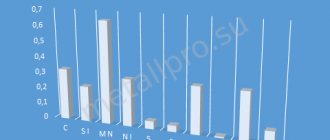
60S2HFA - classification and application of the brand
Material classification: Structural spring steel
Application: responsible and highly loaded springs and leaf springs, made of round calibrated steel.
60S2HFA - chemical composition of the material as a percentage
60S2HFA - mechanical properties at a temperature of 20°
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | s in | s T | d 5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Steel, GOST 14959-79 | 1670 | 1470 | 6 | 25 | Quenching 870 o C, oil, Tempering 470 o C, |
60S2HFA - technological properties
| Weldability: | not applicable to welded structures. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | less inclined. |
60S2HFA - foreign analogues
60S2HFA - decoding of designations, abbreviations, material parameters
| Mechanical properties : | |
| s in | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] |
| s T | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] |
| d 5 | — Elongation at break, [%] |
| y | — Relative narrowing, [%] |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
| Physical properties: | |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20 o - T), [1/degree] |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20 o — T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
| Weldability: | |
| no limits | — welding is performed without heating and without subsequent heat treatment |
| limited weldability | — welding is possible when heated to 100-120 degrees. and subsequent heat treatment |
| difficult to weld | — to obtain high-quality welded joints, additional operations are required: heating to 200-300 degrees. during welding, heat treatment after welding - annealing |
Attention! All information provided about 60S2HFA is for informational purposes only. All characteristics you are interested in must be clarified by specialists.
50ХГ car springs, railway rolling stock springs
3K-7 For the production of cold-drawn wire used for the manufacture of springs that are wound in a cold state and are not subject to hardening.
50ХСА watch mechanism springs, large springs for critical purposes
50HGFA springs for special purposes, passenger car springs
50HGA car springs, railway rolling stock springs
51HFA wire for making springs
50HFA are heavily loaded critical parts that are subject to high fatigue strength requirements, springs operating at temperatures up to 300°C and other parts.
55С2 springs and leaf springs used in the automotive industry, tractor manufacturing, railway transport and other branches of mechanical engineering.
55S2GF for the manufacture of springs for special purposes, vehicle springs
55С2А car springs, railway rolling stock springs
55KhGR for the production of spring strip steel with a thickness of 3-24 mm.
60G flat and round springs, leaf springs, spring rings and other spring-type parts that require high elastic properties and wear resistance - tires, brake drums and bands, brackets, bushings and other parts of general and heavy engineering.
60С2 heavily loaded springs, torsion shafts, spring rings, collets, friction discs, spring washers.
60S2G for the manufacture of automobile and tractor springs, springs for railway rolling stock
60С2А heavy-duty springs, torsion shafts, spring rings, collets, friction discs, Grover washers, etc.
60S2N2A responsible and heavily loaded springs and springs.
60S2ХА for the manufacture of large, highly loaded springs and springs for critical purposes.
65GA heat-treated wire with a diameter of 1.2 - 5.5 mm for the manufacture of springs
65G springs, springs, thrust washers, brake bands, friction discs, gears, flanges, bearing housings, clamping and feed collets and other parts that require increased wear resistance, and parts that operate without shock loads.
properties, characteristics, application. Steel 60s2a in the form of wire.
Metal of this brand is endowed with a very high level of elasticity, therefore it is ideal for creating springs and springs that experience enormous loads. In essence, 60s2a steel is a high-quality alloy alloy that perfectly withstands impact and alternating loads, does not expand when heated, is prone to decarburization, and demonstrates excellent spring properties. Spring rings, friction discs, torsion shafts and Grover washers are made from it. The main purpose of steel of this grade is the production of springs and heavily loaded springs.
Chemical composition of the alloy
In addition to the high relative proportion of the carbon component, 60s2a steel contains the following chemical elements that determine its performance characteristics:
- silicon – 1.6-2.0%
- manganese – 0.60-0.90%
- chromium – up to 0.30%
- nickel – up to 0.25%
- copper – up to 0.20%
- phosphorus – up to 0.025%
- sulfur – up to 0.025%
Steel 60s2a: physical and mechanical properties
Steel 60s2a is endowed with high hardness: HB 10-1 = 269 MPa. It is not prone to temper brittleness and flake formation. Other characteristics can be found below:
Steel wire grade 60С2А
60C2A wire is an alloyed spring wire, and since the dominant element in its composition is silicon, which predominates over carbon and manganese, this material is excellent for the production of springs and other similar products that are subsequently subjected to high deformation loads. The production of 60C2A wire is carried out in accordance with GOST 14963-78, which implies 2 methods of obtaining finished springs: hot coiling and cold coiling. The latest technology is suitable for the production of wire with a diameter of 0.5-14.0 mm. Spring wire can have normal and increased accuracy.
Steel wire grade 60C2A is supplied to enterprises in the form of a coil or rod. The main consumers of products made from such an alloy are machine-building enterprises that need an elastic and durable material for the production of springs and springs for automobile suspensions. Such wire is a typical raw material for spring-coiling equipment, and its diameter can vary between 0.1-14.0 mm.
How to decipher steel grade
Steel, cast iron and alloys of non-ferrous metals are subject to mandatory marking. There are more than 1.5 thousand different types of steels and alloys made from them in the world.
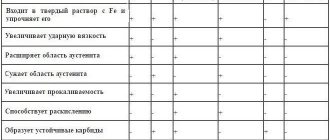
Alloyed steels , unlike unalloyed steels, have a slightly different designation, since they contain elements that are specially introduced in certain quantities to ensure the required physical or mechanical properties. Eg:
- chromium (Cr) increases hardness and strength
- Nickel (Ni) provides corrosion resistance and increases hardenability
- Cobalt (Co) improves heat resistance and increases impact resistance
- Niobium (Nb) helps improve acid resistance and reduces corrosion in welded structures.
