Is stainless steel a non-ferrous metal or a ferrous one?
Very often, at scrap metal collection points, people get confused and do not know which metal is stainless steel - non-ferrous or ferrous. The composition of stainless steel can be different, depending on the brand, type and purpose.
So what is stainless steel? What metals does it belong to, ferrous or non-ferrous? This article from a construction magazine will examine the composition of stainless steel and its main differences from non-ferrous and ferrous metals.
General information
Technically, the division of industrially used metals and their alloys into ferrous and non-ferrous is quite simple: ferrous metal usually includes iron and its alloys - primarily cast iron and various types of steel. Nonferrous metals are additionally conventionally divided into two subgroups: heavy, which includes lead, tin, copper, zinc, nickel and their alloys, and light, which includes magnesium, titanium, aluminum and their alloys. The value of non-ferrous metal and ferrous metal scrap for the receiver is not the same, and in addition to the chemical composition, a number of additional factors play an important role; you can read more about prices here - sdaymetall.ru/tsvetnoj-metall/stal-nerzhavejka/.
Stainless steel
From the point of view of chemical composition, the determining factor in the cost of stainless steel scrap is the content of such a component as nickel. Typically, three groups are conventionally distinguished in order of increasing value:
- stainless steel with nickel content from 2 to 5%%;
- stainless steel with nickel content from 5 to 12%%;
- stainless steel with a nickel content of over 12%%.
If chromium is present in the composition, its share must be at least 17-18% (the actual composition is usually determined on site, using a hand-held analyzer operating on the principle of spectral analysis). For all cases when stainless steel is used, a simple rule is true: metal shavings or powder have the least value, and lump metal has the highest value.
Stainless steel manufacturing plants
At the moment, there are actually three sources of supply for consumers and sellers of stainless steel products: Russian-made corrosion-resistant steel, high-quality metal from European and South American manufacturers, and rolled products from India and Southeast Asia.
Due to the instability of nickel prices, manufacturers are currently refocusing on steel grades other than the 300 series. For China, these are primarily ferritic steels that do not contain nickel at all; for India and commercial enterprises in China - the 200th series with a reduced nickel content and additional additives that reduce the hardness of the alloy and increase its corrosion-resistant properties.
Currently, the market is unevenly divided between steel series. The most expensive 300 series is traditionally used most widely (brands such as AISI 304, AISI 316, AISI 321, AISI 310 S, AISI 309 S and others), the use of the 200 series, which is unfamiliar to domestic manufacturers, is most limited. In recent years, as a result of research and experimentation, steel grades of this series have undergone significant changes in the chemistry and technological rolling process and currently deserve closer attention. Steel 200 groups are cheaper than AISI 304 by approximately 16-17%. AISI 430 (nickel-free) steel is even cheaper - about 50% compared to AISI 304. With rising nickel prices, this difference may increase even more. However, the use of this grade of steel is still controversial in relation to food products and medical technology.
Manufacturing plants in Russia
- Chelyabinsk Metallurgical Plant",
- Volgograd Metallurgical Plant "Red October"
- Izhora factories
Manufacturing plants in Europe
- Acerinox, SA Spain,
- Marcegaglia SpA, Italy,
- Arcelor Stainless Int. France,
- Outokumpu Stainless, Finland,
- ThyssenKrupp, Germany.
Reception of non-ferrous metals
The case of non-ferrous metal is more interesting, since GOST 1639-93 “Categories of scrap and waste of non-ferrous metals and alloys” is used on the territory of the Russian Federation (a reader who is specifically interested in this issue can easily find its text in the public domain on the Internet). So, for example, for the case of copper, the detailed classification of scrap is as follows:
- the most valuable category is formed by the so-called. “heavy copper scrap No. 1” (piece scrap) – this includes current-carrying conductors from wires and cables with a minimum cross-section from
0.15 mm, various electrical busbars, technological waste in the form of copper stampings or cuttings without any additional coating;
- much less valuable “copper scrap No. 2” includes unalloyed copper with slight surface oxidation or traces of soldering (copper wire in varnish insulation, oxidized/burnt electrical wire, winding products such as electrical coils, uncut power cables, etc.);
- copper scrap is assessed even lower in the form of pieces of copper pipes without any foreign inclusions (for example, remnants of fittings);
- a separate category is copper alloyed with beryllium - most often it comes in the form of technological stamping or special-purpose pipes;
- “light copper scrap” is inexpensive - this includes various copper products for household use and items with a large surface area (copper sheet, foil, pipes/gutters);
- The lowest category includes items made of copper-containing alloys with a copper content of at least 30%.
