Steel oxidation
One of the important tasks in preserving metal structures is combating the harmful effects of the environment.
High humidity and the presence of chemically active elements in the air that can destroy the integrity of metal, especially steel, lead to a deterioration in such indicators as reliability and strength. To solve this problem, finished products are coated with various types of protective coatings.
Steel oxidation
There are various methods to improve surface stability and corrosion resistance.
One of these methods is to create a protective film on the surface of steel using special processing methods.
Understanding the essence of the purpose of this process requires an answer to the question - what is oxidation?
The essence is to use the properties of the oxidation-reduction reaction, as a result of which a protective film is formed on the surface of the steel. Steel oxidation is also carried out.
This process allows you to solve the following problems:
- Protect steel structures from corrosion (this is especially important in modern construction where metal structures are used).
- Limit exposure to aggressive components of the external environment (solutions of acids, alkalis, chemical elements that destroy the integrity of steel).
- Create a surface layer with good electrical insulating characteristics.
- Give details, individual elements, and the structure as a whole original decorative and aesthetic properties.
Metal oxidation is carried out using the following methods:
- Using chemical reactions (chemical oxidation of steel).
- Use of electrochemical processes (anodic oxidation).
- Carrying out heat treatment (thermal method).
- Creation of low-temperature plasma (plasma method).
- Laser (special laser installations are used).
Anodized steel
Let's look at each method in more detail.
Chemical oxidation
This process involves the processing of metals with solutions, mixtures, melts of chemical elements (oxides such as chromium oxides).
This oxidation allows for the so-called passivation of the metal surface. It involves the creation of an inactive (passive) formation in a metal layer close to the surface.
A thin surface layer is created that protects the main part of the structure.
Technologically, this process is implemented by lowering the prepared metal part into an alkali or acid solution of a given percentage.
They keep it there for a certain time, which allows the oxidation-reduction reaction to fully occur. Then the part is thoroughly washed, subjected to natural drying, and final processing.
Chemical oxidation of steel
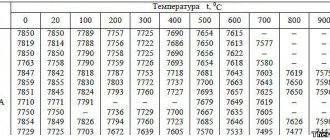
To create an acid bath, three types of chemically active acids are used: hydrochloric, nitric, and orthophosphoric. The acceleration of the chemical reaction is stimulated by adding manganese, potassium, and chromium compounds to the acid solution. The oxidation reaction occurs at a solution temperature in the range from 30 °C to 100 °C.
The use of solutions based on alkaline compounds allows the use of additives of sodium nitrate and manganese dioxide compounds. In this case, the solution temperature must be increased to 180 °C, and with additives up to 300 °C.
After the procedure, the part is washed and dried. Sometimes potassium bichromate is used to consolidate the chemical reaction process.
To increase the shelf life of the formed film, chemical oxidation with oiling is carried out. Sometimes this process is called chemical oxidation.
The final coating with oil results in a reliable anti-corrosion coating with a striking, highly decorative black color.
This type is called electrochemical oxidation of steel. Sometimes it is called anodic oxidation of steel. The term anodizing is also used. It is based on the chemical process of electrolysis. It can be carried out in both solid and liquid electrolytes. The prepared workpiece is placed in a container with an oxide solution.
The electrolysis reaction is possible by creating a potential difference between two elements.
The surface of the oxidized product is characterized by a positive potential. Chemically active elements with a negative potential are isolated from the solution. The interaction of oppositely polar elements is called the electrolysis reaction (in our case, anodization).
Anodic oxidation
The anodization reaction can be performed at home. It is required to strictly comply with safety regulations. The reaction involves harmful reactive fluids and unsafe voltage.
The use of anodic oxidation makes it possible to create protective films of various thicknesses. The creation of thick films is possible through the use of a sulfuric acid solution.
