The need to harden metal in a home environment is not uncommon. It can occur for a number of reasons, for example, if a tool or hardware does not meet the required strength to solve certain problems - it has a soft structure. Also, if the manufacturing process is disrupted, the parts may overheat and become too fragile. If the question arises of how to harden a bolt at home, there is only one answer - study the basic concepts of hardening metal and try to do it in practice.
To begin with, you should not resort to hardening those threaded elements whose strength needs to be increased. It would be more practical to take a defective part from a similar grade of metal and perform a thermal operation on it, and only after that, if the effect is positive, repeat the procedure completely. The article below will provide basic information on the topic of hardening steel at home.
Methodology
In order to carry out the work of hardening steel, you need to take into account how such a process is carried out correctly. Hardening is a process of increasing the hardness of the surface of an iron or alloy, which involves heating a sample to a high temperature and then cooling it. Despite the fact that at first glance the process in question is simple, different groups of metals differ in their unique structure and characteristics.
Heat treatment at home is justified in the following cases:
- If necessary, strengthen the material, for example, at the cutting edge. An example is the hardening of chisels and chisels.
- If it is necessary to increase the plasticity of an object. This is often necessary in the case of hot forging.
Professional hardening of steel is an expensive process. The cost of 1 kg of increasing surface hardness costs approximately 200 rubles. It is possible to organize hardening of steel at home only taking into account all the features of increasing surface hardness.
Process Features
Steel can be hardened taking into account the following points:
- Heating should occur evenly. Only in this case the structure of the material is homogeneous.
- The steel should be heated without the formation of black or blue spots, which indicates severe overheating of the surface.
- The sample cannot be heated to an extreme state, since changes in the structure will be irreversible.
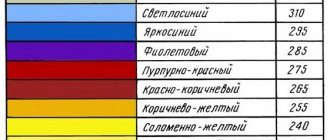
- The bright red color of the metal indicates that the steel has been heated correctly.
- Cooling must also be carried out evenly, for which a water bath is used.
Temperature of the workpiece depending on the color when heated
It is recommended to take these points into account when considering how to harden at home.
Modes of hardening and tempering of steels
What is metal hardening and its types
Hardening is understood as a type of heat treatment of a metal, consisting of heating it to a temperature, upon reaching which a change in the structure of the crystal lattice occurs (polymorphic transformation) and further accelerated cooling in water or an oil medium. The purpose of this heat treatment is to increase the hardness of the metal.
Hardening is also used, in which the heating temperature of the metal prevents a polymorphic transformation from taking place. In this case, its state is recorded, which is characteristic of the metal at the heating temperature. This state is called a supersaturated solid solution.
Polymorphic transformation hardening technology is used mainly for products made of steel alloys. Non-ferrous metals are subjected to hardening without achieving a polymorphic change.
After such treatment, steel alloys become harder, but at the same time they become more brittle, losing their ductility.
To reduce unwanted brittleness after heating with polymorphic change, a heat treatment called tempering is used. It is carried out at a lower temperature with gradual further cooling of the metal. In this way, the stress of the metal is relieved after the hardening process, and its fragility is reduced.
When hardening without polymorphic transformation, there is no problem with excessive brittleness, but the hardness of the alloy does not reach the required value, therefore, during repeated heat treatment, called aging, it is, on the contrary, increased due to the decomposition of the supersaturated solid solution.
Features of steel hardening
Mainly stainless steel products and alloys intended for their manufacture are hardened. They have a martensitic structure and are characterized by increased hardness, leading to brittleness of products.
If you heat treat such products by heating to a certain temperature followed by rapid tempering, you can achieve an increase in viscosity. This will allow the use of such products in various fields.
Types of steel hardening
Depending on the purpose of stainless steel products, it is possible to harden the entire item or only that part of it that must be functional and have increased strength characteristics.
Therefore, hardening of stainless steel products is divided into two methods: global and local.
Video:
Cooling medium
Achieving the required properties of stainless materials largely depends on the choice of cooling method.
Different grades of stainless steel undergo cooling differently. If low-alloy steels are cooled in water or its solutions, then for stainless alloys oil solutions are used for these purposes.
Important: When choosing a medium in which to cool the metal after heating, it should be taken into account that cooling occurs faster in water than in oil! For example, water at a temperature of 18°C can cool an alloy by 600°C in a second, but oil by only 150°C.
In order to obtain high metal hardness, cooling is carried out in running cold water. Also, to increase the hardening effect, a brine solution is prepared for cooling by adding about 10% table salt to the water, or an acidic medium containing at least 10% acid (usually sulfuric) is used.
