1-1180-74; TU 14-1-1183-74; TU 14-1-1190-75; TU 14-1-1197-75; TU 14-1-1214-82; TU 14-1-1215-75; TU 14-1-1303-75; TU 14-1-1494-75; TU 14-1-1497-75; TU 14-1-1531-75; TU 14-1-1541-75; TU 14-1-1554-75; TU 14-1-1644-76; TU 14-1-1655-75; TU 14-1-1671-76; TU 14-1-170-72; TU 14-1-1731-76; TU 14-1-1747-76; TU 14-1-1754-76; TU 14-1-1785-76; TU 14-1-1846-76; TU 14-1-1848-75; TU 14-1-1905-76; TU 14-1-1964-77; TU 14-1-2070-77; TU 14-1-2071-77; TU 14-1-2075-77; TU 14-1-2075-87; TU 14-1-2111-77; TU 14-1-2121-77; TU 14-1-2131-77; TU 14-1-2132-77; TU 14-1-2134-77; TU 14-1-2144-77; TU 14-1-2149-77; TU 14-1-2176-77; TU 14-1-2227-77; TU 14-1-2230-77; TU 14-1-2240-77; TU 14-1-225-72; TU 14-1-2260-77; TU 14-1-2261-77; TU 14-1-230-72; TU 14-123-134-95; TU 14-1-2396-78; TU 14-1-240-72; TU 14-1-2421-78; TU 14-1-2450-78; TU 14-1-2452-79; TU 14-1-2455-78; TU 14-1-2475-78; TU 14-1-2476-78; TU 14-1-2478-78; TU 14-1-2606-79; TU 14-1-2674-79; TU 14-1-2692-79; TU 14-1-2702-79; TU 14-1-2715-79; TU 14-1-284-72; TU 14-1-286-72; TU 14-1-2879-80; TU 14-1-2922-80; TU 14-1-2973-80; TU 14-130-280-96; TU 14-1-3039-80; TU 14-1-3041-80; TU 14-1-3049-80; TU 14-130-60-73; TU 14-1-3071-80; TU 14-1-3109-81; TU 14-131-195-77; TU 14-131-224-75; TU 14-131-404-78; TU 14-1-3140-81; TU 14-1-3148-81; TU 14-1-3164-81; TU 14-131-685-86; TU 14-131-755-85; TU 14-131-756-88; TU 14-131-764-88; TU 14-131-844-91; TU 14-1-3190-81; TU 14-1-3191-81; TU 14-1-3230-81; TU 14-1-3233-81; TU 14-1-3239-81; TU 14-1-3262-81; TU 14-1-3281-81; TU 14-1-3291-81; TU 14-134-277-91; TU 14-1-3490-82; TU 14-1-3528-83; TU 14-1-3546-83; TU 14-1-3547-83; TU 14-1-3587-83; TU 14-1-3622-83; TU 14-1-3639-83; TU 14-1-3652-83; TU 14-1-3660-83; TU 14-1-3686-83; TU 14-1-3760-84; TU 14-1-3768-84; TU 14-1-377-72; TU 14-1-3801-85; TU 14-1-3812-84; TU 14-1-3856-84; TU 14-1-3880-84; TU 14-1-3909-85; TU 14-1-3918-85; TU 14-1-3996-85; TU 14-1-4009-85; TU 14-1-4017-85; TU 14-1-4035-85; TU 14-1-4042-85; TU 14-1-4056-85; TU 14-1-4082-86; TU 14-1-4105-86; TU 14-1-416-72; TU 14-1-4202-87; TU 14-1-4289-87; TU 14-1-4296-87; TU 14-1-4319-87; TU 14-1-4362-87; TU 14-1-4363-87; TU 14-1-4372-87; TU 14-1-4479-88; TU 14-1-4628-89; TU 14-1-4645-89; TU 14-1-4646-89; TU 14-1-4673-89; TU 14-1-4684-89; TU 14-1-4719-89; TU 14-1-4723-89; TU 14-1-4724-89; TU 14-1-4730-89; TU 14-1-4734-89; TU 14-1-4745-89; TU 14-1-4795-90; TU 14-1-4800-90; TU 14-1-4870-90; TU 14-1-4881-90; TU 14-1-4896-90; TU 14-1-489-76; TU 14-1-490-72; TU 14-1-4913-90; TU 14-1-493-72; TU 14-1-4978-91; TU 14-1-4998-91; TU 14-1-5014-91; TU 14-1-5015-91; TU 14-1-5021-91; TU 14-1-5072-91; TU 14-1-5076-91; TU 14-1-5155-92; TU 14-1-5156-92; TU 14-1-5191-92; TU 14-1-5201-93; TU 14-1-5203-93; TU 14-1-5258-94; TU 14-1-52-71; TU 14-1-5350-97; TU 14-1-5361-98; TU 14-1-5366-98; TU 14-1-565-84; TU 14-159-252-95; TU 14-159-93-77; TU 14-1-625-73; TU 14-1-692-73; TU 14-1-756-73; TU 14-1-810-73; TU 14-1-833-74; TU 14-1-894-74; TU 14-1-895-74; TU 14-1-911-74; TU 14-1-927-74; TU 14-1-941-74; TU 14-1-952-74; TU 14-1-975-74; TU 14-226-130-92; TU 14-226-141-98; TU 14-3-1129-82; TU 14-3-1227-83; TU 14-3-1275-83; TU 14-3-1320-85; TU 14-3-1478-87; TU 14-3-1591-88; TU 14-3-1711-90; TU 14-3-1854-92; TU 14-3-396-75; TU 14-3-415-75; TU 14-3-59-72; TU 14-3-694-78; TU 14-3-696-78; TU 14-3-751-78; TU 14-3-763-78; TU 14-3-822-79; TU 14-4-3071-80; TU 302.02.095-90; TU 48-0814-11/0-83; TU 48-0815-80-92; TU 48-0815-84-92; GOST 10160-75 “Precision soft magnetic alloys. Technical conditions.”; GOST 2590-88 “Hot-rolled round steel. Assortment."; GOST 4543-71 “Rolled products from alloy structural steel. Technical conditions.”; GOST 4405-75 “Hot-rolled and forged strips made of tool steel. Assortment."; GOST 14119-85 “Rods made of precision alloys for elastic elements. Technical conditions.”; GOST 5950-2000 “Rods, strips and coils of alloy tool steel. General technical conditions.”; GOST 19265-73 “Rods and strips made of high-speed steel. Technical conditions.”; GOST 28393-89 “Rods and strips made of high-speed steel produced by powder metallurgy. General technical conditions.”; GOST 