Thin films are obtained in solutions of boric or phosphoric acid. Using anodization, you can give the surface layer of metal beautiful decorative shades. For this purpose, the process is carried out in organic acids. Oxalic acid, maleic acid, sulfosalicylic acid are used as such solutions.
Micro-arc oxidation is a special anodizing process. It makes it possible to obtain coatings with high physical and mechanical characteristics.
These include: protective, insulating, decorative, heat-resistant and anti-corrosion properties. In this case, oxidation is carried out under the influence of alternating or pulsed current in special baths filled with electrolyte.
Such electrolytes are weakly alkaline compounds.
Anodic oxidation at home
Anodizing allows you to obtain a surface layer with the following properties:
- reliable anti-corrosion coating;
- good electrical insulators;
- thin but durable surface layer;
- original color scheme.
Anodizing stainless steel requires a special approach. This is due to the fact that such steel is considered a neutral (inert) alloy. Therefore, in production, when anodizing a large number of parts, a two-step procedure is used.
At the first stage, stainless steel is anodized together with another metal that is more suitable for this process. It may be nickel, copper, other metal or alloy.
At the second stage, the stainless steel itself is oxidized directly. To simplify the oxidation process, special additives, so-called passivating pastes, are being developed today. These compounds speed up the reaction process of stainless steel.
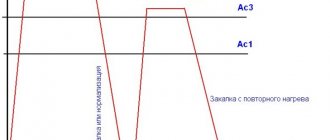
According to the term, oxidation occurs at relatively high temperatures. The value of this indicator depends on the steel grade. For example, the process of thermal oxidation of ordinary steel occurs in special furnaces.
A temperature close to 350 °C is created inside. A class of alloy steels undergo thermal oxidation at higher temperatures. It is necessary to heat the workpiece to 700 °C. Treatment continues for one hour.
This process is called steel bluing.
Steel bluingSteel gun after bluing
Plasma oxidation
This oxidation is carried out in an environment with a high concentration of oxygen using low-temperature plasma. Plasma is created due to discharges that occur when high- or ultra-high-frequency currents are applied.
Plasma oxidation is used to form oxidized films on fairly small surfaces.
It is mainly used in electronics and microelectronics. With its help, layers are formed on the surface of semiconductor compounds, the so-called pn junctions. Such films are used in transistors, diodes (including tunnel diodes), and integrated circuits. In addition, it is used to increase the photosensitive effect in photocathodes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QlH5lBmQDD4
Plasma oxidation
A type of plasma oxidation is oxidation using high-temperature plasma. Sometimes it is replaced by an arc discharge with an increase in temperature to 430 ° C and higher. The use of this technology can significantly improve the quality of the resulting coatings.
Laser oxidation
This technology is quite complex and requires special equipment. To carry out oxidation use:
- pulsed laser radiation;
- continuous radiation.
In both cases, infrared laser systems are used. Due to laser heating of the top layer of material, it is possible to obtain a fairly resistant protective film. However, this method is only applicable to a small surface area.
Laser oxidation
DIY oxidation
You can organize the process of oxidation of small metal products in your home laboratory. By strictly following the sequence of technological operations, high-quality oxidation is achieved.
The whole process should be divided into three stages:
- Preparatory stage (includes preparation of the necessary equipment, reagents, and the part itself).
- Direct oxidation stage.
- The final stage (removing harmful traces of the chemical process).
At the preparatory stage the following work is carried out:
- Rough cleaning of the surface (use a metal brush, sandpaper, polishing machine with appropriate discs).
- Final mechanical polishing of the surface.
- Removing grease and polishing residues. It's called decopying. It is carried out in a five percent solution of sulfuric acid. The residence time of the workpiece in the solution is one minute.
- Washing the part. This procedure is carried out in warm boiled water. It is advisable to carry it out several times.
- The final operation is the so-called passaging. After washing the part after processing, place clean boiled water in which laundry soap is first dissolved. This solution, together with the part, is heated and brought to a boil. The boiling procedure is continued for several minutes.
