Brand VSt3sp – purpose
Structural carbon steel of ordinary quality VSt3sp is used for the manufacture of parts, non-load-bearing/load-bearing components of welded/prefabricated structures operating at positive temperatures.
Additional information:
1. Sheet/shaped rolled products of category 5 with a cross-section up to 10mm – load-bearing components of welded structures operating under variable loads at temperatures of -40 +4250C.
2. Rolled products with a cross-section of 10–25 mm – load-bearing components of welded structures with guaranteed weldability, operating in the temperature range -40 +4250С.
Impact strength of steel VSt3ps
| Type of rental | Pattern cutting direction | Section, mm | Temperature +20 °C | Temperature -20 °C | after mechanical aging |
| no less | |||||
| Sheet | Transverse | 5-9 | 78 | 39 | 39 |
| 10-25 | 29 | 29 | |||
| 26-40 | 49 | — | — | ||
| Wide band | Longitudinal | 5-9 | 98 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 78 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 68 | — | — | ||
| Varietal and shaped | Longitudinal | 5-9 | 108 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 98 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 88 | — | — | ||
cutting
| Initial data | Machinability Ku | |||
| State | HB, MPa | sB, MPa | hard alloy | high speed steel |
| hot rolled | 124 | 400 | 1,8 | 1,6 |
Application of steel St3
When considering different grades of steel, you need to take into account the fact that they are classified according to the degree of deoxidation. This chemical process involves removing oxygen from the composition. Too high an oxygen concentration determines a decrease in physical and mechanical properties.
The classification is carried out as follows:
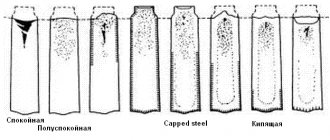
- Calm is characterized by the fact that the composition includes from 0.16 to 0.3% silicon.
- Semi-calm has an average concentration of the element in question.
- Boiling differs in chemical composition from calm in that it contains at least 0.05% silicon.
Read also: How to properly sharpen kitchen knives with a whetstone by hand
St3 material is marked accordingly. Various substances can be used to carry out a chemical process.
It is worth considering that a quiet one is much more expensive than other options. This can be associated with the following points:
- The structure is homogeneous, thereby increasing the degree of protection of the material from environmental influences.
- The composition includes a small amount of oxygen, which determines high performance.
When using mild steel, the following products can be manufactured:
- Rolled sheets and shapes.
- Fittings and parts that can be used to create a pipeline. Various pipes can be used to transport coolant or gas or other media. In order for them to withstand high loads and environmental influences, materials with strength and hardness must be used during production. In addition, attention is paid to cost, since alloys that are too expensive may be less practical to use. Steel 3 is more suitable for the manufacture of such products.
- Primary and secondary elements used in the manufacture of suspended structures and railway elements. In the railway industry, the metals that are most in demand are those that have low cost and high performance. Due to the large size of suspended structures, the price of one square meter is also of great importance.
