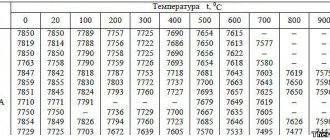
Classification
In the metallurgical industry, more than two hundred types of alloy alloys are distinguished. They differ in the presence of different amounts of additional chemical elements in their composition.
There are four main types of stainless steel.
- Ferritic. These are low-carbon alloys containing more than 20% chromium and less than 0.15% carbon. They have a bulk crystalline structure. Durable, plastic. This type of steel has magnetic properties.
- Austenitic. Corrosion-resistant alloys containing 18% chromium and 8 to 9% nickel. They retain ductility in cold and hot states, are easy to weld, and have high strength. There are unstabilized and stabilized brands. The latter varieties are characterized by the presence of titanium and niobium.
- Martensitic. Steels of this type contain 17% chromium, 0.05% carbon. Metals are ductile, elastic, and do not react with aggressive environments. They are not exposed to high temperatures and are considered a wear-resistant material.
- Combined. There are austenitic-ferritic and austenitic-martensitic steels. The development and production of such alloys is carried out according to customer requirements.
Ferritic alloy grades
Such compounds contain about 30% chromium. The fine-grained structure of the metal is acquired by annealing. These steels include:
- X28.
- 1Х12СУ.
- X25T.
- X17.
- 0Х17Т.
- X18SYU.
The production of ferritic steel goes through the stages of hardening, firing, and subsequently tempering. Due to the fine-grained structure, the alloy can only be heated at a temperature of 180 degrees. An increase in temperature will damage the integrity and make the alloy brittle. Such alloys are used mainly for heat exchange devices.
Stainless steel markings
In Russia, alloying alloys are produced in accordance with GOST 5632-2014. Marking is a combination of numbers and letters. The number at the beginning indicates the carbon content of the alloy. The numbers located after the letters indicate the average mass fraction of the alloying element, which is indicated in the form of letters of the Russian alphabet.
The composition of foreign brands is standardized by the standards existing in the country of origin. AISI, named after the American research institute “The American Iron and Steel Institute,” has become popular in the Russian Federation. The first digit indicates the type of alloy, the next two indicate the serial number in the entire group of this class. The reduced amount of carbon in the AISI system is indicated by an additional letter L.
Correspondence table of popular foreign brands with Russian analogues
| steel grade | GOST 5632-2014 | AISI |
| Ferritic | 08Х13; 12X13; 12Х17 | 409; 410; 430 |
| Austenitic | 12Х18Н10Т; 08Х18Н10; 08Х17Н13М2 | 321; 304; 316 |
| Martensitic | 20Х13; 30Х13; 40 X13 | 420 |
Provider
Are you interested in the processing and production of heat-resistant steel and alloys? The processing and production of heat-resistant steel and alloys from the supplier "Auremo" complies with GOST and international quality standards, the price is optimal. The supplier "Auremo" offers to buy heat-resistant steel and alloys on favorable terms. For wholesale customers the price is preferential. Large selection in stock. Heat-resistant steel and alloys are always available, the price is optimal from the supplier. We are waiting for your orders.
Buy, favorable price
The supplier "Auremo" offers to buy heat-resistant steel and alloys on favorable terms, the price is determined by the technological features of production without including additional costs. The company's website displays the latest information. You can order products with non-standard parameters. The order price depends on the volume and additional delivery conditions. The supplier "Auremo" invites you to buy heat-resistant steel and alloys in bulk or in installments. We have the best price-quality ratio for the entire range of products. It is a profitable supplier in this segment.
Advantages of stainless steels
With the development of economic, scientific and technological progress, the requirements for the quality of materials used in areas of the national economy are growing.
Advantages of alloy metals:
- High level of anti-corrosion properties.
- Compliance with the standards stipulated by fire safety regulations.
- Reliability, long service life without changing technical characteristics.
- Ideal combination with any building materials.
- Variety of surfaces: polished, polished, matte, decorative.
- Wide selection of rolled metal products.
- Ease of processing, molding, and assembly of parts made from this type of steel.
- A wide range of brands with unique properties.