In addition to the choice of cooling medium, the cooling mode and speed are also important. The temperature decrease rate must be at least 150°C per second. Thus, in 3 seconds the temperature of the alloy should drop to 300°C. A further decrease in temperature can be carried out at any speed, since the structure fixed as a result of rapid cooling will no longer be destroyed at low temperatures.
Important: Cooling the metal too quickly leads to its excessive fragility! This should be taken into account when hardening yourself.
The following cooling methods are distinguished:
- Using one medium, when the product is placed in a liquid and kept there until completely cooled.
- Cooling in two liquid media: oil and water (or saline solution) for stainless steels. Products made of carbon steel are first cooled in water, since it is a fast cooling medium, and then in oil.
- Using the jet method, when the part is cooled with a stream of water. This is very convenient when you need to harden a specific area of the product.
- Using the method of step cooling in compliance with temperature conditions.
Temperature
The correct temperature regime for hardening stainless steel products is an important condition for their quality. To achieve good characteristics, they are uniformly heated to 750-850°C, and then quickly cooled to a temperature of 400-450°C.
Important: Heating the metal above the recrystallization point leads to a coarse-grained structure, which worsens its properties: excessive brittleness, leading to cracking!
To relieve stress after heating the metal to the desired hardening temperature, step-by-step cooling of products is sometimes used, gradually lowering the temperature at each heating stage. This technology allows you to completely remove internal stress and obtain a durable product with the required hardness.
Equipment and features of the process
Special equipment is often used to heat the surface. This is due to the fact that heating steel to the melting point is quite difficult. The following equipment is often used at home:
- electric oven;
- blowtorch;
- thermal oven;
- a large fire that is surrounded to redirect the heat.
Mobile forge for heating parts
When choosing a heat source, you should take into account the fact that the part must be completely placed in the oven or fire on which the heating is carried out. It will also be correct to select equipment based on the type of metal that will be processed. The higher the strength of the structure, the more the alloy is heated to impart plasticity.
In cases where only part of the part needs to be hardened, jet hardening is used. It provides for a jet of cold water to hit only a certain part of the part.
A water bath or barrel or bucket is often used to cool steel. It is important to take into account the fact that in some cases gradual cooling is carried out, in others it is rapid and abrupt.
Increased hardness over open fire
In everyday life, hardening is often carried out over an open fire. This method is only suitable for a one-time process of increasing surface hardness.
All work can be divided into several stages:
- First you need to make a fire;
- at the time of lighting the fire, two large containers are prepared that will correspond to the size of the part;
- In order for the fire to produce more heat, you need to provide a large amount of coals. they give a lot of heat for a long time;
- one container should contain water, the other should contain motor oil;
- special tools should be used to hold the hot part being processed. In the video you can often see blacksmith pliers, which are the most effective;
- After preparing the necessary tools, you should place the object in the very center of the flame. in this case, the part can be buried in the very depths of the coals, which will ensure heating of the metal to a fusible state;
- coals that are bright white are hotter than others. The metal smelting process must be closely monitored. the flame should be crimson, but not white. if the fire is white, then there is a possibility of overheating of the metal. in this case, performance deteriorates significantly and service life is reduced;
- the correct color, uniform over the entire surface, determines the uniform heating of the metal;
- if darkening to a blue color occurs, this indicates a strong softening of the metal, that is, it becomes excessively plastic. this should not be allowed, since the structure is significantly disrupted;
- when the metal is completely heated, it should be removed from the source of high temperature;
- after this, the hot metal should be placed in a container with oil with a frequency of 3 seconds;
- The final stage can be called immersing the part in water. In this case, the water is periodically shaken. This is due to the fact that the water quickly heats up around the product.
When performing work, care should be taken as hot oil can cause damage to the skin. In the video you can pay attention to what color the surface should be when the desired degree of plasticity is achieved. But to harden non-ferrous metals, it is often necessary to be exposed to temperatures in the range of 700 to 900 degrees Celsius. It is practically impossible to heat non-ferrous alloys over an open fire, since it is impossible to achieve such a temperature without special equipment. An example is the use of an electric furnace, which is capable of heating the surface up to 800 degrees Celsius.
Checking metal for quality at home
The first step after purchasing a metal item is to check its quality. This can be done using a simple soldering iron. The end of the soldering iron is passed over the metal to identify defects when developing the tool. If the soldering iron sticks to the surface, it means the steel is not hardened, and with frequent use the tool will become deformed. If, on the contrary, the tip of the soldering iron passes smoothly over the steel and almost bounces off it, then the metal is too hardened. In this case, you need to heat treat the steel tool to increase its strength.