8479-70 “Forgings from structural carbon and alloy steel. General technical conditions.”; GOST 14955-77 “High-quality round steel with special surface finishing. Technical conditions.”; GOST 2590-2006 “High-rolled hot-rolled round steel products. Assortment."; GOST 2591-2006 “High-rolled square steel products. Assortment."; GOST 7417-75 “Calibrated round steel. Assortment."; GOST 4405-75 “Hot-rolled and forged strips made of tool steel. Assortment."; GOST 8559-75 “Square calibrated steel. Assortment."; GOST 8560-78 “Calibrated hexagonal rolled products. Assortment."; GOST 1133-71 “Forged steel round and square. Assortment."; GOST 5632-72 “High-alloy steels and corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant alloys. Marks."; GOST 103-2006 “High-rolled hot-rolled steel strip. Assortment."; GOST 5949-75 “Sorted and calibrated steel, corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant. Technical conditions.”; GOST 2879-2006 “Hot-rolled hexagonal long steel products. Assortment."; TU 14-11-245-88 “High precision shaped steel profiles. Technical conditions.”; OST 3-1686-90 “Blanks made of structural steel for mechanical engineering. General technical conditions.”; GOST 10994-74; GOST 1414-75; TU 14-1-3283-81; TU 14-1-4492-88 “Blums and hot-rolled square billets made of high-quality and high-quality carbon steel, alloyed and high-alloyed and alloys”; TU 14-1-3904-84 “Forged square and rectangular blanks made of precision alloys. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-5277-94; TU 14-1-2252-2007; GOST 14117-85 “Tape made of precision alloys for elastic elements. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4693-89 “Hot-rolled and hot-rolled turned rods from structural micro-alloyed calcium-containing steels for controlled forging”; GOST 14080-78 “Tape made of precision alloys with a given temperature coefficient of linear expansion. Technical specifications""; OST 95 10441-2002 “Equipment for working with radioactive media. Welding. Basic provisions""; GOST 14081-78 “Wire made of precision alloys with a specified temperature coefficient of linear expansion. Technical specifications""; TU 14-136-344-98 “Calibrated carbon and alloyed bismuth-containing steel with high cutting machinability””; GOST 14118-85 “Wire made of precision alloys for elastic elements. Technical specifications""; GOST 801-78 “Bearing steel. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1213-75 “Hot-rolled and forged, square and rectangular billets made of high-quality carbon and alloy steel. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4487-88 “Rods made of alloyed hard magnetic steel. Technical specifications""; GOST 12766.1-90 “Wire made of precision alloys with high electrical resistance. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-5022-91 “Rods and coils from alloys of grades 25Kh15KYUBF (EK33, 25Kh15K1) and 22Kh15KTF (EK159, 22Kh15KA). Technical specifications""; GOST 14118-85 “Wire made of precision alloys for elastic elements. Specifications" "; ST TsKBA 016-2005 “Pipeline fittings. Heat treatment of parts, workpieces and welded assemblies made of high-alloy steels, corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant steels""; GOST 12766.2-90 “Tape made of precision alloys with high electrical resistance. Technical specifications (with Amendment No. 1)""; TU 1-83-77-90; TU 14-1-3182-81 “Hot-rolled and forged rods from alloy 58NHVKTBYU-VI (EP877-VI)”; GOST 800-78 “Bearing pipes. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2830-79 “Rods from alloys 79NM-P, 16Kh-IP, melted by plasma-arc remelting. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-3680-83 “Pipe billet from evacuated chromium steel grades ShKh15-V and ShKh15SG-V. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-3911-85 “Pipe blank made of bearing steel. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1875-76; TU 14-1-3397-82 “Hot-rolled and forged rods made of maraging corrosion-resistant steel with increased machinability by cutting grade 04Х13Н8МТУЕ””; TU 14-1-4495-88 “High-precision round bars made of high-strength steel ATs28KhGN2AFB. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1054-74 “Hot-rolled sheets of hard magnetic steel grades EX3 and EX5K5. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2244-2005; TU 14-1-3045-80 “Rods made of corrosion-resistant steel. Brand 11Х18М-ШД double remelting (electroslag + vacuum arc). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-3367-82 “Hot-rolled sheets from alloy grades KHN85MYU-VI (EP797-VI), KHN85MYU-ID (EP797-ID). Technical specifications""; TU 14-134-295-91 “Hot-rolled rods with subsequent grinding from corrosion-resistant steel grade A10Х16Н15Т (ChS117) with high cutting machinability””; TU 14-1-3578-83 “Cold-rolled sheets from alloy grades KHN85MYU-VI (EP797-VI), KHN86MYU-ID (EP797-ID). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-3823-84; TU 14-1-4398-88; TU 14-1-4963-91 “Welding wire made of alloy grade Sv-KhN85MYU-VI (EP797-VI). Technical specifications""; TU 14-19-24-87; GOST 10533-86 “Cold-rolled strip made of thermobimetals. Technical specifications""; GOST 8803-89 “The thinnest round wire made of precision alloys with high electrical resistance for resistive elements. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1373-75 “Cold-rolled strip made of alloy 36НХТУ8М. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1968-77; TU 14-1-2244-2005; TU 14-123-92-2011; TU 14-1-2554-78 “Pipe blank for seamless thin-walled pipes from alloys 36NKhTYu (EI702) and 36NKhTYu5M-VI (EP51-VI). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2740-2010; TU 14-1-2785-79; TU 14-1-279-71 “Cold-rolled strip and cold-drawn wire from alloy 36NKhTYUM8. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-279-72 “Cold-rolled strip made of alloy 36НХТУ8М (EP52). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2880-80 “Cold drawn wire from alloy 36НХТУ8М (EP52). Technical specifications""; TU 14-134-270-90; TU 14-134-357-96 “Rolled products from alloy 38NХМ-VI (ChS129-VI). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-3853-84 “Cold-rolled strip made of precision alloy 12KhNKMTU (SP-22). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-41-71 “Micron wire made of N80ХУД-VI alloy. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4456-88 “Cold-rolled strip made of alloy grade 68NHVKTYU-VI (EP578-VI). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4470-88 “Rods made of alloy 68NHVKTYU-VI (EP578-VI). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4488-88 “Cold-drawn wire from alloy grade 68NHVKTYU-VI (EP578-VI). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4722-89 “Cold-rolled strip made of precision alloy grade 12KhNKMTU (SP-22). Technical specifications""; TU 14-165-301-89 “Spring blanks for wind-up toys made of alloy 12HNKMTU (SP-22). Technical specifications""; TU 14-19-106-90 “Rods made of corrosion-resistant steel grade 60Х13С-ШД with standardized carbide sizes. Technical specifications""; TU 14-3-379-75; TU 14-1-2899-80 “Alloy rods. Grade 49KFA-VI vacuum induction smelting. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-314-72 “Hot-rolled and forged rods from corrosion-resistant automatic steel grades 40Х18Н2М (EP378), 40Х18Н2М-ВД (ЭП378-ВД)”; TU 14-1-3177-81 “Cold drawn wire from alloy 38NKD. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-3761-84 “Cold-drawn wire from alloy KhN50MGYu (EK1). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-5029-91 “Hot-rolled and forged rods from precision alloy grade 34NKD-VI. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-5048-91 “Forgings from precision alloy grade 34NKD-ID. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-604-73; TU 14-1-886-74 “Rods made of non-magnetic automatic corrosion-resistant steel grade 07Х17Н16 (EP626)”; GOST R 51397-99 “Tape and wire made of special alloys for connecting and implantable elements of products for cardiovascular surgery. General technical conditions""; OST 4-020.065-78; ST TsKBA 010-2004 “Pipeline fittings. Forgings, stampings and rolled products. Technical requirements""; TU 14-1-1124-74 “Tape made of precision alloy grade 36NHTYU (EI702). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1129-74 “Rods made of alloy grade (EI702) 36НХТУ. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1285-75 “Cold-drawn wire from 40KKhNM alloy. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2217-2013 “Hot-rolled and hot-rolled rolled products made of alloy structural steel with high cutting machinability””; TU 14-1-2597-79 “Strip made of alloy 10SYU-VI. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2858-79 “Sheets made of precision alloy grade 36NHTYU (EI702)”; TU 14-134-433-2009 “Hot-rolled round steel turned with a cutter from economically alloyed steel grade AS18KhGT””; TU 14-1-3727-84 “Hot-rolled strip from precision alloys of grades 42N, 47ND. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4098-86 “Cold drawn wire from KhN20YUS alloy (EK11). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4312-87 “Cold-rolled strip (roll) in rolls from alloys 47ND and 42N. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4464-88; TU 14-1-4618-89 “Cold-rolled strip made of alloy 36НХТУ. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-469-73 “Thin sheets of 16YUKH-VI alloy of vacuum induction melting. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-899-74 “Cold drawn wire from 40KKhNM alloy. Technical specifications""; OST 1 90005-91 “Steels and alloys. Indicators of tensile strength and hardness. Layer depth during chemical-thermal treatment""; TU 14-1-1060-74 “Cold drawn wire from alloy 46ХНМ (EP630). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2116-77 “Sheets made of precision alloy 46ХНМ (47ХНМ-2, EP630). Specifications" "; TU 14-1-2423-78; TU 14-1-2556-78 “Forged slabs from alloy 46ХНМ (EP630). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2572-78 “Cold-rolled strip made of alloy 47ХНМ-VI. Specifications" "; TU 14-1-3074-80 “Rolled products, hot-rolled sheets, alloy wire and strip (EP218) and 45NХТ-P (EP218-P)”; TU 14-1-3123-81 “Slabs from alloy grade 46ХНМ (EP630). Specifications" "; TU 14-1-3124-81 “Sheets made of precision corrosion-resistant alloy. Brand 46ХНМ (EP630). Specifications" "; TU 14-1-3125-81 “Pipe blank made of precision alloy grade 46ХНМ (EP630). Specifications" "; TU 14-1-3264-81 “Rods made of alloy 32NKD-VD for vacuum arc remelting. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-3494-82 “Rods made of bearing steel grade ШХ15СГ-Ш for railway bearings. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-3505-82 “Tape made of alloy grade 47ХНМ-VI. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4131-86 “Cold drawn wire from alloy 40KNB (EP966). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4278-87 “Forged rods and hot-rolled sheets from alloy 12YU-VI. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4535-88 “Cold-rolled strip made of N50K10-IL alloy. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4605-89 “Hot-rolled rods made of alloy structural steel grades 17ХГ and АЦ16ХГ”; TU 14-1-801-73 “Rods made of ball-bearing steel grade ШХ20СГ. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-918-74 “Forged rods and hot-rolled sheets from alloy 5Х14В (5ХВ14). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-999-73 “Rods made of alloy 46ХНМ (EP630). Specifications" "; TU 14-3-1045-81 “Cold-deformed seamless pipes from alloy 46ХНМ (EP630). Technical specifications""; TU 14-3-1082-82 “Hot-pressed pipes from alloy grade 46ХНМ (EP630). Technical specifications""; TU 8009.00.001; TU 8009.00.002; TU 8009.00.022; TU 14-1-2526-78 “Pipe blank made of alloy 36NH-Sh (EP713-Sh). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2543-78 “Pipe blank made of alloy 36NH-Sh (EP713-Sh). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-3125-81 “Pipe blank made of precision alloy grade 46ХНМ (EP630). Technical specifications""; TU 14-131-987-2002 “Rods with special surface finishing made of 42ХНМ alloy. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4422-88 “Hot-rolled and forged rods from alloys of grades 32NK-VI (EP475-VI), 32NK-EL (EP475-EL), 32NK-IL (EP475-IL). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4425-88 “Hot-rolled sheets, cold-rolled strip made of 32NKA alloy. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-4743-89 “Pipe blank made of alloy 32NK-IL (EP475-IL). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-5436-2001 “Rods made of 42ХНМ alloy. Technical specifications""; TU 14-159-215-92 “Seamless cold-deformed and hot-deformed pipes from alloy 32NK-IL (EP 475-IL). Technical specifications""; GOST 21022-75 “Chromium steel for precision bearings. Technical specifications""; GOST 4727-83 “Bearing wire. Technical specifications""; GOST 808-70 “Rolled steel tape for twisted rollers of bearings. Technical specifications""; OST 4-020.030-78; TU 1142-250-00187211-96; TU 14-1-1185-75 “Hot-rolled and forged rods from alloy 49KF. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1204-74 “Sheets made of 79NM alloy. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1271-75 “High precision shaped steel profiles. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1286-75 “Cold-rolled strip (roll) from alloy 29NK. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1306-75 “Cold-rolled micro-tape made of alloys 79NM and 77NMD. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1328-75 “Cold-rolled strip made of 50NP-IL alloy. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1500-75 “Bearing steel grade ШХ15Ф-Ш (ЭИ760-Ш) electroslag remelted. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1530-75; TU 14-1-1530-75 “Forgings made of steels and alloys for machine parts. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1708-76 “Cold-rolled strip from alloys 77NMD-VI and 80NM. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1740-75 “Tape (roll) made of alloy 79NM and steel grade 09Х15Н8У (Х15Н9У). Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-1833-76 “Rolled slabs from steel 09Х15Н8У (Х15Н9У), 65С2ВА, Sv-08Х19Н10Г2Б (ЭИ898) and alloy 79НМ. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2032-76 “Hot-rolled strips made of ball-bearing steel grade ShKh15. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-232-72; TU 14-1-2357-78 “Pipe billet from alloy 29NK-VI and 29NK. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2398-78 “Roll rod made of ShKh15 steel, sorbitized from rolling heating. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2425-78 “Thick sheet steel. Brand ШХ15. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2545-78 “Slabs from precision alloys of grades 79NM and 29NK. Technical specifications""; TU 14-1-2545-78 “Slabs from precision alloys of grades 79NM and 29NK. Specifications" "; TU 14-1-2664-79 “Cold rolled strip in alloy rolls. Brand 79NM. Technical specifications""; TU 14-131-851-92 “Rolled products from precision alloys 79NM, 44NHMT, 52K13F. Technical specifications""; TU 14-132-173-88 “Calibrated ball-bearing steel grade ShKh15 with ground surface. Specifications "" "; TU 14-1-3815-84 “Steel is hot-rolled, trotted, calibrated brand ShH15 in riots. Experimental party. Specifications "" "; TU 14-1-4039-85; TU 14-1-4346-87 “Cold ribbon from an alloy 29K. Specifications "" "; TU 14-1-468-73; TU 14-1-4786-90 “A tape from a precision magnetic soft alloy of a brand 50n. Specifications "" "; TU 14-1-5088-91 “A ribbon from a precision alloy with a given temperature coefficient of linear expansion of the brand 29NK. Specifications "" "; TU 14-1-5358-98 “The rental is cold and with a special surface finish made of steel of the brand SHX15-V for cold landing. Specifications "" "; TU 14-1-699-73 “A blank of steel of the brand ShH15. Specifications "" "; TU 14-1-841-73; TU 14-1-878-74; TU 14-19-18-87 “Steel sheet hot-rolled brand shh15. Specifications "" "; TU 14-22-139-99; TU 14-3-1203-83 “Bearing pipes from vacuum steel SHX15-B. Specifications "" "; TU 14-3-256-74 “Pipes Special-Wrong-resistant cold-deformed from an alloy of brand 50n. Specifications "" "; TU 14-3-335-75 “Pipes seamless hot-rolled from