Oxidation at home
This concludes the preliminary stage.
The main stage of oxidation consists of the following operations:
- Water is poured into a neutral bowl (preferably with an enamel coating). About caustic soda is dissolved in it. The volume of a substance depends on the amount of water. It is advisable to obtain a solution of about 5 percent.
- The workpiece is completely immersed in the resulting solution.
- The solution with the immersed part is heated to 150 degrees. This is practically a boiling process. It lasts approximately two hours. Using the tool, the quality of the process is checked. If necessary, the time can be increased.
At the final stage, the following operations are performed on the part:
- The part is removed from the reagent bath.
- Place it on a flat surface and allow it to cool naturally (without forced cooling). It is advisable to create conditions that limit contact with ambient air.
- Visually check the quality of the resulting oxidation. The absence of uncovered areas, the density of the formed film, the final color.
Thus, oxidation can be carried out at home. The main thing is to follow these recommendations.
, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Applicable devices and equipment
On an industrial scale, a sulfuric acid solution is used for anodizing steel, which ensures a high process speed and the greatest penetration depth.
Modern installations are fully automatic lines with a minimum number of personnel, whose role is reduced to monitoring the work process. All equipment can be divided into three types:
- Basics. It includes a bath and a cathode. The container must be made of an inert material with high thermal insulation properties - in this case, the electrolyte will not heat up too quickly and will last much longer. The cathode material depends on the type of metal being processed. For example, to anodize aluminum, a lead sheet is used, the size of which should be twice the dimensions of the workpiece.
- Serving. This includes units that are responsible for ensuring the operation of the installation: drive mechanisms and devices for transmitting current.
- Auxiliary. We are talking about equipment on which work is carried out to prepare workpieces for anodizing. This also includes mechanisms for moving parts and storing them.
When selecting a suitable installation, the following features must be taken into account:
- The most labor-intensive operations are loading and unloading the workpiece. Pay attention to the reliability and power consumption of these nodes.
- Productivity depends on the power of the power plant. As practice shows, the optimal rectifier power is 2.5 kW. The presence of stepless voltage level adjustment will be an additional advantage, facilitating the process of anodizing steel.
Stepless regulation will occur after the formation of a protective layer of medium thickness, when in order to maintain the current level it will be necessary to gradually increase the voltage.
- Contact pads made of flexible material should be installed along the rings of the container. Copper elements will cope best with this task.
Anodizing stainless steel - Metalworker's Handbook
One of the important tasks in preserving metal structures is combating the harmful effects of the environment. High humidity and the presence of chemically active elements in the air that can destroy the integrity of metal, especially steel, lead to a deterioration in such indicators as reliability and strength.
To solve this problem, finished products are coated with various types of protective coatings.
Steel oxidation
There are various methods to improve surface stability and corrosion resistance.
One of these methods is to create a protective film on the surface of steel using special processing methods.
Understanding the essence of the purpose of this process requires an answer to the question - what is oxidation?
The essence is to use the properties of the oxidation-reduction reaction, as a result of which a protective film is formed on the surface of the steel. Steel oxidation is also carried out.
This process allows you to solve the following problems:
- Protect steel structures from corrosion (this is especially important in modern construction where metal structures are used).
- Limit exposure to aggressive components of the external environment (solutions of acids, alkalis, chemical elements that destroy the integrity of steel).
- Create a surface layer with good electrical insulating characteristics.
- Give details, individual elements, and the structure as a whole original decorative and aesthetic properties.
Metal oxidation is carried out using the following methods:
- Using chemical reactions (chemical oxidation of steel).
- Use of electrochemical processes (anodic oxidation).
- Carrying out heat treatment (thermal method).
- Creation of low-temperature plasma (plasma method).
- Laser (special laser installations are used).
Anodized steel
Let's look at each method in more detail.
