What is stainless steel
Stainless steel
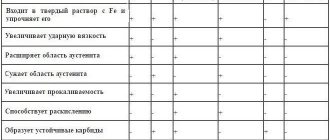
– These are iron-based alloys with various impurities. The most common alloying additives are carbon, chromium, nickel, titanium, and niobium. Each of the elements imparts new physical and mechanical properties to the alloy, thereby increasing its strength or increasing its ductility. The main advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to corrosion; it owes this property to chromium, which is present in every stainless alloy. A sufficient amount of this element ensures the anti-corrosion properties of the metal.
The presence of nickel gives the alloy many important qualities: ductility, heat-resistant properties, improves the quality of weldability, and reduces the rate of corrosion. With the acquisition of anti-corrosion properties, stainless steel is not inferior in strength to ordinary steel. Stainless steel retains all the valuable qualities of metals: it is both strong and ductile, and lends itself well to processing: cutting, welding, rolling, stretching, bending. Due to its good performance, stainless steel is used for the manufacture of stainless steel products. All grades of stainless steel are manufactured in accordance with GOST 5632-2014.
Supply St4sp
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to GOST 2590-88 Hot-rolled round steel, GOST 2591-88 Hot-rolled square steel, GOST 8239-89 Hot-rolled steel I-beams, GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles, GOST 19772 -93 Bent steel angles, unequal flange, GOST 8278-83 Bent steel channels, equal flange, GOST 8281-80 Bent steel channels, unequal flange, GOST 8283-93 Bent steel trough equal flange profiles, GOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality, GOST 8509-93 Steel corners hot-rolled equal flange, GOST 8510-86 Hot-rolled steel angles unequal flange, GOST 8240-97 Hot-rolled steel channels, GOST 535-88 Rolled bars and shaped carbon steel of ordinary quality, GOST 2879-88 Rolled hot-rolled hexagonal steel, GOST 19903-2015 Rolled sheets hot rolled , GOST 19904-90 Cold-rolled sheets, GOST 16523-97 Rolled thin sheets of high-quality and ordinary quality carbon steel for general purpose, GOST 503-81 Cold-rolled low-carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot-rolled steel strip, GOST 82-70 Hot-rolled steel broadband universal, GOST 3282-74 General purpose low-carbon steel wire, GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wire, GOST 10705-80 Electric-welded steel pipes, GOST 10706-76 Straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes, GOST 3262-75 Steel water-gas pipes.
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | GOST 380-2005; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 2591-2006; GOST 8240-97; GOST 8239-89; GOST 8509-93; GOST 5422-73; GOST 535-2005; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 8510-86; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 19425-74; GOST 11474-76; GOST 19240-73; GOST 9234-74; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 19903-74; GOST 14637-89; GOST 16523-97; GOST 14918-80; GOST 103-2006; |
| Ribbons | GOST 3560-73; GOST 6009-74; |
| Rails. Overlays. Linings. Crutches | GOST 12135-75; GOST 22343-90; GOST 3280-84; GOST 5812-82; GOST 16277-93; GOST 7056-77; GOST 8141-56; GOST 8194-75; GOST 8142-89; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 8646-68; GOST 53383-2009; GOST 8644-68; GOST 8642-68; GOST 13663-86; GOST 3262-75; GOST 8639-82; GOST 8731-87; GOST 8732-78; GOST 9567-75; GOST 10707-80; GOST 8638-57; GOST 8645-68; GOST 10705-80; |
Decoding steel markings
Alloy steels are those into which special chemical elements are introduced: nickel, chromium, cobalt, titanium, tungsten. Their addition to the steel composition serves to influence the structure of the metal and obtain improved properties. The marking of steels depends on the chemical composition. At the beginning, numbers are indicated indicating the carbon content in hundredths of a percent (GOST 4543-2016). Next are the letters that indicate alloying elements. In the names of steel and alloy grades, chemical elements are designated by the following letters:
- A (at the beginning of the mark) - sulfur;
- A (in the middle of the mark) - nitrogen;
- B - niobium;
- B - tungsten;
- G - manganese;
- D - copper;
- E - selenium;
- K - cobalt;
- M - molybdenum;
- N - nickel;
- P - phosphorus;
- P - boron;
- C—silicon;
- T - titanium;
- F - vanadium;
- X - chromium;
- C—zirconium;
- Yu - aluminum;
- h - REM (rare earth metals: lanthanum, praseodymium, cerium, etc.).
If the letter A is at the end of the marking, this indicates that the steel is high quality. The letter Ш is placed at the end of the marking for especially high-quality steels.