That is why it is customary to include in the names of alloy steels the chemical elements present in the composition and their percentage content. Chemical elements in such steel grades are designated by Russian letters given in the table.
There is also a marking H, which tells us that the alloy contains rare earth metals, such as cerium, lanthanum, neodymium and others. Cerium (Ce) affects the strength and ductility of steel, while eodymium (Nd) and lanthanum (La) reduce porosity and sulfur content in steel and refine the grain.
Supply of BSt4ps
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to the regulations of GOST 2590-88 Hot-rolled round steel , GOST 2591-88 Hot-rolled square steel , GOST 8239-89 Hot-rolled steel I-beams , GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles, GOST 19772 -93 Bent steel angles, unequal flanges , GOST 8278-83 Bent steel channels, equal flanges , GOST 8281-80 , unequal , GOST 8283-93 steel trough equal flange profiles , GOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 85 09-93 Steel corners hot-rolled equal flange , GOST 8510-86 rolled steel angles unequal-flanged , GOST 8240-97 Hot-rolled steel channels , GOST 535-88 Rolled bars and shaped carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 2879-88 Rolled hot-rolled hexagonal steel, GOST 19903-2015 Hot rolled sheet products , GOST 19904-90 Cold-rolled sheets , GOST 16523-97 Rolled thin sheets of high-quality and ordinary quality carbon steel for general purpose, GOST 503-81 Cold-rolled low-carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot-rolled steel strip , GOST 82-70 Hot-rolled steel Wide-band universal, GOST 3282-74 Wire Steel low-carbon general purposes , GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wires, GOST 10705-80 steel power steel pipes , GOST 10706-76 Pipes steel eight-dimensional , GOST 3262-75 Pipes steel water and gap-pipes .
| B20 - Classification, nomenclature and general standards | GOST 380-2005; |
| B22 – Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 8510-86; GOST 535-2005; GOST 8239-89; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 2591-2006; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 8240-97; GOST 19425-74; GOST 19240-73; GOST 8509-93; GOST 11474-76; GOST 9234-74; GOST 5422-73; |
| B23 - Sheets and strips | GOST 103-2006; GOST 14918-80; GOST 19903-74; GOST 16523-97; GOST 14637-89; |
| B24 - Tapes | GOST 6009-74; GOST 3560-73; |
| B42 - Rails. Overlays. Linings. Crutches | GOST 22343-90; GOST 16277-93; GOST 12135-75; GOST 8194-75; GOST 8142-89; GOST 7056-77; GOST 5812-82; GOST 3280-84; |
| B62 — Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 8646-68; GOST 8644-68; GOST 8642-68; GOST 3262-75; GOST 10705-80; GOST 8645-68; GOST 8638-57; GOST 13663-86; GOST 10707-80; GOST 8639-82; |
An example of decoding steel grade 12Х18Н10Т
12Х18Н10Т is a popular austenitic steel, which is used in welding machines operating in dilute acid solutions, in solutions of alkalis and salts, as well as in parts operating under high pressure and in a wide temperature range. So, what do these mysterious symbols in the name mean, and how to combine them correctly?
The two numbers at the very beginning of the alloy steel grade are the average carbon content in hundredths of a percent. In our case, the carbon content is 0.12%. Sometimes, instead of two numbers, there is only one: it shows how much carbon (C) is contained in tenths of a percent. If there are no numbers at the beginning of the steel grade, this means that there is a fairly decent amount of carbon in it - from 1% and above.
Hardenability of steel 60
| Distance from the end, mm | Note | |||||||||
| 1,5 | 3 | 4,5 | 6 | 7,5 | 9 | 12 | 21 | 33 | 45 | Hardening 820 °C |
| 57,5-63,5 | 56-62 | 51-60,5 | 38,5-59 | 35-56 | 35,5-51,5 | 32-42 | 31,5-40 | 26-38 | 25-34 | Hardness for hardenability strips, HRC∂ |
| Amount of martensite, % | Critical diameter in water | Critical diameter in oil |
| 50 90 | 26-48 15-30 | 10-20 3-12 |
Description U10A
One of the representatives of tool steel is the U10A grade. This is a tool steel with a density of 7810 kg/m3, which is used in the manufacture of various tools whose working edge does not require heating. U10A steel is used to produce woodworking, plumbing and assembly tools, twisted and flat springs, combined pliers and side cutters, screwdrivers, punches, mechanical watch parts, knurling rollers, cutters. Also, steel grade U10A is successfully used in the production of dies for cold stamping.
Source
Steel hardness U10A
| Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | HRC surface | NV |
| Annealing | — | 207 |
| Quenching 770-800 C, water | St. 63 | — |
| Cross section up to 10-12 mm. Quenching 800 C, oil or molten salts at 190 C. Tempering 160-200 C | 57-61 | — |
| Section up to 8 mm. Quenching 800 C, oil or molten salts at 190 C. Tempering 380-480 C. (recommended for springs and spring-type parts) | 44-50 | — |
| Section up to 66 mm. Quenching 770 C, water or 5-10% NaCl solution. Holiday 170 C | 59-63 | — |
| Springs. Isothermal hardening at 800 C in molten salts and water. Isotherm temperature 280-360 C. Vacation 280-360 C | 44-52 | — |
| Surface hardening with induction heating. Holiday 160-200 C | 59-63 | — |
| Quenching 760-780 C, water. Holiday 160-200 C | — | — |
| Quenching 760-780 C, water. Vacation 200-300 C | — | — |
| Quenching 760-780 C, water. Vacation 300-400 C | — | — |
| Quenching 760-780 C, water. Vacation 400-500 C | — | — |