steel brand ShH15. Specifications "" "; TU 14-3-972-80 “Cold-formed pipes of 29NK and 29NK-vi alloys”; TU 14-4-1112-80 “Cold ribbon made of steel SHX15 for parts of electric writing machines. Specifications "" "; TU 14-4-563-74 “Round wire made of steel of the brand ShH15-SSR for super-carbon dash bearings” ”; TU 14-1-4979-91 “Cold ribbon from the alloy of the Ev6 brand. Specifications "" "; TU 14-1-4081-86 “Pipe workpiece from the heat-resistant alloy of the brand KhN55MVC-VI (ChS57-VI)”; TU 14-1-4747-89 "Eucks from the heat-resistant alloy of the brand KhN55MVC-VI (ChS57-V)"; TU 807.2634.388-2012 “Processions processed from the alloy KhN55MVC-VI (ChS57-VI) and HN55MVC-DID (ChS57-DID)”; TU 14-1-3663-83 "Forged rods from the heat-resistant alloy of the brand KhN55MVC-vi (ChS57-VI)"; TU 14-1-4392-2013 “Skorolistovaya Cold-rolled rental from an alloy of the KH55MVC-VA brand; TU 14-1-4400-88 “Hot carpet rental from the alloy of the KhN55MVC-VA brand”; TU 14-134-436-2008 “Holstolistova rental from the heat-resistant alloy of the KhN55MVC-VA brand;
Technological properties of 12Х18Н10Т
Chrome-nickel steels 12Х18Н10Т and 08Х18Н10Т, which have become widespread and popular. They are recognized as a sought-after raw material in the production of gas distribution plants with high power and large dimensions and containers for gases (O2, N2, H2, etc.). They are distinguished by good weldability and have the property of increased viscosity at low temperatures. Steel 12Х18Н10Т, which has a high flexibility, is used after cold deformation, which increases strength. The austenite of such steels is not stable, therefore, under the influence of plastic deformation, incomplete martensitic transformation can be observed. Rods are made from steel 12x18n10t, which, unlike bronze rods, are cheaper and widely used in industry.
| Weldability 12Х18Н10Т: | no limits. |
| Flock sensitivity 12Х18Н10Т: | not sensitive. |
20Х13 (2Х13)
- Products made of steel 20Х13 (2Х13) in stock: Circle
- Sheet
- Band
- Square
- Ribbon
- Hexagon
- Forging
Steel 20Х13 (02Х13, 2Х13, EZh2) chromium, corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant, martensitic class
Substitutes: Steel 12Х13, Steel 14Х17Н2
Steel 20X13 is used: for the manufacture of steam turbine blades operating at temperatures up to +580°C; valves, bolts and pipes; parts with increased plasticity, exposed to shock loads and operating at temperatures up to 450-500 ° C; products exposed to mildly aggressive environments at room temperature; solid rolled rings for various purposes; various aircraft parts (carburetor needles, bushings, aircraft gears, parts of direct fuel injection equipment and compressor blades, heat-treated for HRC hardness
The main purpose of 20x13 is all kinds of components and parts for power engineering. This includes elements of turbine units and furnaces, fittings for cracking units, fastening joints operating at a temperature of 550 ºС.
Rating: 0/5 — 0 votes
Application of steel 12x18n10t
The linear expansion coefficient of 12x18n10t and the thermal conductivity coefficient of 12x18n10t determine the possibility of using the material in the manufacture of products that can be operated at high temperatures. The chemical and oil industries use containers and elements made from 12x18n10t that come into contact with petroleum products and various chemicals. In mechanical engineering, various products are made from 12x18n10t that will be used in high humidity and exposure to chemicals. In the fuel industry and energy industry, 12x18n10t steel is used because it can withstand high temperatures. There are quite a lot of requirements for products used in the food industry. The metal should not interact with food and drinks, so 12x18n10t is used.
Sheets 12x18n10t are widely used as substrates for rubbing parts, replacing brass sheets. Cold-rolled sheets and strips made of heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant steel 12Х18Н10Т are used for the manufacture of structures resistant to aggressive environments and parts for machines.