Steel VSt3sp – chemical composition
Mass fraction of elements no more than, %:
| Silicon | Manganese | Copper | Arsenic | Nickel | Sulfur | Carbon | Phosphorus | Chromium |
| 0,12–0,3 | 0,4–0,65 | 0,3 | 0,08 | 0,3 | 0,05 | 0,14–0,22 | 0,04 | 0,3 |
The closest equivalents (analogues) of steel 03Х17Н14М3
| USA (ASTM/AISI) | 316, 316, S31600, S31603, S31673, S31683 |
| Germany (DIN, WNr) | 1.4404, 1.4435, 1.4436, X2CrNiMo17-12-2, X2CrNiMo17-12-3, X2CrNiMo18-12, X2CrNiMo14-3, X2CrNiMo17-13-3 |
| Japan (JIS) | SUS316L, SCS16 |
| France (AFNOR) | X2CrNiMo18-14-3, X2CrNiMo18-15-4, Z2CND17-12, Z3CND17-11-02, Z3CND17-12-03, Z3CND18-14-03, Z3CND18-14-08, Z3CND19-15-04, Z6CND18-12- 03 |
| England (BS) | 316L, 316S11, 316S13, 316S14, 316S31, 316S33, LW22, LWCF22, X2CrNiMo18-14-3 |
| Euronorms (EN) | 1.4432, 1.4435, X2CrNiMo17-12-3, X2CrNiMo18-14-3 |
| Italy (UNI) | 316LM1, X2CrNiMo17-13, X2CrNiMo17-13KG, X2CrNiMo18-14-3 |
| Spain (UNE) | F.3533, X2CrNiMo17132 |
| China (GB) | 00Cr17Ni14Mo2, 00Cr17Ni14Mo3 |
| Sweden (SS) | 2343, 2353 |
| Hungary (MSZ) | X2CrNiMo18-14-3, KO38LC |
| Romania (STAS) | 2MoNiCr175 |
| Finland (SFS) | X2CrNiMo17-13-3 |
| Czech Republic (CSN) | 17350 |
| Austria (ONORM) | X2CrNiMo18-14-3KW |
| Australia (AS) | 316L |
| South Korea (KS) | STS316L, STSF316L |
Material VSt3sp – mechanical properties
| Assortment | GOST | Dimensions – thickness, diameter | Heat treatment mode | t | KCU | y | d5 | st | sв |
| mm | 0C | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa | |||
| Forgings | up to 100 | Normalization | 640 | 55 | 28 | 175 | 353 | ||
| 100–300 | 590 | 50 | 24 | 175 | 353 | ||||
| Rolled hot rolled products. | up to 20 | Delivery status | 26 | 245 | 370–480 |
Description
Hand over alloy 18хгт (GOST 4543 - 71) in St. Petersburg
St3kp steel is used: for the production of expanded metal sheets, light-loaded elements of welded and non-welded structures and parts operating at temperatures from -40 °C to +400 °C; shaped profiles used in carriage building; forgings with a diameter of up to 300 mm. strength classes KP 175, KP 195; hot-rolled trough and C-shaped profiles for agricultural machines; corrugated diamond and point steel for shipbuilding; profile for the tractor final drive housing; electric welded pipes for the manufacture of parts and structures in the motorcycle and bicycle industry; hot-rolled steel sheets with one-sided rhombic and lenticular corrugation; double-headed, T-bar and P5 type rails intended for ground and overhead tracks; steel bent closed welded square and rectangular sections intended for use in agricultural engineering, tractor manufacturing and other sectors of the national economy; spikes of accuracy class C, designed for fastening railway rails to wooden sleepers and beams.
Endurance limit, MPa
| Assortment | Dimensions – thickness, diameter, mm | sв | N | s-1 |
| The sheet is hot rolled. – smooth sample | 40 | 107 | 191 | |
| notched specimen | 10 | 107 | 93 | |
| 440 | 2x103 | 213 |
Standards
| Name | Code | Standards |
| Sheets and strips | B33 | GOST 10885-85, TU 108.1273-84, TU 14-1-3579-83, TU 14-1-4912-90, TU 14-1-5032-91, TU 302.02.988-92, TU 14-1-5241 -93, TU 14-1-4431-88 |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | IN 20 | GOST 19281-89, GOST 380-2005 |
| Ribbons | B34 | GOST 19851-74 |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | B62 | GOST 3262-75, GOST 8696-74, GOST 10704-91, GOST 10705-80, GOST 10706-76, GOST 10707-80, GOST 12132-66, GOST 20295-85, GOST 24950-81, STO 79814898 105-20 08 , TU 14-3-1160-83, TU 14-3-1428-86, TU 14-3-1473-87, TU 14-3-377-87, TU 1380-001-08620133-93, TU 1380-001 -08620133-05, TU 14-3Р-56-2001, TU 1303-002-08620133-01, TU 1373-013-02949352-2003 |