After the letter there are sometimes numbers indicating the content of the alloying element as a percentage. If there is no number, the content of the element is no more than 1%.
At the beginning of the marking of tool alloy steels, the first place is occupied by a number indicating the average carbon content in average fractions of a percent (GOST 5950-2000). If it is not indicated, then the percentage is 1% or more. Further, the designation of stainless steel coincides with structural steels.
Special-purpose stainless steel grades are marked differently. At the beginning there is a letter indicating the purpose of the steel:
- A – automatic;
- E – electrical;
- Ш – ball bearing;
- R – high-speed.
After that come numbers indicating the average number of the main alloying element.
How to calculate the load
Knowing the strength class helps you choose hardware with optimal characteristics. To do this, use the formula (using the example of an M12 bolt made of A2-70 steel): Np0.2=AsxRp0.2=84.3x450=37935N. Here:
- As – cross-sectional area of the bolt is 84.3 sq. mm (can be found in GOST R ISO3506 in table A1);
- Rp: yield strength of steel.
To calculate the maximum load allowed for a given hardware, divide the resulting value by 20. The result is 1896 kg. This is the maximum permissible load on the bolt. If you want to play it safe and be more secure, divide by 30.
Classification of stainless steel grades
The classification of stainless steel differs in different countries, but there are general similar principles by which stainless steel is divided into several types:
- Austenitic;
- Ferritic;
- Martensitic;
- Duplex.
Austenitic stainless steel
The austenitic group includes alloys with a high content of chromium and nickel. Austenitic stainless steel is characterized by increased strength and flexibility, is easily amenable to various types of processing and has increased anti-corrosion properties. This type of stainless steel has found its application in industry. Austenitic steel is a non-magnetic metal.
This group is divided into several types of stainless steel:
A1
– steel containing a large amount of sulfur. Due to this, it has the lowest corrosion resistance.
A2
– the most commonly used grade of stainless steel. Easy to weld, does not lose its properties at low temperatures. Among the disadvantages, it can be noted that this steel does not withstand an aggressive acidic environment.
A3
– improved version of A2 steel. Components have been added to the composition that allow stainless steel not to change its properties at high temperatures and in an acidic environment.
A4
– an alloy with the addition of molybdenum (up to 3%). Mainly used in shipbuilding, as the steel is characterized by a high level of resistance in an acidic environment.
A5
– has almost the same properties as A4. They differ from each other only in the ratio of additives in the alloy composition. This type of stainless steel is used for increased resistance to ultra-high temperatures.
Ferritic stainless steel
In the group of ferritic alloys, the chromium content in the composition is increased, it reaches 20%. Because of this, this type of stainless steel is sometimes called “chromium.” The chemical composition of ferritic stainless steel is resistant to aggressive external environments. Ferritic steel grades have magnetic properties. Ferritic stainless steel is widely used in industry as it is relatively cheap.
Martensitic stainless steel
A special type of stainless steels are martensitic alloys. They are characterized by high strength and wear resistance. Martensitic steel grades contain a minimum amount of harmful substances that are not released when heated. Martensitic alloys include heat-resistant corrosion steel.
Duplex stainless steel
The last type of stainless steel that combines the properties of all other groups is duplex alloys. Innovative steels are developed individually, depending on the customer’s needs.
The types of stainless steel are not limited to the above, since any percentage change in the substances in the composition can lead to the creation of a new type of stainless steel.
Strength classes
There are only three strength classes, and they are designated, according to GOST R ISO3506-1-2009, by the numbers 50, 70, 80. Below is the tensile strength (in parentheses is the maximum yield capacity) according to the strength classes of stainless fasteners:
- 50: 500 N/sq. mm (210 N/sq. mm);
- 70: 700 N/sq. mm (450 N/sq. mm);
- 80: 800 N/sq. mm (600 N/sq. mm).
The least reliable steel is the first type, annealed. Stainless steel is not hardened; the greatest strength is achieved in a cold-worked state. These are classes 70 and 80.
Application of stainless steel
Previously, stainless steel was used only in industrial production, but over time, stainless steel is widely used in various areas of our lives.
The main areas include:
- Mechanical engineering;
- Chemical industry;
- Energy;
- Pulp and paper industry;
- Food industry;
- Medicine;
- Aerospace sector;
- Construction.
Food grade stainless steel
In the food industry, stainless steel is used - an alloy with a low amount of chemical additives, since the equipment is not exposed to temperature changes and aggressive substances. Frost-resistant materials are used for refrigeration and freezing units.
Stainless steel grades for the food industry AISI 304, AISI 304L, AISI 316, AISI 316L, AISI 316Ti, AISI 321, AISI 430 are widely used.