When producing Ni steels, two heat treatment modes are usually used. When performing normalization, the first stage is carried out at a temperature of approximately 9000C to equalize the presence of nickel in austenite. The second stage of normalization, carried out at 8000C, is intended for crushing the austenite grain. For such steels, due to the high nickel content, ferritic transformation occurs at approximately 5000C, which makes it possible for the γ→α change to be carried out during air cooling, using the martensitic or bainitic method. After heat treatment, microstructures of the martensitic or bainitic type are formed in the steel. High tempering transforms the microstructure in the range of 550...6000C into dispersed sorbitol, which has a certain proportion of persistent retained austenite.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the material?
The pros and cons of the 20X13 alloy, the possibility of its use are taken into account at the stage of designing mechanical engineering products. Its main advantages are:
- heat resistance;
- low thermal conductivity;
- high corrosion resistance;
- a combination of qualities - hardness, plasticity, viscosity.
A large percentage of chromium and carbon content in products is the cause of the main problem that arises when using the alloy - low weldability. For its high-quality implementation, special heat treatment of products is required.
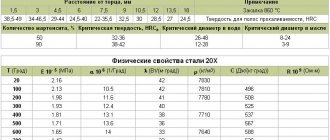
Physical properties of 12Х18Н10Т
| T | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| hail | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 1.98 | 15 | 7920 | 725 | ||
| 100 | 1.94 | 16.6 | 16 | 462 | 792 | |
| 200 | 1.89 | 17 | 18 | 496 | 861 | |
| 300 | 1.81 | 17.2 | 19 | 517 | 920 | |
| 400 | 1.74 | 17.5 | 21 | 538 | 976 | |
| 500 | 1.66 | 17.9 | 23 | 550 | 1028 | |
| 600 | 1.57 | 18.2 | 25 | 563 | 1075 | |
| 700 | 1.47 | 18.6 | 27 | 575 | 1115 | |
| 800 | 18.9 | 26 | 596 | |||
| 900 | 19.3 |
Substitutes
In such a widely demanded field as metallurgy, there cannot be interchangeable products. For any type of steel there is a substitute that fully or partially matches the original in its characteristics and composition. For steel 20Х13 there are the following substitute grades:
- 12X13 is a steel with a lower carbon content, which is somewhat compensated by a higher content of silicon and manganese.
- 14Х17Н2 is an alloy richer in various additives, characterized by a slightly higher carbon content and additional additions of titanium, copper and nickel. A similar grade of steel has better characteristics and, for example, the same steel sheet of this grade will be more preferable for the manufacture of something.
Foreign analogues
The need for metal-containing alloys that are resistant to heat is spreading everywhere, so different countries on different continents are setting up their own production of steels, often very similar in composition to their foreign counterparts. For steel 20Х13 there are the following analogues abroad:
- United States of America - 420 and S42000;
- Japan - SUS420J1;
- Europe - X20Cr13;
- China - 2Cr13.
Knowing these names, anyone will be able, regardless of their geographic location, to purchase a product made from the desired grade of steel in the nearest store.
Technical characteristics of metal 20Х13
Metal of this grade has high manufacturability under conditions of plastic hot deformation. Recommended deformation intervals are:
- about 1100 degrees at the beginning;
- from 875 to 950 degrees at the end.
Heating for rolling or forging should be carried out gradually up to 780 degrees, and after deformation, slow cooling should also be used.
The softening heat treatment of this type of material is annealing at a temperature of about 800 degrees. Cooling with the furnace should be up to 500 degrees, and the final heat treatment-hardening should be carried out at a temperature of about 1000 degrees with oil cooling or outdoors with tempering for corrosion resistance and the required hardness.
The manufacturability of the material is possible both with hot and cold deformation. The steel has a martensitic class, and its critical points are as follows:
- A c1 = 820 degrees;
- A c3 = 950 degrees.
The microscopic structure of the metal in its quenched form includes martensites and carbides, and in the annealed form it is a mixture of carbide and high-chromium ferrite. If you increase the tempering temperature to 450 degrees, the strength is significantly reduced and the ductility of the material increases. But corrosion resistance indicators are also decreasing.
Other brands from this
Please note that this information about the 20X13 brand (another designation 2X13) is provided for informational purposes. The parameters, properties and composition of real material grade 20Х13 (another designation 2Х13) may differ from the values given on this page. More detailed information about grade 20Х13 (another designation 2Х13) can be found on the information resource Brand of steel and alloys. You can check with our managers for information about the availability, delivery times and cost of materials. If you find inaccuracies in the description of materials or errors found, please inform the site administrators using the feedback form. Thanks in advance for your cooperation!