| Ribbons | B24 | GOST 3560-73, GOST 6009-74, STP M309-74 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B22 | GOST 4781-85, GOST 5267.0-90, GOST 5422-73, GOST 5781-82, GOST 8239-89, GOST 8240-97, GOST 8278-83, GOST 8281-80, GOST 8282-83, GOST 8283-93, GOST 8509-93, GOST 8510-86, GOST 9234-74, GOST 10884-94, GOST 11474-76, GOST 12492.1-90, GOST 12492.2-90, GOST 12492.4-90, GOST 12492.5-90, GOST 12492.13 -90, GOST 12492.14-90, GOST 19240-73, GOST 19425-74, GOST 19771-93, GOST 19772-93, GOST 25577-83, GOST 26020-83, GOST 30565-98, GOST 535-2005, GOST 30136-95, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006, GOST 2879-2006, OST 5.9086-85, OST 5.9087-84, TU 14-2-341-78, TU 14-2-949-91, TU 14-1-5282- 94, STO ASChM 20-93, TU 14-1-5283-94, TU 14-105-568-93, TU 14-1-5254-94 |
| Rails. Overlays. Linings. Crutches | B42 | GOST 5812-82, GOST 8142-89, GOST 16277-93 |
| Sheets and strips | B23 | GOST 82-70, GOST 8568-77, GOST 14637-89, GOST 14918-80, GOST 16523-97, GOST 19903-74, GOST 16523-89, GOST 16523-70, GOST 103-2006, GOST 19903-90, TU 36.26.11-5-89, TU 108-1126-82, TU 14-1-3023-80, TU 14-1-4632-93 |
| Metal forming. Forgings | B03 | GOST 8479-70, TU 108-11-908-87, ST TsKBA 010-2004 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B32 | OST 1 92049-76, TU 14-105-454-86, TU 14-2-849-89, TU 14-11-245-88, TU 14-1-1271-75, TU 14-136-367-2008 |
| Blanks. Blanks. Slabs | B31 | OST 3-1686-90, TU 14-1-4944-90 |
| Welding and cutting of metals. Soldering, riveting | B05 | OST 36-58-81, OST 26-260.453-92 |
| Thermal and thermochemical processing of metals | B04 | ST TsKBA 026-2005 |
| Test methods. Package. Marking | B29 | TU 14-106-485-99 |
Brand VSt3sp – physical properties
| t | r | R 109 | E 10-5 | l | a 106 | C |
| 0C | kg/m3 | Ohm m | MPa | W/(m deg) | 1/Grad | J/ (kg deg) |
| 20 | 7850 | 1.94 | ||||
| 100 | 1.92 | |||||
| 200 | 1.87 | |||||
| 300 | 1.83 | |||||
| 400 | 1.78 | |||||
| 500 | 1.67 | |||||
| 600 | 1.59 | |||||
| 700 | 1.46 | |||||
| 800 | 1.2 | |||||
| 900 | 0.99 |
Standards
| Name | Code | Standards |
| Ribbons | B34 | GOST 19851-74 |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | B62 | GOST 3262-75, GOST 8696-74, GOST 10704-91, GOST 10705-80, GOST 10706-76, GOST 10707-80, GOST 12132-66, GOST 20295-85, GOST 24950-81, TU 14-3- 1160-83, TU 14-3-1428-86, TU 1380-001-08620133-05, TU 14-3Р-56-2001, TU 14-3-377-99, TU 1373-013-02949352-2003 |
| Ribbons | B24 | GOST 3560-73, GOST 6009-74, STP M309-74 |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | IN 20 | GOST 380-2005 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B22 | GOST 4781-85, GOST 5267.0-90, GOST 5422-73, GOST 5781-82, GOST 8239-89, GOST 8240-97, GOST 8278-83, GOST 8281-80, GOST 8282-83, GOST 8283-93, GOST 8509-93, GOST 8510-86, GOST 9234-74, GOST 10551-75, GOST 10884-94, GOST 11474-76, GOST 12492.1-90, GOST 12492.2-90, GOST 12492.4-90, GOST 12492.5-90 , GOST 12492.14-90, GOST 19240-73, GOST 19425-74, GOST 19771-93, GOST 19772-93, GOST 25577-83, GOST 26020-83, GOST 30565-98, GOST 535-2005, GOST 30136-95, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006, GOST 2879-2006, OST 5.9086-85, OST 5.9087-84, TU 14-1-3094-80, TU 14-2-341-78, TU 14-2-853- 89, TU 14-2-949-91, TU 14-1-5282-94, STO ASChM 20-93, TU 14-1-5283-94, TU 14-105-568-93, TU 14-1-5254 -94 |
| Rails. Overlays. Linings. Crutches | B42 | GOST 5812-82, GOST 8142-89, GOST 16277-93 |
| Sheets and strips | B23 | GOST 82-70, GOST 8568-77, GOST 14637-89, GOST 14918-80, GOST 16523-97, GOST 19903-74, GOST 16523-89, GOST 16523-70, GOST 103-2006, GOST 19903-90, TU 36.26.11-5-89, TU 14-1-3023-80 |
| Metal forming. Forgings | B03 | GOST 8479-70, ST TsKBA 010-2004 |