Stainless medical steel
Stainless steel plays a huge role in medicine. Medical instruments, utensils and other necessary equipment are made from it. The term “medical stainless steel” means steel grade 12Х18Н10Т; such steel is absolutely safe for humans. It is used in the medical and food industries. It has several advantages over other alloys:
- High corrosion properties, due to which the steel withstands strict hygienic standards of SanPiN;
- Steel does not emit harmful substances when heated;
- Solid and practical, such steel does not form scratches or dents;
- Medical steel can be shaped into any shape during manufacturing.
Additional information about X5CrNiMo17-12-2 steel
Closest analogues
| HDIN/EN | USA | AFNOR | UNI | JIS |
| X5CrNiMo17-12-2 | AISI 316 UNS | — | X5CrNiMo1712 | SUS316 SUS316A |
| X5CrNiMo1810 | S31600 | — | X5CrNiMo1712KG | SUS316FB |
| — | — | — | X5CrNiMo1712KW | SUS316HFB |
| — | — | — | — | SUS316HTB |
| — | — | — | — | SUS316HTF |
| — | — | — | — | SUS316HTP |
| — | — | — | — | SUS316TB |
| — | — | — | — | SUS316TBS |
| — | — | — | — | SUS316TKA |
| — | — | — | — | SUS316TKC |
| — | — | — | — | SUS316TP |
| — | — | — | — | SUSF316 SUSY316 |
Foreign grades of stainless steel
200 series: AISI 201 and AISI 202
Steel grades AISI 201
and
AISI 202
(AISI - American Iron and Steel Institute - American Institute of Steel and Alloys) belong to the austenitic group of alloys. They contain chromium, nickel, manganese, copper and nitrogen. These steels provide a high level of strength to the finished product, are perfectly deformable and change their shape. Due to their balanced composition, steels of these grades are characterized by high anti-corrosion properties.
Stainless steel AISI 201 and AISI 202 are used in the manufacture of household appliances, pipelines and building structures.
The brands differ from each other in the percentage of additives. AISI 201 contains a higher amount of carbon, sulfur, manganese and copper, due to which high strength and ductility of steel are achieved. AISI 202 contains an increased amount of nickel. AISI 201 is considered an improved version of AISI 202. When steel is used in a moderately aggressive environment, both grades do not lose their physical properties.
Russian analogue of AISI 201 - 12Х15Г9НД Russian analogue of AISI 202 - 12Х17Г9АН4
300 series stainless steel grades
According to its chemical composition, this series can belong to the austenitic or duplex group of alloys. The type of stainless steel depends on the percentage of main additives: carbon, nickel, chromium, titanium. This series is universal. Due to its good strength, wear resistance and anti-corrosion properties, stainless steel of this group is in high demand in the market.
AISI 301
AISI 301 refers to non-magnetic steels. It has a high level of strength and ductility. Grade 301 has found its application in environments with reduced aggressiveness. Most often it is used under conditions of standard atmospheric exposure, for example, in the manufacture of parts for automobiles and railway transport, household equipment and medical equipment.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 301, %
- Cr - from 16 to 18
- Ni - from 6 to 8
- Mn - 2
- Si - 1
- C - 0.15
- N - 0.1
- P - 0.045
- S - 0.03
Russian analogue of AISI 301 - 15Х17Н7
AISI 302
AISI 302 stainless steel is used for the manufacture of springs and retaining rings. The material is characterized by high strength and ductility. It is resistant to corrosion.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 302, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 8-10
- Mo - 4-5
- Si - 2-3
- Mn — <2
- C - <0.15
- N — >0.1
- P - <0.045
- S — <0.03
Russian analogue of AISI 302 - 12Х18Н9
AISI 303
Chromium-nickel stainless steel AISI 303 is classified as austenitic steel. The composition has an increased sulfur content, and because of this, the alloy’s resistance to corrosion is reduced. Stainless steel is non-magnetic and is optimally used in mechanical and moving components.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 303, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 8-10
- Mn — <2
- Si — <1
- P - <0.2
- S — >0.15
- C - <0.15
Russian analogue of AISI 303 - 12Х18Н9
AISI 304
304 stainless steel has become famous for its chemical composition and characteristics that allow it to be used in the food industry. In addition to the food industry, steel of this grade is used for pharmaceutical, oil, chemical and textile production. 304 stainless steel has high corrosion resistance and can be used in aggressive environments.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 304, %
- Cr - 18-20
- Ni - 8-10.5
- Mn — <2
- C - <0.08
- P - <0.045
- S — <0.03
Russian analogue of AISI 304 - 08Х18Н10
AISI 316
AISI 316 is a grade of stainless steel containing molybdenum, which increases the material’s resistance to corrosion. The alloy is resistant to elevated temperatures. 316 stainless steel is more expensive than 304, so it is used in narrower industries: shipbuilding, aviation, oil and gas enterprises.