Overall rating of the article:
Published:
2019.02.28
Updated:
2019.02.28
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Black metals
Metals are divided into non-ferrous and ferrous. Ferrous metals , in essence, are iron that contains varying amounts of carbon, as well as different crystal lattice. Ferrous metals include steel and cast iron, which in turn have a fairly large number of main classes. In the production of cast irons and steels of various types, ferrous metals extracted from metal ores are used. In the metal economy, ferrous metals account for more than 90%, indicating their wide distribution. The percentage of carbon determines what properties the material will acquire—cast iron or steel. To improve the quality of ferrous metal, alloying additives (other metals and alloys, as well as chemical elements) are used, which improve the properties of the alloys and give them the desired shade of characteristics depending on its application. Common alloying additives are:
Color spectrum
By using new electrochemical technologies, metallurgists, in addition to the primary colors, have learned to impart the following colors to stainless steel:
- bronze - widely used in the production of gas stoves;
- red - the usual color of a stainless steel refrigerator has become commonplace, while a stylish red stainless steel refrigerator will decorate any kitchen;
- gold - found application in the manufacture of heaters;
- black - black stainless steel is used in the manufacture of gas and electric stoves and electric kettles.
Additionally, by using different color coatings, you can not only significantly expand the color gamut, but also give the same color different shades.
Classification of ferrous metals
In most cases, the classification of ferrous metals is based on the division of elements according to their chemical composition and properties . The content of alloying elements determines the iron and its alloy. In turn, a certain percentage of carbon in the alloy indicates whether it is cast iron or steel. Thus, cast iron contains more than 1.7% carbon, and steel contains from 0.2 to 1.7% carbon. Classification of ferrous metals involves division into the following classes:
Also, the classification of ferrous metals implies the separation of alloyed and unalloyed steels, which are also called carbon steels. Carbon steels include steels in which carbon is the main component, and impurities do not have much effect on the properties of the metal. Alloyed steels have one or more alloyed elements, which have a huge impact on the properties of steel. /Alloy steels are very widely used for the manufacture of critical parts that bear heavy loads, experience different temperatures, and strong frictional effects. The use of such steel is widespread in mechanical engineering, tractor manufacturing, heavy industry and other areas.
Types of ferrous metals
Types of ferrous metals made from steel have many uses. However, all types are different and have their own purpose and area of application. Also, various types of ferrous metals , in particular steel, after undergoing heat treatment, acquire distinctive properties. Many alloys lend themselves well to rolling, pressing, and casting successfully. Others are soft enough to be processed by hand. Such types of ferrous metals as stainless steel, having the necessary alloying elements, have very high resistance to corrosion, great hardness and strength. This type of steel is successfully used in the food industry, medicine, for the manufacture of household items, for the production of turbines, etc. Another type of ferrous metal is cast iron. Cast iron is an alloy of iron and carbon and its content is higher than in steel. Since cast iron has good casting properties, it is mainly used for cast parts. Cast iron is divided into types:
- Foundry cast iron;
- Pig iron;
- Anti-friction cast iron;
- Ductile iron;
- Low alloy cast iron;
- High alloy cast iron;
- Nodular cast iron;
- Cast iron with vermicular graphite for castings.
Foundry cast iron is used for casting; flake graphite contributes well to this. Malleable - has remarkable ductility, can be forged well, which is where the name comes from. Certain types of ferrous metal , for example, nodular graphite cast iron, due to its spherical structure, are used in the manufacture of parts of very high quality.
The use of stainless steels in household appliances
The uniqueness of the stainless steel surface is its density; it has no pores or microcracks for the penetration of dirt or bacteria. Ease of care and cleaning, its environmental neutrality and resistance to aggressive substances compared to other materials make it indispensable for the manufacture of household stoves and other kitchen appliances. An important factor is a good and smooth (without kinks, irregularities or scratches) metal surface.
Strict restrictions on the solubility of heavy metals present in food contact equipment are already in place and will certainly be tightened in the future. According to European standards, the amount of chromium and nickel dissolved from steel during the standard test according to ISO 6486/1 is allowed no more than 2 mg/dm2. For austenitic steels, the amount of dissolved nickel and chromium is less than 0.02 mg/dm2, i.e. about 1% of the permissible value.