| Welding and cutting of metals. Soldering, riveting | B05 | OST 26-260.453-92 |
| Blanks. Blanks. Slabs | B31 | OST 3-1686-90, TU 14-1-4944-90 |
| Thermal and thermochemical processing of metals | B04 | ST TsKBA 026-2005 |
| Sheets and strips | B33 | TU 14-1-3579-83, TU 14-1-4431-88 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B32 | TU 14-105-454-86, TU 14-2-849-89, TU 14-11-245-88, TU 14-1-1271-75, TU 14-136-367-2008 |
| Test methods. Package. Marking | B29 | TU 14-106-485-99 |
| Low carbon steel wire | B71 | TU 14-4-1813-97 |
Hand over the alloy x12m (GOST 5950 - 73, the latest version does not contain the material) in St. Petersburg
Legend
Mechanical properties
| HRСе | HB | KCU | y | d5 | sT | sв |
| MPa | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa | |
| Rockwell hardness | Brinell hardness | Impact strength | Relative narrowing | Elongation at break | Yield strength | Short-term strength limit |
| Ku | s0.2 | t-1 | s-1 |
| Relative machinability factor | Proof of yield strength with 0.2% tolerance when loaded to plastic strain value | Torsional endurance limit (symmetrical cycle) | Endurance limit under compression-tension (symmetrical cycle) |
| N | number of deformation/stress cycles sustained by an object under load before fatigue failure/crack appears |
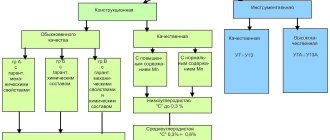
Decoding of St3 stamps
Any brand can be decrypted in accordance with established standards and regulatory documentation. The designation of steel according to GOST allows you to determine the main qualities when deciphering grades. GOST 380 determines the presence of the following types of metal:
It is worth considering that indices must be used for any marking.
Properties of various brands of St3
The brand of material can be deciphered as follows:
- ST is a designation that indicates the ordinary quality of carbon steel. Let's use St3sp5 as an example.
- 3 – a number that is the conventional number of the alloy grade. Depending on the carbon concentration, numbers ranging from 0 to 6 can be used.
- G - in some cases, a similar symbol may be used to designate manganese. A certain type of steel, for example, St3gps, contains 0.8% manganese.
- Sp is the degree of deoxidation of the material. When considering St3ps5, we can say that the structure is semi-quiet, but at the same time the degree of deoxidation is quite high. The designation “ps” is used for semi-quiet alloys, “kp” - boiling alloys.
St3kp2 is deciphered in a similar way relatively recently. Previously, other standards were used for labeling. In addition, previously the metal was divided into several different groups.
Production Features
The properties of the finished material are determined by the substances that make up its composition and largely depend on what technologies were used in the production of a particular alloy.
The basis of the steel alloy is ferrite. It is a component of iron-carbon alloys. It is, in fact, a solid solution of carbon and alloying components. To increase its strength, the melt is saturated with carbon.
Impurities from which nothing but harm can be expected include phosphorus and sulfur, as well as their derivatives. Phosphorus, reacting with ferrite, reduces the ductility of the alloy when exposed to high temperatures and increases brittleness when exposed to cold. During the melting process, iron sulfide may be formed, which can lead to red brittleness. St3 steel contains no more than 0.05% sulfur and 0.04% phosphorus.
For the production of structural steels, two steelmaking technologies are used:
The parameters of the St3 grade, obtained by one or another method, differ little from each other, but the converter technology is simpler and cheaper.