- Environmental safety, hygiene.
The principle of thermal uniform strength
Compare: unlike chrome-plated heat-resistant steel with an oxidation temperature of 750°C, the temperature at which scaling begins in structural and most alloy steels does not exceed 400°C, which is almost 2 times lower than the combustion temperature of birch logs.
But is everything so bad with structural steels? Does it mean that they will burn out twice as fast if their oxidation temperature is lower than Inox steel? No! We have found a solution!
In the production of TMF furnaces, the principle of thermal uniform strength . We increased the thickness of the stove parts subject to the greatest temperature and mechanical load. For stoves made of chrome-plated steel Inox - only 1.5 times to a thickness of 3 mm. And for furnaces made of structural steel - 2 times, and especially loaded ones - 3 times!!!
For example, the bottom of the heater of the Tunguska 2011 Carbon stove is made of 6 mm thick steel, and the lower segment of the closed heater of the Angara 2012 Carbon stove, made of 4 mm thick steel, is additionally protected by a 3 mm thick plate, which in total gives a thickness of 7 mm . In addition, the lower part of the stove fireboxes in the area of the grate is reinforced in a similar way. It is the heat-loaded areas that are protected, which allows you to increase the service life of the stove without practically reducing its thermal efficiency. This is why TMF structural steel furnaces are called “smart furnaces”.
Application
The listed advantages contribute to maintaining a leading position in the rolled metal market. Anti-corrosion alloys are an indispensable material in heavy engineering, energy, oil and gas and agricultural sectors.
The material is in demand in the following areas of the national economy:
- Construction, architecture;
- production of equipment and medical instruments;
- pulp and paper production;
- food industry;
- transport engineering;
- chemical industry;
- electrical power and electronics;
- production of household appliances and household items.
The decorative qualities of stainless metals and the high level of anti-corrosion properties make it possible to use parts and elements made from them for facades, advertising installations, shop windows, and fountains. Railings, doors, stairs, and elevators are made from alloyed material.
Welding features
Modern welding methods make it possible to obtain strong welds that are resistant to the formation of hot cracks on parts made of heat-resistant stainless steels. However, alloys of this type are prone to softening and fracture of the cold weld. To eliminate the disadvantage, general or local heating of the material is carried out in order to minimize the temperature difference at the periphery and at the welding points to reduce stress. After welding, the finished products are tempered for several hours at temperatures up to 2000 °C. As a result of tempering, the main part of the hydrogen dissolved in the structure is removed, and the residual austenite is transformed into martensite.
- Content:
- Which brand of steel is best for a sauna stove?
- Optimal metal thickness for a bathhouse stove
- What electrodes should be used to cook a sauna stove?
Homemade sauna stoves cost on average 3-5 times cheaper than factory products. The savings will be even greater if you do the welding yourself. When making it yourself, you will need to decide on the following:
- What metal to make a sauna stove from?
- What metal thickness will be optimal?
- What type of electrodes should be used to ensure maximum weld strength.
The speed of heating of the steam room, the duration and intensity of operation of a self-made stove depend on the answer to all these questions.
Heat resistant stainless steel
The category of heat-resistant materials includes alloys that are capable of maintaining their structure and not changing their quality characteristics when exposed to temperatures above 550º C. The chemical composition and marking of this type is regulated by GOST 5632 - 2014. According to the production method, such stainless steel can be cast or deformable.
Metals vary in their ability to withstand certain loads at high temperatures. In accordance with these indicators, three types of stainless steel are distinguished.
- Heat resistant stainless steel. Does not corrode at 600°C.
- Heat resistant. Shows inertness to aggressive media at temperatures above 550°C.
- Heat resistant. Resists mechanical loads at 400 - 850°C.
In terms of composition, materials with increased heat resistance are:
- Martensitic. Brands produced using perlite additives. The mixture of metals is hardened at 950 - 1100 ºС. The resulting alloys contain more than 0.15% carbon, 11-17% chromium and small amounts of nickel, tungsten, molybdenum, and vanadium. They do not react with alkalis and acids. Prolonged exposure to a humid environment does not affect their technical characteristics.