Steel production
However, in its original form, steel is not very suitable for use, so metallurgical plants not only smelt the alloy, but also give it a certain shape. In this way, several goals can be achieved at once:
- Formed steel is easier to store.
- It is much easier to transport.
- Buyers know in advance which form factor of the purchased product they prefer.
For steel 20Х13 GOSTs provide several molding options:
- Rods of various calibers.
- Steel strip.
- Steel tape.
- Steel sheet of various thicknesses.
- Forging.
- Pipes of various diameters.
- Steel wire.
Compound
20x13 is corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant grade. The basis of its phase structure is represented by martensite. The brand has a metallic luster with a greenish tint characteristic of this class.
The chemical composition is regulated by the state standard GOST 5632-72, according to which 20x13 steel consists of the following elements:
- Carbon occupies 0.16-0.25% of the total composition. The content of the element greatly affects the strength and technological characteristics of steel. Iron carbides have increased hardness, and they also make it possible to strengthen steel through heat treatment. The reverse effect of such alloying is a deterioration in ductility and weldability.
- Chromium 12-14%. Increases the wear resistance of steel due to the formation of chromium oxides on its surface. In addition, it has a beneficial effect on the ability of the metal to thermally harden and increases resistance to corrosion. Steels alloyed with chromium better withstand loads at elevated temperatures.
- Silicon (up to 0.6%) and manganese (up to 0.6%) are mandatory additives for steel. They are the main deoxidizers and help remove oxygen from its composition. In addition, these components have a good effect on technological properties, such as ductility and weldability. Manganese, among other things, has a positive effect on surface cleanliness.
- Nickel (up to 0.6%). Its main purpose in alloys is to increase heat resistance. But it is worth noting that its content in 20x13 is insignificant to somehow noticeably affect its characteristics.
- Sulfur (up to 0.0025%) and phosphorus (up to 0.03%) are harmful impurities that significantly reduce the strength properties of steel and are responsible for the occurrence of such an effect as brittleness. Sulfur also increases the alloy's tendency to become red-brittle, which means an increased risk of cracking during pressure treatment. Their inclusion in the alloy is inevitable due to the imperfection of the smelting technology and the purity of the chemical composition of the initial charge.
- The rest of the composition is iron.
Features of welding material 20Х13
The type of steel in question can be welded well by such methods as;
- manual welding;
- electric arc;
- argon-arc automatic.
Expert recommendations state that when automatically welding this steel, it is better to use Sv-10X13 or Sv-06X14 wires. But for electric arc welding, fluxes of the AN 18 or AN 17 types are better suited. But if we are talking about manual electric arc welding, then you can use electrodes of the EF-X13 type together with wires similar to those used in automatic welding.
To prevent cold cracks from appearing in welded joints when welding parts with a thickness of 10 mm or more, as well as thinner ones with rigid fastening, it is necessary to use accompanying or preheating up to a temperature of 400 degrees inclusive. After welding work, the joints or products should be tempered, most often this is done at a temperature of about 700 degrees.
The weldability of this steel is of three types:
- without restrictions, when welding work is performed without heating and subsequent heat treatments;
- limitedly weldable metals that can be welded under heating conditions of approximately 100 degrees and which must necessarily be subjected to heat treatment;
- difficult-to-weld parts; in such cases, in order to obtain a high-quality connection, it is necessary to preheat up to 300 degrees and perform annealing as a heat treatment after welding.
These are the application features of such a material as steel 20X13. Now you will know under what conditions and how to apply and process it correctly.
Chemical composition
In many ways, 20x13 steel resembles its analogues, which also contain a large amount of chromium. The chemical composition is represented by a combination of the following substances:
- Carbon largely determines the hardness and strength of the material, as well as the degree of weldability. In the case under consideration, the carbon concentration can vary from 0.16 to 0.25%.
- Chromium is considered the main alloying element. About 12-14% of this chemical is added to the alloy composition. It is chromium that determines heat resistance and corrosion resistance.
- Manganese and nickel are not the main elements of the alloy in question; their concentration is no more than 0.6%.
Almost all metals contain phosphorus and sulfur. These chemical elements are present in the composition at a concentration of no more than 0.03%.
Stainless steel sheet 20X13
Foreign manufacturers also produce alloys with similar chemical compositions. For example, the Japanese analogue of steel 20x13 was called SUS420J1, the French alloys z20c13 and X20Cr13.