Anodic oxidation
This type is called electrochemical oxidation of steel. Sometimes it is called anodic oxidation of steel. The term anodizing is also used. It is based on the chemical process of electrolysis. It can be carried out in both solid and liquid electrolytes. The prepared workpiece is placed in a container with an oxide solution.
The electrolysis reaction is possible by creating a potential difference between two elements.
The surface of the oxidized product is characterized by a positive potential. Chemically active elements with a negative potential are isolated from the solution. The interaction of oppositely polar elements is called the electrolysis reaction (in our case, anodization).
Anodic oxidation
The anodization reaction can be performed at home. It is required to strictly comply with safety regulations. The reaction involves harmful reactive fluids and unsafe voltage.
The use of anodic oxidation makes it possible to create protective films of various thicknesses. The creation of thick films is possible through the use of a sulfuric acid solution.
Thin films are obtained in solutions of boric or phosphoric acid. Using anodization, you can give the surface layer of metal beautiful decorative shades. For this purpose, the process is carried out in organic acids. Oxalic acid, maleic acid, sulfosalicylic acid are used as such solutions.
Micro-arc oxidation is a special anodizing process. It makes it possible to obtain coatings with high physical and mechanical characteristics.
These include: protective, insulating, decorative, heat-resistant and anti-corrosion properties. In this case, oxidation is carried out under the influence of alternating or pulsed current in special baths filled with electrolyte.
Such electrolytes are weakly alkaline compounds.
Anodic oxidation at home
Anodizing allows you to obtain a surface layer with the following properties:
- reliable anti-corrosion coating;
- good electrical insulators;
- thin but durable surface layer;
- original color scheme.
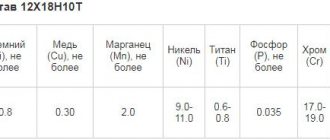
Anodizing stainless steel requires a special approach. This is due to the fact that such steel is considered a neutral (inert) alloy. Therefore, in production, when anodizing a large number of parts, a two-step procedure is used.
At the first stage, stainless steel is anodized together with another metal that is more suitable for this process. It may be nickel, copper, other metal or alloy.
At the second stage, the stainless steel itself is oxidized directly. To simplify the oxidation process, special additives, so-called passivating pastes, are being developed today. These compounds speed up the reaction process of stainless steel.
Thermal oxidation
According to the term, oxidation occurs at relatively high temperatures.
The value of this indicator depends on the steel grade. For example, the process of thermal oxidation of ordinary steel occurs in special furnaces. A temperature close to 350 °C is created inside. A class of alloy steels undergo thermal oxidation at higher temperatures. It is necessary to heat the workpiece to 700 °C. Treatment continues for one hour.
This process is called steel bluing.
Steel bluingSteel gun after bluing
How to anodize metal at home?
Many people associate the beautiful and incomprehensible word “anodizing” with complex physical and chemical technologies, laboratory conditions and other scientific paraphernalia. Few people know that this useful and simple process can be carried out using improvised means: it is possible to anodize titanium and other metals even at home. But what is it, and why is it needed for metal?
Anodizing stainless steel
One of the important tasks in preserving metal structures is combating the harmful effects of the environment. High humidity and the presence of chemically active elements in the air that can destroy the integrity of metal, especially steel, lead to a deterioration in such indicators as reliability and strength.
To solve this problem, finished products are coated with various types of protective coatings.
Steel oxidation
There are various methods to improve surface stability and corrosion resistance.
One of these methods is to create a protective film on the surface of steel using special processing methods.
Understanding the essence of the purpose of this process requires an answer to the question - what is oxidation?
The essence is to use the properties of the oxidation-reduction reaction, as a result of which a protective film is formed on the surface of the steel. Steel oxidation is also carried out.
This process allows you to solve the following problems:
- Protect steel structures from corrosion (this is especially important in modern construction where metal structures are used).
- Limit exposure to aggressive components of the external environment (solutions of acids, alkalis, chemical elements that destroy the integrity of steel).