AISI 316Ti steel grade is enriched with titanium, which makes the material resistant to chlorine. Titanium also makes the alloy more durable and resistant to high temperatures. 316Ti has no magnetic properties. Stainless steel of this brand is mainly used in the following areas:
- Equipment for the chemical and pharmaceutical industries;
- Manufacturing of architectural elements and roofing structures;
- Construction of heat exchangers.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 316, %
- Cr - 15-17
- Ni - 14-16
- Mo - 2.5-3
- C - up to 0.03
Titanium has been added to the 316Ti grade up to 1%.
Russian analogue of AISI 316 - 03Х17Н14М3 and 04Х17Н13М2 Russian analogue of AISI 316Тi - 10Х17Н13М2Т
AISI 321
An improved version of these grades is AISI 321. This grade of stainless steel is characterized by a high titanium content, it contains almost 10%. The alloy is easily amenable to any type of processing and is resistant to elevated temperatures, up to 800 degrees.
AISI 321 stainless steel is used in the production of seamless pipes, in the manufacture of seam products and boilers, as well as in the construction of furnace systems. Steel 321 is used in mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, and aviation.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 321, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 9-11
- Mn — <2
- Ti — <1
- Si - <0.8
- Cu - <0.3
Russian analogue of AISI 321 - 08Х18Н10Т
Stainless steel grades 400 series
The main feature of stainless steels in this group is considered to be a low percentage of carbon additives and the presence of a large amount of chromium. This affects the cost of stainless steel grades of this series; it is lower than the 200 and 300 series.
The 400 series is popular in industrial applications where it is necessary to form various structures. This is due to the low carbon content, which allows the alloy to be ductile.
AISI 403
According to its characteristics, the alloy belongs to the martensitic-ferritic group. Stainless steel is characterized by increased ductility and resistance to high temperatures. Finished parts can withstand loads in a slightly aggressive environment.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 403, %
- Fe - 86
- Cr - 12.3
- Mn - 1
- Si - 0.5
- C - 0.15
- P - 0.04
- S - 0.03
Russian analogue of AISI 403 - 15Х12
AISI 409
AISI 409 differs from AISI 403 in its increased chromium content and the addition of nickel. This allows this brand of stainless steel to be amenable to all types of processing. Finished products are characterized by plasticity. AISI 409 is used to make parts that will be subject to shock loads during operation: press and pump valves, household items. AISI 409 is also used in the manufacture of products exposed to mildly aggressive environments: steam turbine blades, valves, bolts and pipes.
Chemical composition and decoding of AISI 409,%
- Fe - ~84
- Cr - 12 - 14
- Mn - up to 0.8
- Si - up to 0.8
- Ni - up to 0.6
- C - up to 0.08
- P - up to 0.03
- S - up to 0.025
Russian analogue AISI 409 - 08Х13
AISI 410
AISI 410 stainless steel is ductile and durable. It withstands high temperatures without changing its characteristics even at 500 degrees. This grade of stainless steel does not corrode in aggressive environments. This grade of steel is used to make parts that will be used at high temperatures.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 410, %
- Cr - 13.5
- Mn - 1.0
- Si - 1.0
- Ni - 0.6
- C - 0.15
- P - 0.045
- Si - 0.03
It is used for the manufacture of cutting tools, turbine and boiler parts, and kitchen utensils. Suitable for use in thermal and separation screens, filters.
Russian analogue AISI 410 - 12Х13
AISI 416
AISI 416 belongs to the martensitic stainless steel group. Sheet metal, metal profiles, and pipeline products are made from it.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 416, %
- Cr - 12-14
- Mn - 1.25
- Si - 1
- Se — >0.15
- C - 0.15
- P - 0.06
- S - 0.06
AISI 420
Characteristics of AISI 420 steel: increased level of wear resistance, heat resistance and anti-corrosion. The cost of the alloy is significantly lower than that of other brands in this series, since it does not contain expensive elements.
Chemical composition and decoding AISI 420,%
- Fe - ~84
- Cr - 12-14
- Si - up to 0.6
- Mn - up to 0.6
- Ni - up to 0.6
- C - 0.35-0.44
- P - up to 0.03
- S - up to 0.025
This combination of elements allows us to achieve good physical properties of stainless steel. The alloy belongs to the martensitic group. This brand is in demand in various industries: food, chemical, construction.