- Austenitic. Steels have a homogeneous or heterogeneous structure. The homogeneous composition, which is not subjected to hardening, contains an increased amount of carbon and a maximum of alloying elements: Ni, Cr, Mn, Mo, V, Nb. Such alloys are resistant to temperatures up to 500°C. This class includes: 06Х14Н6Б, 08Х18Н12Т, 20Х23Н18, 07XI6H9M2. Heterogeneous grades undergo hardening and aging during the production process. This is necessary for the formation of carbide, carbide-nitride and intermetallic compounds. They strengthen the boundaries of the matrix and impart the necessary heat resistance to the alloy at temperatures from 700 to 750°C. Representatives of this type are steels: 08Х17Н13М2Т, 20Х25Н20С2, 45Х14Н14В2М.
- Nickel and cobalt. These are some of the best heat-resistant materials, capable of maintaining all technical parameters unchanged at temperatures up to 900°C. These grades are divided into homogeneous and heterogeneous alloys. These include: KHN77TYU, KHN55VMTFKYU, KHN70MVTYUB.
Application of heat-resistant steels
Alloy metals, resistant to high thermal loads, are used for the production of pipes, parts, components of machines, units, and industrial equipment. This list includes:
- parts of thermal furnaces;
- parts of conveyor belts for furnace conveyors;
- heat treatment units;
- fuel combustion chambers;
- motors, gas turbines;
- methane conversion devices;
- furnace screens;
- exhaust systems; heating elements.
Heat-resistant stainless metal is the best material for the production of parts and mechanisms that will be used in aggressive environments at elevated temperatures.
Conformity table of foreign and Russian brands
| Steel grade | AISI | GOST 5632-2014 |
| Austenitic | 303 | 12Х18Н9 12Х18Н10Э |
| 304 | 08Х18Н10 12X18H10 | |
| 304 L | 03Х18Н11 | |
| 316 | 08X17H13M2 | |
| 316 L | 03X17H13M2 | |
| 316 Ti | 08X17H13M2T | |
| 321 | 12Х18Н10Т 08Х18Н10 | |
| Ferritic | 409 | 08Х13 |
| 430 | 12X17 | |
| 439 | 08X17T | |
| Martensitic | 420 | 20Х13 |
| 431 | 20Х17Н2 |
Refractory metals
Refractory metals include zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, niobium, tantalum, chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, and rhenium. The most widely used high-temperature structural materials are tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum, and niobium. Recently, chromium, vanadium and rhenium have been increasingly used, which, although less refractory, due to their specific properties are beginning to play a major role in the production of heat-resistant materials.
The technology for producing refractory metals includes obtaining powders, molding blanks and further processing.
Thus, sintered tungsten products are made from powder obtained by the reduction of tungsten anhydride with hydrogen or the carbonyl method. Powders are pressed in steel molds. To improve compressibility, lubricants and adhesives are added to the powder. The sintering process of products is carried out in two stages. The first stage is carried out in hydrogen at relatively low temperatures for tungsten (1100–1300 °C). The second stage of sintering is carried out at temperatures of 2900–3000 °C, which is created by passing an electric current through a product strengthened by preliminary sintering. This sintering stage, called “welding,” is carried out in hydrogen in special furnaces called welding machines. The sintering mode in this case is usually controlled not by measuring the temperature, but by the amount of current passed. Large-sized workpieces are sintered in induction furnaces at temperatures of 2400–2500 °C. A similar technology for manufacturing products from molybdenum powder. The powder obtained by the reduction of molybdenum with hydrogen is pressed, as a rule, with a lubricant. Preliminary sintering is carried out in hydrogen at 1100–1200 °C. Then the products are welded at a current strength of 90% of the remelting current, which corresponds to 2200–2400 °C.
Sintering of large workpieces can be carried out in a vacuum methodical furnace with graphite heaters, which allows for simultaneous preliminary and final sintering at temperatures of 1900–1950 °C.