The following grades are classified as food grade corrosion-resistant steels:
| Steel grade according to GOST 5632-72 | Analogous to ASTM A240/A 240M-05a |
| 08Х18H10 | 304 |
| 08Х18Н10Т | 321 |
| 12Х18Н10Э (T) | 303 |
Types of scrap metal: ferrous, non-ferrous and precious metals
The official classification of metal waste is extensive and multi-stage. It takes into account numerous characteristics by which or the combination of which this or that scrap metal belongs to a certain type, group, class, category.
In the usual practice adopted in relations between organizations that procure secondary metals and deliverers, types of scrap metal are categorized more simply, which ensures optimal mutual understanding and a transparent system of purchase prices when making delivery/reception transactions.
Types of scrap metal: separation according to main characteristics
When classifying scrap metal as one type or another, the following characteristics are primarily taken into account:
- chemical composition;
- physical structure;
- origin;
- mass and dimensional characteristics of fragments;
- degree of purity;
- quality indicators.
The basis of any classification is the division of secondary metals into ferrous and non-ferrous.
The first category includes metals and iron-based alloys - steel and cast iron.
The second is much more extensive, and combines numerous non-magnetic metals and their alloys.
“Stainless” steels stand somewhat apart: in some cases they are classified as ferrous metals, sometimes (some grades with a high content of alloying elements) as non-ferrous.
Scrap of noble (precious) metals also occupies a special place.
Types of scrap metal (table by group)
Stainless alloys with low alloy content
Other
Steel tarnish colors
Iron alloys, including corrosion-resistant ones, when heated, become covered with a thin film of iron oxides of a wide variety of color shades and tarnish colors appear, which correlate with certain heating temperatures. There are so-called “heat-resistant” alloys, in which the temperature at which oxides begin to form is higher than that of other alloys, but such grades are not food grade and are very expensive due to their high nickel content.
For carbon steel
| Heating temperature | Tarnish color |
| 220 | light yellow |
| 240 | dark yellow |
| 255 | brown-yellow |
| 265 | brown-red |
| 275 | purple-red |
| 285 | violet |
| 295 | cornflower blue |
| 315 | light blue |
| 330 | grey |
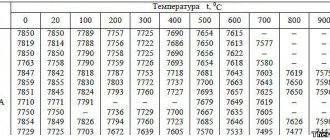
For stainless steels
| Temperature | 12Х18Н9Т | ХН75МБТУ |
| 300 | light straw | — |
| 400 | straw | light yellow |
| 500 | reddish brown | yellow |
| 600 | violet blue | brown |
| 650 | blue | blue |
| 750 | — | blue |
Most importantly, the duration of heating has a significant impact on the color of the surface. Indeed, more or less prolonged processing can cause steel to turn blue at a temperature lower than that required for the appearance of even a straw-yellow color.
Types of ferrous metal scrap
This includes items made from steel, cast iron and stainless alloys with low additive content.
The categorization of this recyclable material is regulated by the requirements of GOST 2787-75.
- According to carbon content, 2 classes are defined - steel, cast iron;
- based on the presence or absence of alloying additives, 2 classes have been established (carbon, alloyed); the latter, in turn, are divided by the state standard into 67 groups depending on the types and percentage of alloying elements.
- According to quality criteria, there is a division into 28 categories.
Another principle for categorizing this type of waste is dimensional, mass and geometric parameters.
Thus, one of the most common categories 3A includes pieces of metal with maximum dimensions of 1500x500x500 mm, weighing from 1 to 600 kg, and a number of others; 5A is oversized waste; category 12A combines industrial and household batch grade scrap, 13A is wire and fittings.
Other types of ferrous scrap are also standardized according to these criteria.
Of particular importance is the division depending on origin:
- recycled products and their parts (parts of machines and building structures, rails, pipes, fittings, household items, etc.);
- industrial (waste from foundry and metalworking industries - shavings, trimmings, scrap, defective parts);
- stale metal (not used, which has lost its original performance properties as a result of long-term storage and is subject to recycling).
Separately, groups are determined by contamination indicator (the amount of foreign, including non-metallic, impurities).
Types of non-ferrous metal scrap
It includes numerous items made of metals that do not belong to the first category, except for precious ones.
The categorization of this recyclable material is regulated by the requirements of GOST 1639-2009.