Russian analogue of AISI 420 - 40Х13
AISI 430
AISI 430 steel is considered the most corrosion-resistant alloy. The grade belongs to the group of ferritic steels. A balanced composition and good performance characteristics are the advantages of AISI 430 stainless steel. The absence of expensive elements makes the steel affordable and in demand.
Chemical composition and decoding AISI 430,%
- Fe - ~81
- Cr - 16-18
- C - up to 0.12
- Si - up to 0.8
- Mn - up to 0.8
- P - up to 0.035
- S - up to 0.025
Area of application of AISI 430:
- Oil industry;
- Food industry;
- Construction;
- Mechanical engineering;
- Chemical industry.
Russian analogue AISI 430 - 12Х17
AISI 439
AISI 439 is a stainless steel belonging to the ferritic group. Does not contain nickel and is stabilized with titanium. It is characterized by high levels of corrosion resistance in various moderately aggressive and aggressive environments.
The AISI 439 brand is used in mechanical engineering, food industry, architecture and construction. Internal and external fittings and service tools are made from stainless steel.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 439, %
- Fe - ~79
- Cr - 16-18
- Si - up to 0.8
- Mn - up to 0.8
- Ti - up to 0.8
- Ni - up to 0.6
- Cu - up to 0.3
- C - up to 0.08
- P - up to 0.035
- S - up to 0.025
The presence of aluminum and titanium in AISI 439 stainless steel, combined with a reduced carbon content, guarantees its good plastic and strength properties.
Russian analogue AISI 439 - 08Х17Т
AISI 441
AISI 441 steel belongs to the group of ferritic alloys. 441 stainless steel is stabilized with titanium and niobium. The composition contains a large amount of chromium, making it a corrosion-resistant grade of stainless steel. Advantages of the AISI 441 brand:
- Low coefficient of thermal expansion;
- High level of thermal conductivity;
- Inertial overheating of the material is not allowed.
Chemical composition and interpretation of AISI 441, %
- Cr - 16-18
- Si - up to 0.8
- Mn - up to 0.8
- Ti - up to 0.8
- Ni - up to 0.6
- Cu - up to 0.3
- C - up to 0.08
- P - up to 0.035
- S - up to 0.025
AISI 441 stainless steel is used in the automotive industry, in the production of heat exchangers and pipes, and for the construction of architectural elements. The material is suitable for the manufacture of exhaust systems. Steel welding is carried out at low temperatures. The alloy can be used at temperatures of 500-800 degrees.
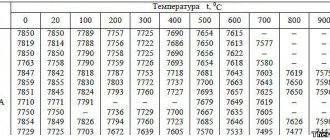
Mechanical properties St4sp
| Type of delivery | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Heat treatment |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Pipes, GOST 8731-87 | 412 | 245 | 20 | |||||
| Pipes, GOST 10705-80 | 412 | 245 | 21 | |||||
| Rolled goods, GOST 535-2005 | 410-530 | 235-265 | 21-24 | |||||
| Thick sheet, GOST 14637-89 | 410-530 | 235-265 | 21-23 |
Domestic grades of stainless steel
The modern market offers different grades of stainless steel for use in different industries.
06ХН28МДТ
Stainless steel 06ХН28МДТ is used for the manufacture of welded chemical equipment operating at temperatures up to 80 degrees in highly aggressive environments.
Chemical composition and decoding 06ХН28МДТ, %
- Ni - 26-29
- Cr - 22-25
- Cu - 2.5-3.5
- Mo - 2.5-3
- Si - ≤0.8
- Mn - ≤0.8
- Ti - 0.5-0.9
- C — ≤0.06
- P — ≤0.035
- S — ≤0.02
- Fe - rest.
The alloy can be welded manually or automatically.
Imported analogue 06ХН28МДТ - AISI 904L
08Х17Н13М2Т
One of the popular options for domestic stainless steel is grade 08Х17Н13М2Т. The composition of this brand of stainless steel is characterized by a high content of molybdenum. It is this element that increases anti-corrosion properties and allows you not to be exposed to aggressive environments. In addition, molybdenum increases resistance to high temperatures. Stainless steel of this grade is characterized by high ductility, is easily molded and does not have magnetic properties.
Scope of application of brand 08Х17Н13М2Т:
- Food industry;
- Chemical industry;
- Manufacturing of medical products;
- Manufacturing of equipment and tools.