In the manufacture of tantalum products, the initial powder obtained by sodium thermal reduction or electrolysis is pressed into blanks. Before pressing, a solution of glycerin in alcohol or some other liquid binder is introduced into the tantalum powder, which is completely removed during sintering. Sintering of workpieces is carried out in vacuum. The blanks are pre-sintered at 1000–1200 °C. The sintered workpieces are cooled together with the furnace. Welding is carried out in a vacuum, selecting the mode in such a way as to ensure complete decomposition and evaporation of impurities. At a welding temperature of 2600–2700 °C, hold until all gases are completely removed.
After welding, the workpieces are cooled in a vacuum and forged. Then secondary sintering (annealing) is carried out in a vacuum welding machine. As a result of this processing, a pore-free workpiece with a dense structure is obtained.
Sintered niobium and rhenium are prepared in the same way as discussed above.
Products from zirconium and vanadium powders are manufactured using similar technologies. The powders are pressed in molds and the blanks are sintered in a vacuum. Zirconium blanks are sintered at 1200–1300 °C, and vanadium blanks at 1400–1700 °C.
Polished stainless steel
This type of stainless steel is a material with an absolutely smooth surface and a high reflective effect. The technological process of its production differs from other types of stainless steel in the method of surface treatment. It is carried out on special equipment using control and measuring instruments.
Stages of grinding sheet metal.
- Processing with abrasive materials using a special tape.
- Sanding with fine-grained sandpaper or brushes.
- Finish with grinding wheels to a mirror finish.
Areas of application of polished stainless steel:
- Sanded pipes are used to transport oil, gas, liquid foods and alcohol.
- Polished metal products are in demand among designers. It allows you to create creative architectural projects.
- The material is widely used for the manufacture of household appliances, medical equipment and tools, and devices for the food industry.
Polished alloy metals are used in all areas of the national economy where an absolutely smooth and durable material that meets environmental safety standards is required.
Choosing a steel grade for stoves or baths
Heat-resistant steels for home use differ significantly from industrial options. For a furnace, for example, you should select alloys that can heat up to 500 degrees. Moreover, it is possible to use different alloy options depending on the structural element used. Steel grades, including heat-resistant steel, for individual furnace parts:
- 08Х17Т, AISI430 – suitable for separating the firebox. If difficulties arise in purchasing these grades, then St-10 steel can replace them.
- 08PS, 08Yu - used for heat shields.
- St-3 – suitable for the furnace body.
- Most grades of heat-resistant steel can be used for furnace walls. In some cases cast iron may be used.
To build a sauna stove, steel is used, which contains at least 12% chromium. It is important to consider the thickness of the steel sheet. For such a design it should be 5 mm. Heat-resistant steel is used for equipment that heats a large area.
Food grade stainless steel
This type of rolled metal is ground and differs from other types in a special way of treating its surface. The final layer of food-grade material is sanded until shiny. This type of stainless steel is environmentally friendly and does not react with acids, alkalis, or detergents.
Popular brands and their applications:
- 08Х18Н10 – widely used for the production of food equipment.
- 08Х13 – metal suitable for making kitchenware and cutlery.
- 20Х13, 40Х13 are ideal materials for the production of sinks and containers in which thermal and hygienic processing of products is carried out. It is used to produce equipment intended for the production of wine, alcohol, and food.
- 08X17 is a popular material for cookware exposed to high temperatures.
The optimal amount of alloying elements included in the composition of stainless steel forms a protective film on the surface of the metal. The use of this type of steel is necessary for the production of products that are exposed to long-term exposure to water vapor, heating and boiling of liquid food products. Due to the properties of food grade steel, when cooking food, there is no chemical interaction between the products and the container in which they are located.
Martensite and ferrite - steel grades
It is worth noting that steel can be martensitic-ferritic. This material is used in mechanical engineering. A distinctive feature is resistance to temperatures of 600 degrees. With such exposure, even long-term, the performance properties of steel do not change.
Steel grades of the following composition:
- 2Х12ВМБФР;
- X6SYU;
- 1Х12В2МФ;
- 1Х13;
- 1Х12ВНМФ;
- 1 X11MF.
A characteristic of the composition of martensitic-ferritic alloys is the presence of chromium no more than 14% and no less than 10%. Tungsten, vanadium and molybdenum are used as additional metals.