- Create a surface layer with good electrical insulating characteristics.
- Give details, individual elements, and the structure as a whole original decorative and aesthetic properties.
Metal oxidation is carried out using the following methods:
- Using chemical reactions (chemical oxidation of steel).
- Use of electrochemical processes (anodic oxidation).
- Carrying out heat treatment (thermal method).
- Creation of low-temperature plasma (plasma method).
- Laser (special laser installations are used).
Anodized steel
Let's look at each method in more detail.
Application of etching
The etching process is widely used in production during the cleaning of the upper layers of steel from welds, scale, oxides and rust. It is used when searching for internal defects by removing the top layer of the workpiece or to study the structure of the metal.
This procedure cleans the material, thereby increasing the adhesion of the top layer. This is necessary for the successful connection of a metal workpiece with another surface, after which a paint, enamel, galvanic layer or other protective coating is applied.
This type of processing not only ensures quick cleaning of the workpiece, but also creates a specified pattern on the top layer of metal. Using etching, you can cut out a channel of any thickness or create a complex image. Processing of large workpieces and rolled products is also possible. You can easily adjust the processing depth down to microns, making it possible to process surfaces with complex areas and small grooves. The procedure is used to carry out analysis that determines the formation of intercrystalline corrosion in stainless steel.
In addition, this process is widely used during the processing of carbon, low-alloy and high-alloy steels, non-ferrous metals and titanium. This technology is indispensable when processing small metal parts, watch gears. It is used to manufacture semiconductor chips and printed circuit boards in electronics. This processing method ensures the formation of a conductive channel on the microcircuits. In aircraft manufacturing, etching plays an important role, since through this process the thickness of metal sheets is reduced, thereby reducing the weight of the aircraft. This operation also plays a big role in applying drawings and inscriptions. Etching produces a relief image created by destroying a metal surface according to specific patterns. In everyday life, the operation helps clean the pipeline.
Problems of stainless steel oxidation
The information presented in this article will be useful for materials scientists, technologists and engineers involved in the processing and study of the properties of metals.
The production of decorative coatings is increasingly being used in various branches of mechanical engineering, the automotive industry, and in the production of household items.
Let's consider one of the most popular methods of creating a film - oxidation of stainless steel.
Terms, definitions, types of stainless steel oxidation
By definition, this term refers to the creation of a film of oxides on the surface of stainless steel due to redox reactions.
In addition to the protective function and decorative finishing, the use of this process is involved when it is necessary to create dielectric layers and change surface physical processes occurring in an environment of high magnetic and electric fields.
Depending on how the oxidation was obtained, they are distinguished:
- Thermal process
- Chemical exposure
- Electrochemical process
- Plasma oxidation
Let's look at these processes in more detail.
Thermal process
The thermal oxidation process involves treating metal at certain temperatures in an environment of oxygen or water vapor. Low-alloy steels and iron, when exposed to this effect, obtain a film called bluing. The temperature for bluing is 300-350 degrees Celsius. For high-alloy and high-chromium steels, this figure increases to 700 degrees.
Interesting information: bluing stainless steel at home is quite possible for anyone. There are several ways to do this. Any method must be preceded by grinding the metal and degreasing it. Dip the part or product into oil. It can be olive, machine, or best of all, weapon.
After making sure that the application is even and that the oil gets into hard-to-reach places, we remove the workpiece and let the oil drain. After this, we begin heating with a blowtorch. The lower the heating rate, the higher the probability of complete removal of light fractions and obtaining a uniform bluing layer. After overcoming the threshold of 400 degrees, a characteristic black color appears on the surface.
When finished, polish with soft felts and paste.
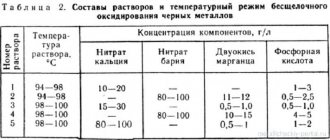
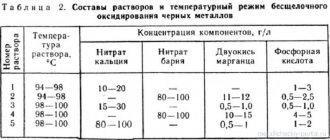
Electrochemical oxidation
Electrochemical oxidation of stainless steels is a method that is widely used in industry. It consists in the fact that the parts are suspended on special holders.