Chemical composition and decoding 08Х17Н13М2Т, %
- C - up to 0.08
- Si - up to 0.8
- Mn - up to 2
- Ni - 12-14
- S - up to 0.02
- P - up to 0.035
- Cr - 16-18
- Mo - 2-3
- Cu - up to 0.3
- (5 C - 0.7) Ti
- Fe - ~61
Imported analogue 08Х17Н13М2Т - AISI 316Ti
08Х18Н9
Steel 08Х18Н9 – austenitic stainless steel with a high chromium content. A widely used grade of high-alloy stainless steel. Stainless steel is characterized by high levels of heat resistance and anti-corrosion. The alloy is easy to weld. It is used in the production of steel seams, fittings, and heat exchange equipment.
Chemical composition and decoding 08Х18Н9, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 8-10
- C - 0.8
- Si - 0.8
- Ti - 0.5
- Cu - 0.3
- Mn - 0.2
- P - 0.035
- S - 0.02
08Х18Н10
Stainless steel grade 08Х18Н10 also belongs to the austenitic group of alloys. It is characterized by increased strength, ductility and resistance to ultra-high temperatures. The alloy has no magnetic properties.
Scope of application 08Х18Н10
- Construction;
- Mechanical engineering;
- Food industry;
- Mining industry;
- Manufacturing of rolled metal, equipment and fittings.
Chemical composition and decoding 08Х18Н10, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 9-11
- C - 0.8
- Si - 0.8
- Ti - 0.5
- Cu - 0.3
- Mn - 0.2
- P - 0.035
- S - 0.02
Imported analogue 08Х18Н10 - AISI 304
08Х18Н10Т
An analogue of the previous brand is 08Х18Н10Т. High-alloy steel of this grade belongs to the austenitic group. It is a corrosion-resistant alloy and is characterized by high heat resistance. There are no magnetic properties. It is used for the manufacture of folds, heat exchange equipment, and parts of furnace fittings.
Scope of application 08Х18Н10Т
- Construction;
- Mechanical engineering;
- Electric power industry;
- Food, fuel, chemical industries.
Chemical composition and decoding of alloy 08Х18Н10Т, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 9-11
- Mn - up to 2
- Si - up to 0.8
- Ti - 0.4-0.7
- Cu - up to 0.3
- S - up to 0.2
- C - up to 0.08
- P - up to 0.035
- Fe - ~69
Imported analogue 08Х18Н10Т - AISI 321
08Х22Н6Т
Stainless steel 08Х22Н6Т belongs to the austenitic-ferritic group of alloys. It is an anti-corrosion alloy and does not lose its properties even when used in an aggressive environment. The scope of application of this grade of stainless steel is extensive; welded equipment and various vessels are made from it.
Chemical composition and decoding 08Х22Н6Т, %
- Cr - 21-23
- Si - up to 0.8
- Mn - up to 0.8
- Ni - up to 0.8
- Cu - up to 0.3
- C - up to 0.08
- P - up to 0.035
- S - up to 0.025
- (5 C - 0.65) Ti
- the rest is Fe
Any type of welding can be used on stainless steel grade 08Х22Н6Т. The weld seam is also protected from rust and external mechanical influence.
10Х17Н13М2Т
Steel 10Х17Н13М2Т belongs to the group of austenitic alloys. Basically, this brand is used in the manufacture of welded structures that are used in aggressive environments. Stainless steel retains its physical properties and characteristics even at high temperatures (up to 600 degrees).
Chemical composition and decoding 10Х17Н13М2Т, %
- Cr - 16-18
- Ni - 12-14
- Mo - 2-3
- Mn - no more than 2
- Si - no more than 0.8
- Ti - 0.5-0.7
- Cu - no more than 0.3
- P - no more than 0.035
- S - no more than 0.02
Any type of welding can be used with stainless steel of this brand: manual, automatic electric arc, gas.
Imported analogue 10Х17Н13М2Т - AISI 316Ti
10Х18Н10Т
Heat-resistant stainless steel 10Х18Н10Т is used for the manufacture of parts for welded equipment operating in aggressive environments. Suitable for the production of furnace equipment, heat exchangers and pipes.
Chemical composition and decoding of 10Х18Н10Т, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 10-11
- Mn - 1-2
- Si - up to 0.8
- C - up to 0.1
- P - up to 0.035
- S - up to 0.02
- 5(C - 0.02) < Ti < 0.6
10Х23Н18
Stainless steel 10Х23Н18 belongs to the austenitic group of alloys. High-alloy, high-temperature resistant stainless steel. Thanks to special elements, grade 10Х23Н18 is plastic, and parts of any shape can be made from it. It is used in the manufacture of pipes, tubular and sheet parts, as well as in the production of fittings.