The main types of non-ferrous metal scrap are:
- aluminum;
- copper;
- bronze;
- brass;
- lead;
- zinc and TsAM;
- nickel-containing alloys;
- magnesium;
- rare metal scrap;
- semiconductor scrap.
Among the listed types, aluminum predominates quantitatively.
The state standard establishes 32 types of waste, but in common practice it is customary to distinguish some, among which the most common are:
When sorting at collection points, car wheels and radiators are usually also separated.
A special place is occupied by shavings and drink cans.
Other aluminum belongs to the conventional “mix” category, i.e. contains parts and fragments of different composition, geometry and size.
It should be noted that the name can sometimes confuse the sender; Thus, the usual pots, bowls, mugs, and milk flasks belong to the “food” category, but frying pans have nothing to do with it.
Among copper items, one should highlight cable copper, wire (from the windings of transformers and electric motors), electrical parts (terminals, conductive clamps, shoes, etc.), a special category of “shine” and some others; Waste of different quality and structure belongs to the “mix” category.
Among bronze and brass products, plumbing fixtures (taps, mixers, their fasteners), car radiators, fittings, and household items predominate.
Metalworking waste from industries using these materials stands separately.
It is sometimes easy for an inexperienced deliverer to make a mistake: often products made from other metals look like they contain copper; For example, aluminum wires coated with copper, zinc faucets that look like brass, and even lamps or door handles made of ferrous metal that imitate bronze due to electroplating are widespread.
Scrap lead includes cable protective sheathing, battery plates, balancing weights, as well as the so-called “self-melt”, which are homogeneous shapeless or hand-molded pieces.
Often, at non-ferrous metal collection points, batteries are accepted in their entirety, both drained and filled.
There are certain features in the categorization of other types of non-ferrous metal scrap.
What is ferrous metal | Metall
29/04/2013
In the modern world, a variety of building materials have appeared on the world market. But despite such a wide choice, the demand for metal does not fall, because rolled metal is the basis of almost all building structures and structures. As we know, no construction can do without metal structures. Also, the metallurgical industry is used in other types of production, such as mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, machine tool building and many other types of industries.
In order for the design, no matter in which direction of production, to be of high quality and reliable, it is worth choosing the right rolled metal. As practice shows, ferrous metallurgy is most widespread. This wide demand for it is due to its longer service life and excellent advantages of durability and reliability.
Products made of ferrous metal are divided into several groups, differing from each other in the method of application, type and method of production.
Let's look at the most basic types of rolled metal:
1- Rolled metal products, the main types of which include reinforcement, rails, wire rod, beam, circle, strip, hexagon, square, etc. The most common today is reinforcement.
2- Shaped rolled products, which include products such as angles, I-beams, and channels. These products are usually used in the construction of prefabricated buildings.
3- Rolled sheets are a special group of rolled metal products, which includes cold-rolled sheets, steel sheets, hot-rolled sheets, galvanized sheets and other types of sheets. This group, consisting of ferrous metal, is used mainly in construction and mechanical engineering.
4- Art rental includes products where the name speaks for itself. To a greater extent, this type of product was formed thanks to fashion and new trends in style. That is, it has become widely used in the design of houses, these are bent and forged rods, as well as various intricate products that have found their place in interior design, both external and internal.
5- Rolled stainless steel. Everything is simple here - stainless steel products.
What type of rolled metal products are found in production? Of course, such products include:
— Wire rod, which consists of carbon steel of standard quality. It is mainly used for stringing onto wire.
— The beam is produced in the form of an I-beam.
— The channel has a cross-section in the form of the letter “P.”
The hero (Michael Douglas) of this seemingly simple film is fed up with the perfectly organized life of an extremely rich man, but inside his soul there is a darkness of emptiness caused by the fact that his father committed suicide by throwing himself from the roof of the house on the day of his fortieth birthday in front of his son. https://smotret-film-online.info/kino/thriller/1029-igra-1997-besplatno.html.
a-kranm.com
Types of precious metal scrap
This category includes:
- jewelry, put out of use for various reasons, and its fragments;
- elements of silver-zinc batteries, catalysts, chemical equipment and other devices containing precious metals;
- parts and elements of radio-electronic devices;
- some other products.
The procedure for receiving and storing precious metal scrap differs significantly from the usual due to the need to ensure its proper accounting and proper storage conditions.