Using this device, they are lowered into a solution with alkali, after which the bath in which it is located is connected to the negative cathode. The parts are connected to the positive anode.
When direct current is passed, according to a physics course, electrolysis processes occur, accompanied by an increase in temperature. The speed of application and the thickness of the resulting film depends on many factors. Main influencing factors:
- Density of flowing current.
- Electrical conductivity of the solution in which the parts are placed
- Electrolyte temperature
- Geometry and part configuration
Interesting fact: at the end of the previous decade, one of the giant Japanese automakers used galvanic blackening of stainless steel on the body of their cars. Research has shown that in the area where the roof bends into the pillars, the oxidized layer was of insufficient thickness.
Long-term research into changing the place where the electrodes are attached to the body, changing the current density, and changing the exposure time did not lead to the expected result.
Only by changing the electrical conductivity of the alkaline solution and adding special additives did the layer become uniform and sufficient for the quality level of the enterprise.
Complex geometry, sharp corners, curved shapes in the contours of the part lead to differences in potentials arising on the surface of stainless steel and, accordingly, lead to differences in film thickness. For such parts, it is advisable to use the previous oxidation method.
Difficulties of blackening work associated with stainless steel
All the methods described above are ideal for ferrous alloys and low alloy steels. A special approach is required, a set of measures for blackening stainless steel as a conditionally inert alloy. The scattered data in the literature on direct blackening of stainless steel is contradictory and does not always work in practice.
On a production scale, it is customary to solve this issue with a two-step approach. The first stage is anodizing stainless steel with another metal that is more prone to oxidation. This is mainly nickel, less often copper. The second stage is oxidation of the resulting surface.
Chemists in many countries are developing special passivating pastes and compositions for blackening stainless steels that can induce them to oxidize.
To apply a decorative film that does not work when exposed to temperature changes, on a surface that does not experience large mechanical loads, the following oxidation method can be used:
- Etching in 10% oxalic acid solution
- Washing and processing in 1% sodium sulfide solution to the required degree of blackening
- Oiling a stainless steel sample.
Based on the information presented, we can conclude that the use of blackening for stainless steel is in the nature of a commercial decorative coating.
The use of oxidation to achieve higher metal characteristics is not justified and cannot be guaranteed.
To obtain protective films that expand the scope of application of stainless steels, it is worth considering other methods and methods.
Dangerous moments
When using acids as electrolytes, safety precautions must be strictly observed. Neglecting them can lead to accidents:
- In case of contact with skin, due to the fact that the drug is diluted, minor burns are possible. But such a concentration is dangerous for the eyes, so you should not neglect protective glasses and gloves.
- Under the influence of current, oxygen and hydrogen vapors are released, which, when mixed, form an explosive gas. When working in a poorly ventilated area, you can get an explosion from any spark, which can be fatal.
By following safety precautions and the stages of technological processing, you can get durable, beautiful things: chrome plating car wheels, creating gold-look jewelry, adding strength to parts of household mechanisms, depending on the technologies used.
Source
Where did the term itself come from?
When electrochemically creating an oxide film on the surface of metals, the part/product is dipped into a bath of electrolyte. Most often this is an acid solution. Electrolytes are electrically conductive (as the name suggests). When a direct current is passed through the solution (it is important that the current constantly flows in one direction!), hydrogen is released at the cathode, and oxygen is released at the anode, with the help of which an oxide, that is, purposefully oxidized, layer is formed with predetermined properties depending on current strength and acid solution concentration. And since this part in the “cathode-electrolyte-part” system is an anode, the creation of a protective film was called “anodizing”. Or "oxidation".
By varying the current strength and the use of special additives, you can achieve almost any color of the anodized coating.