Chemical composition and decoding 10Х23Н18, %
- Cr - 22-25
- Ni — 17-20
- Mn - up to 2
- Si - up to 1
- Cu - 0.035
- Ti - 0.3
- C - up to 0.1
- S - up to 0.02
- P - up to 0.02
Imported analogue 10Х23Н18 - AISI 310S
12Х18Н9
Stainless steel 12Х18Н9 is a high-alloy, corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant stainless steel. Belongs to the group of austenitic alloys. Stainless steel is a universal material and has a high level of strength. Steel is weakly magnetic. It is used in the manufacture of parts that subsequently undergo a hardening stage: parts of furnace fittings, heat exchangers, rotors, couplings. The stainless steel of this brand can withstand both low and high temperatures. Operating temperature range from –196 to +800 degrees.
Chemical composition and decoding of 12Х18Н9, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 8-10
- Mn — ≤ 2
- Si - ≤ 0.8
- Ti - ≤0.5
- Mo - ≤0.5
- Cu - ≤0.3
- C — ≤ 0.12
- P — ≤0.035
- S — ≤0.02
- Fe - base, about 70
Imported analogue 12Х18Н9 - AISI 301, 302, 303, S30200
12Х18Н9Т
Stainless steel 12Х18Н9Т is an improved version of the previous grade. The alloy contains a larger amount of titanium, which increases the technical properties of the material. Titanium increases the strength of the metal and resistance to intercrystalline corrosion. Stainless steel of this brand is the basis for the manufacture of rolled metal products. It is used to produce wire, rods, tapes, and pipes.
Steel does not come into contact with other materials, due to which it can be used in the food and medical industries. After heat treatment, stainless steel becomes non-magnetic.
Chemical composition and decoding of 12Х18Н9Т, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 8-9.5
- Mn — ≤2
- Si - ≤0.8
- Mo - ≤0.5
- Cu - ≤0.3
- C — ≤0.12
- P — ≤0.035
- S — ≤0.02
- Ti - 5*C - 0.8
- Fe - base, about 70%
Imported analogue 12Х18Н9Т - AISI 321
12Х18Н10Т
12Х18Н10Т – austenitic stainless steel. Corrosion-resistant steel, which has found its application in various industries. But, first of all, steel grade 12Х18Н10Т is used in the food, pharmaceutical and chemical industries. In addition, it is popular in the petrochemical industry, mechanical engineering, and energy.
The properties and characteristics of the finished product made from this grade of stainless steel are such that it is resistant to aggressive environments and can be used at high temperatures. 12x18n10t is used to produce welded apparatus and vessels, as well as water pipes.
Chemical composition and decoding 12Х18Н10Т, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 9-11
- Mn - no more than 2
- Si - no more than 0.8
- Ti - 0.6-0.8
- Cu - no more than 0.3
- P - no more than 0.035
- S - no more than 0.02
Imported analogue 12Х18Н10Т - AISI 321, 321H
12Х18Н12Т
Stainless steel 12Х18Н12Т is a popular brand among chromium alloys. The material resists corrosion in aggressive environments and has a high level of resistance to high temperatures. Belongs to the type of austenitic alloys. High-alloy steel is used in the manufacture of parts operating at elevated temperatures. Stainless steel can be used in aggressive environments.
Chemical composition and decoding 12Х18Н12Т, %
- Cr - 17-19
- Ni - 11 - 13
- Mn - up to 2
- Si - up to 0.8
- Cu - up to 0.3
- C - up to 0.12
- P - up to 0.035
- S - up to 0.02
- (5 C - 0.7) Ti
- the rest is Fe
14Х17Н2
Stainless steel grade 14Х17Н2 belongs to the martensitic-ferritic group of alloys. Stainless steel is difficult to weld and is prone to temper brittleness. It is used to produce work equipment, machine parts, and pipeline fittings.
Chemical composition and decoding of steel 14Х17Н2, %
- Cr - 16-18
- Ni - 1.5-2.5
- Si - 0.8
- Mn - 0.8
- Cu - 0.3
- C - 0.11-0.17
- P - 0.03
- Ti - 0.2
Imported analogue 14Х17Н2 - AISI 431
20Х23Н18
High-alloy steel 20Х23Н18 is a heat-resistant material. Used for the production of individual combustion chambers, clamps, suspensions, and fastening parts. Seamless pipes are also made from steel of this grade, which will be used at high temperatures.
Chemical composition and decoding 20Х23Н18, %
- Cr - 22-25
- Ni — 17-20
- Mn - no more than 2
- Si - no more than 1
- Cu - no more than 0.3
- Ti - no more than 0.2
- P - no more than 0.035
- S - no more than 0.02
Imported analogue 20Х23Н18 - AISI 310
08Х13
Stainless steel 08Х13 belongs to the group of ferritic alloys. It has good corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures. It is used for the manufacture of parts used in mildly aggressive environments: valves, bolts, steam turbine blades.
Chemical composition and decoding 08Х13, %
- Cr - 12-14
- Si - 0.8
- Mn - 0.8
- Ni - 0.6
- C - 0.08
- P - 0.03
- S - 0.025
Imported analogue 08X13 - AISI 403, 409, 410S, 429
08Х17
Stainless steel grade 08Х17 also belongs to the ferritic group of alloys. It is characterized by a high chromium content, due to which the material becomes even stronger. Stainless steel 08X17 is used in mechanical engineering, food and chemical industries. The material functions well in oxidizing and atmospheric conditions.
Chemical composition and decoding 08Х17, %
- Cr - 16-18
- Si - 0.8
- Mn - 0.8
- Ni - 0.6
- C - 0.08
- P - 0.03
- S - 0.025
Imported analogue 08X17 - AISI 430
08Х17Т
An improved version of 08x17 is stainless steel grade 08X17T. In terms of their technical characteristics, they are identical, the difference between the alloys is only in the percentage of elements. This brand also contains titanium, which increases strength and ductility.
Chemical composition and decoding 08Х17Т, %
- Cr - 16-18
- Si - 0.8
- Mn - 0.8
- Ti - 0.8
- Ni - 0.6
- C - 0.08
- P - 0.035
- Cu - 0.03
- S - 0.025
Imported analogue 08Х17Т - AISI 430, 439
12Х13
Chromium stainless steel 12X13 is a rather brittle material that is difficult to weld. Belongs to the martensitic-ferritic class. It is corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant stainless steel. Steel has found its application in the production of parts with increased ductility: steam turbine blades, boiler parts, compressor blades, and aircraft parts. The alloy is intended for use under conditions of shock loads and high temperatures.
Chemical composition and decoding of steel 12Х13, %
- Cr - 12-14
- Si - 0.8
- Mn - 0.8
- Ni - 0.6
- C - 0.1
- P - 0.03
- S - 0.025
Imported analogue 12Х13 - AISI 410
12Х17
For the manufacture of parts for fastening equipment and products for mechanical engineering, stainless steel grade 12X17 can be used. According to its characteristics, the alloy belongs to the ferritic group. This grade of stainless steel does not lose its properties, even when exposed to acids and salt solutions. The material is difficult to weld and prone to temper brittleness.
Chemical composition and decoding of steel 12Х17, %
- Cr - 16-18
- Si - 0.8
- Mn - 0.8
- C - 0.12
- P - 0.035
- S - 0.025
Imported analogue 12Х17 - AISI 430
20Х13
Characteristics of stainless steel grade 20Х13: belongs to the martensitic class of alloys, intended for the manufacture of power engineering parts, furnace equipment, various fasteners and fittings. Stainless steel is difficult to weld and is prone to temper brittleness.
Chemical composition and decoding of steel 20Х13, %
- Cr - 12-14
- Si - 0.6
- Mn - 0.6
- Ni - 0.6
- C - 0.2
- P - 0.033
- S - 0.025
Imported analogue 20X13 - AISI 420
30Х13
Characteristics of steel 30Х13: corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant material. Belongs to the martensitic class. The material is not suitable for welding. Stainless steel has found its application in the manufacture of springs, compressor parts and other devices. When working in a slightly aggressive environment, this is a highly wear-resistant stainless steel grade.
Chemical composition and decoding of steel 30Х13, %
- Cr - 12-14
- Si - 0.8
- Mn - 0.8
- Ni - 0.6
- C - 0.3
- Cu - 0.3
- Ti - 0.2
- P - 0.03
- S - 0.025
Imported analogue 30X13 - AISI 420S, 420F
Mechanical properties of St4sp at normal temperature
| Type of delivery | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Heat treatment |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Pipes, GOST 8696-74 | 372 | 245 | 23 | |||||
| Pipes, GOST 10705-80 | 372 | 225 | 22 | |||||
| Rolled goods, GOST 535-2005 | 370-490 | 205-255 | 23-26 | |||||
| Thick sheet, GOST 14637-89 | 370-480 | 205-245 | 23-26 | |||||
| Fittings, GOST 5781-82 | 373 | 235 | 25 | |||||
| Wire rod, GOST 30136-95 | 490-540 | 60 |